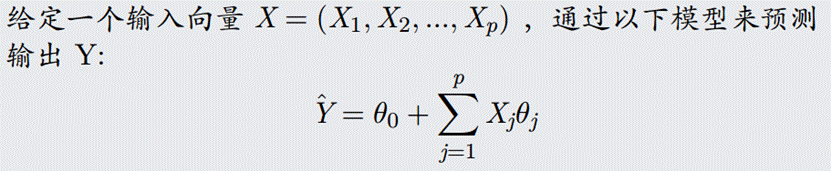ML introduction
机器学习:从数据中学习,而不依赖于规则下编程的一种算法
Goal: \(min_{w,b}(J(w, b))\) - 提供一种衡量一组特定参数与训练数据拟合程度的方法
Supervised Learning
right answer &&
x -> ylabel
categories
- Regression
- Classification
Unsupervised Learning
structure || pattern
categories
- Clustering
- Anomaly detection 异常检测
- Dimensionality reduction 降维
Liner Regression with One Variable
预测数字问题
这部分主要内容包括单变量线性回归的模型表示、代价函数、梯度下降法和使用梯度下降法求解代价函数的最小值。
线性回归模型
数学表达式
代码
ndarray:n维数组类对象
scalar:标量
# 迭代
def compute_model_output(x, w, b):
"""
Computes the prediction of a linear model
Args:
x (ndarray (m,)): Data, m examples
w,b (scalar) : model parameters
Returns
y (ndarray (m,)): target values
"""
m = x.shape[0]
f_wb = np.zeros(m)
for i in range(m):
f_wb[i] = w * x[i] + b
return f_wb
# 向量
def compute_model_output(x, w, b):
"""
single predict using linear regression
Args:
x (ndarray): Shape (n,) example with multiple features
w (ndarray): Shape (n,) model parameters
b (scalar): model parameter
Returns:
p (scalar): prediction
"""
yhat = np.dot(x, w) + b
return yhat
Cost Function
数学表达式
参数表:
| m | y | error |
|---|---|---|
| 训练样例 | 真值 | \(f_{w, b}(x^{(i)}) - y^{(i)}\) |
代码
# 迭代
def compute_cost(x, y, w, b):
"""
Computes the cost function for linear regression.
Args:
x (ndarray (m,)): Data, m examples
y (ndarray (m,)): target values
w,b (scalar) : model parameters
Returns
total_cost (float): The cost of using w,b as the parameters for linear regression
to fit the data points in x and y
"""
# number of training examples
m = x.shape[0]
cost_sum = 0
for i in range(m):
f_wb = w * x[i] + b
cost = (f_wb - y[i]) ** 2
cost_sum = cost_sum + cost
total_cost = (1 / (2 * m)) * cost_sum
return total_cost
# 向量
def compute_cost(X, y, theta):
"""
Computes the cost function for linear regression.
Args:
X (ndarray (m,)): Data, m examples
y (ndarray (m,)): target values
theta (b (ndarray (m,), w (ndarray (m,))): model parameters
Returns
total_cost (float): The cost of using theta as the parameters for linear regression
to fit the data points in X and y
"""
error = (X * theta.T) - y
inner = np.power(error, 2)
total_cost = np.sum(inner)/(2 * len(X))
return total_cost
数学原理
求导:不同的w对应不同的J,对多个点拟合出的曲线求导,以期找到最小的J对应的w
function of w
function of w
function of w
function of w
Gradient Descent
(迭代)=> 极值点
大样本:每次梯度更新都抽部分样本
数学表达式
\(\alpha\): 学习率,控制更新模型参数w和b时采取的步骤大小
代码
# 迭代
def compute_gradient(x, y, w, b):
"""
Computes the gradient for linear regression
Args:
x (ndarray (m,)): Data, m examples
y (ndarray (m,)): target values
w,b (scalar) : model parameters
Returns
dj_dw (scalar): The gradient of the cost w.r.t. the parameters w
dj_db (scalar): The gradient of the cost w.r.t. the parameter b
"""
# Number of training examples
m = x.shape[0]
dj_dw = 0
dj_db = 0
for i in range(m):
f_wb = w * x[i] + b
dj_dw_i = (f_wb - y[i]) * x[i]
dj_db_i = f_wb - y[i]
dj_db += dj_db_i
dj_dw += dj_dw_i
dj_dw = dj_dw / m
dj_db = dj_db / m
return dj_dw, dj_db
def gradient_descent(x, y, w_in, b_in, alpha, num_iters, cost_function, gradient_function):
"""
Performs gradient descent to fit w,b. Updates w,b by taking
num_iters gradient steps with learning rate alpha
Args:
x (ndarray (m,)) : Data, m examples
y (ndarray (m,)) : target values
w_in,b_in (scalar): initial values of model parameters
alpha (float): Learning rate
num_iters (int): number of iterations to run gradient descent
cost_function: function to call to produce cost
gradient_function: function to call to produce gradient
Returns:
w (scalar): Updated value of parameter after running gradient descent
b (scalar): Updated value of parameter after running gradient descent
J_history (List): History of cost values
p_history (list): History of parameters [w,b]
"""
w = copy.deepcopy(w_in) # avoid modifying global w_in
# An array to store cost J and w's at each iteration primarily for graphing later
J_history = []
p_history = []
b = b_in
w = w_in
for i in range(num_iters):
# Calculate the gradient and update the parameters using gradient_function
dj_dw, dj_db = gradient_function(x, y, w , b)
# Update Parameters using equation (3) above
b = b - alpha * dj_db
w = w - alpha * dj_dw
# Save cost J at each iteration
if i<100000: # prevent resource exhaustion
J_history.append( cost_function(x, y, w , b))
p_history.append([w,b])
# Print cost every at intervals 10 times or as many iterations if < 10
if i% math.ceil(num_iters/10) == 0:
print(f"Iteration {i:4}: Cost {J_history[-1]:0.2e} ",
f"dj_dw: {dj_dw: 0.3e}, dj_db: {dj_db: 0.3e} ",
f"w: {w: 0.3e}, b:{b: 0.5e}")
return w, b, J_history, p_history #return w and J,w history for graphing
# 向量
def gradient_descent(X, y, theta, alpha, iters):
"""
Performs gradient descent to fit w,b. Updates w,b by taking
num_iters gradient steps with learning rate alpha
Args:
X (ndarray (m,)) : Data, m examples
y (ndarray (m,)) : target values
theta (ndarray (m,)): initial values of model parameters
alpha (float) : Learning rate
iters (scalar) : number of interations
Returns:
theta (ndarray (m,)): Updated parameter of parameter after running gradient descent
cost (ndarray (m,)) : Record the cost after each iteration
"""
tmp = np.matrix(np.zeros(theta.shape)) # 构造零值矩阵
parameters = int(theta.ravel().shape[1]) # theta的列即参数的个数
cost = np.zeros(iters) # 构建iters个()的数组
# 迭代
for i in range(iters):
error = (X * theta.T) - y
for j in range(parameters):
term = np.multiply(error, X[:, j]) # 求内积 np.multiply
tmp[0, j] = theta[0, j] - ((alpha / len(X) * np.sum(term)))
theta = tmp
cost[i] = computeCost(X, y, theta)
return theta, cost
数学原理
(w和b要同时更新)
最小二乘法
形式:$$标函数 = sum(观测值 - 理论值)^2$$文章来源:https://www.toymoban.com/news/detail-615693.html
解法:https://www.cnblogs.com/pinard/p/5976811.html文章来源地址https://www.toymoban.com/news/detail-615693.html
- 代数法:偏导数求最值
- 矩阵法:normal equation(有局限性)
到了这里,关于【机器学习】单变量线性回归的文章就介绍完了。如果您还想了解更多内容,请在右上角搜索TOY模板网以前的文章或继续浏览下面的相关文章,希望大家以后多多支持TOY模板网!