参考:(文中部分图/文字/代码来自以下文章,部分内容由于时间久远已经找不到原作者,可联系注明或删除)
PYTHON串口数据打包发送STM32接收数据解析
openmv中文文档
这里以openmv循迹代码为例
main.py
THRESHOLD = (74, 100, -128, 127, -128, 127) # 识别白线
import sensor, image, time
from pyb import LED,UART
uart = UART(3, 115200)
uart.init(115200, bits=8, parity=None, stop=1) # 定义串口
sensor.reset()
sensor.set_vflip(True)
sensor.set_hmirror(True)
sensor.set_pixformat(sensor.RGB565)
sensor.set_framesize(sensor.QQQVGA)
clock = time.clock()
def sending_data(rho_err,theta_error): #发送函数
global uart
data = ustruct.pack("<bbhhb", # 解释见下文
0x2C,
0x12,
int(rho_err),
int(theta_error),
0x5B)
uart.write(data);
while(True):
clock.tick()
img = sensor.snapshot().binary([THRESHOLD])
line = img.get_regression([(100,100)], robust = True)
if (line):
rho_err = abs(line.rho())-img.width()/2
theta_error = line.theta()
if (line.theta()>90):
theta_error = line.theta()-180
print('rho:', rho_err, 'theta:', theta_error)
img.draw_line(line.line(), color = 127)
sending_data(rho_err, theta_error) # 发送数据,这里发送了两个数据
time.sleep_ms(10)
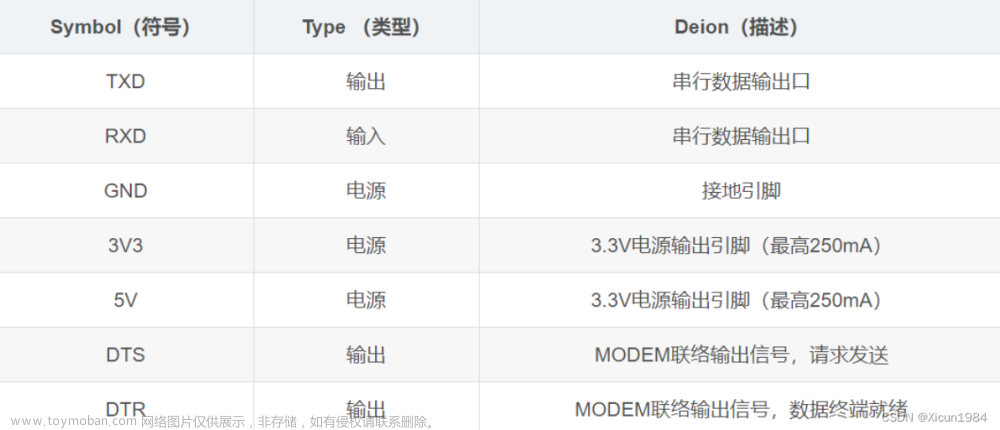
关于struct.pack:
函数原型:struct.pack(fmt, v1, v2, …)
- fmt是格式字符串
- v1,v2是要转换的python值,详情见下表

注1.q和Q只在机器支持64位操作时有意思;
注2.每个格式前可以有一个数字,表示个数;
注3.s格式表示一定长度的字符串,4s表示长度为4的字符串,但是p表示的是pascal字符串;
注4.P用来转换一个指针,其长度和机器字长相关;
注5.最后一个可以用来表示指针类型的,占4个字节;
为了同c中的结构体交换数据,还要考虑有的c或c++编译器使用了字节对齐,通常是以4个字节为单位的32位系统,故而struct根据本地机器字节顺序转换.可以用格式中的第一个字符来改变对齐方式.定义如下:
大端和小端的区别:
小端:较高的有效字节存放在较高的的存储器地址,较低的有效字节存放在较低的存储器地址。
大端:较高的有效字节存放在较低的存储器地址,较低的有效字节存放在较高的存储器地址。
例如0x12345678 ,在大端模式的排列:0x01(低地址),0x23,0x45,0x67,0x89(高地址)。
在小端模式的排列:0x89(低地址),0x67,0x45,0x23,0x01(高地址)。
在stm32中的代码如下:
openmv.c文章来源:https://www.toymoban.com/news/detail-620220.html
#include "openmv.h"
#include "stm32f10x.h"
void USART2_Init(void){ //串口2初始化并启动
//GPIO端口设置
GPIO_InitTypeDef GPIO_InitStructure; //串口端口配置结构体变量
USART_InitTypeDef USART_InitStructure; //串口参数配置结构体变量
NVIC_InitTypeDef NVIC_InitStructure;//串口中断配置结构体变量
RCC_APB1PeriphClockCmd(RCC_APB1Periph_USART2, ENABLE); //打开串口复用时钟
RCC_APB2PeriphClockCmd(RCC_APB2Periph_GPIOA, ENABLE); //打开PC端口时钟
//USART2 TX PA2;
GPIO_InitStructure.GPIO_Pin = GPIO_Pin_2; //PA2
GPIO_InitStructure.GPIO_Speed = GPIO_Speed_50MHz;//设定IO口的输出速度为50MHz
GPIO_InitStructure.GPIO_Mode = GPIO_Mode_AF_PP; //复用推挽输出
GPIO_Init(GPIOA, &GPIO_InitStructure); //初始化PA2
//USART2 RX PA3;
GPIO_InitStructure.GPIO_Pin = GPIO_Pin_3; //PA3
GPIO_InitStructure.GPIO_Mode = GPIO_Mode_IN_FLOATING;//浮空输入
GPIO_Init(GPIOA, &GPIO_InitStructure); //初始化PA3
//Usart1 NVIC 配置
NVIC_InitStructure.NVIC_IRQChannel = USART2_IRQn;
NVIC_InitStructure.NVIC_IRQChannelPreemptionPriority=0 ;//抢占优先级0
NVIC_InitStructure.NVIC_IRQChannelSubPriority = 2; //子优先级2
NVIC_InitStructure.NVIC_IRQChannelCmd = ENABLE; //IRQ通道使能
NVIC_Init(&NVIC_InitStructure); //根据指定的参数初始化VIC寄存器
//USART 初始化设置
USART_InitStructure.USART_BaudRate = 115200;//串口波特率为115200
USART_InitStructure.USART_WordLength = USART_WordLength_8b;//字长为8位数据格式
USART_InitStructure.USART_StopBits = USART_StopBits_1;//一个停止位
USART_InitStructure.USART_Parity = USART_Parity_No;//无奇偶校验位
USART_InitStructure.USART_HardwareFlowControl = USART_HardwareFlowControl_None;//无硬件数据流控制
USART_InitStructure.USART_Mode = USART_Mode_Rx | USART_Mode_Tx; //收发模式
USART_Init(USART2, &USART_InitStructure); //初始化串口1
USART_ITConfig(USART2, USART_IT_RXNE, ENABLE);//开启ENABLE
USART_Cmd(USART2, ENABLE); //使能串口1
//如下语句解决第1个字节无法正确发送出去的问题
USART_ClearFlag(USART2, USART_FLAG_TC); //清串口2发送标志
}
//串口2中断处理函数
void USART2_IRQHandler(void) //串口2全局中断服务函数
{
u8 temp;
if( USART_GetITStatus(USART2,USART_IT_RXNE)!=RESET )
{
USART_ClearITPendingBit(USART2,USART_IT_RXNE);//清除中断标志
temp = USART_ReceiveData(USART2);
Openmv_Receive_Data(temp);//openmv数据处理函数
}
}
u8 RxCounter1 = 0;//接受OpenMV数据里用到的
u8 RxBuffer1[18];//接受OpenMV数据里用到的数组
u16 rho_err = 0,theta_err = 0;//rho偏差和theta偏差
//接收OpenMV传过来的数据
void Openmv_Receive_Data(int16_t data)
{
static u8 state = 0;
if(state==0&&data==0x2C)
{
state=1;
RxBuffer1[RxCounter1++]=data;
}
else if(state==1&&data==18)
{
state=2;
RxBuffer1[RxCounter1++]=data;
}
else if(state==2)
{
RxBuffer1[RxCounter1++]=data;
if(RxCounter1>19||data == 0x5B) state=3; //最后字符是openmv[19]
}
else if(state==3) //state == 3 检测是否接受到结束标志
{
if(RxBuffer1[RxCounter1-1] == 0x5B)
{
state = 0;
USART_ITConfig(USART2,USART_IT_RXNE,DISABLE);//关闭DTSABLE中断
rho_err = RxBuffer1[3]<<8 | RxBuffer1[2]; //这时已经赋值给rho_err和theta_err
theta_err = RxBuffer1[5]<<8 | RxBuffer1[4];
RxCounter1 = 0;
USART_ITConfig(USART2,USART_IT_RXNE,ENABLE);//开启ENABLE中断
}
else //错误
{
state = 0;
RxCounter1=0;
}
}
else //错误
{
state = 0;
RxCounter1=0;
}
}
//这段代码的原稿是一位博主贡献的,由于时间久远已经找不到原文章,侵删或联系注明
openmv.h文章来源地址https://www.toymoban.com/news/detail-620220.html
#ifndef __OPENMV_H_
#define __OPENMV_H_
#include "stm32f10x.h"
extern u16 USART1_RX_STA; //接受状态标记
extern u8 RxCounter1; //接受OpenMV数据里用到的
extern u8 RxBuffer1[18]; //接受OpenMV数据里用到的数组
extern u16 rho_err;
extern u16 theta_err;
extern u8 state;
void USART2_Init(void);//串口2初始化并启动
void Openmv_Receive_Data(int16_t data);//接收OpenMV传过来的数据
#endif
到了这里,关于【嵌入式】openmv与stm32的串口通信的文章就介绍完了。如果您还想了解更多内容,请在右上角搜索TOY模板网以前的文章或继续浏览下面的相关文章,希望大家以后多多支持TOY模板网!




![[嵌入式软件][启蒙篇][仿真平台] STM32F103实现串口输出输入、ADC采集](https://imgs.yssmx.com/Uploads/2024/01/814721-1.gif)