1.模拟实现list
list使用文章

1.1构造函数

析构函数

在定义了一个类模板list时。我们让该类模板包含了一个内部结构体_list_node,用于表示链表的节点。该结构体包含了指向前一个节点和后一个节点的指针以及节点的值。在list中保存了链表的头节点指针和链表长度大小。
namespace my_list
{
//用类模板定义一个list结点
template<class T>
struct _list_node
{
//list结点的构造函数,T()作为缺省值,当未转参时调用
_list_node(const T& val = T())
:_next(nullptr)
, _prev(nullptr)
, _val(val)
{}
//list_node的成员函数,list为带头双向循环链表
_list_node* _prev;
_list_node* _next;
T _val;
};
//用类模拟实现list
template<class T>
class list
{
private:
typedef _list_node<T> Node;
public:
//list的构造函数,初始化头节点指针
list()
{
_head = new Node;
_head->_prev = _head;
_head->_next = _head;
_size = 0;
}
//析构函数
~list()
{
iterator it = begin();
while (it != end())
{
it = erase(it);
}
_size = 0;
delete _head;
_head = nullptr;
}
private:
//成员函数为list的头节点指针,和链表长度
Node* _head;
size_t _size;
};
}
1.2迭代器类的实现


因为list的底层实现和之前的vector和string不同,vector和string是数组和顺序表,而list底层是链表。而对于数组和顺序表,我们可以直接使用指针来实现其迭代器,但是对于list类型就无法使用指针来实现它的迭代器,因为迭代器++无法访问到他的下一个节点。所以我们这里建立一个迭代器的结构体,用来封装node指针,来实现list的专属迭代器
这段代码定义了一个名为__list_iterator的迭代器结构体,用于遍历链表。该结构体模板有三个模板参数:T表示链表中节点的数据类型,Ref表示引用类型T&,Ptr表示指针类型 T* _node:指向链表节点的指针。构造函数__list_iterator(Node* node):用于初始化迭代器对象,将指针node赋值给_node。通过_node就可以实现各种操作符重载。
定义了一个迭代器结构体,用于在链表中进行遍历和操作。通过重载运算符,可以使用迭代器对象像指针一样访问链表中的元素。
//使用类进行封装Node*,来实现list的专属迭代器
//list迭代器和一些内置类型迭代器不一样,++无法准确访问到下一个位置
//typedef __list_iterator<T, T&> iterator;
//typedef __list_iterator<T, const T&> iterator;
template<class T, class Ref, class Ptr>
struct __list_iterator
{
typedef _list_node<T> Node;
typedef __list_iterator<T, Ref, Ptr> self;
Node* _node;
//迭代器的构造函数
__list_iterator(Node* node)
:_node(node)
{}
//重载*
Ref operator*()
{
return _node->_val;
}
//重载->
Ptr operator->()
{
return &_node->_val;
}
//重载前置++
self& operator++()
{
_node = _node->_next;
return *this;
}
//重载后置++
self operator++(int)
{
__list_iterator<T> tmp(*this);
_node = _node->_next;
return tmp;
}
//重载前置--
self& operator--()
{
_node = _node->_prev;
return *this;
}
//重载后置--
self operator--(int)
{
self tmp(*this);
_node = _node->_prev;
return tmp;
}
//重载!=
bool operator!=(const self& it) const
{
return _node != it._node;
}
//重载==
bool operator==(const self& it) const
{
return _node == it._node;
}
};
通过建立一个新的结构体来重载迭代器,我们即可实现list专属迭代器对其链表进行++、- -等操作。
typedef __list_iterator<T, T&, T*> iterator;
typedef __list_iterator<T, const T&, const T*> const_iterator;
//list迭代器实现
iterator begin()
{
//隐式类型转换,内置类型转换为自定义类型,实现迭代器功能
//return _head->_next;
return iterator(_head->_next);
}
iterator end()
{
//return _head;
return iterator(_head);
}
const_iterator begin() const
{
//return _head->_next;
return const_iterator(_head->_next);
}
const_iterator end() const
{
//return _head;
return const_iterator(_head);
}
1.3运算符重载
迭代器的运算符重载在上面的代码中,已经都基本实现了。

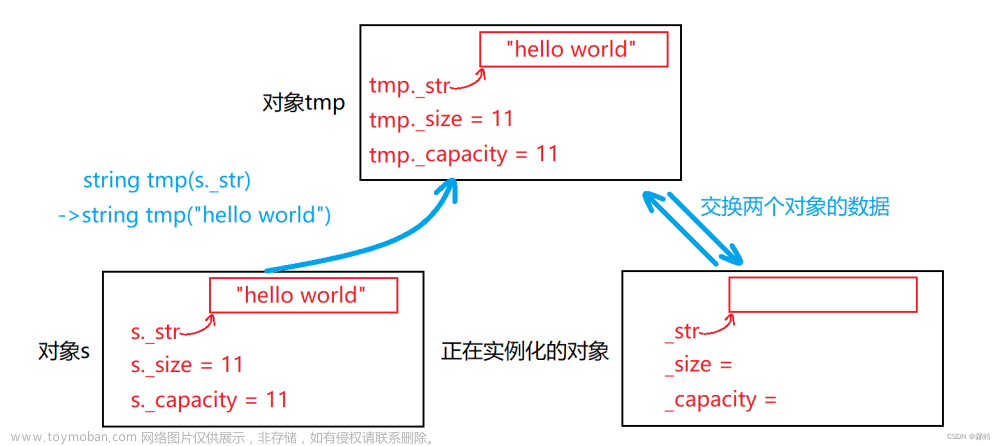
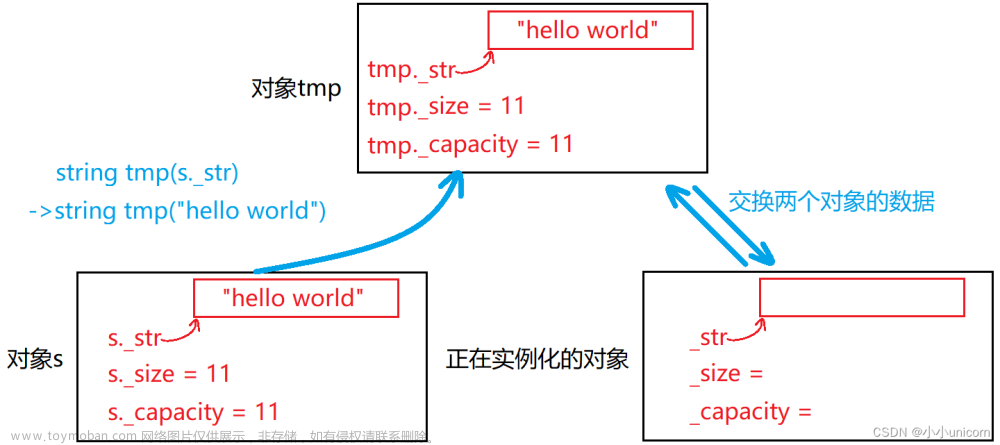
赋值运算符重载函数operator=首先创建了一个临时的链表对象lt,并将传入的链表对象的副本赋值给lt。然后,调用swap函数,将当前链表对象和临时链表对象进行交换。这样做的原因是为了实现异常安全的赋值操作。通过将传入的链表对象的副本赋值给临时链表对象,可以确保在交换过程中不会影响到传入的链表对象。 最后,返回当前链表对象的引用。
通过这样的实现逻辑,可以实现链表对象之间的赋值操作,并且保证在异常发生时不会破坏数据的完整性。
//交换
void swap(list<T>& lt)
{
std::swap(_head, lt._head);
std::swap(_size, lt._size);
}
//赋值运算符重载
list<T>& operator=(list<T> lt)
//list& operator=(list lt)
{
swap(lt);
return *this;
}
1.4增删查改
push_back

和带头双向循环链表的尾插一样。首先,创建一个新的链表节点newnode,节点的值为传入的参数x。然后,获取到链表的尾指针tail,即头节点的前一个节点。
接着,将新节点newnode插入到链表的尾部。首先,将新节点的前驱指针指向尾节点tail,将尾节点的后继指针指向新节点。这样就将新节点连接到了链表的尾部。
然后,将新节点的后继指针指向头节点,将头节点的前驱指针指向新节点。这样就将新节点连接到了链表的头部。
//尾插
void push_back(const T& x)
{
//创建一个新的链表结点,且获取到链表的尾指针
Node* newnode = new Node(x);
Node* tail = _head->_prev;
//连接尾结点
newnode->_prev = tail;
tail->_next = newnode;
//连接头节点
_head->_prev = newnode;
newnode->_next = _head;
++_size;
}
insert

和上面的逻辑类似。
//在pos位置之前插入
iterator insert(iterator pos, const T& x)
{
Node* cur = pos._node;
Node* prev = cur->_prev;
Node* newnode = new Node(x);
prev->_next = newnode;
newnode->_next = cur;
cur->_prev = newnode;
newnode->_prev = prev;
++_size;
return newnode;
}
erase

首先,通过断言判断传入的迭代器pos不等于链表的末尾迭代器。如果等于末尾迭代器,表示要删除的节点不存在,会导致错误。然后,根据传入的迭代器pos获取到要删除的节点cur,以及其前驱节点prev和后继节点next。
接着,将前驱节点的后继指针指向后继节点,将后继节点的前驱指针指向前驱节点。这样就将要删除的节点从链表中断开。然后,释放要删除的节点的内存。还要将链表的大小减1。
为了避免迭代器失效,返回下一个节点的指针作为新的迭代器。这样可以保证在删除节点后,仍然可以使用返回的迭代器进行遍历和操作。
//删除
iterator erase(iterator pos)
{
assert(pos != end());
Node* cur = pos._node;
Node* prev = cur->_prev;
Node* next = cur->_next;
prev->_next = next;
next->_prev = prev;
delete cur;
--_size;
//为了避免迭代器失效,返回下一个结点指针
return next;
}
完整实现文章来源:https://www.toymoban.com/news/detail-622614.html
#pragma once
#include<assert.h>
namespace my_list
{
//用类模板定义一个list结点
template<class T>
struct _list_node
{
//list结点的构造函数,T()作为缺省值,当未转参时调用
_list_node(const T& val = T())
:_next(nullptr)
, _prev(nullptr)
, _val(val)
{}
//list_node的成员函数,list为带头双向循环链表
_list_node* _prev;
_list_node* _next;
T _val;
};
//使用类进行封装Node*,来实现list的专属迭代器
//list迭代器和一些内置类型迭代器不一样,++无法准确访问到下一个位置
//typedef __list_iterator<T, T&> iterator;
//typedef __list_iterator<T, const T&> iterator;
template<class T, class Ref, class Ptr>
struct __list_iterator
{
typedef _list_node<T> Node;
typedef __list_iterator<T, Ref, Ptr> self;
Node* _node;
//迭代器的构造函数
__list_iterator(Node* node)
:_node(node)
{}
//重载*
Ref operator*()
{
return _node->_val;
}
//重载->
Ptr operator->()
{
return &_node->_val;
}
//重载前置++
self& operator++()
{
_node = _node->_next;
return *this;
}
//重载后置++
self operator++(int)
{
__list_iterator<T> tmp(*this);
_node = _node->_next;
return tmp;
}
//重载前置--
self& operator--()
{
_node = _node->_prev;
return *this;
}
//重载后置--
self operator--(int)
{
self tmp(*this);
_node = _node->_prev;
return tmp;
}
//重载!=
bool operator!=(const self& it) const
{
return _node != it._node;
}
//重载==
bool operator==(const self& it) const
{
return _node == it._node;
}
};
//实现const类型迭代器
/*template<class T>
struct __list_const_iterator
{
typedef list_node<T> Node;
Node* _node;
__list_const_iterator(Node* node)
:_node(node)
{}
const T& operator*()
{
return _node->_val;
}
__list_const_iterator<T>& operator++()
{
_node = _node->_next;
return *this;
}
__list_const_iterator<T> operator++(int)
{
__list_const_iterator<T> tmp(*this);
_node = _node->_next;
return tmp;
}
bool operator!=(const __list_const_iterator<T>& it)
{
return _node != it._node;
}
bool operator==(const __list_const_iterator<T>& it)
{
return _node == it._node;
}
};*/
//用类模拟实现list
template<class T>
class list
{
private:
typedef _list_node<T> Node;
public:
typedef __list_iterator<T, T&, T*> iterator;
typedef __list_iterator<T, const T&, const T*> const_iterator;
//list迭代器实现
iterator begin()
{
//隐式类型转换,内置类型转换为自定义类型,实现迭代器功能
//return _head->_next;
return iterator(_head->_next);
}
iterator end()
{
//return _head;
return iterator(_head);
}
const_iterator begin() const
{
//return _head->_next;
return const_iterator(_head->_next);
}
const_iterator end() const
{
//return _head;
return const_iterator(_head);
}
//初始化
void empty_init()
{
_head = new Node;
_head->_prev = _head;
_head->_next = _head;
_size = 0;
}
//list的构造函数,初始化头节点指针
list()
{
empty_init();
}
//拷贝构造
list(const list<T>& lt)
//list(const list& lt)
{
empty_init();
for (auto& e : lt)
{
push_back(e);
}
}
//交换
void swap(list<T>& lt)
{
std::swap(_head, lt._head);
std::swap(_size, lt._size);
}
//赋值运算符重载
list<T>& operator=(list<T> lt)
//list& operator=(list lt)
{
swap(lt);
return *this;
}
//析构函数
~list()
{
clear();
delete _head;
_head = nullptr;
}
//清理
void clear()
{
iterator it = begin();
while (it != end())
{
it = erase(it);
}
_size = 0;
}
//尾插
void push_back(const T& x)
{
//创建一个新的链表结点,且获取到链表的尾指针
Node* newnode = new Node(x);
Node* tail = _head->_prev;
//连接尾结点
newnode->_prev = tail;
tail->_next = newnode;
//连接头节点
_head->_prev = newnode;
newnode->_next = _head;
++_size;
//insert(end(), x);
}
//头插
void push_front(const T& x)
{
insert(begin(), x);
}
//尾删
void pop_back()
{
erase(--end());
}
//头删
void pop_front()
{
erase(begin());
}
//在pos位置之前插入
iterator insert(iterator pos, const T& x)
{
Node* cur = pos._node;
Node* prev = cur->_prev;
Node* newnode = new Node(x);
prev->_next = newnode;
newnode->_next = cur;
cur->_prev = newnode;
newnode->_prev = prev;
++_size;
return newnode;
}
//删除
iterator erase(iterator pos)
{
assert(pos != end());
Node* cur = pos._node;
Node* prev = cur->_prev;
Node* next = cur->_next;
prev->_next = next;
next->_prev = prev;
delete cur;
--_size;
//为了避免迭代器失效,返回下一个结点指针
return next;
}
//返回size
size_t size()
{
/*size_t sz = 0;
iterator it = begin();
while (it != end())
{
++sz;
++it;
}
return sz;*/
return _size;
}
private:
//成员函数为list的头节点指针,和链表长度
Node* _head;
size_t _size;
};
//打印函数
void print(const list<int>& lt)
{
list<int>::const_iterator it = lt.begin();
while (it != lt.end())
{
// (*it) += 1;
cout << *it << " ";
++it;
}
cout << endl;
}
}
测试代码文章来源地址https://www.toymoban.com/news/detail-622614.html
#define _CRT_SECURE_NO_WARNINGS 1
#include<iostream>
#include<list>
using namespace std;
#include"list.h"
void test_list1()
{
//list<int> lt;
//lt.push_back(1);
//lt.push_back(2);
//lt.push_back(3);
//lt.push_back(4);
//for (auto e : lt)
//{
// cout << e << " ";
//}
//cout << endl;
my_list::list<int> lt;
lt.push_back(1);
lt.push_back(2);
lt.push_back(3);
lt.push_back(4);
my_list::list<int>::iterator it = lt.begin();
while (it != lt.end())
{
cout << *it << " ";
++it;
}
cout << endl;
auto itt = lt.begin();
while (itt != lt.end())
{
++(*itt);
++itt;
}
for (auto e: lt)
{
cout << e << " ";
}
cout << endl;
}
struct A
{
A(int a1 = 0, int a2 = 0)
:_a1(a1)
, _a2(a2)
{}
int _a1;
int _a2;
};
void test_list2()
{
my_list::list<A> lt;
lt.push_back(A(1, 1));
lt.push_back(A(2, 2));
lt.push_back(A(3, 3));
lt.push_back(A(4, 4));
auto it = lt.begin();
while (it != lt.end())
{
//cout << *(it)._a1 << " " << *(it)._a2 <<endl;
cout << it->_a1 << " " << it->_a2 << endl;
++it;
}
cout << endl;
}
void test_list3()
{
my_list::list<int> lt;
lt.push_back(1);
lt.push_back(2);
lt.push_back(3);
lt.push_back(4);
for (auto e : lt)
{
cout << e << " ";
}
cout << endl;
lt.push_front(5);
lt.push_front(6);
print(lt);
lt.pop_front();
lt.pop_back();
print(lt);
lt.clear();
lt.push_back(10);
lt.push_back(20);
lt.push_back(30);
lt.push_back(40);
print(lt);
cout << lt.size() << endl;
}
int main()
{
//test_list1();
//test_list2();
test_list3();
return 0;
}
到了这里,关于【C++】STL——list的模拟实现、构造函数、迭代器类的实现、运算符重载、增删查改的文章就介绍完了。如果您还想了解更多内容,请在右上角搜索TOY模板网以前的文章或继续浏览下面的相关文章,希望大家以后多多支持TOY模板网!

![[ C++ ] STL---反向迭代器的模拟实现](https://imgs.yssmx.com/Uploads/2024/04/852660-1.gif)