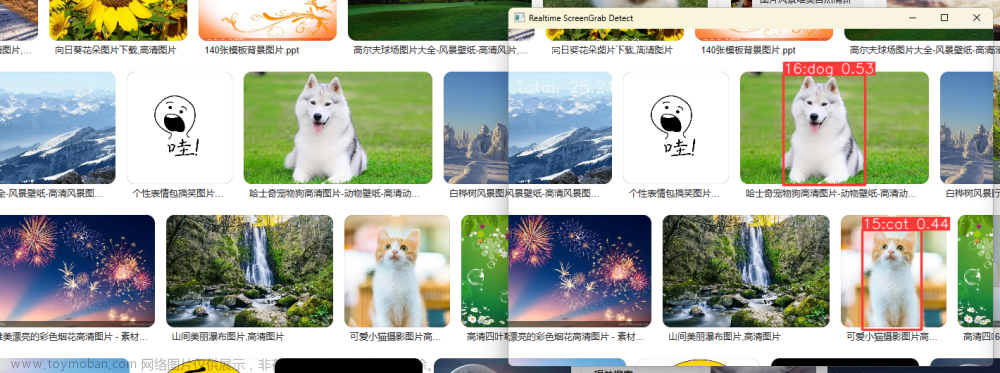
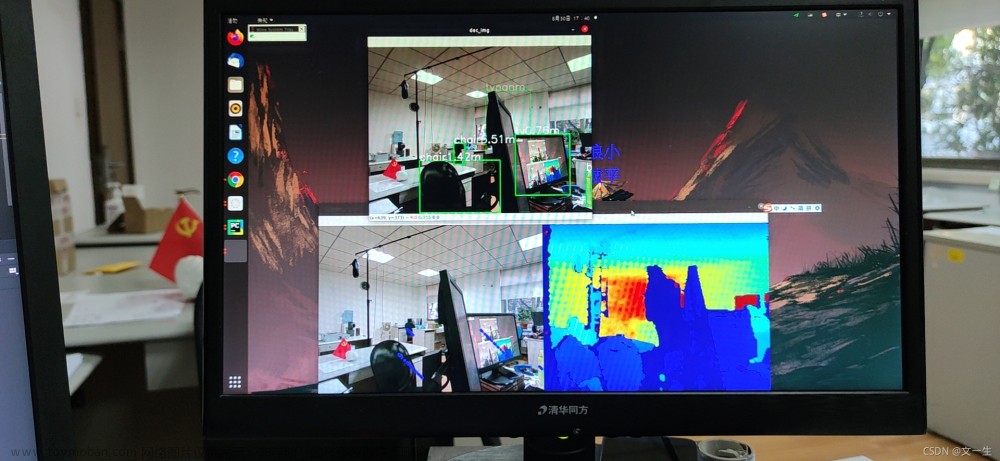
项目实验结果展示:
基于yolo v5与Deep Sort进行车辆以及速度检测与目标跟踪实战——项目可以私聊
该项目可以作为毕业设计,以及企业级的项目开发,主要包含了车辆的目标检测、目标跟踪以及车辆的速度计算,同样可以进行二次开发。
这里附上主要的检测代码文章来源:https://www.toymoban.com/news/detail-625107.html
import torch
import numpy as np
from models.experimental import attempt_load
from utils.general import non_max_suppression, scale_coords
from utils.torch_utils import select_device
from utils.datasets import letterbox
import cv2
from deep_sort.utils.parser import get_config
from deep_sort.deep_sort import DeepSort
from haversine import haversine, Unit
from sys import platform as _platform
class Detector:
"""
yolo目标检测
"""
def __init__(self):
self.img_size = 1280
self.conf_thres = 0.5
self.iou_thres=0.5
# 目标检测权重
self.weights = 'weights/highway_m_300.pt'
self.device = '0' if torch.cuda.is_available() else 'cpu'
self.device = select_device(self.device)
model = attempt_load(self.weights, map_location=self.device)
model.to(self.device).eval()
# 判断系统,支持MACOS 和 windows
if _platform == "darwin":
# MAC OS X
model.float()
else:
# Windows
model.half()
#
self.m = model
self.names = model.module.names if hasattr(
model, 'module') else model.names
# 图片预处理
def preprocess(self, img):
img = letterbox(img, new_shape=self.img_size)[0]
img = img[:, :, ::-1].transpose(2, 0, 1)
img = np.ascontiguousarray(img)
img = torch.from_numpy(img).to(self.device)
if _platform == "darwin":
# MAC OS X
img = img.float()
else:
# Windows
img = img.half()
img /= 255.0 # 图像归一化
if img.ndimension() == 3:
img = img.unsqueeze(0)
return img
# 目标检测
def yolo_detect(self, im):
img = self.preprocess(im)
pred = self.m(img, augment=False)[0]
pred = pred.float()
pred = non_max_suppression(pred, self.conf_thres, self.iou_thres )
pred_boxes = []
for det in pred:
if det is not None and len(det):
det[:, :4] = scale_coords(
img.shape[2:], det[:, :4], im.shape).round()
for *x, conf, cls_id in det:
lbl = self.names[int(cls_id)]
x1, y1 = int(x[0]), int(x[1])
x2, y2 = int(x[2]), int(x[3])
pred_boxes.append(
(x1, y1, x2, y2, lbl, conf))
return pred_boxes
class Tracker:
"""
deepsort追踪
"""
def __init__(self):
cfg = get_config()
cfg.merge_from_file("deep_sort/configs/deep_sort.yaml")
self.deepsort = DeepSort(cfg.DEEPSORT.REID_CKPT,
max_dist=cfg.DEEPSORT.MAX_DIST, min_confidence=cfg.DEEPSORT.MIN_CONFIDENCE,
nms_max_overlap=cfg.DEEPSORT.NMS_MAX_OVERLAP, max_iou_distance=cfg.DEEPSORT.MAX_IOU_DISTANCE,
max_age=cfg.DEEPSORT.MAX_AGE, n_init=cfg.DEEPSORT.N_INIT, nn_budget=cfg.DEEPSORT.NN_BUDGET,
use_cuda=True)
def update_tracker(self,image, yolo_bboxes):
bbox_xywh = []
confs = []
clss = []
for x1, y1, x2, y2, cls_id, conf in yolo_bboxes:
obj = [
int((x1+x2)/2), int((y1+y2)/2),
x2-x1, y2-y1
]
bbox_xywh.append(obj)
confs.append(conf)
clss.append(cls_id)
xywhs = torch.Tensor(bbox_xywh)
confss = torch.Tensor(confs)
#更新追踪结果
outputs = self.deepsort.update(xywhs, confss, clss, image)
bboxes2draw = []
for value in list(outputs):
x1, y1, x2, y2, cls_, track_id = value
bboxes2draw.append(
(x1, y1, x2, y2, cls_, track_id)
)
return bboxes2draw
class PixelMapper(object):
"""
Create an object for converting pixels to geographic coordinates,
using four points with known locations which form a quadrilteral in both planes
Parameters
----------
pixel_array : (4,2) shape numpy array
The (x,y) pixel coordinates corresponding to the top left, top right, bottom right, bottom left
pixels of the known region
lonlat_array : (4,2) shape numpy array
The (lon, lat) coordinates corresponding to the top left, top right, bottom right, bottom left
pixels of the known region
"""
def __init__(self, pixel_array, lonlat_array):
assert pixel_array.shape==(4,2), "Need (4,2) input array"
assert lonlat_array.shape==(4,2), "Need (4,2) input array"
self.M = cv2.getPerspectiveTransform(np.float32(pixel_array),np.float32(lonlat_array))
self.invM = cv2.getPerspectiveTransform(np.float32(lonlat_array),np.float32(pixel_array))
def pixel_to_lonlat(self, pixel):
"""
Convert a set of pixel coordinates to lon-lat coordinates
Parameters
----------
pixel : (N,2) numpy array or (x,y) tuple
The (x,y) pixel coordinates to be converted
Returns
-------
(N,2) numpy array
The corresponding (lon, lat) coordinates
"""
if type(pixel) != np.ndarray:
pixel = np.array(pixel).reshape(1,2)
assert pixel.shape[1]==2, "Need (N,2) input array"
pixel = np.concatenate([pixel, np.ones((pixel.shape[0],1))], axis=1)
lonlat = np.dot(self.M,pixel.T)
return (lonlat[:2,:]/lonlat[2,:]).T
def lonlat_to_pixel(self, lonlat):
"""
Convert a set of lon-lat coordinates to pixel coordinates
Parameters
----------
lonlat : (N,2) numpy array or (x,y) tuple
The (lon,lat) coordinates to be converted
Returns
-------
(N,2) numpy array
The corresponding (x, y) pixel coordinates
"""
if type(lonlat) != np.ndarray:
lonlat = np.array(lonlat).reshape(1,2)
assert lonlat.shape[1]==2, "Need (N,2) input array"
lonlat = np.concatenate([lonlat, np.ones((lonlat.shape[0],1))], axis=1)
pixel = np.dot(self.invM,lonlat.T)
return (pixel[:2,:]/pixel[2,:]).T
class SpeedEstimate:
def __init__(self):
# 配置相机画面与地图的映射点,需要根据自己镜头和地图上的点重新配置
quad_coords = {
"lonlat": np.array([
[30.221866, 120.287402], # top left
[30.221527,120.287632], # top right
[30.222098,120.285806], # bottom left
[30.221805,120.285748] # bottom right
]),
"pixel": np.array([
[196,129],# top left
[337,111], # top right
[12,513], # bottom left
[530,516] # bottom right
])
}
self.pm = PixelMapper(quad_coords["pixel"], quad_coords["lonlat"])
def pixel2lonlat(self,x,y):
# 像素坐标转为经纬度
return self.pm.pixel_to_lonlat((x,y))[0]
def pixelDistance(self,pa_x,pa_y,pb_x,pb_y):
# 相机画面两点在地图上实际的距离
lonlat_a = self.pm.pixel_to_lonlat((pa_x,pa_y))
lonlat_b = self.pm.pixel_to_lonlat((pb_x,pb_y))
lonlat_a = tuple(lonlat_a[0])
lonlat_b = tuple(lonlat_b[0])
return haversine(lonlat_a, lonlat_b, unit='m')
项目需求+V: gldz_super 文章来源地址https://www.toymoban.com/news/detail-625107.html
到了这里,关于基于yolo v5与Deep Sort进行车辆以及速度检测与目标跟踪实战的文章就介绍完了。如果您还想了解更多内容,请在右上角搜索TOY模板网以前的文章或继续浏览下面的相关文章,希望大家以后多多支持TOY模板网!