InferOnnx项目
本项目gitee链接:点击跳转
本项目资源链接:点击跳转
欢迎批评指正。
环境设置
CPU:i5-9400F
GPU:GTX1060
参考文档
yolov5使用onnxruntime进行c++部署:跳转链接
详细介绍 Yolov5 转 ONNX模型 + 使用 ONNX Runtime 的 C++ 部署(包含官方文档的介绍):跳转链接
yolov5-v6.1-opencv-onnxrun:跳转链接
【推理引擎】从源码看ONNXRuntime的执行流程 :跳转链接
推理
整个ONNXRuntime的运行可以分为三个阶段

相关结构体
定义两个结构体 Net_config 和 BoxInfo。
结构体 Net_config 包含了一些模型配置参数,包括:
- confThreshold:置信度阈值;
- nmsThreshold:非极大值抑制阈值;
- objThreshold:物体置信度阈值;
- modelpath:模型路径;
- gpu:是否使用 GPU。
结构体 BoxInfo 包含了每个检测框的信息,包括: - x1:检测框左上角 x 坐标;
- y1:检测框左上角 y 坐标;
- x2:检测框右下角 x 坐标;
- y2:检测框右下角 y 坐标;
- score:检测框的置信度得分;
- label:检测框的标签。
这两个结构体在目标检测算法中经常被用于存储模型配置参数和检测结果等信息,方便代码的编写和阅读。
struct Net_config
{
float confThreshold; // Confidence threshold
float nmsThreshold; // Non-maximum suppression threshold
float objThreshold; // Object Confidence threshold
string modelpath; // model path
bool gpu = false; // using gpu
};
typedef struct BoxInfo
{
float x1;
float y1;
float x2;
float y2;
float score;
int label;
} BoxInfo;
实现YOLO类
我们需要一段代码来一个 YOLO 类,用于目标检测的模型推理。
首先,初始化YOLO类时需要根据输入的参数来生成模型;方法就是根据上一段的Net_config 结构体参数进行生成。之后模型需要一个外部接口用于模型推理的成员变量和函数。
因此,类中主要函数包括:
- YOLO(Net_config config):构造函数,用于初始化模型配置参数;
- void detect(Mat& frame):目标检测函数,用于对输入的图像进行检测,并输出检测结果。
成员变量包括:
- float* anchors:每层特征图所使用的 anchor 数组;
- int num_stride:anchor 采样的步长;
- int inpWidth:输入图像的宽度;
- int inpHeight:输入图像的高度;
- int nout:网络输出节点的数量;
- int num_proposal:每个特征点预测目标框的数量;
- vector class_names:目标类别名称的列表;
- int num_class:目标类别的数量;
- int seg_num_class:分割图像的类别数量;
- float confThreshold:目标置信度得分的阈值;
- float nmsThreshold:非最大值抑制的阈值;
- float objThreshold:目标置信度得分的阈值;
- const bool keep_ratio:是否保持原始图像宽高比;
- vector input_image_:输入图像的数据指针;
- env:ONNX 运行环境;
- ort_session:ONNX 模型的运行会话;
- sessionOptions:ONNX 会话配置参数;
- input_names:输入节点的名称列表;
- output_names:输出节点的名称列表;
- input_node_dims:输入节点的维度列表;
- output_node_dims:输出节点的维度列表;
- In_AllocatedStringPtr:输入节点的数据指针列表;
- Out_AllocatedStringPtr:输出节点的数据指针列表。
成员函数包括:
- void normalize_(Mat img):对输入图像进行像素归一化;
- void nms(vector& input_boxes):对检测结果进行非最大值抑制;
- Mat resize_image(Mat srcimg, int *newh, int *neww, int *top, int *left):调整输入图像的大小以适应模型输入节点的要求。
class YOLO
{
public:
YOLO(Net_config config);
void detect(Mat& frame);
private:
float* anchors;
int num_stride;
int inpWidth;
int inpHeight;
int nout;
int num_proposal;
vector<string> class_names;
int num_class;
int seg_num_class;
float confThreshold;
float nmsThreshold;
float objThreshold;
const bool keep_ratio = true;
vector<float> input_image_;
void normalize_(Mat img);
void nms(vector<BoxInfo>& input_boxes);
Mat resize_image(Mat srcimg, int *newh, int *neww, int *top, int *left);
Env env = Env(ORT_LOGGING_LEVEL_ERROR, "yolov5s");
Ort::Session *ort_session = nullptr;
SessionOptions sessionOptions = SessionOptions();
vector<const char* > input_names;
vector<const char* > output_names;
vector<vector<int64_t>> input_node_dims; // >=1 outputs
vector<vector<int64_t>> output_node_dims; // >=1 outputs
std::vector<AllocatedStringPtr> In_AllocatedStringPtr;
std::vector<AllocatedStringPtr> Out_AllocatedStringPtr;
};
相关代码
.h文件
#ifndef INFERONNX_H
#define INFERONNX_H
#include <fstream>
#include <sstream>
#include <opencv2/imgproc.hpp>
#include <opencv2/highgui.hpp>
#include <onnxruntime_cxx_api.h>
using namespace std;
using namespace cv;
using namespace Ort;
struct Net_config
{
float confThreshold; // Confidence threshold
float nmsThreshold; // Non-maximum suppression threshold
float objThreshold; // Object Confidence threshold
string modelpath; // model path
bool gpu = false; // using gpu
};
typedef struct BoxInfo
{
float x1;
float y1;
float x2;
float y2;
float score;
int label;
} BoxInfo;
int endsWith(string s, string sub);
const float anchors_640[3][6] = { {10.0, 13.0, 16.0, 30.0, 33.0, 23.0},
{30.0, 61.0, 62.0, 45.0, 59.0, 119.0},
{116.0, 90.0, 156.0, 198.0, 373.0, 326.0} };
const float anchors_1280[4][6] = { {19, 27, 44, 40, 38, 94},{96, 68, 86, 152, 180, 137},{140, 301, 303, 264, 238, 542},
{436, 615, 739, 380, 925, 792} };
class YOLO
{
public:
YOLO(Net_config config);
void detect(Mat& frame);
private:
float* anchors;
int num_stride;
int inpWidth;
int inpHeight;
int nout;
int num_proposal;
vector<string> class_names;
int num_class;
int seg_num_class;
float confThreshold;
float nmsThreshold;
float objThreshold;
const bool keep_ratio = true;
vector<float> input_image_;
void normalize_(Mat img);
void nms(vector<BoxInfo>& input_boxes);
Mat resize_image(Mat srcimg, int *newh, int *neww, int *top, int *left);
Env env = Env(ORT_LOGGING_LEVEL_ERROR, "yolov5s");
Ort::Session *ort_session = nullptr;
SessionOptions sessionOptions = SessionOptions();
vector<const char* > input_names;
vector<const char* > output_names;
vector<vector<int64_t>> input_node_dims; // >=1 outputs
vector<vector<int64_t>> output_node_dims; // >=1 outputs
std::vector<AllocatedStringPtr> In_AllocatedStringPtr;
std::vector<AllocatedStringPtr> Out_AllocatedStringPtr;
};
#endif // INFERONNX_H
CPP文件
#include "InferOnxx.h"
int endsWith(string s, string sub) {
return s.rfind(sub) == (s.length() - sub.length()) ? 1 : 0;
}
YOLO::YOLO(Net_config config)
{
this->confThreshold = config.confThreshold;
this->nmsThreshold = config.nmsThreshold;
this->objThreshold = config.objThreshold;
string classesFile = "D:/workspace/C++/Onnx/InferOnxx/InferOnxx/class.names";
string model_path = config.modelpath;
std::wstring widestr = std::wstring(model_path.begin(), model_path.end());
if (config.gpu) {
OrtSessionOptionsAppendExecutionProvider_CUDA(sessionOptions, 0); //CUDA加速开启
}
sessionOptions.SetGraphOptimizationLevel(ORT_ENABLE_BASIC); //设置图优化类型
ort_session = new Session(env, widestr.c_str(), sessionOptions); // 创建会话,把模型加载到内存中
size_t numInputNodes = ort_session->GetInputCount(); //输入输出节点数量
size_t numOutputNodes = ort_session->GetOutputCount();
for (int i = 0; i < numInputNodes; i++) // onnxruntime1.12版本后不能按照从前格式写
{
AllocatorWithDefaultOptions allocator; // 配置输入输出节点内存
In_AllocatedStringPtr.push_back(ort_session->GetInputNameAllocated(i, allocator));
input_names.push_back(In_AllocatedStringPtr.at(i).get()); // 内存
Ort::TypeInfo input_type_info = ort_session->GetInputTypeInfo(i); // 类型
auto input_tensor_info = input_type_info.GetTensorTypeAndShapeInfo();
auto input_dims = input_tensor_info.GetShape(); // 输入shape
input_node_dims.push_back(input_dims); // 输入维度信息
}
for (int i = 0; i < numOutputNodes; i++)
{
AllocatorWithDefaultOptions allocator;
Out_AllocatedStringPtr.push_back(ort_session->GetOutputNameAllocated(i, allocator));
output_names.push_back(Out_AllocatedStringPtr.at(i).get());
Ort::TypeInfo output_type_info = ort_session->GetOutputTypeInfo(i);
auto output_tensor_info = output_type_info.GetTensorTypeAndShapeInfo();
auto output_dims = output_tensor_info.GetShape();
output_node_dims.push_back(output_dims);
}
this->inpHeight = input_node_dims[0][2];
this->inpWidth = input_node_dims[0][3];
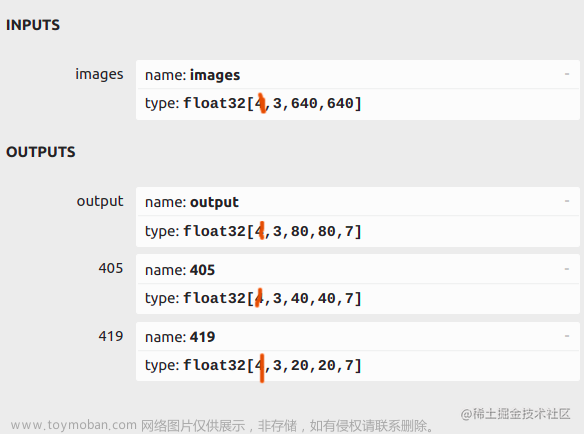
this->nout = output_node_dims[0][2]; // 5+classese 85
this->num_proposal = output_node_dims[0][1]; // 3*(小检测框+中检测框+大检测框) 3*((20*20)+(40*40)+(80*80))
ifstream ifs(classesFile.c_str());
string line;
while (getline(ifs, line)) this->class_names.push_back(line);
this->num_class = class_names.size();
if (endsWith(config.modelpath, "6.onnx")) // 判断版本
{
anchors = (float*)anchors_1280;
this->num_stride = 4;
}
else
{
anchors = (float*)anchors_640;
this->num_stride = 3;
}
}
Mat YOLO::resize_image(Mat srcimg, int *newh, int *neww, int *top, int *left)
{
int srch = srcimg.rows, srcw = srcimg.cols;
*newh = this->inpHeight;
*neww = this->inpWidth;
Mat dstimg;
if (this->keep_ratio && srch != srcw) {
float hw_scale = (float)srch / srcw;
if (hw_scale > 1) { // srch>srcw
*newh = this->inpHeight;
*neww = int(this->inpWidth / hw_scale); // set/scale
resize(srcimg, dstimg, Size(*neww, *newh), INTER_AREA); // resize(nw,nh)
*left = int((this->inpWidth - *neww) * 0.5); // 计算padding距离
copyMakeBorder(dstimg, dstimg, 0, 0, *left, this->inpWidth - *neww - *left, BORDER_CONSTANT, 114); // padding
}
else {
*newh = (int)this->inpHeight * hw_scale;
*neww = this->inpWidth;
resize(srcimg, dstimg, Size(*neww, *newh), INTER_AREA);
*top = (int)(this->inpHeight - *newh) * 0.5;
copyMakeBorder(dstimg, dstimg, *top, this->inpHeight - *newh - *top, 0, 0, BORDER_CONSTANT, 114);
}
}
else {
resize(srcimg, dstimg, Size(*neww, *newh), INTER_AREA);
}
return dstimg;
}
void YOLO::normalize_(Mat img)
{
// img.convertTo(img, CV_32F);
int row = img.rows;
int col = img.cols;
this->input_image_.resize(row * col * img.channels());
for (int c = 0; c < 3; c++)
{
for (int i = 0; i < row; i++)
{
for (int j = 0; j < col; j++)
{
float pix = img.ptr<uchar>(i)[j * 3 + 2 - c]; // HWC to CHW, BGR to RGB,j * 3 + 2 - c即完成转换
this->input_image_[c * row * col + i * col + j] = pix / 255.0;
}
}
}
}
void YOLO::nms(vector<BoxInfo>& input_boxes)
{
sort(input_boxes.begin(), input_boxes.end(), [](BoxInfo a, BoxInfo b) { return a.score > b.score; }); // 按照置信度排序, []Lambda 表达式
vector<float> vArea(input_boxes.size()); // 记录每个检测框面积
for (int i = 0; i < int(input_boxes.size()); ++i) // 遍历所有检测框
{
vArea[i] = (input_boxes.at(i).x2 - input_boxes.at(i).x1 + 1)
* (input_boxes.at(i).y2 - input_boxes.at(i).y1 + 1);
}
vector<bool> isSuppressed(input_boxes.size(), false); // 记录是否抑制,默认为FALSE
for (int i = 0; i < int(input_boxes.size()); ++i) // 遍历所有检测框
{
if (isSuppressed[i]) { continue; } // 是否已经判断过
for (int j = i + 1; j < int(input_boxes.size()); ++j) // 第二个指针遍历
{
if (isSuppressed[j]) { continue; }
float xx1 = (max)(input_boxes[i].x1, input_boxes[j].x1);
float yy1 = (max)(input_boxes[i].y1, input_boxes[j].y1);
float xx2 = (min)(input_boxes[i].x2, input_boxes[j].x2);
float yy2 = (min)(input_boxes[i].y2, input_boxes[j].y2);
float w = (max)(float(0), xx2 - xx1 + 1);
float h = (max)(float(0), yy2 - yy1 + 1);
float inter = w * h;
float ovr = inter / (vArea[i] + vArea[j] - inter); // 计算miou
if (ovr >= this->nmsThreshold)
{
isSuppressed[j] = true; // 大于设定的阈值,则抑制
}
}
}
// return post_nms;
int idx_t = 0;
// remove_if()函数 remove_if(beg, end, op) //移除区间[beg,end)中每一个“令判断式:op(elem)获得true”的元素
input_boxes.erase(remove_if(input_boxes.begin(), input_boxes.end(), [&idx_t, &isSuppressed](const BoxInfo& f) { return isSuppressed[idx_t++]; }), input_boxes.end());
}
void YOLO::detect(Mat& frame)
{
int newh = 0, neww = 0, padh = 0, padw = 0; // padh:上下边的padding距离; padw:左右padding的距离
Mat dstimg = this->resize_image(frame, &newh, &neww, &padh, &padw);
this->normalize_(dstimg);
array<int64_t, 4> input_shape_{ 1, 3, this->inpHeight, this->inpWidth };
auto memory_info = MemoryInfo::CreateCpu(OrtDeviceAllocator, OrtMemTypeCPU);
Value input_tensor_ = Value::CreateTensor<float>(memory_info, input_image_.data(), input_image_.size(), input_shape_.data(), input_shape_.size());
vector<Value> ort_outputs = ort_session->Run(RunOptions{ nullptr }, &input_names[0], &input_tensor_, 1, output_names.data(), output_names.size());
vector<BoxInfo> generate_boxes;
const float* pdata = ort_outputs[0].GetTensorMutableData<float>(); // 数组,存放预测数据 [bs,anchor'classes,anchor'number,pos+conf+ num'classes]
float ratioh = (float)frame.rows / newh, ratiow = (float)frame.cols / neww; // 计算缩放倍数
for (int i = 0; i < num_proposal; ++i) // 遍历所有的num_pre_boxes 3*((20*20)+(40*40)+(80*80))
{
int index = i * nout; // 索引
float obj_conf = pdata[index + 4]; // 第四个为置信度分数
if (obj_conf > this->objThreshold) // 大于阈值
{
// 求最大分数和索引
int class_idx = 0; // 记录类别id
float max_class_socre = 0; // 记录最大概率
for (int k = 0; k < this->num_class; ++k) // K个类别里循环
{
if (pdata[k + index + 5] > max_class_socre) // 判断分数
{
max_class_socre = pdata[k + index + 5]; // 记录分数
class_idx = k; // 记录类别数
}
}
max_class_socre *= obj_conf; // 最大的类别分数*置信度
if (max_class_socre > this->confThreshold) // 再次筛选
{
float cx = pdata[index]; //x:检测框中心点
float cy = pdata[index + 1]; //y
float w = pdata[index + 2]; //w:检测框宽
float h = pdata[index + 3]; //h
// 映射到原来的图像上
float xmin = (cx - padw - 0.5 * w)*ratiow; // (推理位置-左边padding距离-0.5*宽)*缩放倍数=原图像左上角x位置
float ymin = (cy - padh - 0.5 * h)*ratioh; // (推理位置-上边padding距离-0.5*高)*缩放倍数=原图像左上角y位置
float xmax = (cx - padw + 0.5 * w)*ratiow; //
float ymax = (cy - padh + 0.5 * h)*ratioh; //
generate_boxes.push_back(BoxInfo{ xmin, ymin, xmax, ymax, max_class_socre, class_idx }); //记录相关数据
}
}
}
// Perform non maximum suppression to eliminate redundant overlapping boxes with
// lower confidences
nms(generate_boxes);
for (size_t i = 0; i < generate_boxes.size(); ++i)
{
int xmin = int(generate_boxes[i].x1);
int ymin = int(generate_boxes[i].y1);
rectangle(frame, Point(xmin, ymin), Point(int(generate_boxes[i].x2), int(generate_boxes[i].y2)), Scalar(0, 0, 255), 2);
string label = format("%.2f", generate_boxes[i].score);
label = this->class_names[generate_boxes[i].label] + ":" + label;
putText(frame, label, Point(xmin, ymin - 5), FONT_HERSHEY_SIMPLEX, 0.75, Scalar(0, 255, 0), 1);
}
}
推理结果
在coco验证集上推理图片所花的时间如下
-
cpu推理两张图片

-
gpu推理两张图片

-
cpu推理100张图片

-
gpu推理100张图片

-
推理部分结果


值得注意的地方
版本不同引起的相关改动
- 开启cuda加速
1.12版本后一句话就可以开启cuda加速OrtSessionOptionsAppendExecutionProvider_CUDA(sessionOptions, 0); //CUDA加速开启 - 获取输入输出节点数
for (int i = 0; i < numInputNodes; i++) // onnxruntime1.12版本后不能按照从前格式写
{
AllocatorWithDefaultOptions allocator; // 配置输入输出节点内存
In_AllocatedStringPtr.push_back(ort_session->GetInputNameAllocated(i, allocator));
input_names.push_back(In_AllocatedStringPtr.at(i).get()); // 内存
Ort::TypeInfo input_type_info = ort_session->GetInputTypeInfo(i); // 类型
auto input_tensor_info = input_type_info.GetTensorTypeAndShapeInfo();
auto input_dims = input_tensor_info.GetShape(); // 输入shape
input_node_dims.push_back(input_dims); // 输入维度信息
}
for (int i = 0; i < numOutputNodes; i++)
{
AllocatorWithDefaultOptions allocator;
Out_AllocatedStringPtr.push_back(ort_session->GetOutputNameAllocated(i, allocator));
output_names.push_back(Out_AllocatedStringPtr.at(i).get());
Ort::TypeInfo output_type_info = ort_session->GetOutputTypeInfo(i);
auto output_tensor_info = output_type_info.GetTensorTypeAndShapeInfo();
auto output_dims = output_tensor_info.GetShape();
output_node_dims.push_back(output_dims);
}
这里如果按照之前版本写,会造成内存泄漏,从而引发异常
这段代码定义了 YOLO 类中的像素归一化函数 normalize_()。该函数接收一个 cv::Mat 类型的图像作为输入,并将其像素值归一化至 [0,1] 的范围内,将像素数据存储到 input_image_ 数组中。值得注意的是,在读取像素点时,使用 img.ptr<uchar>(i)[j * 3 + 2 - c] 获取像素点的值,其中 i 表示行数,j 表示列数,c 表示当前通道数。由于输入图像的通道顺序为 BGR,而在存储到 input_image_ 数组中时需要按照 RGB 通道的顺序进行存储,因此需要使用 j * 3 + 2 - c 对通道顺序进行转换。最终将 input_image_ 数组的大小设置为 row * col * img.channels(),即所有像素点的数量。文章来源:https://www.toymoban.com/news/detail-626418.html
相关知识点学习
cv::glob
cv::glob:提取目录下的文件地址
// 提取文件名称
string path = "路径"
int sttr_start = path.find_last_of("\\");
int sttr_size = path.size();
string sub_path = path.substr(sttr_start, sttr_size - 1);
归一化函数
void YOLO::normalize_(Mat img)
{
// img.convertTo(img, CV_32F);
int row = img.rows;
int col = img.cols;
this->input_image_.resize(row * col * img.channels());
for (int c = 0; c < 3; c++)
{
for (int i = 0; i < row; i++)
{
for (int j = 0; j < col; j++)
{
float pix = img.ptr<uchar>(i)[j * 3 + 2 - c]; // HWC to CHW, BGR to RGB,j * 3 + 2 - c即完成转换
this->input_image_[c * row * col + i * col + j] = pix / 255.0;
}
}
}
}
YOLOv5head
YOLOv5的输出是检测框的中心点位置,以及检测框的高宽,因此最后画框的时候需要转换坐标轴位置文章来源地址https://www.toymoban.com/news/detail-626418.html
if (max_class_socre > this->confThreshold) // 再次筛选
{
float cx = pdata[index]; //x:检测框中心点
float cy = pdata[index + 1]; //y
float w = pdata[index + 2]; //w:检测框宽
float h = pdata[index + 3]; //h
// 映射到原来的图像上
float xmin = (cx - padw - 0.5 * w)*ratiow; // (推理位置-左边padding距离-0.5*宽)*缩放倍数=原图像左上角x位置
float ymin = (cy - padh - 0.5 * h)*ratioh; // (推理位置-上边padding距离-0.5*高)*缩放倍数=原图像左上角y位置
float xmax = (cx - padw + 0.5 * w)*ratiow; //
float ymax = (cy - padh + 0.5 * h)*ratioh; //
generate_boxes.push_back(BoxInfo{ xmin, ymin, xmax, ymax, max_class_socre, class_idx }); //记录相关数据
}
到了这里,关于YOLOv5在C++中通过Onnxruntime在window平台上的cpu与gpu推理的文章就介绍完了。如果您还想了解更多内容,请在右上角搜索TOY模板网以前的文章或继续浏览下面的相关文章,希望大家以后多多支持TOY模板网!