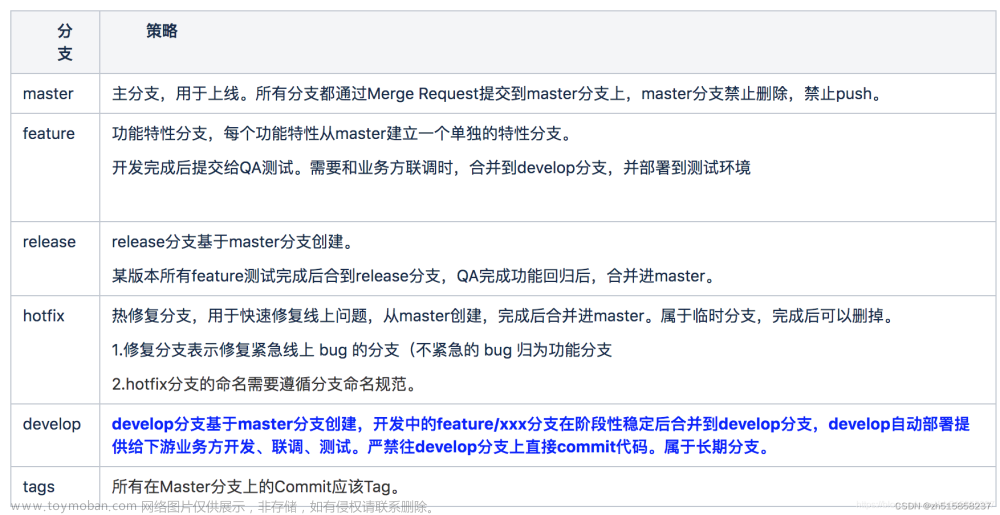
6 屏幕截图与图像定位

PyAutoGUI可以拍摄屏幕截图,将其保存到文件中,并在屏幕中定位图像。OSX使用操作系统附带的screencapture命令。Linux使用scrot命令,可以通过运行sudo-apt-get-install-scrot来安装该命令。文章来源:https://www.toymoban.com/news/detail-627386.html
功能介绍:一个需要点击的按钮,并且想在屏幕上找到它。文章来源地址https://www.toymoban.com/news/detail-627386.html
6.1 屏幕截图
import pyautogui
# 截取全屏 在1920 x 1080屏幕上,screenshot()函数大约需要100毫秒-不快但不慢。
im1 = pyautogui.screenshot()
# 截取全屏,并以图片保存
im2 = pyautogui.screenshot('my_screenshot.png')
# 截取指定位置,传递要捕获的区域的左侧、顶部、宽度和高度的四个整数元组:
im = pyautogui.screenshot(region=(0,0, 300, 400))
6.2 定位单个目标
import pyautogui
# ---------------------------------------------------------------
# 获取感兴趣区域的 (left, top, width, height)
button7location = pyautogui.locateOnScreen('looksLikeThis.png')
print(button7location)
print(button7location[0])
print(button7location.left)
# 计算感兴趣区域的中心点的xy坐标
button7point = pyautogui.center(button7location)
print(button7point)
print(button7point[0])
print(button7point.x)
# 点击感兴趣区域的中心点坐标
button7x, button7y = button7point
pyautogui.click(button7x, button7y)
# ---------------------------------------------------------------
# 快速点击感兴趣区域
pyautogui.click('looksLikeThis.png')
# ---------------------------------------------------------------
# 设置置信度 需要安装opencv
button7location = pyautogui.locateOnScreen('looksLikeThis.png', confidence=0.9)
print(button7location)
print(button7location[0])
print(button7location.left)
# ---------------------------------------------------------------
# 获取感兴趣区域的中心点位置坐标,并且点击
x, y = pyautogui.locateCenterOnScreen('looksLikeThis.png')
pyautogui.click(x, y)
6.3 定位全部目标的位置
import pyautogui
# 这些“定位”功能相当昂贵;他们可以用整整一秒钟的时间跑。
for pos in pyautogui.locateAllOnScreen('someButton.png')
print(pos)
# 提高速度的最佳方法:传递一个区域参数(一个4整型元组(左、上、宽、高)),以仅搜索屏幕的较小区域,而不是全屏:
pyautogui.locateOnScreen('someButton.png', region=(0,0, 300, 400))
6.4 灰度匹配
import pyautogui
button7location = pyautogui.locateOnScreen('looksLikeThis.png', grayscale=True)
print(button7location)
6.5 像素匹配(获取屏幕截图中像素的RGB颜色)
import pyautogui
# 获取屏幕截图中像素的RGB颜色方案①
im = pyautogui.screenshot()
color_RGB = im.getpixel((100, 200))
print(color_RGB) #(130, 135, 144)
# 获取屏幕截图中像素的RGB颜色方案②
pix = pyautogui.pixel(100, 200)
print(pix) # RGB(red=130, green=135, blue=144)
print(pix[0]) # 130
print(pix.red) # 130
# 如果只需要验证单个像素是否与给定像素匹配,请调用pixelMatchesColor()函数,将其表示的颜色的X坐标、Y坐标和RGB元组传递给它:
pyautogui.pixelMatchesColor(100, 200, (130, 135, 144)) # True
pyautogui.pixelMatchesColor(100, 200, (0, 0, 0)) # False
# tolerance关键字参数指定红色、绿色和蓝色值在仍匹配时可以变化多少:
pyautogui.pixelMatchesColor(100, 200, (140, 125, 134)) # False
pyautogui.pixelMatchesColor(100, 200, (140, 125, 134), tolerance=10) # True
到了这里,关于【PyAutoGUI操作指南】05 屏幕截图与图像定位:截图+定位单个目标+定位全部目标+灰度匹配+像素匹配+获取屏幕截图中像素的RGB颜色的文章就介绍完了。如果您还想了解更多内容,请在右上角搜索TOY模板网以前的文章或继续浏览下面的相关文章,希望大家以后多多支持TOY模板网!