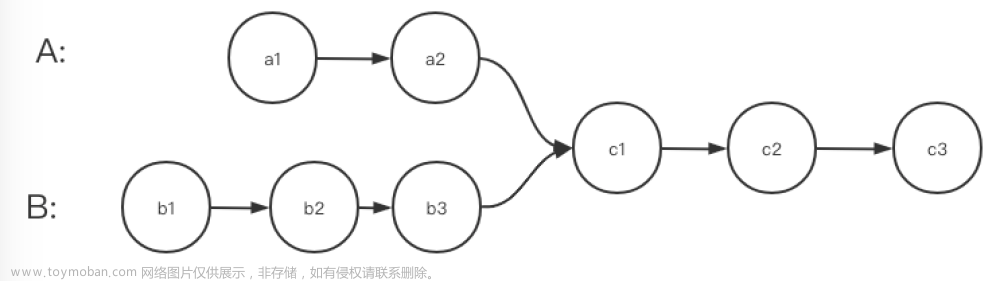
内容

链表的定义
class ListNode {
int val;
ListNode next;
ListNode(int val) {
this.val = val;
}
}
找到两个链表第一个公共子节点
剑指office 52题
public class 链表相交 {
class Solution {
//1. 哈希集
/* public ListNode getIntersectionNode(ListNode headA, ListNode headB) {
Set<ListNode> set = new HashSet<>();
while (headA != null) {
set.add(headA);
headA = headA.next;
}
while (headB != null) {
if (set.contains(headB)) {
return headB;
}
headB = headB.next;
}
return headB;
}*/
//2. 栈
/* public ListNode getIntersectionNode(ListNode headA, ListNode headB) {
Stack<ListNode> a=new Stack<>();
Stack<ListNode> b=new Stack<>();
ListNode pre=null;
while(headA!=null){
a.push(headA);
headA=headA.next;
}
while(headB!=null){
b.push(headB);
headB=headB.next;
}
while(a.size()>0 &&b.size()>0){
if(a.peek()==b.peek()){
pre=a.pop();
b.pop();
}else{
break;
}
}
return pre;
}
*/
//3.双指针
/* public ListNode getIntersectionNode(ListNode headA, ListNode headB) {
if ( headA== null || headB== null) {
return null;
}
ListNode p1 =headA ;
ListNode p2 =headB ;
while (p1 != p2) {
p1 = p1.next;
p2 = p2.next;
//不加上,如果没有相同结点就死循环了
if (p1 != p2) {
if (p1 == null) {
p1 =headB ;
}
if (p2 == null) {
p2 =headA ;
}
}
}
return p1;
}*/
//4. 差和双指针
//因为公共只会出现在较短的链表中,所以让它们一起开始遍历;
public ListNode getIntersectionNode(ListNode headA, ListNode headB) {
if (headA == null || headB == null) {
return null;
}
ListNode pre1 = headA;
ListNode pre2 = headB;
int len1 = 0, len2 = 0;
while (pre1 != null) {
len1++;
pre1 = pre1.next;
}
while (pre2 != null) {
len2++;
pre2 = pre2.next;
}
//一样长的无变化
int sub = len1 > len2 ? len1 - len2 : len2 - len1;
pre1 = headA;
pre2 = headB;
if (len1 > len2) {
//长的先走sub步
for (int i = 0; i < sub; i++) {
pre1 = pre1.next;
}
}
if (len2 > len1) {
//长的先走sub步
for (int i = 0; i < sub; i++) {
pre2 = pre2.next;
}
}
while (pre1 != pre2) {
pre1 = pre1.next;
pre2 = pre2.next;
}
return pre1;
}
}
}
判断链表是否为回文序列
LeetCode234题
public class 回文链表 {
class Solution {
//1. 栈
/*
public boolean isPalindrome(ListNode head) {
ListNode temp=head;
Stack<Integer> stack=new Stack<>();
int len=0;
while(temp!=null){
stack.push(temp.val);
temp=temp.next;
len++;
}
while(stack.size()>=len/2 &&head!=null){
if(head.val!=stack.pop()){
return false;
}
head=head.next;
}
return true;
}
*/
//2.快慢指针
public boolean isPalindrome(ListNode head) {
if (head == null || head.next == null) {
return true;
}
//slow和fast是快慢指针,slow到一半,fast到结尾了,prepre指针作用是不断翻转前一半的链表,pre最后会变成中间结点的前一个结点,因为中间结点一定相同,然后处在中间的slow往右移到一个单位,就能开始和pre指针的遍历比较了。
ListNode slow = head, fast = head;
ListNode pre = head, prepre = null;
while (fast != null && fast.next != null) {
pre = slow;
slow = slow.next;
fast = fast.next.next;
pre.next = prepre;
prepre = pre;
}
if (fast != null) {
slow = slow.next;
}
while (pre != null && slow != null) {
if (pre.val != slow.val) {
return false;
}
pre = pre.next;
slow = slow.next;
}
return true;
}
//Definition for singly-linked list.
public class ListNode {
int val;
ListNode next;
ListNode() {
}
ListNode(int val) {
this.val = val;
}
ListNode(int val, ListNode next) {
this.val = val;
this.next = next;
}
}
}
}
合并两个有序链表
LeetCode 21
class Solution {
public ListNode mergeTwoLists(ListNode list1, ListNode list2) {
//方法1:
/* ListNode newHead = new ListNode(-1);
ListNode res = newHead;
while (list1 != null && list2 != null) {
if (list1.val < list2.val) {
newHead.next = list1;
list1 = list1.next;
} else if (list1.val > list2.val) {
newHead.next = list2;
list2 = list2.next;
} else { //相等的情况,分别接两个链
newHead.next = list2;
list2 = list2.next;
newHead = newHead.next;
newHead.next = list1;
list1 = list1.next;
}
newHead = newHead.next;
}
while (list1 != null) {
newHead.next = list1;
list1 = list1.next;
newHead = newHead.next;
}
while (list2 != null) {
newHead.next = list2;
list2 = list2.next;
newHead = newHead.next;
}
/*
//最开始没有一点优化的版本
/* ListNode pre=new ListNode(-1);
ListNode res=pre;
while(list1!=null ||list2!=null){
if(list1!=null &&list2!=null){
if(list1.val<list2.val){
pre.next=list1;
list1=list1.next;
}else if(list1.val>list2.val){
pre.next=list2;
list2=list2.next;
}else if(list1.val==list2.val){
pre.next=list1;
list1=list1.next;
pre=pre.next;
pre.next=list2;
list2=list2.next;
}
pre=pre.next;
}else if(list1==null &&list2!=null){
pre.next=list2;
list2=list2.next;
pre=pre.next;
}else if(list1!=null &&list2==null){
pre.next=list1;
list1=list1.next;
pre=pre.next;
}
}
return res.next;*/
//方法2:优化方法1
/* ListNode l1=list1;
ListNode l2=list2;
ListNode prehead = new ListNode(-1);
ListNode prev = prehead;
while (l1 != null && l2 != null) {
if (l1.val <= l2.val) {
prev.next = l1;
l1 = l1.next;
} else {
prev.next = l2;
l2 = l2.next;
}
prev = prev.next;
}
// 最多只有一个还未被合并完,直接接上去就行了,这是链表合并比数组合并方便的地方
prev.next = l1 == null ? l2 : l1;
return prehead.next; */
//方法3:递归
ListNode l1 = list1;
ListNode l2 = list2;
if (l1 == null) {
return l2;
}
if (l2 == null) {
return l1;
}
if (l1.val < l2.val) {
l1.next = mergeTwoLists(l1.next, l2);
return l1;
} else {
l2.next = mergeTwoLists(l1, l2.next);
return l2;
}
}
}
合并K个升序链表
LeetCode 23
class Solution {
public ListNode mergeKLists(ListNode[] lists) {
ListNode res = null;
for (ListNode list : lists) {
res = mergeTwoListsMoreSimple(res, list);
}
return res;
}
public static ListNode mergeTwoListsMoreSimple(ListNode l1, ListNode l2) {
ListNode prehead = new ListNode(-1);
ListNode prev = prehead;
while (l1 != null && l2 != null) {
if (l1.val <= l2.val) {
prev.next = l1;
l1 = l1.next;
} else {
prev.next = l2;
l2 = l2.next;
}
prev = prev.next;
}
// 最多只有一个还未被合并完,直接接上去就行了,这是链表合并比数组合并方便的地方
prev.next = l1 == null ? l2 : l1;
return prehead.next;
}
}
合并两个链表
LeetCode 1669
class Solution {
public ListNode mergeInBetween(ListNode list1, int a, int b, ListNode list2) {
ListNode pre1=list1;
ListNode pre2=list1;
ListNode pre3=list2;
int i=0,j=0;
//j<b 防止i==a-1,j==b时候,循环出不去了;
while(pre1!=null &&pre2!=null &&j<b){
//到a前面一个结点
if(i!=a-1){
pre1=pre1.next;
i++;
}
//到b
if(j!=b){
pre2=pre2.next;
j++;
}
}
pre2=pre2.next;
//到list2最后
while(pre3.next!=null){
pre3=pre3.next;
}
//链1尾链住2头,链2尾接链1后半部分的头
pre1.next=list2;
pre3.next=pre2;
return list1;
}
}
链表的中间结点
LeetCode 876
class Solution {
//快慢指针
public ListNode middleNode(ListNode head) {
ListNode pre1=head;
ListNode pre2=head;
while(pre2!=null && pre2.next!=null){
pre1=pre1.next;
pre2=pre2.next.next;
}
return pre1;
}
}
链表中倒数第k个节点
剑指 Offer 22
class Solution {
//假设有五个结点,找倒数第二个,那么它就是正数第四个结点,想达到这个目标只需要走n-k步,也就是5-2=3步即可,因为走到最后那个位置要n步,所以我让快指针先走k步(2步),到达正数第三个位置,然后还有三步两个一起走n-k步即可;
public ListNode getKthFromEnd(ListNode head, int k) {
ListNode pre1=head;
ListNode pre2=head;
while(pre1!=null&& k>0){
pre1=pre1.next;
k--;
}
while(pre1!=null){
pre2=pre2.next;
pre1=pre1.next;
}
return pre2;
}
}
旋转链表
LeetCode 61
//双指针找到倒数第k个位置,分成123和45两个序列,快指针先走k步,然后一起走,快指针到尾部时候,慢指针到了倒数第k个结点的前一个结点,也就是3,将4赋值给res后,3指向null,快指针代表的5也指向了头结点1,完成了旋转,最后是45123;
class Solution {
public ListNode rotateRight(ListNode head, int k) {
if (head == null || k == 0) {
return head;
}
ListNode temp = head;
ListNode fast = head;
ListNode slow = head;
int len = 0;
while (head != null) {
head = head.next;
len++;
}
if (k % len == 0) {
return temp;
}
while ((k % len) > 0) {
k--;
fast = fast.next;
}
while (fast.next != null) {
fast = fast.next;
slow = slow.next;
}
ListNode res = slow.next;
slow.next = null;
fast.next = temp;
return res;
}
}
删除指定结点
LeetCode 203
class Solution {
public ListNode removeElements(ListNode head, int val) {
//方法1:
//如果要删除的值为val的是头结点,可能新的头结点值也为val,题目要求
//删除所有值为val的,所以使用while循环;
while(head!=null && head.val==val){
head=head.next;
}
if(head==null){
return head;
}
ListNode prev=head;
while(prev.next!=null){
if(prev.next.val==val){
prev.next=prev.next.next;
}else{
prev=prev.next;
}
}
return head;
//方法2:虚拟头结点
/* ListNode dNode=new ListNode(val-1);
dNode.next=head;
ListNode prev=dNode;
//共用一个内存了
while(prev.next!=null){
if(prev.next.val==val){
prev.next=prev.next.next;
}else{
prev=prev.next;
}
}
return dNode.next; */
}
}
删除链表的倒数第 N 个结点
LeetCode 19
class Solution {
//方法1:双指针,因为这次要删倒数第k个,要找前一个,所以从虚拟结点开始;
//建立头结点,方便删除第一个结点
/* public ListNode removeNthFromEnd(ListNode head, int n) {
ListNode pre1=head;
ListNode pre3=new ListNode(0);
pre3.next=head;
ListNode pre2=pre3;
while(pre1!=null && n>0){
n--;
pre1=pre1.next;
}
while(pre1!=null){
pre2=pre2.next;
pre1=pre1.next;
}
pre2.next=pre2.next.next;
return pre3.next;
} */
//方法2:利用栈
public ListNode removeNthFromEnd(ListNode head, int n) {
// ListNode pre1=head;
ListNode pre3=new ListNode(0);
pre3.next=head;
ListNode pre2=pre3;
Stack<ListNode> stack=new Stack<>();
while(pre2!=null){
stack.push(pre2);
pre2=pre2.next;
}
for(int i=0;i<n;i++){
stack.pop();
}
//此时栈顶就是倒数第n个结点的前一个结点
pre2 = stack.peek();
pre2.next=pre2.next.next;
return pre3.next;
}
}
删除排序链表中的重复元素(保留一个)
LeetCode 83 文章来源:https://www.toymoban.com/news/detail-630360.html
文章来源:https://www.toymoban.com/news/detail-630360.html
class Solution {
public ListNode deleteDuplicates(ListNode head) {
if(head==null){
return head;
}
ListNode pre=head;
while(pre.next!=null){
if(pre.val==pre.next.val){
pre.next=pre.next.next;
}else{
pre=pre.next;
}
}
return head;
}
}
删除排序链表中的重复元素(重复元素都不要)
LeetCode 82 文章来源地址https://www.toymoban.com/news/detail-630360.html
文章来源地址https://www.toymoban.com/news/detail-630360.html
class Solution {
//因为有删头结点的可能性,所以设置虚拟头结点
public ListNode deleteDuplicates(ListNode head) {
ListNode pre=new ListNode(0);
pre.next=head;
ListNode cur=pre;
while(cur.next!=null &&cur.next.next!=null){
if(cur.next.val == cur.next.next.val){
int x=cur.next.val;
//这个while作用是一次性把重复的删干净
while(cur.next!=null &&cur.next.val==x){
cur.next=cur.next.next;
}
}else{
cur=cur.next;
}
}
return pre.next;
}
}
到了这里,关于算法通关村第一关——链表经典问题的文章就介绍完了。如果您还想了解更多内容,请在右上角搜索TOY模板网以前的文章或继续浏览下面的相关文章,希望大家以后多多支持TOY模板网!