目录:
- 双向LSTM
- torch.nn.embedding()实现词嵌入层
- nn.LSTM
- nn.LSTMCell
- LSTM 情感分类例子
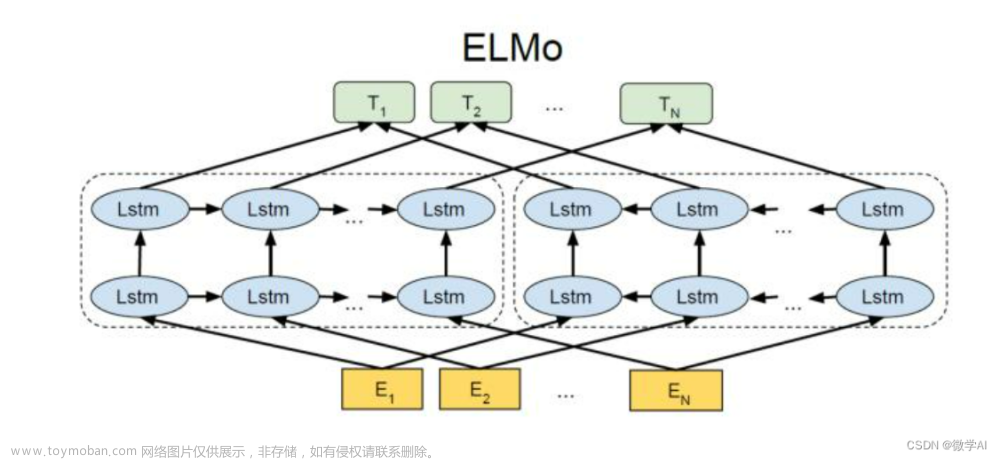
一 双向LSTM
1 原理
![[PyTorch][chapter 47][LSTM -2],pytorch,lstm,人工智能](https://imgs.yssmx.com/Uploads/2023/08/635165-1.png)
![[PyTorch][chapter 47][LSTM -2],pytorch,lstm,人工智能](https://imgs.yssmx.com/Uploads/2023/08/635165-2.png)
正向输出的结果是
反向输出的结果是
nn.LSTM模块他在最后会将正向和反向的结果进行拼接concat.得到
# -*- coding: utf-8 -*-
"""
Created on Fri Aug 4 11:27:19 2023
@author: chengxf2
"""
import torch
import torch.nn as nn
class MyLSTM(nn.Module):
def __init__(self, input_size, hidden_size, nOut):
super(MyLSTM, self).__init__()
self.rnn = nn.LSTM(input_size, hidden_size, bidirectional=True)
self.linear = nn.Linear(hidden_size * 2, nOut)
def forward(self, input):
#这里面的hidden 是concat 以后的结果
hidden, _ = self.rnn(input)
print("\n hidden ",hidden.shape) #[seq_len, batch_size, hidden_size*2]
T, b, h = hidden.size()
print(T,b,h)
h_rec = hidden.view(T * b, h)
output = self.linear(h_rec) # [T * b, nOut]
output = output.view(T, b, -1)
print("\n out ",output.shape)
return output
seq_len = 5
batch_size =1
input_size = 2
hidden_size = 10
N = 2
model = MyLSTM(input_size,hidden_size, N)
X = torch.randn((seq_len, batch_size, input_size))
output = model(X)二 torch.nn.embedding()实现词嵌入层
意义
输入: 词的编号索引,输出: 对应符号的嵌入向量。
参数:
| 参数 |
意思 |
| Num_embeddings |
词典的大小尺寸,比如总共出现100个词,那就输入100 |
| embeddding _ dim |
词对应向量的维度 |
| padding_idx |
输入长度为100,但是每次的句子长度并不一样,后面就需要用统一的数字填充,而这里就是指定这个数字,这样,网络在遇到填充id时,就不会计算其与其它符号的相关性。(初始化为0) |
| max_norm |
最大范数,如果嵌入向量的范数超过了这个界限,就要进行再归一化 |
| norm_type |
指定利用什么范数计算,并用于对比max_norm,默认为2范数 |
| scale_grad_by_freq |
根据单词在mini-batch中出现的频率,对梯度进行放缩。默认为False. |
| sparse |
若为True,则与权重矩阵相关的梯度转变为稀疏张量。 |
# -*- coding: utf-8 -*-
"""
Created on Fri Aug 4 15:08:09 2023
@author: chengxf2
"""
import torch
import torch.nn as nn
word_to_idx = {'my':0,'name':1,'is':2,"jack":3}
num_embeddings = len(word_to_idx.keys())
embedding_dim = 10
#<class 'torch.nn.modules.sparse.Embedding'>
embeds = nn.Embedding(num_embeddings, embedding_dim)
text = 'is name'
text_idx = torch.LongTensor([word_to_idx[i] for i in text.split()])
#词嵌入得到词向量 [2,10]
hello_embed = embeds(text_idx)
print(hello_embed.shape, hello_embed.type)
三 nn.LSTM
1.1 模型参数
| nn.LSTM 参数 |
作用 |
| Input_size |
输入层的维度 |
| Hidden _ size |
隐藏层的维数 |
| Num_layers |
堆叠的层数,默认值是1层,如果设置为2。第一层的隐藏值h,作为第二层的输入层的输入 |
| bias |
隐层状态是否带bias,默认为true。 |
| batch_first |
默认False [T, batch_size, input_size] |
| dropout |
默认值0 |
| bidirectional |
是否是双向 RNN,默认为:false |
1.2 forward 定义
x shape: [seq,batch_size, input_size]
h,c shape: [num_layer, batch_size, hidden_size]
out shape: [seq, batch_size, hidden_size]
# -*- coding: utf-8 -*-
"""
Created on Thu Aug 3 16:29:49 2023
@author: chengxf2
"""
import torch
import torch.nn as nn
import torch.nn.functional as F
import torch.optim as optim
lstm = nn.LSTM(input_size=50, hidden_size=20, num_layers=1)
print(lstm)
x = torch.randn(10,5,50)
out, (h,c)= lstm(x)
print("\n out shape ",out.shape)
print("\n hidden shape ",h.shape)
print("\n c shape ",c.shape)![[PyTorch][chapter 47][LSTM -2],pytorch,lstm,人工智能](https://imgs.yssmx.com/Uploads/2023/08/635165-3.png)
四 nn.LSTMCell
2.1 参数基本一样,主要区别是forward 过程不一样
| nn.LSTM 参数 |
作用 |
| Input_size |
输入层的维度 |
| Hidden _ size |
隐藏层的维数 |
| Num_layers |
堆叠的层数,默认值是1层,如果设置为2。第一层的隐藏值h,作为第二层的输入层的输入 |
2.2 forward
的shape: [batch_size, input_size]
的shape: [batch_size, input_size]
# -*- coding: utf-8 -*-
"""
Created on Thu Aug 3 16:39:42 2023
@author: chengxf2
"""
import torch
import torch.nn as nn
import torch.nn.functional as F
print('lstmCell')
batch_size =2
input_size = 20
hidden_size =10
seq_num = 5
cell = nn.LSTMCell(input_size, hidden_size)
X = torch.randn((seq_num,batch_size,input_size))
H0 = torch.zeros(batch_size,hidden_size)
C0= torch.zeros(batch_size, hidden_size)
for xt in X:
ht,ct = cell(xt,[H0,C0])
print("\n ht.shape",ht.shape)
print("\n ct.shape",ht.shape)![[PyTorch][chapter 47][LSTM -2],pytorch,lstm,人工智能](https://imgs.yssmx.com/Uploads/2023/08/635165-4.png)
五 LSTM 情感分类
![[PyTorch][chapter 47][LSTM -2],pytorch,lstm,人工智能](https://imgs.yssmx.com/Uploads/2023/08/635165-5.png)
5.1 环境安装
torch text 有兼容性要求
pip install torchtext==0.11.0 --user
pip install SpaCy
安装完可以打印看一下,版本是否兼容
# -*- coding: utf-8 -*-
"""
Created on Mon Aug 7 15:49:15 2023
@author: chengxf2
"""
import torch
import torchtext
print(torch.__version__)
print(torchtext.__version__)
-----------------------------
runfile('D:/AI/LSTM/untitled0.py', wdir='D:/AI/LSTM')
1.10.0+cpu
0.11.01.2 加载数据集
文件名: loadcorpus.py
import torch
from torchtext.legacy import data
from torchtext.legacy import datasets
def load_data():
'''
Step 1: Create a dataset object
legacy code:
Field class is used for data processing, including tokenizer and numberzation.
To check out the dataset, users need to first set up the TEXT/LABEL fields.
'''
TEXT = data.Field(tokenize=data.get_tokenizer('basic_english'),
init_token='', eos_token='', lower=True)
LABEL = data.LabelField(dtype = torch.long)
# 按照(TEXT, LABEL) 分割成 训练集:25000,测试集:25000
legacy_train, legacy_test = datasets.IMDB.splits(TEXT, LABEL) # datasets here refers to torchtext.legacy.datasets
print('len of train data:', len(legacy_train)) # 25000
print('len of test data:', len(legacy_test)) # 25000
# torchtext.data.Example : 用来表示一个样本,数据+标签
#print(legacy_test.examples[15].text) #文本:句子的单词列表:字符串
#print(legacy_train.examples[15].label) # 标签: 字符串
return TEXT, LABEL,legacy_train, legacy_test
def create_vocabulary(TEXT,LABEL, legacy_train):
'''
Step 2 Build the data processing pipeline
legacy code:
The default tokenizer implemented in the Field class is the built-in python split() function.
Users choose the tokenizer by calling data.get_tokenizer(),
and add it to the Field constructor.
For the sequence model:
it's common to append <BOS> (begin-of-sentence)
and <EOS> (end-of-sentence) tokens,
and the special tokens need to be defined in the Field class.
Things you can do with a vocabuary object
1: Total length of the vocabulary
2: String2Index (stoi) and Index2String (itos)
3: A purpose-specific vocabulary which contains word appearing more than N times
'''
TEXT.build_vocab(legacy_train,max_size=9997)
LABEL.build_vocab(legacy_train)
legacy_vocab = TEXT.vocab
#10003
vocab_size = len(legacy_vocab)
print("\n length of the TEXT vocab is", vocab_size)
print("\n length of the LABEL vocab is", len(LABEL.vocab))
#print('pretrained_embedding:', pretrained_embedding.shape) # torch.Size([10002, 100])
legacy_stoi = legacy_vocab.stoi
#print("The index of 'example' is", legacy_stoi['example'])
legacy_itos = legacy_vocab.itos
#print("The token at index 466 is: ", legacy_itos[466])
# Set up the mim_freq value in the Vocab class
#TEXT.build_vocab(legacy_train, min_freq=10)
#legacy_vocab2 = TEXT.vocab
#print("The length of the legacy vocab is: ", len(legacy_vocab2))
return vocab_size
def create_iterator(batchs ,train_data, test_data):
'''
Step 3: Generate batch iterator
legacy code:
To train a model efficiently,
it's recommended to build an iterator to generate data batch.
'''
device = torch.device("cuda" if torch.cuda.is_available() else "cpu")
legacy_train_iterator, legacy_test_iterator = data.Iterator.splits(
(train_data, test_data), batch_size=batchs, device = device)
return legacy_train_iterator, legacy_test_iterator
def iterator_data(legacy_train_iterator):
'''
Step 4: Iterate batch to train a model
batch.text.shape: [seq_len, batch_size]
'''
for i, batch in enumerate(legacy_train_iterator):
continue
#print("\n shape: ",batch.text.shape,"\t i:",i,"\t text: ",batch.text[:,0][0:3])
def load_corpus():
print("\n ==> Step 1: Create a dataset object ")
TEXT, LABEL,train_data, test_data = load_data()
print("\n ==> Step 2: Build the data processing pipeline")
vocab_size= create_vocabulary(TEXT, LABEL, train_data)
print("\n ==> Step 3: Generate batch iterator")
legacy_train_iterator, legacy_test_iterator =create_iterator(30, train_data, test_data)
#print("\n ==> Step 4: iterator_data ")
#iterator_data(legacy_train_iterator)
return vocab_size,legacy_train_iterator, legacy_test_iterator
1.3 创建模型
文件名: lstmModule
# -*- coding: utf-8 -*-
"""
Created on Mon Aug 7 11:58:41 2023
@author: chengxf2
"""
import torch
import torch.nn as nn
class LSTM(nn.Module):
def __init__(self, vocab_size,embedding_dim, hidden_dim,bidirectional):
super(LSTM, self).__init__()
self.category_num = 1 #最后分类的种类,二分类为1
self.bidirectional = 2#双向
#[0-10001]=>[100]
#vovcab_size: 单词数量 embedding_dim: 词向量维度
self.embedding =nn.Embedding(vocab_size, embedding_dim)
#[100]=>[256]
#双向LSTM,FC层使用hidden_dim*2
self.lstm = nn.LSTM(embedding_dim, hidden_dim, num_layers=2,
bidirectional=bidirectional, dropout= 0.5)
#[256*2]=>1
self.fc = nn.Linear(hidden_dim*2 , self.category_num)
self.dropout = nn.Dropout(0.5)
if True == bidirectional:
self.bidirectional = 2
def forward(self, X):
'''
X: [seq_len, batch] 开始输入的是词的索引构成的向量
'''
#转换为向量形式[seq_len, batch]=>[seq_len, batch, input_size]
embedding = self.embedding(X)
embedding = self.dropout(embedding)
#output.shape: [seq, batch_size,hidd_dim*2] 实际上就是隐藏层
#hidden.shape: [num_layer*self.bidirectional, batch_size, hid_dim]
#cell.shape: [num_layer*self.bidirectional, batch_size, hid_dim]
output, (hidden, cell) = self.lstm(embedding)
#print("\n output",output.shape, "\t hidden ",hidden.shape, "\t cell ",cell.shape)
#双向,要把最后两个输出拼接 hidden.shape :torch.Size([4, 30, 100])
if 2 == self.bidirectional:
output = torch.cat([hidden[-2], hidden[-1]], dim=1)
#output.shape [batch_size, hid_dim*2]
output = self.dropout(output)
#[seq_num, category_num]
out = self.fc(output)
return out
1.4 main.py 训练部分
# -*- coding: utf-8 -*-
"""
Created on Tue Aug 8 10:06:05 2023
@author: chengxf2
"""
import torch
from torch import nn
from torch.nn import functional as F
import lstmModule
from lstmModule import LSTM as lstm
import loadcorpus
from loadcorpus import load_corpus
from torch import optim
import numpy as np
'''
def predict():
#模型预测
for batch in test_iterator:
# batch_size个预测
preds = rnn(batch.text).squeeze(1)
preds = predice_test(preds)
# print(preds)
i = 0
for text in batch.text:
# 遍历一句话里的每个单词
for word in text:
print(TEXT.vocab.itos[word], end=' ')
print('')
# 输出3句话
if i == 3:
break
i = i + 1
i = 0
for pred in preds:
idx = int(pred.item())
print(idx, LABEL.vocab.itos[idx])
# 输出3个结果(标签)
if i == 3:
break
i = i + 1
break
'''
def evaluate(rnn, iterator, criteon):
'''
数据集分为3部分:
train, validate, test
训练的时候:
每轮结束要用validate 数据集来验证一下,防止过拟合
'''
avg_acc = []
rnn.eval() # 表示进入测试模式
with torch.no_grad():
for batch in iterator:
pred = rnn(batch.text).squeeze(1) # [b, 1] => [b]
acc = binary_acc(pred, batch.label).item()
avg_acc.append(acc)
avg_acc = np.array(avg_acc).mean()
print('test acc:', avg_acc)
def binary_acc(preds, y):
'''定义一个函数用于计算准确率
'''
preds = torch.round(torch.sigmoid(preds))
correct = torch.eq(preds, y).float()
acc = correct.sum() / len(y)
return acc
def train(model, iterator, optimizer, criteon):
#训练函数
avg_acc = []
model.train() # 表示进入训练模式
for i, batch in enumerate(iterator):
# [seq, b] => [b, 1] => [b]
# batch.text 就是上面forward函数的参数text,压缩维度是为了和batch.label维度一致
pred = model(batch.text)
#pred.shape: [seq,1]=>[seq]
pred = pred.squeeze(1)
target = batch.label.float()
loss = criteon(pred, target)
# 计算每个batch的准确率
acc = binary_acc(pred, batch.label).item()
avg_acc.append(acc)
optimizer.zero_grad() # 清零梯度准备计算
loss.backward() # 反向传播
optimizer.step() # 更新训练参数
if i % 2 == 0:
print("\n i:%d"%i,"\t acc : %4.2f"%acc)
avg_acc = np.array(avg_acc).mean()
print('avg acc:', avg_acc)
def main():
print("---main---")
maxIter = 5
input_size = 128
hidden_size = 256
vocab_size,train_iterator, test_iterator = load_corpus()
net = lstm(vocab_size, input_size, hidden_size,True)
device = torch.device("cuda" if torch.cuda.is_available() else "cpu")
optimizer = optim.Adam(net.parameters(), lr=1e-4)
# BCEWithLogitsLoss是针对二分类的CrossEntropy
criteon = nn.BCEWithLogitsLoss()
criteon.to(device)
net.to(device)
print("\n ---train--")
for epoch in range(maxIter):
# 训练模型
train(net, train_iterator, optimizer, criteon)
# 评估模型
evaluate(net, test_iterator, criteon)
if __name__ == "__main__":
main()参考:
深度学习与Pytorch入门实战(十六)情感分类实战(基于IMDB数据集)_Douzi1024的博客-CSDN博客
https://github.com/pytorch/text/blob/master/examples/legacy_tutorial/migration_tutorial.ipynb文章来源:https://www.toymoban.com/news/detail-635165.html
LSTM情感分类(上) - 知乎
Google Colab 快速上手 - 知乎
深度学习与Pytorch入门实战(十六)情感分类实战(基于IMDB数据集)_Douzi1024的博客-CSDN博客
https://github.com/pytorch/text/blob/master/examples/legacy_tutorial/migration_tutorial.ipynb
https://github.com/renjunxiang/Text-Classification/blob/master/TextClassification/data/data_single.csv文章来源地址https://www.toymoban.com/news/detail-635165.html
到了这里,关于[PyTorch][chapter 47][LSTM -2]的文章就介绍完了。如果您还想了解更多内容,请在右上角搜索TOY模板网以前的文章或继续浏览下面的相关文章,希望大家以后多多支持TOY模板网!