- 我们前面学会了启动和停止服务的方法,但是服务虽然是在活动里启动的,但是启动服务之后,活动与服务之间基本没什么关系了。
- 正常情况,我们在Activity里调用startService()方法启动MyService这个服务,然后MyService的onCreate()和onStartCommand()方法就会得到执行。之后服务会一直处于运行状态,具体运行什么逻辑,活动控制不了。
- 如果我们想让活动和服务的关系更紧密一些。例如在活动中指挥服务去干什么,服务就去干什么。就要使用我们刚刚忽略的
onBind()方法
1. 绑定服务
1.1 绑定服务的流程
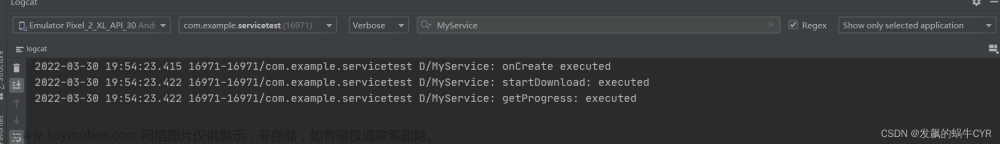
- 下面举一个例子:我们希望在MyService里实现一个下载功能,然后在
Activity可以决定何时开始下载,以及随时查看下载的进度。 - 我们可以专门创建一个Binder对象来对下载功能进行管理。
public class MyService extends Service {
public MyService() {
}
class DownloadBinder extends Binder{
public void startDownload(){
Log.d("MyService", "startDownload executed");
}
public void getProgress(){
Log.d("MyService", "getProgress execute");
}
}
//一个Binder对象来对下载功能进行管理
private DownloadBinder mBinder = new DownloadBinder();
@Override
public IBinder onBind(Intent intent) {
return mBinder;
}
}
- MainActivity中创建连接,调用
bindService进行服务和Activity之间的绑定。
public class MainActivity extends AppCompatActivity {
//1.获取Binder
private MyService.DownloadBinder downloadBinder;
//2.获取connection
private ServiceConnection connection = new ServiceConnection() {
//这两个方法会在活动与服务成功绑定以及解除绑定前后调用
@Override
public void onServiceConnected(ComponentName name, IBinder service) {
//向下转型获得mBinder
downloadBinder = (MyService.DownloadBinder) service;
downloadBinder.startDownload();
downloadBinder.getProgress();
}
@Override
public void onServiceDisconnected(ComponentName name) {
}
};
@Override
protected void onCreate(Bundle savedInstanceState) {
super.onCreate(savedInstanceState);
setContentView(R.layout.activity_main);
Intent intent = new Intent(this , MyService.class);
bindService(intent , connection , BIND_AUTO_CREATE);
unbindService(connection);
}
}
1.2 绑定服务的相关知识点
-
IBinder
- 可以将多个客户端同时连接到某项Service。
- 系统会缓存IBinder服务通信通道。当第一个客户端绑定Service时,系统会调用onBind()方法生成IBinder。系统会将该IBinder传递给其他所有客户端(绑定了当前Service的)。无需再次调用onBind()
- 当最后一个客户端取消与Service的绑定时,系统会销毁该Service(除非还通过startService启动了当前Service)
-
bindService()
- bindService()的返回值指示所请求的Service是否存在,以及是否允许客户端访问该Service。
- 返回false,说明客户端与Service之间并无有效连接。不过,客户端仍然需要调用unbindService()。否则客户端会使Service无法在空闲时关闭。
-
Intent(第一个参数)
- 第一个参数是Intent,用来显示命名要绑定的Service。
- 隐式Intent启动Service存在安全隐患,让用户无法确定哪些服务器启动了。所以在Android5.0开始使用隐式Intent调用bindService()系统会抛出异常
-
ServiceConnection(第二个参数)
- 必须提供ServiceConnection的实现,用于监控与Service的连接。
- Android系统创建客户端与Service之间的连接时,会对ServiceConnection调用onServiceConnected()。onServiceConnected方法包含一个IBinder参数,客户端随后会使用该参数与绑定Service通信
-
绑定选项的标记(第三个参数)
- 如果要创建尚未处于活动状态的Service,此参数通常为BIND_AUTO_CREATE。
- 其他可能的值为BIND_DEBUG_UNBIND和BIND_NOT_FOREGROUND,或者0(表示无参数)
2. Service与Activity之间的通信
- 通过Binder进行通信
- 通过BroadCast
- 通过Messenger
2.1 Binder
- 在Service中拓展
Binder类,并从onBind()返回该类的实例。 - 客户端收到Binder后,可以利用它直接访问 Binder实现 或 Service中提供的公共方法。
具体流程(代码见1.1)
1. 在Service中自定义一个Binder类,并创建可执行以下某种操作的Binder实例:
- 包含Activity客户端可以调用的 public方法。
- 返回当前的Service实例,该实例中包含客户端可调用的公共方法。
- 返回由Service承载的其他类的实例,其中包含客户端可调用的公共方法。
2.从onBind()方法返回此Binder实例
3. 在客户端中,在ServiceConnection的onServiceConnected()回调方法中接收Binder,并使用提供的方法调用绑定Service。
- 这样我们就可以通过这个Binder对象去调用我们定义的方法去控制Service。
代码2
- LocalService(返回的是Service的实例,实例中包含客户端可以调用的方法getRandomNumber)
public class LocalService extends Service {
private final IBinder binder = new LocalBinder();
private final Random mGenerator = new Random();
public class LocalBinder extends Binder {
LocalService getService() {
return LocalService.this;
}
}
@Override
public IBinder onBind(Intent intent) {
return binder;
}
public int getRandomNumber() {
return mGenerator.nextInt(100);
}
}
- BindingActivity
public class BindingActivity extends Activity {
LocalService mService;
boolean mBound = false;
@Override
protected void onCreate(Bundle savedInstanceState) {
super.onCreate(savedInstanceState);
setContentView(R.layout.main);
}
@Override
protected void onStart() {
super.onStart();
// 绑定服务
Intent intent = new Intent(this, LocalService.class);
bindService(intent, connection, Context.BIND_AUTO_CREATE);
}
@Override
protected void onStop() {
super.onStop();
//解绑服务
unbindService(connection);
mBound = false;
}
public void onButtonClick(View v) {
if (mBound) {
int num = mService.getRandomNumber();
Toast.makeText(this, "number: " + num, Toast.LENGTH_SHORT).show();
}
}
//连接,监听Service
private ServiceConnection connection = new ServiceConnection() {
@Override
public void onServiceConnected(ComponentName className , IBinder service) {
//向下转型获取Binder
//获取Service
LocalBinder binder = (LocalBinder) service;
mService = binder.getService();
mBound = true;
}
@Override
public void onServiceDisconnected(ComponentName arg0) {
mBound = false;
}
};
}
2.2 Broadcast
- 发送广播也可以实现Service和Activity的通信
- 在服务里面发送广播
@Override
public int onStartCommand(Intent intent, int flags, int startId) {
Log.d("Ning", "onStartCommand: ");
Intent newIntent = new Intent();
newIntent.putExtra("key" , "text");
newIntent.setAction("location.report");
sendBroadcast(newIntent);
return super.onStartCommand(intent, flags, startId);
}
- MainActivity中创建广播接收器
//内部类,实现BroadcastReceiver,创建内部类作为广播接收器
public class LocationReceiver extends BroadcastReceiver{
@Override
public void onReceive(Context context, Intent intent) {
String intentAction = intent.getAction();
if(intentAction.equals("location.report")){
Log.d("Ning", "onReceive: 111111111");
}
}
}
- onCreate注册广播和onDestroy注销广播
LocationReceiver locationReceiver;
@Override
protected void onCreate(Bundle savedInstanceState) {
super.onCreate(savedInstanceState);
setContentView(R.layout.activity_main);
locationReceiver = new LocationReceiver();
IntentFilter intentFilter = new IntentFilter();
intentFilter.addAction("location.report");
registerReceiver(locationReceiver , intentFilter);
Log.d("Ning", "onReceive: 11111");
Intent intent = new Intent(this , MyService.class);
startService(intent);
}
@Override
protected void onDestroy() {
unregisterReceiver(locationReceiver);
super.onDestroy();
}
2.3 使用Messenger
- 如需让接口跨不同进程工作,可以使用Messenger为Service提供接口。
- 这种方式,Service会绑定一个Handler,用于响应不同类型的Message对象。在Service中创建一个Messenger对象并绑定Handler,重写handler的handleMessage。
- Messenger是执行进程间通信(IPC)最为简单的方式,因为Messenger会在单个线程中创建包含所有请求的队列,这样就不必对Service进行线程安全设计。

public class MessengerService extends Service {
static final int MSG_SAY_HELLO = 1;
//1.实现IncomingHandler来接收客户端的每个回调
static class IncomingHandler extends Handler{
private Context applicationContext;
IncomingHandler(Context context){
applicationContext = context.getApplicationContext();
}
@Override
public void handleMessage(@NonNull Message msg) {
switch (msg.what){
case MSG_SAY_HELLO:
Toast.makeText(applicationContext, "hello", Toast.LENGTH_SHORT).show();
break;
default:
super.handleMessage(msg);
}
}
}
Messenger mMessenger;
@Nullable
@Override
public IBinder onBind(Intent intent) {
Toast.makeText(getApplicationContext(), "binding", Toast.LENGTH_SHORT).show();
//2.使用Handler创建Messenger对象,
mMessenger = new Messenger(new IncomingHandler(this));
//3.Messenger创建一个IBinder
return mMessenger.getBinder();
}
}
- 接下来,Service会在Handler的handleMessage()方法中接收传入的Message,并根据what决定下一步操作。
- 客户端只需根据Service返回的IBinder创建Messenger,使用send()发送消息。
public class ActivityMessenger extends Activity {
Messenger mService = null;
boolean bound;
//连接
//这里用和服务端一样的IBinder创建一个Messenger
private ServiceConnection mConnection = new ServiceConnection() {
public void onServiceConnected(ComponentName className, IBinder service) {
mService = new Messenger(service);
bound = true;
}
public void onServiceDisconnected(ComponentName className) {
mService = null;
bound = false;
}
};
//通过这个Messenger发送Message
public void sayHello(View v) {
if (!bound) return;
Message msg = Message.obtain(null, MessengerService.MSG_SAY_HELLO, 0, 0);
try {
mService.send(msg);
} catch (RemoteException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
@Override
protected void onCreate(Bundle savedInstanceState) {
super.onCreate(savedInstanceState);
setContentView(R.layout.main);
}
@Override
protected void onStart() {
super.onStart();
bindService(new Intent(this, MessengerService.class), mConnection,
Context.BIND_AUTO_CREATE);
}
@Override
protected void onStop() {
super.onStop();
if (bound) {
unbindService(mConnection);
bound = false;
}
}
}
3. 相关问题
3.1 Service中更新UI?
 文章来源:https://www.toymoban.com/news/detail-645909.html
文章来源:https://www.toymoban.com/news/detail-645909.html
3.2 如何保证Service不被杀死?
 文章来源地址https://www.toymoban.com/news/detail-645909.html
文章来源地址https://www.toymoban.com/news/detail-645909.html
到了这里,关于Android复习(Android基础-四大组件)——Service与Activity通信的文章就介绍完了。如果您还想了解更多内容,请在右上角搜索TOY模板网以前的文章或继续浏览下面的相关文章,希望大家以后多多支持TOY模板网!