目录
1、卷积运算
2、经典卷积神经网络
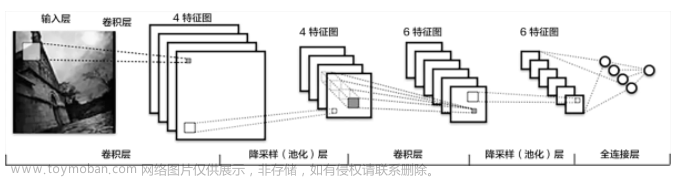
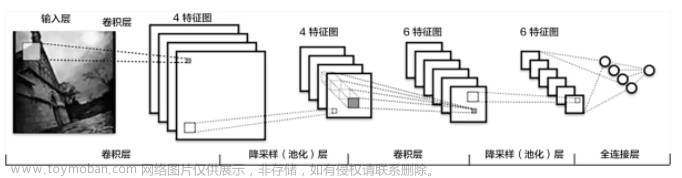
2.1 Lenet
网络构架
代码实现
2.2 Alexnet
网络构架
代码实现
2.3 VGG
VGG16网络构架
代码实现
2.4 ResNet
ResNet50网络构架
代码实现
1、卷积运算

在二维卷积运算中,卷积窗口从输入张量的左上角开始,从左到右、从上到下滑动。 当卷积窗口滑动到新一个位置时,包含在该窗口中的部分张量与卷积核张量进行按元素相乘,得到的张量再求和得到一个单一的标量值,由此我们得出了这一位置的输出张量值。 在如上例子中,输出张量的四个元素由二维互相关运算得到,这个输出高度为2、宽度为2,如下所示:

import torch
from torch import nn
def Conv2d(X, K):
"""计算二维卷积运算"""
h, w = K.shape
Y = torch.zeros((X.shape[0] - h + 1, X.shape[1] - w + 1))
for i in range(Y.shape[0]):
for j in range(Y.shape[1]):
Y[i, j] = (X[i:i + h, j:j + w] * K).sum()
return Y2、经典卷积神经网络
2.1 Lenet
网络构架:

代码实现:
import torch
import torch.nn as nn
class LeNet(nn.Module):
def __init__(self, num_classes=10):
super(LeNet, self).__init__()
self.conv1 = nn.Conv2d(in_channels=1, out_channels=6, kernel_size=5)
self.pool1 = nn.MaxPool2d(kernel_size=2)
self.conv2 = nn.Conv2d(in_channels=6, out_channels=16, kernel_size=5)
self.pool2 = nn.MaxPool2d(kernel_size=2)
self.fc1 = nn.Linear(in_features=16*5*5, out_features=120)
self.fc2 = nn.Linear(in_features=120, out_features=84)
self.fc3 = nn.Linear(in_features=84, out_features=num_classes)
def forward(self, x):
x = self.pool1(torch.relu(self.conv1(x)))
x = self.pool2(torch.relu(self.conv2(x)))
x = x.view(-1, 16*5*5)
x = torch.relu(self.fc1(x))
x = torch.relu(self.fc2(x))
x = self.fc3(x)
return x
# 创建LeNet模型
model = LeNet(num_classes=10)
print(model)
LeNet实现适用于MNIST数据集,其中输入图像大小为28x28,输出类别数为10(0-9的手写数字)。
2.2 Alexnet
网络构架:


代码实现:
import torch
import torch.nn as nn
class AlexNet(nn.Module):
def __init__(self, num_classes=1000):
super(AlexNet, self).__init__()
self.features = nn.Sequential(
nn.Conv2d(3, 64, kernel_size=11, stride=4, padding=2),
nn.ReLU(inplace=True),
nn.MaxPool2d(kernel_size=3, stride=2),
nn.Conv2d(64, 192, kernel_size=5, padding=2),
nn.ReLU(inplace=True),
nn.MaxPool2d(kernel_size=3, stride=2),
nn.Conv2d(192, 384, kernel_size=3, padding=1),
nn.ReLU(inplace=True),
nn.Conv2d(384, 256, kernel_size=3, padding=1),
nn.ReLU(inplace=True),
nn.Conv2d(256, 256, kernel_size=3, padding=1),
nn.ReLU(inplace=True),
nn.MaxPool2d(kernel_size=3, stride=2),
)
self.avgpool = nn.AdaptiveAvgPool2d((6, 6))
self.classifier = nn.Sequential(
nn.Dropout(),
nn.Linear(256 * 6 * 6, 4096),
nn.ReLU(inplace=True),
nn.Dropout(),
nn.Linear(4096, 4096),
nn.ReLU(inplace=True),
nn.Linear(4096, num_classes),
)
def forward(self, x):
x = self.features(x)
x = self.avgpool(x)
x = torch.flatten(x, 1)
x = self.classifier(x)
return x
# 创建AlexNet模型
model = AlexNet(num_classes=1000)
print(model)
代码中的AlexNet实现适用于ImageNet数据集,其中输入图像大小为224x224,输出类别数为1000。
2.3 VGG
VGG16网络构架:

代码实现:
import torch
import torch.nn as nn
class VGG16(nn.Module):
def __init__(self, num_classes=1000):
super(VGG16, self).__init__()
self.features = nn.Sequential(
nn.Conv2d(3, 64, kernel_size=3, padding=1),
nn.ReLU(inplace=True),
nn.Conv2d(64, 64, kernel_size=3, padding=1),
nn.ReLU(inplace=True),
nn.MaxPool2d(kernel_size=2, stride=2),
nn.Conv2d(64, 128, kernel_size=3, padding=1),
nn.ReLU(inplace=True),
nn.Conv2d(128, 128, kernel_size=3, padding=1),
nn.ReLU(inplace=True),
nn.MaxPool2d(kernel_size=2, stride=2),
nn.Conv2d(128, 256, kernel_size=3, padding=1),
nn.ReLU(inplace=True),
nn.Conv2d(256, 256, kernel_size=3, padding=1),
nn.ReLU(inplace=True),
nn.Conv2d(256, 256, kernel_size=3, padding=1),
nn.ReLU(inplace=True),
nn.MaxPool2d(kernel_size=2, stride=2),
nn.Conv2d(256, 512, kernel_size=3, padding=1),
nn.ReLU(inplace=True),
nn.Conv2d(512, 512, kernel_size=3, padding=1),
nn.ReLU(inplace=True),
nn.Conv2d(512, 512, kernel_size=3, padding=1),
nn.ReLU(inplace=True),
nn.MaxPool2d(kernel_size=2, stride=2),
nn.Conv2d(512, 512, kernel_size=3, padding=1),
nn.ReLU(inplace=True),
nn.Conv2d(512, 512, kernel_size=3, padding=1),
nn.ReLU(inplace=True),
nn.Conv2d(512, 512, kernel_size=3, padding=1),
nn.ReLU(inplace=True),
nn.MaxPool2d(kernel_size=2, stride=2),
)
self.classifier = nn.Sequential(
nn.Linear(512 * 7 * 7, 4096),
nn.ReLU(inplace=True),
nn.Dropout(),
nn.Linear(4096, 4096),
nn.ReLU(inplace=True),
nn.Dropout(),
nn.Linear(4096, num_classes),
)
def forward(self, x):
x = self.features(x)
x = x.view(x.size(0), -1)
x = self.classifier(x)
return x
# 创建VGG16模型
model = VGG16(num_classes=1000)
print(model)
代码中的VGG16实现适用于ImageNet数据集,其中输入图像大小为224x224,输出类别数为1000。
2.4 ResNet
ResNet50网络构架:
 代码实现:
代码实现:
import torch
import torch.nn as nn
# 定义残差块
class ResidualBlock(nn.Module):
def __init__(self, in_channels, out_channels, stride=1):
super(ResidualBlock, self).__init__()
self.conv1 = nn.Conv2d(in_channels, out_channels, kernel_size=3, stride=stride, padding=1, bias=False)
self.bn1 = nn.BatchNorm2d(out_channels)
self.relu = nn.ReLU(inplace=True)
self.conv2 = nn.Conv2d(out_channels, out_channels, kernel_size=3, stride=1, padding=1, bias=False)
self.bn2 = nn.BatchNorm2d(out_channels)
if stride != 1 or in_channels != out_channels:
self.downsample = nn.Sequential(
nn.Conv2d(in_channels, out_channels, kernel_size=1, stride=stride, bias=False),
nn.BatchNorm2d(out_channels)
)
else:
self.downsample = None
def forward(self, x):
identity = x
x = self.conv1(x)
x = self.bn1(x)
x = self.relu(x)
x = self.conv2(x)
x = self.bn2(x)
if self.downsample is not None:
identity = self.downsample(identity)
x += identity
x = self.relu(x)
return x
# 定义ResNet-50
class ResNet50(nn.Module):
def __init__(self, num_classes=1000):
super(ResNet50, self).__init__()
self.in_channels = 64
self.conv1 = nn.Conv2d(3, 64, kernel_size=7, stride=2, padding=3, bias=False)
self.bn1 = nn.BatchNorm2d(64)
self.relu = nn.ReLU(inplace=True)
self.maxpool = nn.MaxPool2d(kernel_size=3, stride=2, padding=1)
self.layer1 = self._make_layer(64, 3, stride=1)
self.layer2 = self._make_layer(128, 4, stride=2)
self.layer3 = self._make_layer(256, 6, stride=2)
self.layer4 = self._make_layer(512, 3, stride=2)
self.avgpool = nn.AdaptiveAvgPool2d((1, 1))
self.fc = nn.Linear(512 * 4, num_classes)
def _make_layer(self, out_channels, num_blocks, stride):
layers = []
layers.append(ResidualBlock(self.in_channels, out_channels, stride))
self.in_channels = out_channels
for _ in range(1, num_blocks):
layers.append(ResidualBlock(out_channels, out_channels))
return nn.Sequential(*layers)
def forward(self, x):
x = self.conv1(x)
x = self.bn1(x)
x = self.relu(x)
x = self.maxpool(x)
x = self.layer1(x)
x = self.layer2(x)
x = self.layer3(x)
x = self.layer4(x)
x = self.avgpool(x)
x = x.view(x.size(0), -1)
x = self.fc(x)
return x
# 创建ResNet-50模型
model = ResNet50(num_classes=1000)
print(model)
代码中的ResNet50实现适用于ImageNet数据集,其中输入图像大小为224x224,输出类别数为1000。
【图像分类】 理论篇(1) 图像分类的测评指标_TechMasterPlus的博客-CSDN博客
【图像分类】理论篇(3)交叉熵损失函数的理解与代码实现_TechMasterPlus的博客-CSDN博客文章来源:https://www.toymoban.com/news/detail-646556.html
【图像分类】理论篇(4)图像增强opencv实现_TechMasterPlus的博客-CSDN博客文章来源地址https://www.toymoban.com/news/detail-646556.html
到了这里,关于【图像分类】理论篇(2)经典卷积神经网络 Lenet~Densenet的文章就介绍完了。如果您还想了解更多内容,请在右上角搜索TOY模板网以前的文章或继续浏览下面的相关文章,希望大家以后多多支持TOY模板网!