数据的解析
解析数据的方式大概有三种
- xpath
- JsonPath
- BeautifulSoup
xpath
安装xpath插件

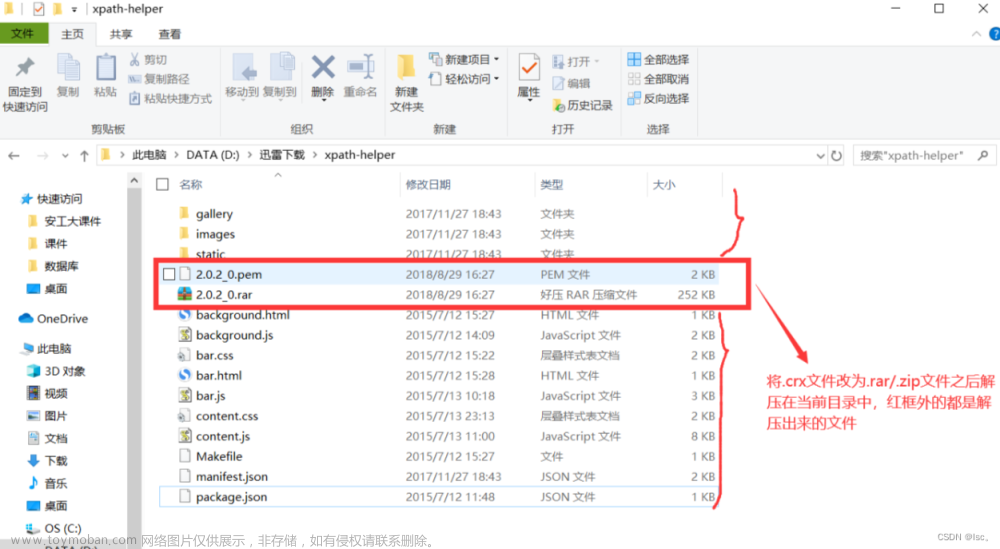
打开谷歌浏览器扩展程序,打开开发者模式,拖入插件,重启浏览器,ctrl+shift+x,打开插件页面
安装lxml库
安装在python环境中的Scripts下边,这里就是python库的位置,例如我的地址为:E:\python\python3.10.11\Scripts
pip install lxml -i https://pypi.tuna.tsinghua.edu.cn/simple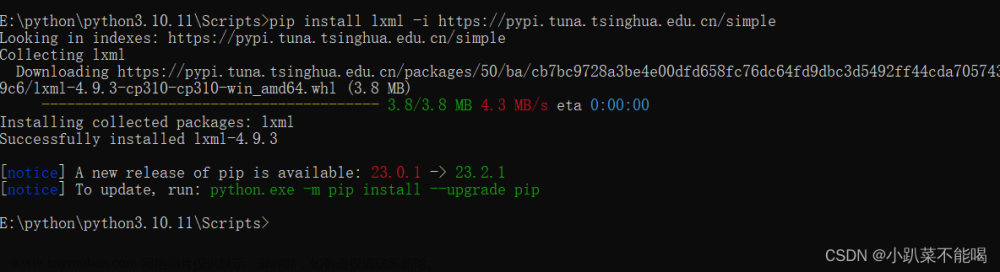
xpath使用和基本语法
解析本地文件etree.parse( 'xx.html')4.etree.HTML()
解析服务器响应文件html_tree = etree.HTML(response.read().decode( 'utf-8')4.html tree.xpath(xpath路径)
xpath基本语法:
路径查询
// : 查找所有子孙节点,不考虑层级关系
/ :找直接子节点
谓词查询
//div[@id] :包含id属性的div
//div[@id="maincontent"] :id = maincontent的div
属性查询
//@class : 返回指定标签的class属性
模糊查询
//div[contains(@id,"he")] : 包含
//div[starts-with(@id,"he")] :以he开头
内容查询
//div/h1/text() : text()显示内容
逻辑运算
//div[@id="head" and @class="s down"] : 逻辑&&
xpath解析本地文件
本地文件如下
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8"/>
<title>Title</title>
</head>
<body>
<ul>
<li id="00" class="beijing">北京</li>
<li>上海</li>
<li>深圳</li>
<li>广州</li>
</ul>
<ul>
<li id="11" class="shenyang">沈阳</li>
<li>南京</li>
</ul>
</body>
</html>解析本地文件
from lxml import etree
# 解析本地文件 使用etree.parse
tree = etree.parse('Test.html')
# 找到所有的ul
ul_list = tree.xpath("//ul")
# 查找所有的li
li_list = tree.xpath("//ul/li")
# 查找所有包含id的li
id_li_list = tree.xpath("//ul/li[@id]")
# 查找id为00的li,并找到内容 注意引号问题
content_list = tree.xpath("//ul/li[@id='00']/text()")
# 查找id包含0的li的内容
contains_list = tree.xpath("//ul/li[contains(@id,'0')]/text()")
# 获取id为11的li class属性值@class
li = tree.xpath("//ul/li[@id='11']/@class")
print(ul_list)
print(li_list)
print(id_li_list)
print(contains_list)
print(content_list)
print(li)
"""
输出结果:
[<Element ul at 0x22c26c38240>, <Element ul at 0x22c26c38600>]
[<Element li at 0x22c26c38640>, <Element li at 0x22c26c385c0>, <Element li at 0x22c26c38680>, <Element li at 0x22c26c386c0>, <Element li at 0x22c26c38700>, <Element li at 0x22c26c38780>]
[<Element li at 0x22c26c38640>, <Element li at 0x22c26c38700>]
['北京']
['北京']
['shenyang']
"""xpath解析服务器文件
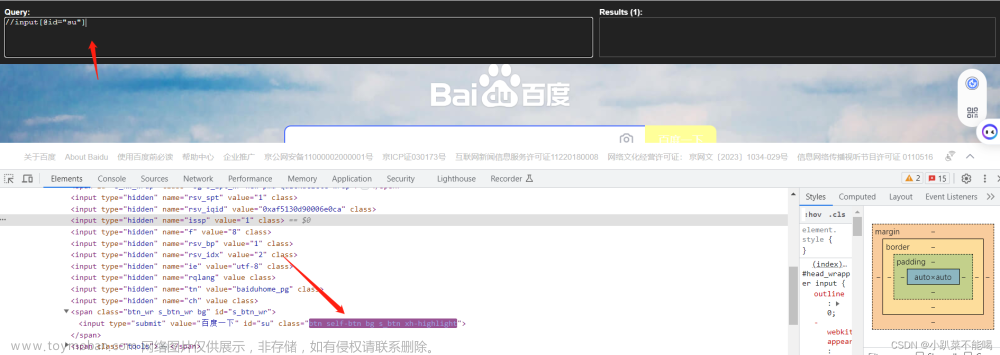
使用xpath插件检查xpath路径的匹配,解析定位dom
from lxml import etree
import urllib.request as request
# 下载图片
url = "https://www.baidu.com/"
headers = {
'User-Agent': 'Mozilla/5.0 (Windows NT 10.0; Win64; x64) AppleWebKit/537.36 (KHTML, like Gecko) Chrome/115.0.0.0 Safari/537.36',
}
# 构建的请求对象
geneRequest=request.Request(url=url,headers = headers)
# 模拟浏览器发送请求
response = request.urlopen(geneRequest)
# 获取内容
content = response.read().decode('utf-8')
# 解析服务器文件
tree = etree.HTML(content)
# 找到百度一下的值
result = tree.xpath('//input[@id="su"]/@value')
print(result)
"""
输出结果:['百度一下']
"""
jsonpath
jsonpath是一种信息抽取类库,是从JSON文档中抽取指定信息的工具,只能读取本地的json文件,与xpath类似,只不过对应符号不同
jsonpath安装
pip install jsonpath -i https://pypi.tuna.tsinghua.edu.cn/simple
xpath和jsonpath的对应关系
| XPath | JSONPath | 描述 |
| / | $ | 根节点 |
| . | @ | 现行节点 |
| / | .or[] | 取子节点 |
| 、、 | n/a | 取父节点,Jsonpath未支持 |
| // | 、、 | 就是不管位置,选择所有符合条件的条件 |
| * | * | 匹配所有元素节点 |
| @ | n/a | 根据属性访问,Json不支持,因为Json是个Key-value递归结构,不需要 |
| [] | [] | 迭代器标识(可以在里边做简单的迭代操作,如数组下标,根据内容选值等 |
| [] | ?() | 支持过滤操作 |
| | | [,] | 支持迭代器中做多选 |
| n/a | () | 支持表达式计算 |
| () | n/a | 分组,JsonPath不支持 |
jsonpath解析
准备json
{
"store": {
"book":[
{ "category": "射手",
"author": "鲁班七号",
"title": "王者荣耀",
"price": 8.95
},
{
"category": "打野",
"author": "李白",
"title": "大河之水天上来",
"price": 22.99
}
],
"bicycle": {
"color": "red",
"price": 19.95
}
}
}
通过jsonpath解析json数据
import json
import jsonpath
obj = json.load(open('test.json',"r",encoding="utf-8"))
# 查看store下的bicycle的color属性 $ 对应xpath/
colorAttr = jsonpath.jsonpath(obj, "$.store.bicycle.color")
# 输出book节点的第一个对象
bookFirst = jsonpath.jsonpath(obj, "$.store.book[0]")
# 输出book节点中所有对象对应的属性title值
titles = jsonpath.jsonpath(obj, "$.store.book[*].title")
# 输出book节点中所有价格小于10的对象 ?() 对应xpath [] @ 对应当前节点
books = jsonpath.jsonpath(obj, "$.store.book[?(@.price<10)]")
print(colorAttr)
print(bookFirst)
print(titles)
print(books)
"""
输出结果:
['red']
[{'category': '射手', 'author': '鲁班七号', 'title': '王者荣耀', 'price': 8.95}]
['王者荣耀', '大河之水天上来']
[{'category': '射手', 'author': '鲁班七号', 'title': '王者荣耀', 'price': 8.95}]
"""BeautifulSoup
Beautifulsoup简称bs4,Beautifulsoup,和lxml一样,是一个html的解析器,主要功能也是解析和提取数据
- 缺点: 效率没有1xm1的效率高
- 优点: 接口设计人性化,使用方便
BeautifulSoup安装
pip install bs4 - i https://pypi.tuna.tsinghua.edu.cn/simple
BeautifulSoup节点定位规则
soup = soup = Beautifulsoup(response.read().decode(),'Ixml') 解析服务器文件
soup = soup = Beautifulsoup(open('1.html').lxml') 解析本地文件
根据标签名查找节点
soup.a 只能找到第一个a
soup.a.namesoup.a.attrs 获取标签的属性和属性值函数查找
.find (返回一个对象 只能找到第一个a标签)
find('a')
find('a',title='名字')
find('a',class='名字')
.find_all (返回一个列表 )
find all('a')
find all(['a’,'span']) 返回所有的a和span
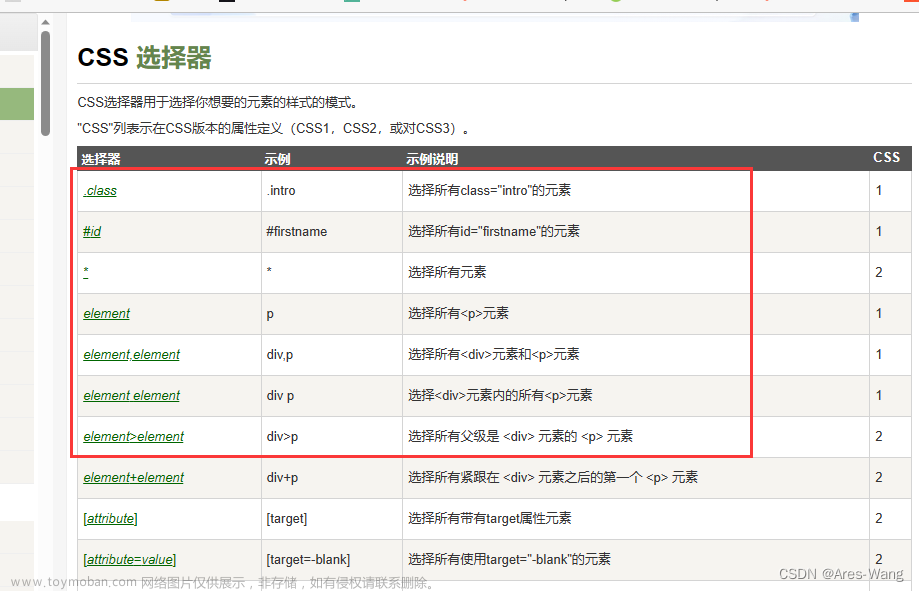
.select(根据选择器得到节点对象)[推荐]
element
eg: div
class
eg:.firstname
id
eg:#firstname
属性选择器
eg:li = soup.select('li[class]')
eg:li = soup.select('li[class="hengheng"]')
层级选择器
element element
div p
eg:soup = soup.select('a span')
element>element
div>p
eg:soup = soup.select('a>span')
element,element
div,p
eg:soup = soup.select('a,span')
BeautifulSoup节点信息
获取节点内容
obj.string
obj.get_text()[推荐]
获取节点的属性
eg:tag = find('li)
tag.name 获取标签名
tag.attrs将属性值作为一个字典返回
获取节点属性
obj.attrs.get('title')[常用]
obj.get('title')
obj['title']文章来源:https://www.toymoban.com/news/detail-648211.html
BeautifulSoup解析文件
以上述xpath中的本地文件Test.html为例,上边已经写过,这里直接上代码文章来源地址https://www.toymoban.com/news/detail-648211.html
from bs4 import BeautifulSoup
soup = BeautifulSoup(open('Test.html',encoding='utf-8'),'lxml')
# 查找第一个ul
print(soup.find("ul"))
# 查找所有的ul
print(soup.find_all("ul"))
# 选择查找 li class为beijing的标签
print(soup.select("li[class =beijing]"))
#层级选择查找ul下的class为beijing的li节点
nodeli=soup.select("ul li[class = beijing]")[0]
# 获取li节点内容
print(nodeli.get_text())
# 获取li标签名
print(nodeli.name)
#获取li的属性
print(nodeli.attrs)
# 获取li的id属性
print(nodeli.attrs.get('id'))
"""
输出结果:
<ul>
<li class="beijing" id="00">北京</li>
<li>上海</li>
<li>深圳</li>
<li>广州</li>
</ul>
[<ul>
<li class="beijing" id="00">北京</li>
<li>上海</li>
<li>深圳</li>
<li>广州</li>
</ul>, <ul>
<li class="shenyang" id="11">沈阳</li>
<li>南京</li>
</ul>]
[<li class="beijing" id="00">北京</li>]
北京
li
{'id': '00', 'class': ['beijing']}
00
"""到了这里,关于python爬虫数据解析xpath、jsonpath,bs4的文章就介绍完了。如果您还想了解更多内容,请在右上角搜索TOY模板网以前的文章或继续浏览下面的相关文章,希望大家以后多多支持TOY模板网!