😎博客昵称:博客小梦
😊最喜欢的座右铭:全神贯注的上吧!!!
😊作者简介:一名热爱C/C++,算法等技术、喜爱运动、热爱K歌、敢于追梦的小博主!
😘博主小留言:哈喽!😄各位CSDN的uu们,我是你的博客好友小梦,希望我的文章可以给您带来一定的帮助,话不多说,文章推上!欢迎大家在评论区唠嗑指正,觉得好的话别忘了一键三连哦!😘
前言🙌
哈喽各位友友们😊,我今天又学到了很多有趣的知识,现在迫不及待的想和大家分享一下! 都是精华内容,可不要错过哟!!!😍😍😍
C语言中的字符串
C语言中,字符串是以’\0’结尾的一些字符的集合,为了操作方便,C标准库中提供了一些str系列的库函数,但是这些库函数与字符串是分离开的,不太符合OOP的思想,而且底层空间需要用户自己管理,稍不留神可
能还会越界访问。
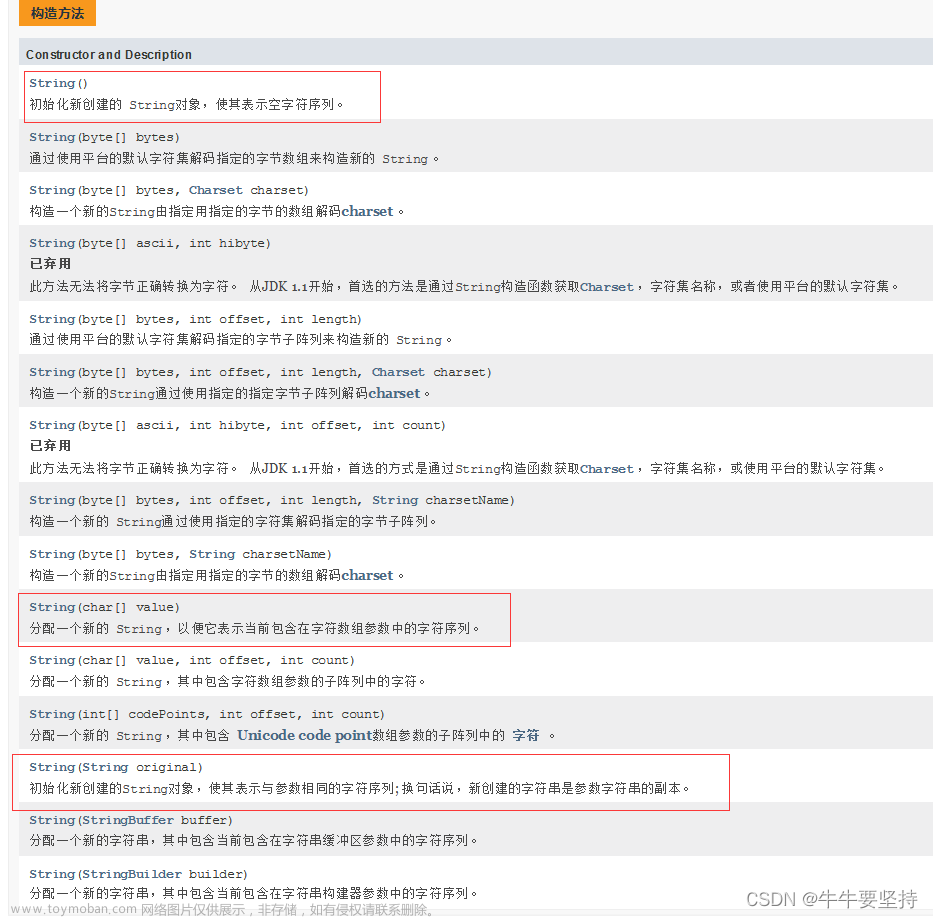
标准库中的string类
- string是表示字符串的字符串类
- 该类的接口与常规容器的接口基本相同,再添加了一些专门用来操作string的常规操作。
- string在底层实际是:basic_string模板类的别名,typedef basic_string<char, char_traits, allocator> string;
- 不能操作多字节或者变长字符的序列。在使用string类时,必须包含#include头文件以及using namespace std;
string 比较常使用的接口




























 文章来源:https://www.toymoban.com/news/detail-656013.html
文章来源:https://www.toymoban.com/news/detail-656013.html
对上述函数和其他函数的测试代码演示:
#include<iostream>
#include<string>
using namespace std;
void Teststring1()
{
string s1;
string s2("hello bit");
string s3(s2);
string s4(s2.begin(), s2. end());
s1 = "abcdef";
cout << s1 << endl;
cout << s2 << endl;
cout << s3 << endl;
cout << s4<< endl;
}
void test_string3()
{
string s1("hello world");
string s2 = "hello world";
for (size_t i = 0; i < s1.size(); i++)
{
cout << s1[i] << " ";
}
cout << endl;
string::iterator it = s1.begin();
while (it != s1.end())
{
cout << *it << " ";
it++;
}
cout << endl;
for (auto ch : s2)
{
cout << ch << " ";
}
cout << endl;
}
void func(const string & s)
{
//string::const_iterator it = s.begin();
//auto it = s.begin();
//while (it != s.end())
//{
// //*it = 'a';
// cout << *it << " ";
// it++;
//}
//cout << endl;
//string::const_reverse_iterator rit = s.rbegin();
/*auto rit = s.rbegin();
while (rit != s.rend())
{
cout << *rit << " ";
++rit;
}
cout << endl;*/
auto rit = s.rbegin();
while (rit != s.rend())
{
cout << *rit << " ";
++rit;
}
cout << endl;
}
void test_string4()
{
string s1("hello world");
string s2 = "hello world";
func(s1);
}
void test_string5()
{
string s1("hello worldxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxyyyyyyyyyyyyyyyyyy");
string s2(s1);
cout << s2 << endl;
string s3(s1, 6, 5);
cout << s3 << endl;
string s4(s1, 6, 3);
cout << s4 << endl;
string s5(s1, 6);
cout << s5 << endl;
string s6(s1, 6, s1.size() - 6);
cout << s6 << endl;
string s7(10, 'a');
cout << s7 << endl;
string s8(++s7.begin(), --s7.end());
cout << s8 << endl;
s8 = s7;
s8 = "xxx";
s8 = 'y';
}
void test_string6()
{
string s1("hello world");
string s2 = "hello world";
cout << s1.size() << endl;
cout << s1.capacity() << endl;
s1.clear();
cout << s1.size() << endl;
cout << s1.capacity() << endl;
}
void test_string7()
{
string s;
/*s.reserve(100);
for (auto ch : s)
{
cout << ch << " ";
}
cout << endl;
s.push_back('x');
s.push_back('x');
s.push_back('x');
s.push_back('x');
s += 'n';
s += "bit helloc";
for (auto ch : s)
{
cout << ch;
}
cout << endl;*/
//size_t old = s.capacity();
//cout << "初始" << s.capacity() << endl;
//for (size_t i = 0; i < 100; i++)
//{
// s.push_back('x');
// if (s.capacity() != old)
// {
// cout << "扩容:" << s.capacity() << endl;
// old = s.capacity();
// }
//}
//s.reserve(10);
//cout << s.capacity() << endl;
s = "hello bit";
cout << s.size() << endl;
cout << s.capacity() << endl;
s.resize(10, 'a');
cout << s << endl;
cout << s.size() << endl;
cout << s.capacity() << endl;
}
void test_string8()
{
string s = "hello";
s.append(" bit");
cout << s << endl;
string s3 = "hello";
string s2;
s2 = s3 + " bit";
cout << s2 << endl;
s2 += s2;
cout << s2 << endl;
//s += '#';
//s += "hello";
//s += ss;
//cout << s << endl;
//string ret1 = ss + '#';
//string ret2 = ss + "hello";
//cout << ret1 << endl;
//cout << ret2 << endl;
}
void test_string9()
{
std::string str("xxxxxxx");
std::string base = "The quick brown fox jumps over a lazy dog.";
str.assign(base);
std::cout << str << '\n';
str.assign(base, 5, 10);
std::cout << str << '\n';
}
void test_string10()
{
// 空格替换为20%
std::string s2("The quick brown fox jumps over a lazy dog.");
string s3;
for (auto ch : s2)
{
if (ch != ' ')
{
s3 += ch;
}
else
{
s3 += "%20";
}
}
for (auto ch : s3)
{
cout << ch;
}
cout << endl;
printf("s2:%p\n", s2.c_str());
printf("s3:%p\n", s3.c_str());
swap(s2, s3);
//s2.swap(s3);
printf("s2:%p\n", s2.c_str());
printf("s3:%p\n", s3.c_str());
}
void test_string11()
{
string s1("test.cpp.tar.zip");
//size_t i = s1.find('.');
size_t i = s1.rfind('.');
string s2 = s1.substr(i);
cout << s2 << endl;
//string s3("https://legacy.cplusplus.com/reference/string/string/rfind/");
//string s3("ftp://www.baidu.com/?tn=65081411_1_oem_dg");
string s3("https://leetcode.cn/problems/first-unique-character-in-a-string/submissions/");
// 协议 https
// 域名 leetcode.cn
// 资源名 problems/first-unique-character-in-a-string/submissions/
string sub1, sub2, sub3;
i = s3.find(':');
sub1 = s3.substr(0, i);
cout << sub1 << endl;
size_t len = s3.find('/', i + 3);
sub2 = s3.substr(i + 3, len - (i + 3));
cout << sub2 << endl;
sub3 = s3.substr(len + 1);
cout << sub3 << endl;
}
void test_string12()
{
std::string str("Please, replace the vowels in this sentence by asterisks.");
std::size_t found = str.find_first_not_of("abc");
while (found != std::string::npos)
{
str[found] = '*';
found = str.find_first_not_of("abcdefg", found + 1);
}
std::cout << str << '\n';
/*std::string str("Please, replace the vowels in this sentence by asterisks.");
std::size_t found = str.find_first_of("abcd");
while (found != std::string::npos)
{
str[found] = '*';
found = str.find_first_of("abcd", found + 1);
}
std::cout << str << '\n';*/
}
int main()
{
/*string s1, s2;
cin >> s1 >> s2;
cout << s1 << endl;
cout << s2 << endl;*/
string str;
//cin >> str;
getline(cin, str, '!');
cout << str;
/*size_t i = str.rfind(' ');
if (i != string::npos)
{
cout << str.size() - (i + 1) << endl;
}
else
{
cout << str.size() << endl;
}*/
//Teststring1();
//test_string2();
//test_string3();
//test_string4();
//test_string5();
//test_string6();
//test_string7();
//test_string8();
//test_string9();
//test_string11();
//test_string12();
return 0;
}
总结撒花💞
本篇文章旨在分享的是string 使用知识。希望大家通过阅读此文有所收获!
😘如果我写的有什么不好之处,请在文章下方给出你宝贵的意见😊。如果觉得我写的好的话请点个赞赞和关注哦~😘😘😘文章来源地址https://www.toymoban.com/news/detail-656013.html
到了这里,关于【小梦C嘎嘎——启航篇】string介绍以及日常使用的接口演示的文章就介绍完了。如果您还想了解更多内容,请在右上角搜索TOY模板网以前的文章或继续浏览下面的相关文章,希望大家以后多多支持TOY模板网!


![[C/C++]string类常用接口介绍及模拟实现string类](https://imgs.yssmx.com/Uploads/2024/03/842434-1.png)