✅博主简介:热爱科研的Matlab仿真开发者,修心和技术同步精进,Matlab项目合作可私信。
🍎个人主页:海神之光
🏆代码获取方式:
海神之光Matlab王者学习之路—代码获取方式
⛳️座右铭:行百里者,半于九十。
更多Matlab仿真内容点击👇
Matlab图像处理(进阶版)
路径规划(Matlab)
神经网络预测与分类(Matlab)
优化求解(Matlab)
语音处理(Matlab)
信号处理(Matlab)
车间调度(Matlab)
⛄一、fmincon
fmincon函数是MATLAB中的一个它可以用于无人机航路避障规划问题。下面是使用fmincon函数进行无人机航路避障规划的基本步骤:
定义问题:明确无人机的起点、目标和障碍物的位置。将问题抽象为一个目标函数和约束条件的优化问题。
定义目标函数:目标函数定义为无人机从起点到目标的路径长度或时间。这个函数应该参数化无人机路径,并与避开障碍物的要求相匹配。
设置约束条件:约束障碍物以及满足工作空间限制等。这些约束条件应该表达为等式约束和不等式约束。
定义变量边界:指定各个决策变量的取值范围,例如无人机的位置坐标、速度、飞行角选择一个合适的起始路径作为初始解,这有助求解器更快地收敛。
调用fmin:根据上述步骤设置好目标函数、约束条件、变量边界和初始解,调用fmincon函数来求解最优路径。将目标函数和约束条件提供给fmincon函数,并指定变量边界和初始解。
解析结果:分析求解器返回的最优路径结果,检查是否满足要求。根据需要,可以进行进一步的优化或调整。
请注意,具体的问题设置、目标函数和约束条件会根据实际应用情况而有所不同。以上步骤提供了一个基本的框架,您可能需要根据具体的无人机航路避障规划问题进行适当的调整和扩展
⛄二、部分源代码
clear; clc; close all;
%Add paths
addpath(genpath(‘.\Objective_Functions’));
addpath(genpath(‘.\Constraints’));
addpath(genpath(‘.\ColorPath’));
addpath(genpath(‘.\Compare’));
addpath(genpath(‘.\OptimalPathGuesses’));
addpath(genpath(‘.\CalculateEnergyUse’));
%profiling tools
%profile on
%-------global variables----------%
global xf; %final position
global x0; %current starting pointPath_bez
global step_max; %max step distance
global step_min; %minimum step distance
global t; %parameterization variable
global n_obs; %number of obstacles
global obs; %positions of obstacles
global obs_rad; %radius of obstacles
global turn_r; %minimum turn radius
global Pmid; %needed to match derivatives
global num_path; %number of segments optimized
global x_new;
global Dynamic_Obstacles;
global x_next; %used in multi_start function
global uav_ws; %UAV wing span
global start;
global initial; % to calculate d_l_min
global uav_finite_size;
global rho f W span eo;
global summer_c cool_c copper_c parula_c winter_c blue_red blue_magenta_red green_purple blue_gray_red shortened_viridis_c shortened_inferno_c;
global shortened_parula_c;
global obj_grad cons_grad ag acg;
global max_speed min_speed D_eta_opt;
global l_l_last;
%------------Algorithm Options------------%
% use genetic algorithm
use_ga = 0;
Dynamic_Obstacles = 0;
num_path = 3; %Receding Horizon Approach (any number really, but 3 is standard)
ms_i = 3; %number of guesses for multi start (up to 8 for now, up to 3 for smart)
uav_finite_size = 1; %input whether want to include UAV size
check_viability = 1; %Exits if unable to find viable path
%Objective Function
optimize_energy_use = 0; %changes which objective function is used
optimize_time = 0; %if both are zero, then path length is optimized
max_func_evals = 10000;
max_iter = 50000;
initial = 1;
% Plot Options
totl = 1; %turn off tick labels
square_axes = 1; %Square Axes
radar = 0; %Plots UAV’s limit of sight
show_sp = 0; %Plots P1 of Bezier curve
Show_Steps = 0; %Needs to be turned on when Dynamic_Obstacles is turned on
linewidth = 4; %Line width of traversed path segment
traversedwidth = 2;
dashedwidth = 2;
fwidth = 2; %width of UAV path in FinalPlot.m
show_end = 0; %for calc_fig
compare_num_path = 0;
save_path = 0; %save path data to use in compare
sds = 0; %Allows a closer view of dynamic obstacle avoidance
cx = 50;
%plot color options
speed_color = 1; %use if you want color to represent speed
d_speed_color = 0; %use if you want color to be discretized over path length
cb = 1; %color brightness
summer_c = 0; % http://www.mathworks.com/help/matlab/ref/colormap.html#buq1hym
cool_c = 0;
copper_c = 0;
parula_c = 0;
winter_c = 0;
blue_red = 0;
blue_magenta_red = 0;
green_purple = 0;
blue_gray_red = 0;
shortened_parula_c = 1;
shortened_viridis_c = 0;
shortened_inferno_c = 0;
color_bar = 0;
%----------------------------------------%
create_video = 1; %saves the solutions of the multistart approach at each iteration
% Gradient Calculation Options
obj_grad = 1; %if this is 1 and below line is 0, complex step method will be used to calculate gradients
if obj_grad == 1
analytic_gradients = 1;
ag = analytic_gradients;
end
cons_grad = 1; %if this is 1 and below line is 0, complex step method will be used to calculate gradients
if cons_grad == 1
analytic_constraint_gradients = 1;
acg = analytic_constraint_gradients;
end
%----------------plane geometry/info----------------%
%UAV parameter values
rho = 1.225; %air density
f = .2; %equivalent parasite area
W = 10; %weight of aircraft
span = .20; %span
eo = 0.9; %Oswald’s efficiency factor
if optimize_energy_use == 1
%Defined in paper “Fuel Efficiency of Small Aircraft” (2nd column, page 2)
A = rhof/(2W);
B = 2W/(rhospan^2pieo);
%find minimum d_l, and minimum efficiency
if initial == 1
V_possible = 0.1 : 0.01 : 25;
for i = 1 : length(V_possible)
D_L = A*V_possible(i)^2 + B/V_possible(i)^2; % we want to maximize l_d, or minimize d_l
eta_pos = calc_eff(V_possible(i));
%calculate D_L/eta
D_eta(i) = D_L/eta_pos;
end
%find optimal D_eta
D_eta_opt = min(D_eta);
end
end
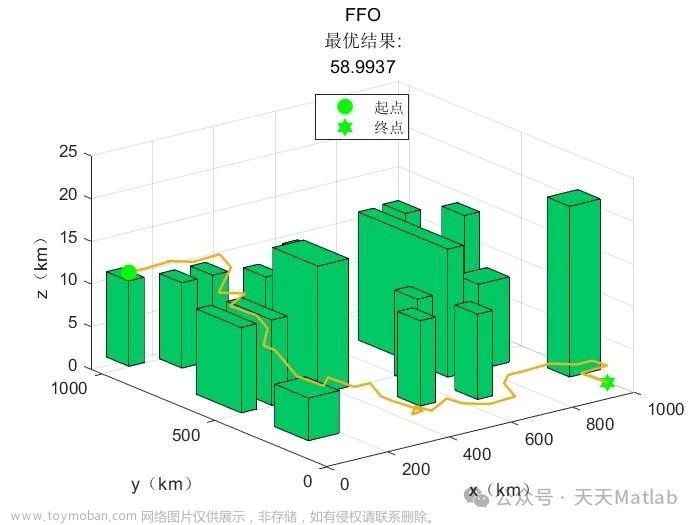
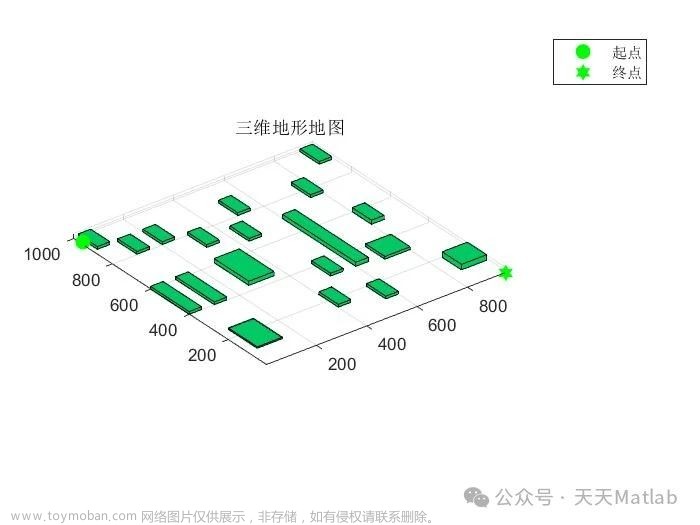
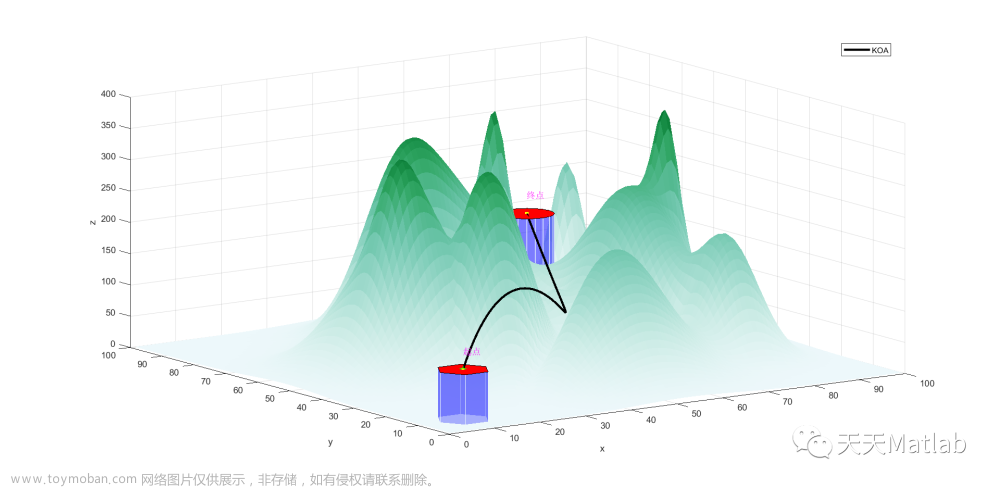
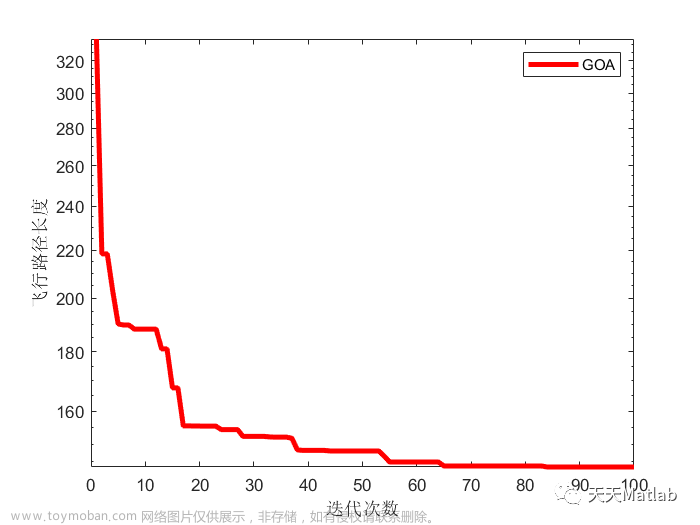
⛄三、运行结果

⛄四、matlab版本及参考文献
1 matlab版本
2014a
2 参考文献
[1]钱程,许映秋,谈英姿.A Star算法在RoboCup救援仿真中路径规划的应用[J].指挥与控制学报. 2017,3(03)
3 备注
简介此部分摘自互联网,仅供参考,若侵权,联系删除
🍅 仿真咨询
1 各类智能优化算法改进及应用
生产调度、经济调度、装配线调度、充电优化、车间调度、发车优化、水库调度、三维装箱、物流选址、货位优化、公交排班优化、充电桩布局优化、车间布局优化、集装箱船配载优化、水泵组合优化、解医疗资源分配优化、设施布局优化、可视域基站和无人机选址优化
2 机器学习和深度学习方面
卷积神经网络(CNN)、LSTM、支持向量机(SVM)、最小二乘支持向量机(LSSVM)、极限学习机(ELM)、核极限学习机(KELM)、BP、RBF、宽度学习、DBN、RF、RBF、DELM、XGBOOST、TCN实现风电预测、光伏预测、电池寿命预测、辐射源识别、交通流预测、负荷预测、股价预测、PM2.5浓度预测、电池健康状态预测、水体光学参数反演、NLOS信号识别、地铁停车精准预测、变压器故障诊断
3 图像处理方面
图像识别、图像分割、图像检测、图像隐藏、图像配准、图像拼接、图像融合、图像增强、图像压缩感知
4 路径规划方面
旅行商问题(TSP)、车辆路径问题(VRP、MVRP、CVRP、VRPTW等)、无人机三维路径规划、无人机协同、无人机编队、机器人路径规划、栅格地图路径规划、多式联运运输问题、车辆协同无人机路径规划、天线线性阵列分布优化、车间布局优化
5 无人机应用方面
无人机路径规划、无人机控制、无人机编队、无人机协同、无人机任务分配
6 无线传感器定位及布局方面
传感器部署优化、通信协议优化、路由优化、目标定位优化、Dv-Hop定位优化、Leach协议优化、WSN覆盖优化、组播优化、RSSI定位优化
7 信号处理方面
信号识别、信号加密、信号去噪、信号增强、雷达信号处理、信号水印嵌入提取、肌电信号、脑电信号、信号配时优化
8 电力系统方面
微电网优化、无功优化、配电网重构、储能配置
9 元胞自动机方面
交通流 人群疏散 病毒扩散 晶体生长文章来源:https://www.toymoban.com/news/detail-657163.html
10 雷达方面
卡尔曼滤波跟踪、航迹关联、航迹融合文章来源地址https://www.toymoban.com/news/detail-657163.html
到了这里,关于【路径规划】基于matlab fmincon无人机航路避障规划【含Matlab源码 2723期】的文章就介绍完了。如果您还想了解更多内容,请在右上角搜索TOY模板网以前的文章或继续浏览下面的相关文章,希望大家以后多多支持TOY模板网!