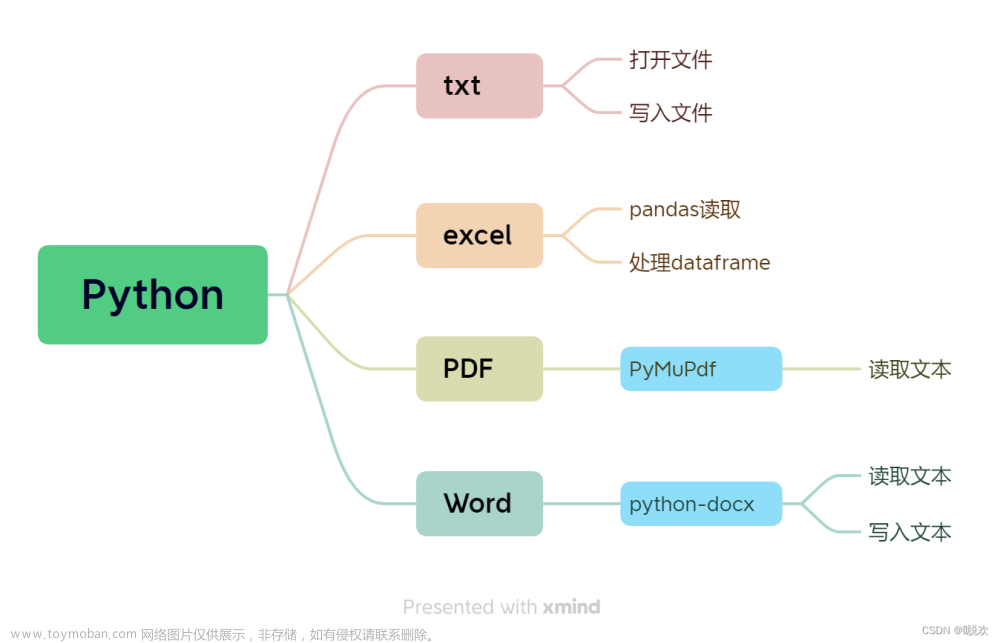
使用Python处理Word文件
- 安装外部模块python-docx
pip install python-docx
1. 从Python看Word文件结构
在python-docx模块中,将Word文件结构分成3层:
- Document:最高层,代表整个Word文件。
-
Paragraph:一个Word文件由许多段落组成,在Python中,整份文件的定义是Document,这些段落的定义就是Paragraph对象。在Python中,一个段落代表一个
Paragraph对象,所有段落以Paragraph对象列表方式存在。 - Run:Word文件要考虑的有字号、字体样式、色彩等,统称为样式。一个Run对象指的是Paragraph对象中相同样式的连续文字,如果文字发生样式变化,Python将以新的Run对象代表。
2. 读取Word文件内容
- 读取简单word文件
# author:mlnt
# createdate:2022/8/15
import docx # 导入docx模块
# 1.创建docx对象
document = docx.Document('test.docx')
# 2.获得Paragraph和Run数量
# 使用len()方法获得Paragraph数量
paragraph_count = len(document.paragraphs)
print(f'段落数:{paragraph_count}')
for i in range(0, paragraph_count):
# 获取Paragraph的Run数量
paragraph_run_count = len(document.paragraphs[i].runs) # i为Paragraph编号
print(document.paragraphs[i].text) # 打印Paragraph内容
print(document.paragraphs[i].runs[i].text) # 打印第i段第i个Run内容
def getFile(filename):
"""读取文件与适度编辑文件"""
document = docx.Document(filename) # 建立Word文件对象
content = []
for paragraph in document.paragraphs:
print(paragraph.text) # 输出文件所读取的Paragraph内容
content.append(paragraph.text) # 将每一段Paragraph组成列表
return '\n\n'.join(content) # 将列表转成字符串并隔行输出
print(getFile('test.docx'))
# 存储文件
document.save('out_test.docx') # 将文件复制到新文件
test.docx:
out_test.docx
- 读取含表格的word文档内容
# author:mlnt
# createdate:2022/8/15
import docx # 导入docx模块
from docx.document import Document
from docx.oxml import CT_P, CT_Tbl
from docx.table import _Cell, Table, _Row
from docx.text.paragraph import Paragraph
def iter_block_items(parent):
"""
依次遍历文档内容
按文档顺序生成对父级中每个段落和表子级的引用。
每个返回值都是表或段落的实例。
父对象通常是对主文档对象的引用,但也适用于_Cell对象,它本身可以包含段落和表格。
:param parent:
:return:
"""
# 判断传入的是否为word文档对象,是则获取文档内容的全部子对象
if isinstance(parent, Document):
parent_elm = parent.element.body
# 判断传入的是否为单元格,是则获取单元格内全部子对象
elif isinstance(parent, _Cell):
parent_elm = parent.tc
# 判断是否为表格行
elif isinstance(parent, _Row):
parent_elm = parent.tr
else:
raise ValueError("something's not right")
# 遍历全部子对象
for child in parent_elm.iterchildren():
# 判断是否为段落,是则返回段落对象
if isinstance(child, CT_P):
yield Paragraph(child, parent)
# 判断是否为表格,是则返回表格对象
if isinstance(child, CT_Tbl):
yield Table(child, parent)
# 1.创建docx对象
document = docx.Document('test.docx')
# 遍历word文档,最后调用函数没有返回值时停止遍历
for block in iter_block_items(document):
# 判断是否为段落
if isinstance(block, Paragraph):
print(block.text)
# 判断是否为表格
elif isinstance(block, Table):
for row in block.rows:
row_data = []
for cell in row.cells:
for paragraph in cell.paragraphs:
row_data.append(paragraph.text)
print("\t".join(row_data))
测试文档:
读取效果:
3. 创建文件内容
-
创建docx对象
# 1.创建docx对象 document = docx.Document() -
设置页面
# 设置页眉 run_header = document.sections[0].header.paragraphs[0].add_run("test") document.sections[0].header.paragraphs[0].alignment = WD_PARAGRAPH_ALIGNMENT.CENTER # 居中对齐 -
添加标题
# 2.添加标题 """ add_heading():建立标题 - document.add_heading('content_of_heading', level=n) """ document.add_heading('侠客行', level=1) # 标题1格式 document.add_heading('李白', level=2) # 标题2格式 -
添加段落
# 3.添加段落 # 创建段落对象 """ add_paragraph():建立段落Paragraph内容 - document.add_paragraph('paragraph_content') """ paragraph_object = document.add_paragraph('赵客缦胡缨,吴钩霜雪明。') document.add_paragraph('银鞍照白马,飒沓如流星。') document.add_paragraph('十步杀一人,千里不留行。') document.add_paragraph('事了拂衣去,深藏身与名。') document.add_paragraph('闲过信陵饮,脱剑膝前横。') document.add_paragraph('将炙啖朱亥,持觞劝侯嬴。') document.add_paragraph('三杯吐然诺,五岳倒为轻。') document.add_paragraph('眼花耳热后,意气素霓生。') document.add_paragraph('救赵挥金槌,邯郸先震惊。') document.add_paragraph('千秋二壮士,烜赫大梁城。') document.add_paragraph('纵死侠骨香,不惭世上英。') document.add_paragraph('谁能书阁下,白首太玄经。') prior_paragraph_object = paragraph_object.insert_paragraph_before('') # 在paragraph前插入新段落 -
建立Run内容,设置样式
# 4.建立Run内容 """ Paragraph是由Run组成,使用add_run()方法可以在Paragraph中插入内容,语法如下: paragraph_object.add_run('run_content') """ run1 = prior_paragraph_object.add_run('*'*13) run2 = prior_paragraph_object.add_run('%'*13) # 设置Run的样式 """ bold: 加粗 italic:斜体 underline:下划线 strike:删除线 """ run1.bold = True run2.underline = True # 设置段落居中对齐 for i in range(len(document.paragraphs)): document.paragraphs[i].alignment = WD_PARAGRAPH_ALIGNMENT.CENTER # 居中对齐 -
添加换页符
# 5.添加换页符 # add_page_break() document.add_page_break() -
插入图片
# 6.插入图片 # add_picture(),调整图片宽高需导入docx.shared模块 document.add_picture('libai.jpeg', width=Pt(200), height=Pt(300)) # 设置居中对齐 document.paragraphs[len(document.paragraphs)-1].alignment = WD_PARAGRAPH_ALIGNMENT.CENTER # 居中对齐 -
创建表格,添加数据并设置简单样式
# 7.创建表格 """ add_table(rows=n, cols=m) """ table = document.add_table(rows=2, cols=5) # 添加表格内容 # 添加第1行数据 row = table.rows[0] row.cells[0].text = '姓名' row.cells[1].text = '字' row.cells[2].text = '号' row.cells[3].text = '所处时代' row.cells[4].text = '别称' # 添加第2行数据 row = table.rows[1] row.cells[0].text = '李白' row.cells[1].text = '太白' row.cells[2].text = '青莲居士' row.cells[3].text = '唐朝' row.cells[4].text = '诗仙' # 插入行 new_row = table.add_row() # 增加表格行 new_row.cells[0].text = '白居易' new_row.cells[1].text = '乐天' new_row.cells[2].text = '香山居士' new_row.cells[3].text = '唐朝' new_row.cells[4].text = '诗魔' # 插入列 new_column = table.add_column(width=Inches(1)) # 增加表格列 new_column.cells[0].text = '代表作' new_column.cells[1].text = '《侠客行》、《静夜思》' new_column.cells[2].text = '《长恨歌》、《琵琶行》' # 计算表格的rows和cols的长度 rows = len(table.rows) cols = len(table.columns) print(f'rows: {rows}') print(f'columns: {cols}') # 打印表格内容 # for row in table.rows: # for cell in row.cells: # print(cell.text) # 设置表格样式 # table.style = 'LightShading-Accent1' # UserWarning: style lookup by style_id is deprecated. Use style name as key instead. table.style = 'Light Shading Accent 1' # 循环将每一行,每一列都设置为居中 for r in range(rows): for c in range(cols): table.cell(r, c).vertical_alignment = WD_CELL_VERTICAL_ALIGNMENT.CENTER # 垂直居中 table.cell(r, c).paragraphs[0].paragraph_format.alignment = WD_TABLE_ALIGNMENT.CENTER # 水平居中 -
设置页码并保存
# 设置页码 add_page_number(document.sections[0].footer.paragraphs[0]) # 保存文件 document.save('test2.docx') -
设置页码的代码(page_num.py)
from docx import Document from docx.enum.text import WD_PARAGRAPH_ALIGNMENT from docx.oxml import OxmlElement, ns def create_element(name): return OxmlElement(name) def create_attribute(element, name, value): element.set(ns.qn(name), value) def add_page_number(paragraph): paragraph.alignment = WD_PARAGRAPH_ALIGNMENT.CENTER page_run = paragraph.add_run() t1 = create_element('w:t') create_attribute(t1, 'xml:space', 'preserve') t1.text = 'Page ' page_run._r.append(t1) page_num_run = paragraph.add_run() fldChar1 = create_element('w:fldChar') create_attribute(fldChar1, 'w:fldCharType', 'begin') instrText = create_element('w:instrText') create_attribute(instrText, 'xml:space', 'preserve') instrText.text = "PAGE" fldChar2 = create_element('w:fldChar') create_attribute(fldChar2, 'w:fldCharType', 'end') page_num_run._r.append(fldChar1) page_num_run._r.append(instrText) page_num_run._r.append(fldChar2) of_run = paragraph.add_run() t2 = create_element('w:t') create_attribute(t2, 'xml:space', 'preserve') t2.text = ' of ' of_run._r.append(t2) fldChar3 = create_element('w:fldChar') create_attribute(fldChar3, 'w:fldCharType', 'begin') instrText2 = create_element('w:instrText') create_attribute(instrText2, 'xml:space', 'preserve') instrText2.text = "NUMPAGES" fldChar4 = create_element('w:fldChar') create_attribute(fldChar4, 'w:fldCharType', 'end') num_pages_run = paragraph.add_run() num_pages_run._r.append(fldChar3) num_pages_run._r.append(instrText2) num_pages_run._r.append(fldChar4) -
完整代码文章来源:https://www.toymoban.com/news/detail-660740.html
import docx from docx.enum.table import WD_TABLE_ALIGNMENT, WD_CELL_VERTICAL_ALIGNMENT from docx.enum.text import WD_PARAGRAPH_ALIGNMENT from docx.shared import Pt, Inches from page_num import add_page_number # 1.创建docx对象 document = docx.Document() # 设置页眉 run_header = document.sections[0].header.paragraphs[0].add_run("test") document.sections[0].header.paragraphs[0].alignment = WD_PARAGRAPH_ALIGNMENT.CENTER # 居中对齐 print(len(document.sections)) # 2.添加标题 """ add_heading():建立标题 - document.add_heading('content_of_heading', level=n) """ document.add_heading('侠客行', level=1) # 标题1格式 document.add_heading('李白', level=2) # 标题2格式 # 3.添加段落 # 创建段落对象 """ add_paragraph():建立段落Paragraph内容 - document.add_paragraph('paragraph_content') """ paragraph_object = document.add_paragraph('赵客缦胡缨,吴钩霜雪明。') document.add_paragraph('银鞍照白马,飒沓如流星。') document.add_paragraph('十步杀一人,千里不留行。') document.add_paragraph('事了拂衣去,深藏身与名。') document.add_paragraph('闲过信陵饮,脱剑膝前横。') document.add_paragraph('将炙啖朱亥,持觞劝侯嬴。') document.add_paragraph('三杯吐然诺,五岳倒为轻。') document.add_paragraph('眼花耳热后,意气素霓生。') document.add_paragraph('救赵挥金槌,邯郸先震惊。') document.add_paragraph('千秋二壮士,烜赫大梁城。') document.add_paragraph('纵死侠骨香,不惭世上英。') document.add_paragraph('谁能书阁下,白首太玄经。') prior_paragraph_object = paragraph_object.insert_paragraph_before('') # 在paragraph前插入新段落 # 4.建立Run内容 """ Paragraph是由Run组成,使用add_run()方法可以在Paragraph中插入内容,语法如下: paragraph_object.add_run('run_content') """ run1 = prior_paragraph_object.add_run('*'*13) run2 = prior_paragraph_object.add_run('%'*13) # 设置Run的样式 """ bold: 加粗 italic:斜体 underline:下划线 strike:删除线 """ run1.bold = True run2.underline = True # 设置段落居中对齐 for i in range(len(document.paragraphs)): document.paragraphs[i].alignment = WD_PARAGRAPH_ALIGNMENT.CENTER # 居中对齐 # 5.添加换页符 # add_page_break() document.add_page_break() # print(len(document.paragraphs)) # 6.插入图片 # add_picture(),调整图片宽高需导入docx.shared模块 document.add_picture('libai.jpeg', width=Pt(200), height=Pt(300)) # 设置居中对齐 document.paragraphs[len(document.paragraphs)-1].alignment = WD_PARAGRAPH_ALIGNMENT.CENTER # 居中对齐 # 7.创建表格 """ add_table(rows=n, cols=m) """ table = document.add_table(rows=2, cols=5) # 添加表格内容 # 添加第1行数据 row = table.rows[0] row.cells[0].text = '姓名' row.cells[1].text = '字' row.cells[2].text = '号' row.cells[3].text = '所处时代' row.cells[4].text = '别称' # 添加第2行数据 row = table.rows[1] row.cells[0].text = '李白' row.cells[1].text = '太白' row.cells[2].text = '青莲居士' row.cells[3].text = '唐朝' row.cells[4].text = '诗仙' # 插入行 new_row = table.add_row() # 增加表格行 new_row.cells[0].text = '白居易' new_row.cells[1].text = '乐天' new_row.cells[2].text = '香山居士' new_row.cells[3].text = '唐朝' new_row.cells[4].text = '诗魔' # 插入列 new_column = table.add_column(width=Inches(1)) # 增加表格列 new_column.cells[0].text = '代表作' new_column.cells[1].text = '《侠客行》、《静夜思》' new_column.cells[2].text = '《长恨歌》、《琵琶行》' # 计算表格的rows和cols的长度 rows = len(table.rows) cols = len(table.columns) print(f'rows: {rows}') print(f'columns: {cols}') # 打印表格内容 # for row in table.rows: # for cell in row.cells: # print(cell.text) # 设置表格样式 # table.style = 'LightShading-Accent1' # UserWarning: style lookup by style_id is deprecated. Use style name as key instead. table.style = 'Light Shading Accent 1' # 循环将每一行,每一列都设置为居中 for r in range(rows): for c in range(cols): table.cell(r, c).vertical_alignment = WD_CELL_VERTICAL_ALIGNMENT.CENTER # 垂直居中 table.cell(r, c).paragraphs[0].paragraph_format.alignment = WD_TABLE_ALIGNMENT.CENTER # 水平居中 # 设置页码 add_page_number(document.sections[0].footer.paragraphs[0]) # 保存文件 document.save('test2.docx')效果:
 文章来源地址https://www.toymoban.com/news/detail-660740.html
文章来源地址https://www.toymoban.com/news/detail-660740.html
参考:
- https://blog.csdn.net/m0_62184088/article/details/122522009
- https://www.cnpython.com/qa/1290238
- https://blog.csdn.net/qq_39147299/article/details/125544621
- https://blog.csdn.net/hwwaizs/article/details/121186150
- https://blog.csdn.net/I_fole_you/article/details/121028608
- python-docx官方文档:https://python-docx.readthedocs.io/en/latest/
- https://blog.csdn.net/qq_38870145/article/details/124076591
- https://www.cnblogs.com/wl0924/p/16531087.html
- https://blog.csdn.net/qq_39905917/article/details/83503486
- https://qa.1r1g.com/sf/ask/2046849521/
到了这里,关于使用Python处理Word文件的文章就介绍完了。如果您还想了解更多内容,请在右上角搜索TOY模板网以前的文章或继续浏览下面的相关文章,希望大家以后多多支持TOY模板网!

](https://imgs.yssmx.com/Uploads/2024/01/803807-1.png)