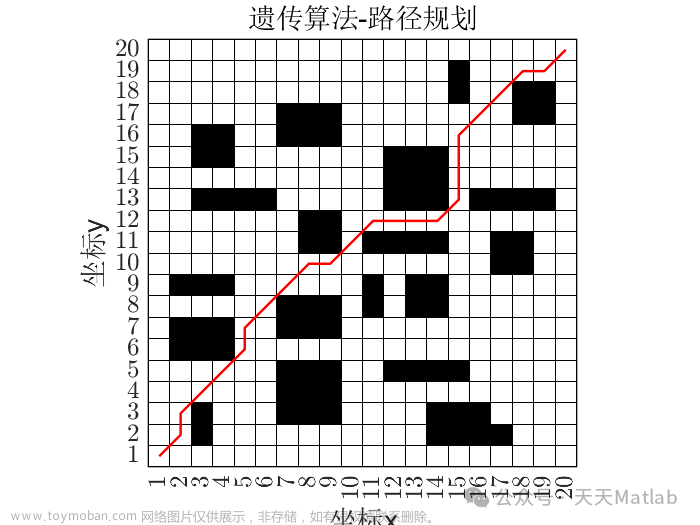
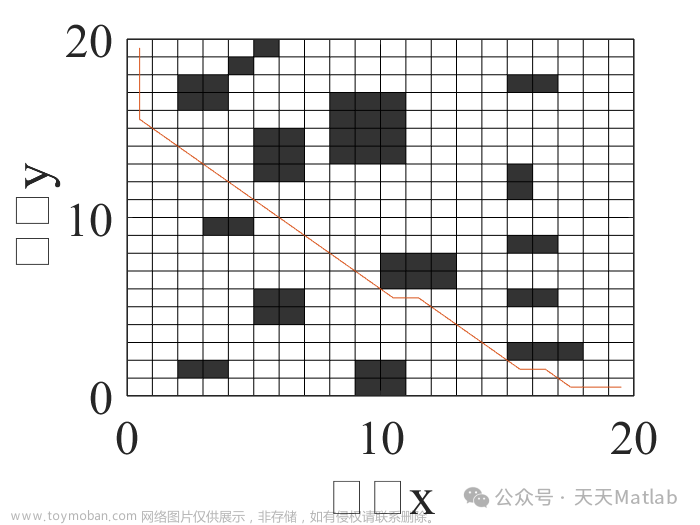
RRT算法
%%
%% 初始化
map=im2bw(imread('map2.bmp')); % bmp无损压缩图像500x500,im2bw把灰度图转换成二值图像01
source=[10 10]; % 起始点位置
goal=[490 490]; % 目标点位置
stepsize=20; % RRT每步步长
disTh=20; % 直到qnearest和目标点qgaol距离小于一个阈值
maxFailedAttempts = 10000; % 最大尝试次数
display=true; % RRT是否展示
%% %%%% 参数 %%%%%
tic; % 保存当前时间
if ~feasiblePoint(source,map), error('source lies on an obstacle or outside map'); end
if ~feasiblePoint(goal,map), error('goal lies on an obstacle or outside map'); end
if display, imshow(map);rectangle('position',[1 1 size(map)-1],'edgecolor','k'); end %展示图像,并创建带有尖角的矩形边框
RRTree=double([source -1]); % RRT 从起点开始(索引为-1),经过的结点和索引
failedAttempts=0; % 已经尝试失败的次数
counter=0; % 循环计数
pathFound=false; % 是否找到路径的flag
while failedAttempts<=maxFailedAttempts % RRT循环
if rand < 0.5,
sample=rand(1,2) .* size(map); % 50%几率随机采点
else
sample=goal; % 50%几率向目标前进
end
% 每一个分支都会继续分支
[A, I]=min( distanceCost(RRTree(:,1:2),sample) ,[],1); % 发现结点和随机采样点最小距离的一行,并返回对应索引,[],1可以去掉
closestNode = RRTree(I(1),1:2); %树结点最近点坐标,最近点可能多个(1)不可取
theta=atan2(sample(1)-closestNode(1),sample(2)-closestNode(2)); % 产生新结点的方向
newPoint = double(int32(closestNode(1:2) + stepsize * [sin(theta) cos(theta)])); % 产生新结点,先计算纵坐标,再计算横坐标
if ~checkPath(closestNode(1:2), newPoint, map) % 检测最近结点到新结点的路径是否可行
failedAttempts=failedAttempts+1;
continue;
end
if distanceCost(newPoint,goal)<disTh, pathFound=true;break; end % 检测新结点是否到达目标点,即小于一定的阈值
[A, I2]=min( distanceCost(RRTree(:,1:2),newPoint) ,[],1); % 检测检点是否已经存在树结点中
if distanceCost(newPoint,RRTree(I2(1),1:2))<disTh, failedAttempts=failedAttempts+1;continue; end %如果新结点在树结点中,记失败一次
RRTree=[RRTree;newPoint I(1)]; % 将新结点介入到如结点中
failedAttempts=0;
% 每扩展一个新结点,画一条线
if display,
line([closestNode(2);newPoint(2)],[closestNode(1);newPoint(1)]);
counter=counter+1;M(counter)=getframe;
end
end
% 补充最后一个新结点和终点的连线
if display && pathFound
line([closestNode(2);goal(2)],[closestNode(1);goal(1)]);
counter=counter+1;M(counter)=getframe;
end
if display
disp('click/press any key');
waitforbuttonpress;
end
if ~pathFound, error('no path found. maximum attempts reached'); end
%% 重现原轨迹
path=[goal];
prev=I(1);
while prev>0
path=[RRTree(prev,1:2);path];
prev=RRTree(prev,3);
end
pathLength=0;
for i=1:length(path)-1, pathLength=pathLength+distanceCost(path(i,1:2),path(i+1,1:2)); end
fprintf('processing time=%d \nPath Length=%d \n\n', toc,pathLength); % 打印运行时间toc和路径长度
imshow(map);rectangle('position',[1 1 size(map)-1],'edgecolor','k');
line(path(:,2),path(:,1));
仿真视频:
多地图RRT算法规划
地图一:
算法过程:
最终规划成的路线:
地图二:
算法过程:
最终规划成的路线:
地图三:
算法过程:
最终规划成的路线:
地图四:
算法过程:
最终规划成的路线:
地图五:
算法过程:
最终规划成的路线:文章来源:https://www.toymoban.com/news/detail-661061.html

需要源代码私聊我。文章来源地址https://www.toymoban.com/news/detail-661061.html
到了这里,关于多地图-RRT算法规划路径的文章就介绍完了。如果您还想了解更多内容,请在右上角搜索TOY模板网以前的文章或继续浏览下面的相关文章,希望大家以后多多支持TOY模板网!