线性数据结构
链表 LinkList
链表的数据结构
一组由节点组成的数据结构,每个元素指向下一个元素,是线性序列。
最简单的链表结构:
- 数据
- 指针(存放执行下一个节点的指针)
不适合的场景:
- 需要循环遍历将导致时间复杂度的提升
链表分类—单向链表
链表结构:
- 数据
- 指针 Next(指向下一个节点)
链表分类-双向列表
链表结构:
- 数据
- 指针 Next(指向下一个节点)
- 指针 Prev(指向前一个节点)
链表分类-循环列表
链表结构:
- 数据
- 指针 Next(指向下一个节点,最后一个节点指向第一个节点)
实现一个双向链表
实现链表节点:
public class Node<E> {
E item;
Node<E> prev;
Node<E> next;
public Node(E item, Node<E> prev, Node<E> next) {
this.item = item;
this.prev = prev;
this.next = next;
}
}
在头节点之前插入节点:
void insertNodeBeforeHead(E e){
final Node<E> oldHeadNode=head;
final Node<E> newHeadNode=new Node<E>(e,null,oldHeadNode);
head=newHeadNode;
if(oldHeadNode==null){
// 说明原先链表中没有元素
tail=newHeadNode;
}else{
// 如果有元素,则需要改变头节点的指针指向
oldHeadNode.prev=newHeadNode;
}
size++;
}
在尾节点之后插入节点:
void insertNodeAfterTail(E e){
final Node<E> oldTailNode=tail;
final Node<E> newTailNode=new Node<E>(e,oldTailNode,null);
tail=newTailNode;
if(oldTailNode==null){
head=newTailNode;
}else{
oldTailNode.next=newTailNode;
}
size++;
}
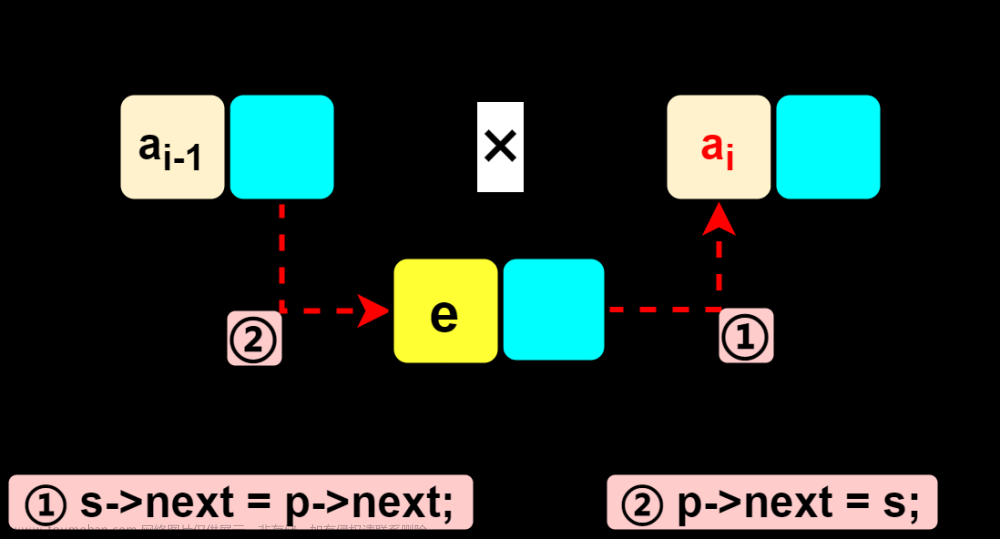
拆除链表:
E unlinkByNode(Node<E> node){
final E element=node.item;
final Node<E> prevNode=node.prev;
final Node<E> nextNode=node.next;
// 改变前一个元素的next指针指向的元素
if(prevNode==null){
// 说明是头节点
head=nextNode;
}else{
prevNode.next=nextNode;
node.prev=null;
}
// 改变后一个元素的prev指针指向的元素
if(nextNode==null){
// 说明是尾节点,没有下一个元素
tail=prevNode;
}else{
nextNode.prev=prevNode;
node.next=null;
}
size--;
node.item=null;
return null;
}
移除元素:
public boolean removeNodeByElement(E e){
if(e==null){
for(Node<E> start=head;start!=null;start=start.next){
if(start.item==null){
unlinkByNode(start);
return true;
}
}
}else{
for(Node<E> start=head;start!=null;start=start.next){
if(start.item.equals(e)){
unlinkByNode(start);
return true;
}
}
}
return false;
}
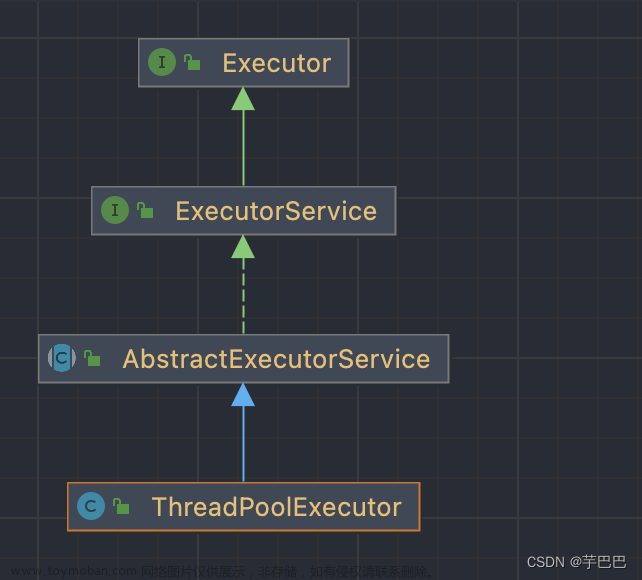
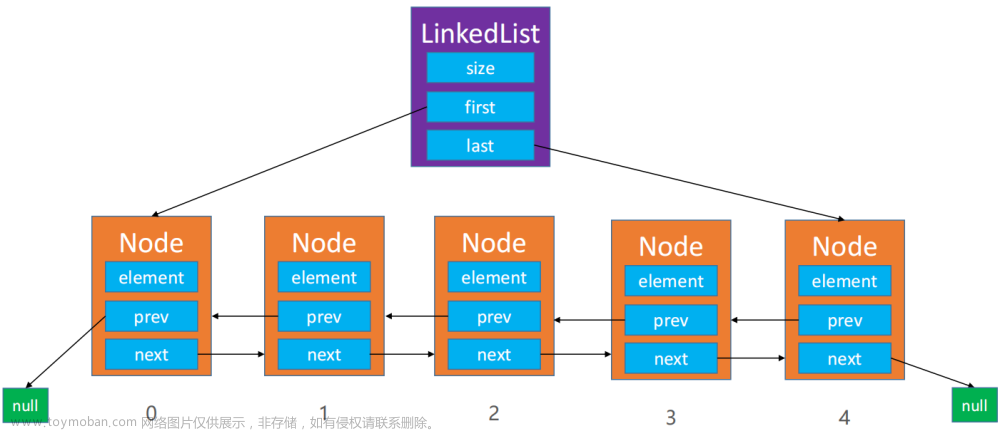
LinkedList 源码解读
继承关系

关键属性
transient int size=0;
/**
* Pointer to first node.
* Invariant: (first == null && last == null) ||
* (first.prev == null && first.item != null)
*/
transient Node<E> first;
/**
* Pointer to last node.
* Invariant: (first == null && last == null) ||
* (last.next == null && last.item != null)
*/
transient Node<E> last;
Node
其中节点 Node 的数据结构如下,是 LinkedList 的内部类:
private static class Node<E> {
E item; // 存储数据
Node<E> next; // 指向下一个节点
Node<E> prev; // 指向前一个节点
Node(Node<E> prev, E element, Node<E> next) {
this.item = element;
this.next = next;
this.prev = prev;
}
}
transient 的作用
首先,需要理解 Java 中序列化和反序列化的作用:
- 序列化:将内存中的对象信息转化为二进制数组的方法,可以将数组保存和传输,然后使用原来的类模板恢复对象的信息。
- 反序列化:使用原来的类模板将序列化后的二进制数组恢复为 Java 对象。
如何实现序列化和反序列化:
- 实现 Serializable 接口:
- 写对象信息:ObjectOutputStream.writeObject(Object object),该方法会判断 object 是否重写了 writeObject
方法,如果重写了,则通过反射调用重写后的方法,完成序列化 - 读对象信息:ObjectInputStream.readObject()
- 写对象信息:ObjectOutputStream.writeObject(Object object),该方法会判断 object 是否重写了 writeObject
什么情况下不需要序列化:
- 节省空间,去除部分无用的属性
- 持有对象的引用(对象在内存中的地址值)
LinkedList 将 first 和 last 修饰成 transient 的原因:
- 节省空间
- 重新连接链表:结点中保存前驱和后继的引用,序列化之后前序结点和后继结点的地址发生了改变,需要连接新的节点。
writeObject && readObject
LinkedList 重写了 writeObject 和 readObject 方法,自定义了序列化和反序列化的过程,用于重新链接节点:
序列化:writeObject
/**
* Saves the state of this {@code LinkedList} instance to a stream
* (that is, serializes it).
*
* @serialData The size of the list (the number of elements it
* contains) is emitted (int), followed by all of its
* elements (each an Object) in the proper order.
*/
private void writeObject(java.io.ObjectOutputStream s)
throws java.io.IOException{
// Write out any hidden serialization magic 调用默认的序列化方法
s.defaultWriteObject();
// Write out size 指定序列化的容量,单位:32 bit int
s.writeInt(size);
// Write out all elements in the proper order.
// 只把结点中的值序列化,前序和后继的引用不序列化
for(Node<E> x=first;x!=null;x=x.next)
s.writeObject(x.item);
}
反序列化:readObject
/**
* Reconstitutes this {@code LinkedList} instance from a stream
* (that is, deserializes it).
*/
@SuppressWarnings("unchecked")
private void readObject(java.io.ObjectInputStream s)
throws java.io.IOException,ClassNotFoundException{
// Read in any hidden serialization magic 用默认的反序列化方法
s.defaultReadObject();
// Read in size 指定读的容量
int size=s.readInt();
// Read in all elements in the proper order.
// 读取每一个结点保存的值,创建新结点,重新连接链表。
for(int i=0;i<size; i++)
linkLast((E)s.readObject()); // linkLast是向链表中的尾部插入节点的方法
}
向链表的最后一个节点插入元素值为 e 的节点:linkLast(E e)
核心流程:
- 拿到当前的尾节点,记为 l
- 使用需要创建的元素 e 创建一个新的节点 newNode,prev 属性为 l 节点,next 属性为 null
- 将当前尾节点设置为上面新创建的节点 newNode
- 如果 l 节点为空则代表当前链表为空, 将 newNode 设置为头结点,否则将 l 节点的 next 属性设置为 newNode
/**
* Links e as last element.
*/
void linkLast(E e){
final Node<E> l=last;
final Node<E> newNode=new Node<>(l,e,null);
last=newNode;
if(l==null)
first=newNode;
else
l.next=newNode;
size++;
modCount++;
}
向指定节点前插入元素值为 e 的节点: linkBefore(E e, Node succ)
核心流程:
- 拿到 succ 节点的 prev 节点
- 使用 e 创建一个新的节点 newNode,其中 prev 属性为 pred 节点,next 属性为 succ 节点
- 将 succ 节点的 prev 属性设置为 newNode
- 如果 pred 节点为 null,则代表 succ 节点为头结点,要把 e 插入 succ 前面,因此将 first 设置为 newNode,否则将 pred 节点的 next 属性设为 newNode
/**
* Inserts element e before non-null Node succ.
*/
void linkBefore(E e,Node<E> succ){
// assert succ != null;
final Node<E> pred=succ.prev;
final Node<E> newNode=new Node<>(pred,e,succ);
succ.prev=newNode;
if(pred==null)
first=newNode;
else
pred.next=newNode;
size++;
modCount++;
}
移除链接上的节点 x(取消链接 x):E unlink(Node x)
核心流程:
- 定义 element 为 x 节点的值,next 为 x 节点的下一个节点,prev 为 x 节点的上一个节点
- 如果 prev 为空,则代表 x 节点为头结点,则将 first 指向 next 即可;否则,x 节点不为头结点,将 prev 节点的 next 属性指向 x 节点的 next 属性,并将 x 的 prev 属性清空
- 如果 next 为空,则代表 x 节点为尾节点,则将 last 指向 prev 即可;否则,x 节点不为尾节点,将 next 节点的 prev 属性指向 x 节点的 prev 属性,并将 x 的 next 属性清空
- 将 x 的 item 属性清空,以便垃圾收集器回收 x 对象
/**
* Unlinks non-null node x.
*/
E unlink(Node<E> x){
// assert x != null;
final E element=x.item;
final Node<E> next=x.next;
final Node<E> prev=x.prev;
if(prev==null){
first=next;
}else{
prev.next=next;
x.prev=null;
}
if(next==null){
last=prev;
}else{
next.prev=prev;
x.next=null;
}
x.item=null;
size--;
modCount++;
return element;
}
插入元素:add
默认插入方法,尾部插入:boolean add(E e)
直接插入链表尾部
/**
* Appends the specified element to the end of this list.
*
* <p>This method is equivalent to {@link #addLast}.
*
* @param e element to be appended to this list
* @return {@code true} (as specified by {@link Collection#add})
*/
public boolean add(E e){
linkLast(e);
return true;
}
指定位置插入元素:add(int index,E element)
流程:
- 检查索引 index 是否越界(只要用到了索引 index,都会判断是否越界)
- 如果索引 index 和链表当前的长度 size 相同,则执行尾部插入
- 否则,将 element 插入原 index 位置节点的前面
/**
* Inserts the specified element at the specified position in this list.
* Shifts the element currently at that position (if any) and any
* subsequent elements to the right (adds one to their indices).
*
* @param index index at which the specified element is to be inserted
* @param element element to be inserted
* @throws IndexOutOfBoundsException {@inheritDoc}
*/
public void add(int index,E element){
checkPositionIndex(index);
if(index==size)
linkLast(element);
else
linkBefore(element,node(index));
}
获取节点:get
核心流程:
- 根据 index,调用 node 方法,寻找目标节点,返回目标节点的 item。
/**
* Returns the element at the specified position in this list.
*
* @param index index of the element to return
* @return the element at the specified position in this list
* @throws IndexOutOfBoundsException {@inheritDoc}
*/
public E get(int index){
checkElementIndex(index);
return node(index).item;
}
根据指定索引 index 位置查找节点
核心流程:
- 如果 index 的长度是链表长度的一半,则在链表前半部分,从头节点开始遍历
- 否则,从尾节点开始遍历
/**
* Returns the (non-null) Node at the specified element index.
*/
Node<E> node(int index){
// assert isElementIndex(index);
if(index< (size>>1)){
Node<E> x=first;
for(int i=0;i<index; i++)
x=x.next;
return x;
}else{
Node<E> x=last;
for(int i=size-1;i>index;i--)
x=x.prev;
return x;
}
}
替换指定位置的元素:set
核心流程:
- 调用 node 方法寻找到目标节点
- 将目标节点的 item 属性,替换为目标元素
/**
* Replaces the element at the specified position in this list with the
* specified element.
*
* @param index index of the element to replace
* @param element element to be stored at the specified position
* @return the element previously at the specified position
* @throws IndexOutOfBoundsException {@inheritDoc}
*/
public E set(int index,E element){
checkElementIndex(index);
Node<E> x=node(index);
E oldVal=x.item;
x.item=element;
return oldVal;
}
移除节点
移除指定元素的节点:boolean remove(Object o)
核心流程:
- 因为普通元素值和 null 判断存在区别,所以需要判断 o 是否为 null,如果 o 为 null,则遍历链表寻找 item 属性为空的节点,并调用 unlink 方法将该节点移除
- 否则,遍历链表寻找 item 属性跟 o 相同的节点,并调用 unlink 方法将该节点移除。
/**
* Removes the first occurrence of the specified element from this list,
* if it is present. If this list does not contain the element, it is
* unchanged. More formally, removes the element with the lowest index
* {@code i} such that
* <tt>(o==null ? get(i)==null : o.equals(get(i)))</tt>
* (if such an element exists). Returns {@code true} if this list
* contained the specified element (or equivalently, if this list
* changed as a result of the call).
*
* @param o element to be removed from this list, if present
* @return {@code true} if this list contained the specified element
*/
public boolean remove(Object o){
if(o==null){
for(Node<E> x=first;x!=null;x=x.next){
if(x.item==null){
unlink(x);
return true;
}
}
}else{
for(Node<E> x=first;x!=null;x=x.next){
if(o.equals(x.item)){
unlink(x);
return true;
}
}
}
return false;
}
移除指定索引位置的节点:remove(int index)
核心流程:
- 调用 unlink 方法,移除 index 位置的节点
/**
* Removes the element at the specified position in this list. Shifts any
* subsequent elements to the left (subtracts one from their indices).
* Returns the element that was removed from the list.
*
* @param index the index of the element to be removed
* @return the element previously at the specified position
* @throws IndexOutOfBoundsException {@inheritDoc}
*/
public E remove(int index){
checkElementIndex(index);
return unlink(node(index));
}
清除链表中的所有元素:clear
从 first 节点开始遍历,将所有的节点的 item、next、prev 值设置为 null。
public void clear(){
// Clearing all of the links between nodes is "unnecessary", but:
// - helps a generational GC if the discarded nodes inhabit
// more than one generation
// - is sure to free memory even if there is a reachable Iterator
for(Node<E> x=first;x!=null;){
Node<E> next=x.next;
x.item=null;
x.next=null;
x.prev=null;
x=next;
}
first=last=null;
size=0;
modCount++;
}
question
- 描述链表的数据结构
- Java 中的 LinkedList 的数据结构和原理
Node 的源码:
- 有 Next 指针、Prev 指针,说明是双向链表

LinkedList 的 linkLast 向尾元素后插入元素的方法源码:
- 尾元素的 prev 指针没有指向头元素,说明非循环

结论:非循环双向链表
- 链表中数据的插入、删除和获取的时间复杂度分析
获取:O(n)
插入:
- 有前置节点(头尾插入):O(1)
- 无前置节点:O(n)
- 什么场景下更适合使用链表
在不确定数据量且需要频繁插入和删除操作的场景下。文章来源:https://www.toymoban.com/news/detail-662180.html
leetcode 题目
707 设计链表
707 设计链表文章来源地址https://www.toymoban.com/news/detail-662180.html
到了这里,关于Java数据结构学习和源码阅读(线性数据结构)的文章就介绍完了。如果您还想了解更多内容,请在右上角搜索TOY模板网以前的文章或继续浏览下面的相关文章,希望大家以后多多支持TOY模板网!