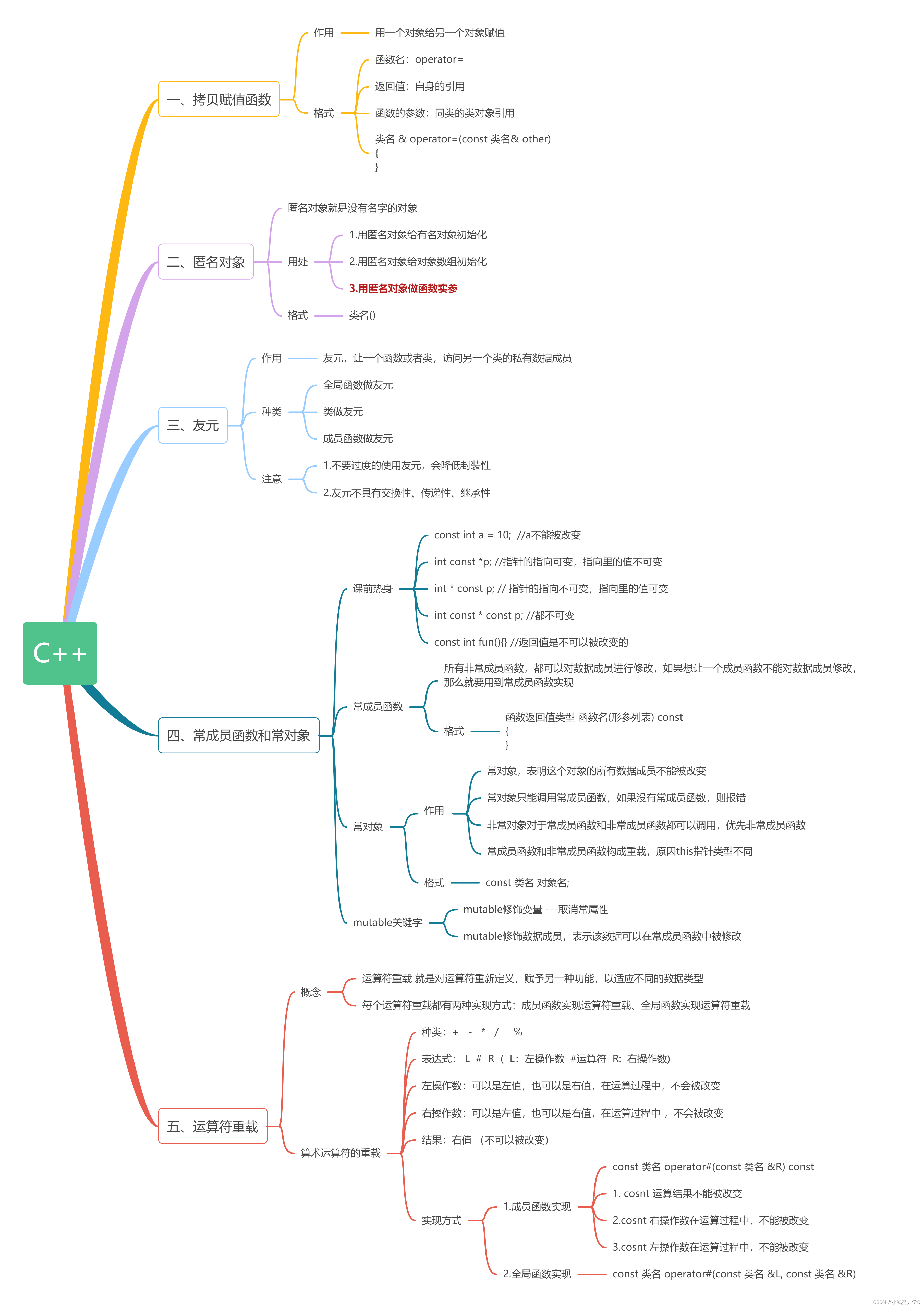
友元
c++是面向对象的,目的之一:封装
封装:
优点之一,就是安全。
缺点:在某些特殊的场合,不是很方便。
华为与IBM 40亿的咨询故事


IBM需要对华为各级部门做深度咨询分析,
为了提高咨询效率,由任正非直接授权,直接获取各部门的所有权限。
使用前提:
某个类需要实现某种功能,但是这个类自身,因为各种原因,无法自己实现。
需要借助于“外力”才能实现。
友元函数
使用全局函数作为友元函数
需求:
计算机和计算机的升级
Computer.h
#pragma once
#include <string>
class Computer
{
public:
Computer();
// 使用全局函数作为友元函数 友元函数可以访问类的所有数据成员
friend void upgrade(Computer* computer);
std::string description();
private:
std::string cpu; //CPU芯片
};computer.cpp
#include "Computer.h"
#include <sstream>
Computer::Computer()
{
cpu = "i7";
}
std::string Computer::description()
{
std::stringstream ret;
ret << "CPU:" << cpu;
return ret.str();
}main.cpp
#include <stdio.h>
#include <iostream>
#include <Windows.h>
#include "Computer.h"
void upgrade(Computer* computer) {
computer->cpu = "i9"; //直接访问对象的私有数据成员!!!
}
int main(void) {
Computer shanxing;
std::cout << shanxing.description() << std::endl;
upgrade(&shanxing);
std::cout << shanxing.description() << std::endl;
system("pause");
return 0;
}使用类的成员函数作为友元函数
需求:
计算机和计算机的升级
computer.h
#pragma once
#include <string>
#include <iostream>
#include <sstream>
#include "Computerservice.h"
using namespace std;
class Computer
{
public:
Computer();
string description();
friend void Computerservice::upgrade(Computer* computer);
//friend void upgrade(Computer* computer);//把外部的全局函数申明为这个类的友元函数
private:
string cpu;
};
computerservice.h
#pragma once
class Computer;
class Computerservice
{
public:
void upgrade(Computer* computer);
};computer.cpp
#include "Computer.h"
Computer::Computer()
{
this->cpu = "i7";
}
string Computer::description()
{
stringstream des;
des << "CPU" << cpu;
return des.str();
}
computerservice.cpp
#include "Computerservice.h"
#include "Computer.h"
void Computerservice::upgrade(Computer* computer)
{
this->cpu = "i9";
}
main.cpp
#include "Computer.h"
#include <iostream>
#include "Computerservice.h"
//void upgrade(Computer * computer) {
// computer->cpu = "i9";
//}
int main(void) {
Computer computer;
Computerservice serviece;
cout << computer.description() << endl;
serviece.upgrade(&computer);
cout << computer.description() << endl;
return 0;
}功能上,这两种形式,都是相同,应用场合不同。
一个是,使用普通的全局函数,作为自己的朋友,实现特殊功能。
一个是,使用其他类的成员函数,作为自己的朋友,实现特殊功能。
友元类
友元类的作用
如果把A类作为B类的友元类,
那么A类的所有成员函数【在A类的成员函数内】,就可以直接访问【使用】B类的私有成员。
即,友元类可以直接访问对应类的所有成员!!!
Demo
Computer.h
#pragma once
#include <string>
#include <iostream>
#include <sstream>
#include "Computerservice.h"
using namespace std;
class ComputerService;
class Computer
{
public:
friend class Computerservice;
Computer();
string description();
private:
string cpu;
};
Computer.cpp
#include "Computer.h"
#include "Computerservice.h"
Computer::Computer()
{
this->cpu = "i7";
}
string Computer::description()
{
stringstream des;
des << "CPU" << cpu;
return des.str();
}ComputerService.h
#pragma once
class Computer;
class Computerservice
{
public:
void upgrade(Computer* computer);
void clear(Computer* computer);
void kill(Computer* computer);
};ComputerService.cpp
#include "Computerservice.h"
#include "Computer.h"
void Computerservice::upgrade(Computer* computer)
{
computer->cpu = "i9";
}
void Computerservice::clear(Computer* computer)
{
cout << "正在对电脑执行清理[CPU:" << computer->cpu << "]" < endl;
}
void Computerservice::kill(Computer* computer)
{
cout << "杀毒" << endl;
}main.cpp
#include "Computer.h"
#include <iostream>
#include "Computerservice.h"
int main(void) {
Computer computer;
Computerservice serviece;
cout << computer.description() << endl;
serviece.upgrade(&computer);
cout << computer.description() << endl;
serviece.clear(&computer);
serviece.kill(&computer);
return 0;
}使用注意
友元类,和友元函数,使用friend关键字进行声明即可,与访问权限无关,
所以,可以放在private/pulic/protected任意区域内。
万物可运算-运算符重载
为什么要使用运算符重载
C/C++的运算符,支持的数据类型,仅限于基本数据类型。
问题:一头牛+一头马 = ?(牛马神兽?)
一个圆 +一个圆 = ? (想要变成一个更大的圆)
一头牛 – 一只羊 = ? (想要变成4只羊,原始的以物易物:1头牛价值5只羊)
解决方案:使用运算符重载
运算符重载基本用法
方式1-使用成员函数重载运算符
使用成员函数重载运算符
需求: // 规则:
// 一斤牛肉:2斤猪肉
// 一斤羊肉:3斤猪肉
Cow.h
#pragma once
class Pork;
class Goat;
class Cow
{
public:
Cow(int weight);
// 参数此时定义为引用类型,更合适,避免拷贝
Pork operator+(const Cow& cow); //同类型进行运算,很频繁
Pork operator+(const Goat& goat); //不同类型进行运算,比较少见
private:
int weight = 0;
};
Cow.cpp
#include "Cow.h"
#include "Pork.h"
#include "Goat.h"
Cow::Cow(int weight)
{
this->weight = weight;
}
// 规则:
// 一斤牛肉:2斤猪肉
// 一斤羊肉:3斤猪肉
Pork Cow::operator+(const Cow &cow)
{
int tmp = (this->weight + cow.weight) * 2;
return Pork(tmp);
}
Pork Cow::operator+(const Goat& goat)
{
// 不能直接访问goat.weight
//int tmp = this->weight * 2 + goat.weight * 3;
int tmp = this->weight * 2 + goat.getWeight() * 3;
return Pork(tmp);
}
Goat.cpp
#include "Goat.h" Goat::Goat(int weight) { this->weight = weight; } int Goat::getWeight(void) const { return weight; }
Goat.h
#pragma once class Goat { public: Goat(int weight); int getWeight(void) const; private: int weight = 0; };
Pork.h
#pragma once
#include <iostream>
class Pork
{
public:
Pork(int weight);
std::string description(void);
private:
int weight = 0;
};Pork.cpp
#include "Pork.h"
#include <sstream>
Pork::Pork(int weight)
{
this->weight = weight;
}
std::string Pork::description(void)
{
std::stringstream ret;
ret << weight << "斤猪肉";
return ret.str();
}main.cpp
#include <iostream> #include "Pork.h" #include "Cow.h" #include "Goat.h" int main(void) { Cow c1(100); Cow c2(200); // 调用c1.operator+(c2); //相当于:Pork p = c1.operator+(c2); Pork p = c1 + c2; std::cout << p.description() << std::endl; Goat g1(100); p = c1 + g1; std::cout << p.description() << std::endl; system("pause"); return 0; }
方式二 - 使用非成员函数【友元函数】重载运算符
Cow.h
#pragma once
class Pork;
class Goat;
class Cow
{
public:
Cow(int weight);
// 有友元函数实现运算符重载
friend Pork operator+(const Cow& cow1, const Cow& cow2);
friend Pork operator+(const Cow& cow1, const Goat& goat);
private:
int weight = 0;
};main.cpp
其他文件不变
两种方式的区别
区别:
-
使用成员函数来实现运算符重载时,少写一个参数,因为第一个参数就是this指针。
两种方式的选择:
-
一般情况下,单目运算符重载,使用成员函数进行重载更方便(不用写参数)
-
一般情况下,双目运算符重载,使用友元函数
#include <iostream> #include "Pork.h" #include "Cow.h" #include "Goat.h" Pork operator+(const Cow &cow1, const Cow &cow2) { int tmp = (cow1.weight + cow2.weight) * 2; return Pork(tmp); } Pork operator+(const Cow& cow1, const Goat& goat) { int tmp = cow1.weight * 2 + goat.getWeight() * 3; return Pork(tmp); } int main(void) { Cow c1(100); Cow c2(200); Goat g1(100); Pork p = c1 + c2; std::cout << p.description() << std::endl; p = c1 + g1; // 思考:如何实现:p = g1 + c1; std::cout << p.description() << std::endl; system("pause"); return 0; }更直观
方便实现a+b和b+a相同的效果,成员函数方式无法实现。
例如: 100 + cow; 只能通过友元函数来实现
cow +100; 友元函数和成员函数都可以实现
特殊情况:
(1) = () [ ] -> 不能重载为类的友元函数!!!(否则可能和C++的其他规则矛盾),只能使用成员函数形式进行重载。
(2)如果运算符的第一个操作数要求使用隐式类型转换,则必须为友元函数(成员函数方式的第一个参数是this指针)
注意:
同一个运算符重载, 不能同时使用两种方式来重载,会导致编译器不知道选择哪一个(二义性)
运算符重载的禁区和规则
为了防止对标准类型进行运算符重载,
C++规定重载运算符的操作对象至少有一个不是标准类型,而是用户自定义的类型
比如不能重载 1+2
但是可以重载 cow + 2 和 2 + cow // cow是自定义的对象
2.不能改变原运算符的语法规则, 比如不能把双目运算符重载为单目运
不能改变原运算符的优先级
4.不能创建新的运算符,比如 operator*就是非法的, operator是可以的
不能对以下这四种运算符,使用友元函数进行重载
= 赋值运算符,()函数调用运算符,[ ]下标运算符,->通过指针访问类成员
不能对禁止重载的运算符进行重载
不能被重载的运算符
| 成员访问 | . |
|---|---|
| 域运算 | :: |
| 内存长度运算 | sizeof |
| 三目运算 | ? : : |
| 预处理 | # |
可以被重载的运算符
| 双目运算符 | + - * / % |
|---|---|
| 关系运算符 | == != < <= > >= |
| 逻辑运算符 | && || ! |
| 单目运算符 | +(正号) -(负号) *(指针) &(取地址) ++ -- |
| 位运算 | & | ~ ^ <<(左移) >>(右移) |
| 赋值运算符 | = += -= *= /= %= &= |= ^= <<= >>= |
| 内存分配 | new delete new[ ] delete[ ] |
| 其他 | ( ) 函数调用-> 成员访问 [ ] 下标, 逗号 |
重载运算符实例
重载赋值运算符=
Boy.h
#pragma once
#include <string>
using namespace std;
class Boy
{
public:
Boy(const char* name = NULL, int age = 0,int salary = 0,int darkHorse = 0);
~Boy();
string description();
Boy& operator= (const Boy & boy);
private:
char* name;
int age;
int salary;
int darkHorse;//潜力系数
unsigned int id;//编号
static int LAST_ID;
};Boy.cpp
#include "Boy.h"
#include <string.h>
#include <sstream>
using namespace std;
int Boy::LAST_ID = 0;
Boy::Boy(const char* name, int age, int salary, int darkHorse)
{
if (!name) {
;name = "未命名";
}
this->name = new char[strlen(name) + 1];
strcpy_s(this->name, strlen(name) +1, name);
this->age = age;
this->salary = salary;
this->darkHorse = darkHorse;
this->id = ++LAST_ID;
}
Boy::~Boy()
{
if (name) {
delete name;
}
}
string Boy::description()
{
stringstream des;
des << "ID:" << id << "\t姓名:" << name << "\t年龄" << age << "\t薪资" << salary << "/t黑马系数" << darkHorse;
return des.str();
}
Boy& Boy::operator=(const Boy& boy)
{
// TODO: 在此处插入 return 语句
if (name) {
delete name;
}
this->name = new char[strlen(boy.name) + 1];
strcpy_s(this->name, strlen(boy.name) + 1,boy.name);
this->age = boy.age;
this->darkHorse = boy.darkHorse;
this->salary = boy.salary;
//this->id
return *this;//返回这个对象
}Main.cpp
#include <iostream>
#include "boy.h"
int main(void) {
Boy boy1("lucifer", 16, 10000, 10);
Boy boy2, boy3;
std::cout << boy1.description() << std::endl;
std::cout << boy2.description() << std::endl;
std::cout << boy3.description() << std::endl;
boy3 = boy2 = boy1;
std::cout << boy2.description() << std::endl;
std::cout << boy3.description() << std::endl;
system("pause");
return 0;
}重载运算符> < ==
Boy.h 的方法加入
public:
bool operator>(const Boy& boy);
bool operator<(const Boy& boy);
bool operator==(const Boy& boy);
private:
int power() const; //综合能力值Boy.cpp
bool Boy::operator>(const Boy& boy)
{
// 设置比较规则:
// 薪资 * 黑马系数 + (100-年龄)*100
if (power() > boy.power()) {
return true;
}
else {
return false;
}
}
bool Boy::operator<(const Boy& boy)
{
if (power() < boy.power()) {
return true;
}
else {
return false;
}
}
bool Boy::operator==(const Boy& boy)
{
if (power() == boy.power()) {
return true;
}
else {
return false;
}
}下标运算符重载[ ]
Boy.h
#pragma once
#include <string>
class Boy
{
public:
Boy(const char* name=NULL, int age=0, int salary=0, int darkHorse=0);
~Boy();
Boy& operator=(const Boy& boy);
bool operator>(const Boy& boy);
bool operator<(const Boy& boy);
bool operator==(const Boy& boy);
int operator[](std::string index);
int operator[](int index);
std::string description(void);
private:
char* name;
int age;
int salary;
int darkHorse; //黑马值,潜力系数
unsigned int id; // 编号
static int LAST_ID;
int power() const; //综合能力值
};Boy.cpp
#include "boy.h"
#include <string.h>
#include <sstream>
int Boy::LAST_ID = 0; //初始值是0
Boy::Boy(const char* name, int age, int salary, int darkHorse)
{
if (!name) {
name = "未命名";
}
this->name = new char[strlen(name) + 1];
strcpy_s(this->name, strlen(name)+1, name);
this->age = age;
this->salary = salary;
this->darkHorse = darkHorse;
this->id = ++LAST_ID;
}
Boy::~Boy()
{
if (name) {
delete name;
}
}
Boy& Boy::operator=(const Boy& boy)
{
if (name) {
delete name; //释放原来的内存
}
name = new char[strlen(boy.name) + 1]; //分配新的内存
strcpy_s(name, strlen(boy.name)+1, boy.name);
this->age = boy.age;
this->salary = boy.salary;
this->darkHorse = boy.darkHorse;
//this->id = boy.id; //根据需求来确定是否要拷贝id
return *this;
}
bool Boy::operator>(const Boy& boy)
{
// 设置比较规则:
// 薪资 * 黑马系数 + (100-年龄)*100
if (power() > boy.power()) {
return true;
}
else {
return false;
}
}
bool Boy::operator<(const Boy& boy)
{
if (power() < boy.power()) {
return true;
}
else {
return false;
}
}
bool Boy::operator==(const Boy& boy)
{
if (power() == boy.power()) {
return true;
}
else {
return false;
}
}
int Boy::operator[](std::string index)
{
if (index == "age") {
return age;
}
else if (index == "salary") {
return salary;
}
else if (index == "darkHorse") {
return darkHorse;
}
else if (index == "power") {
return power();
}
else {
return -1;
}
}
int Boy::operator[](int index)
{
if (index == 0) {
return age;
}
else if (index == 1) {
return salary;
}
else if (index == 2) {
return darkHorse;
}
else if (index == 3) {
return power();
}
else {
return -1;
}
}
std::string Boy::description(void)
{
std::stringstream ret;
ret << "ID:" << id << "\t姓名:" << name << "\t年龄:" << age << "\t薪资:"
<< salary << "\t黑马系数:" << darkHorse;
return ret.str();
}
int Boy::power() const
{
// 薪资* 黑马系数 + (100 - 年龄) * 1000
int value = salary * darkHorse + (100 - age) * 100;
return value;
}main.cpp
#include <iostream>
#include "boy.h"
int main(void) {
Boy boy1("Rock", 38, 58000, 5);
Boy boy2("Jack", 25, 50000, 10);
std::cout << "age:" << boy1["age"] << std::endl;
std::cout << "salary:" << boy1["salary"] << std::endl;
std::cout << "darkHorse:" << boy1["darkHorse"] << std::endl;
std::cout << "power:" << boy1["power"] << std::endl;
std::cout << "[0]:" << boy1[0] << std::endl;
std::cout << "[1]:" << boy1[1] << std::endl;
std::cout << "[2]:" << boy1[2] << std::endl;
std::cout << "[3]:" << boy1[3] << std::endl;
system("pause");
return 0;
}输入输出的重载<< >>
为了更方便的实现复杂对象的输入和输出。
方式1(使用成员函数)
不推荐,该方式没有实际意义
Boy.h
#pragma once
#include <string>
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
class Boy
{
public:
Boy(const char* name = NULL, int age = 0, int salary = 0, int darkHorse = 0);
~Boy();
Boy& operator=(const Boy& boy);
bool operator>(const Boy& boy);
bool operator<(const Boy& boy);
bool operator==(const Boy& boy);
int operator[](std::string index);
int operator[](int index);
ostream& operator<<(ostream& os) const;
std::string description(void);
private:
char* name;
int age;
int salary;
int darkHorse; //黑马值,潜力系数
unsigned int id; // 编号
static int LAST_ID;
int power() const; //综合能力值
};boy.cpp
#include "boy.h"
#include <string.h>
#include <sstream>
int Boy::LAST_ID = 0; //初始值是0
Boy::Boy(const char* name, int age, int salary, int darkHorse)
{
if (!name) {
name = "未命名";
}
this->name = new char[strlen(name) + 1];
strcpy_s(this->name, strlen(name) + 1, name);
this->age = age;
this->salary = salary;
this->darkHorse = darkHorse;
this->id = ++LAST_ID;
}
Boy::~Boy()
{
if (name) {
delete name;
}
}
Boy& Boy::operator=(const Boy& boy)
{
if (name) {
delete name; //释放原来的内存
}
name = new char[strlen(boy.name) + 1]; //分配新的内存
strcpy_s(name, strlen(boy.name) + 1, boy.name);
this->age = boy.age;
this->salary = boy.salary;
this->darkHorse = boy.darkHorse;
//this->id = boy.id; //根据需求来确定是否要拷贝id
return *this;
}
bool Boy::operator>(const Boy& boy)
{
// 设置比较规则:
// 薪资 * 黑马系数 + (100-年龄)*100
if (power() > boy.power()) {
return true;
}
else {
return false;
}
}
bool Boy::operator<(const Boy& boy)
{
if (power() < boy.power()) {
return true;
}
else {
return false;
}
}
bool Boy::operator==(const Boy& boy)
{
if (power() == boy.power()) {
return true;
}
else {
return false;
}
}
int Boy::operator[](std::string index)
{
if (index == "age") {
return age;
}
else if (index == "salary") {
return salary;
}
else if (index == "darkHorse") {
return darkHorse;
}
else if (index == "power") {
return power();
}
else {
return -1;
}
}
int Boy::operator[](int index)
{
if (index == 0) {
return age;
}
else if (index == 1) {
return salary;
}
else if (index == 2) {
return darkHorse;
}
else if (index == 3) {
return power();
}
else {
return -1;
}
}
ostream& Boy::operator<<(ostream& os) const
{
os << "ID:" << id << "\t姓名:" << name << "\t年龄:" << age << "\t薪资:"
<< salary << "\t黑马系数:" << darkHorse;
return os;
}
std::string Boy::description(void)
{
std::stringstream ret;
ret << "ID:" << id << "\t姓名:" << name << "\t年龄:" << age << "\t薪资:"
<< salary << "\t黑马系数:" << darkHorse;
return ret.str();
}
int Boy::power() const
{
// 薪资* 黑马系数 + (100 - 年龄) * 1000
int value = salary * darkHorse + (100 - age) * 100;
return value;
}mian.cpp
#include <iostream>
#include "boy.h"
int main(void) {
Boy boy1("Rock", 38, 58000, 5);
Boy boy2("Jack", 25, 50000, 10);
// 调用: boy1.operator<<(cout);
boy1 << cout;
// 先调用 boy1.operator<<(cout)
// 再调用 boy2.operator<<(cout)
boy2 << (boy1 << cout);
system("pause");
return 0;
}使用取来不方便
方式二(使用友元函数)
Boy.h
#pragma once
#include <string>
#include <iostream>
#define AGE_KEY "age"
#define SALARY_KEY "salary"
#define DARK_HORSE_KEY "darkHorse"
#define POWER_KEY "power"
typedef enum {
AGE,
SALARY,
DARK_HORSE,
POWER
}BOY_KEY_TYPE;
using namespace std;
class Boy
{
public:
Boy(const char* name = NULL, int age = 0, int salary = 0, int darkHorse = 0);
~Boy();
Boy& operator=(const Boy& boy);
bool operator>(const Boy& boy);
bool operator<(const Boy& boy);
bool operator==(const Boy& boy);
// 下标运算符的重载
int operator[](std::string index);
int operator[](int index);
// 该方式不适合
//ostream& operator<<(ostream& os) const;
friend ostream& operator<<(ostream& os, const Boy& boy);
friend istream& operator>>(istream& is, Boy& boy);
std::string description(void);
private:
char* name;
int age;
int salary;
int darkHorse; //黑马值,潜力系数
unsigned int id; // 编号
static int LAST_ID;
int power() const; //综合能力值
};Boy.cpp
#include "boy.h"
#include <string.h>
#include <sstream>
int Boy::LAST_ID = 0; //初始值是0
Boy::Boy(const char* name, int age, int salary, int darkHorse)
{
if (!name) {
name = "未命名";
}
this->name = new char[strlen(name) + 1];
strcpy_s(this->name, strlen(name) + 1, name);
this->age = age;
this->salary = salary;
this->darkHorse = darkHorse;
this->id = ++LAST_ID;
}
Boy::~Boy()
{
if (name) {
delete name;
}
}
Boy& Boy::operator=(const Boy& boy)
{
if (name) {
delete name; //释放原来的内存
}
name = new char[strlen(boy.name) + 1]; //分配新的内存
strcpy_s(name, strlen(boy.name) + 1, boy.name);
this->age = boy.age;
this->salary = boy.salary;
this->darkHorse = boy.darkHorse;
//this->id = boy.id; //根据需求来确定是否要拷贝id
return *this;
}
bool Boy::operator>(const Boy& boy)
{
// 设置比较规则:
// 薪资 * 黑马系数 + (100-年龄)*100
if (power() > boy.power()) {
return true;
}
else {
return false;
}
}
bool Boy::operator<(const Boy& boy)
{
if (power() < boy.power()) {
return true;
}
else {
return false;
}
}
bool Boy::operator==(const Boy& boy)
{
if (power() == boy.power()) {
return true;
}
else {
return false;
}
}
int Boy::operator[](std::string index)
{
if (index == AGE_KEY) {
return age;
}
else if (index == SALARY_KEY) {
return salary;
}
else if (index == DARK_HORSE_KEY) {
return darkHorse;
}
else if (index == POWER_KEY) {
return power();
}
else {
return -1;
}
}
int Boy::operator[](int index)
{
if (index == 0) {
return age;
}
else if (index == 1) {
return salary;
}
else if (index == 2) {
return darkHorse;
}
else if (index == 3) {
return power();
}
else {
return -1;
}
}
//ostream& Boy::operator<<(ostream& os) const
//{
// os << "ID:" << id << "\t姓名:" << name << "\t年龄:" << age << "\t薪资:"
// << salary << "\t黑马系数:" << darkHorse;
// return os;
//}
std::string Boy::description(void)
{
std::stringstream ret;
ret << "ID:" << id << "\t姓名:" << name << "\t年龄:" << age << "\t薪资:"
<< salary << "\t黑马系数:" << darkHorse;
return ret.str();
}
int Boy::power() const
{
// 薪资* 黑马系数 + (100 - 年龄) * 1000
int value = salary * darkHorse + (100 - age) * 100;
return value;
}Main.cpp
#include <iostream>
#include "Boy.h"
using namespace std;
ostream& operator<<(ostream& os, const Boy& boy) {
os << "ID:" << boy.id << "\t姓名:" << boy.name << "\t年龄:" << boy.age << "\t薪资:"
<< boy.salary << "\t黑马系数:" << boy.darkHorse;
return os;
}
istream& operator>>(istream& is, Boy& boy)
{
string name2;
is >> name2 >> boy.age >> boy.salary >> boy.darkHorse;
boy.name = (char*)malloc((name2.length()+1) * sizeof(char));
strcpy_s(boy.name, name2.length() + 1, name2.c_str());
return is;
}
int main(void) {
Boy boy1("Rock", 38, 58000, 5);
Boy boy2("Jack", 25, 50000, 10);
cout << boy1 << endl;
cin >> boy1;
cout << boy1;
system("pause");
return 0;
}重载-普通类型 =>类类型
调用对应的只有一个参数【参数的类型就是这个普通类型】的构造函数
需求: Boy boy1 = 10000; // 薪资 构造函数Boy(int);
Boy boy2 = "Rock" // 姓名 构造函数Boy(char *)
Boy.h
Boy(int salary);
Boy(const char*);Boy.cpp
Boy::Boy(int salary)
{
const char* defaultName = "Unknow";
this->name = new char[strlen(defaultName) + 1];
strcpy_s(this->name, strlen(defaultName) + 1, defaultName);
this->age =0;
this->salary = salary;
this->darkHorse = 0;
this->id = ++LAST_ID;
}
Boy::Boy(const char* name)
{
this->name = new char[strlen(name) + 1];
strcpy_s(this->name, strlen(name) + 1, name);
this->age = 0;
this->salary = 0;
this->darkHorse = 0;
this->id = ++LAST_ID;
}
重载类类型=> 普通类型
调用特殊的运算符重载函数,类型转换函数,不需要写返回类型
类型转换函数:operator 普通类型 ( )
需求:
Boy boy1(“Rock”, 28, 10000, 5); int power = boy1; // power(); char *name = boy1; // “Rock”
Boy.h
#pragma once
#include <string>
#include <iostream>
#define AGE_KEY "age"
#define SALARY_KEY "salary"
#define DARK_HORSE_KEY "darkHorse"
#define POWER_KEY "power"
typedef enum {
AGE,
SALARY,
DARK_HORSE,
POWER
}BOY_KEY_TYPE;
using namespace std;
class Boy
{
public:
Boy(const char* name , int age, int , int darkHorse);
Boy(int salary);
Boy(const char*);
~Boy();
Boy& operator=(const Boy& boy);
bool operator>(const Boy& boy);
bool operator<(const Boy& boy);
bool operator==(const Boy& boy);
// 下标运算符的重载
int operator[](std::string index);
int operator[](int index);
//类型运算符重载 不需要返回类型
operator char* ()const;
operator int()const;
// 该方式不适合
//ostream& operator<<(ostream& os) const;
friend ostream& operator<<(ostream& os, const Boy& boy);
friend istream& operator>>(istream& is, Boy& boy);
std::string description(void);
private:
char* name;
int age;
int salary;
int darkHorse; //黑马值,潜力系数
unsigned int id; // 编号
static int LAST_ID;
int power() const; //综合能力值
};Boy.cpp
#include "boy.h"
#include <string.h>
#include <sstream>
int Boy::LAST_ID = 0; //初始值是0
Boy::Boy(const char* name, int age, int salary, int darkHorse)
{
if (!name) {
name = "未命名";
}
this->name = new char[strlen(name) + 1];
strcpy_s(this->name, strlen(name) + 1, name);
this->age = age;
this->salary = salary;
this->darkHorse = darkHorse;
this->id = ++LAST_ID;
}
Boy::Boy(int salary)
{
const char* defaultName = "Unknow";
this->name = new char[strlen(defaultName) + 1];
strcpy_s(this->name, strlen(defaultName) + 1, defaultName);
this->age =0;
this->salary = salary;
this->darkHorse = 0;
this->id = ++LAST_ID;
}
Boy::Boy(const char* name)
{
this->name = new char[strlen(name) + 1];
strcpy_s(this->name, strlen(name) + 1, name);
this->age = 0;
this->salary = 0;
this->darkHorse = 0;
this->id = ++LAST_ID;
}
Boy::~Boy()
{
if (name) {
delete name;
}
}
Boy& Boy::operator=(const Boy& boy)
{
if (name) {
delete name; //释放原来的内存
}
name = new char[strlen(boy.name) + 1]; //分配新的内存
strcpy_s(name, strlen(boy.name) + 1, boy.name);
this->age = boy.age;
this->salary = boy.salary;
this->darkHorse = boy.darkHorse;
//this->id = boy.id; //根据需求来确定是否要拷贝id
return *this;
}
bool Boy::operator>(const Boy& boy)
{
// 设置比较规则:
// 薪资 * 黑马系数 + (100-年龄)*100
if (power() > boy.power()) {
return true;
}
else {
return false;
}
}
bool Boy::operator<(const Boy& boy)
{
if (power() < boy.power()) {
return true;
}
else {
return false;
}
}
bool Boy::operator==(const Boy& boy)
{
if (power() == boy.power()) {
return true;
}
else {
return false;
}
}
int Boy::operator[](std::string index)
{
if (index == AGE_KEY) {
return age;
}
else if (index == SALARY_KEY) {
return salary;
}
else if (index == DARK_HORSE_KEY) {
return darkHorse;
}
else if (index == POWER_KEY) {
return power();
}
else {
return -1;
}
}
int Boy::operator[](int index)
{
if (index == 0) {
return age;
}
else if (index == 1) {
return salary;
}
else if (index == 2) {
return darkHorse;
}
else if (index == 3) {
return power();
}
else {
return -1;
}
}
Boy::operator char* () const
{
return name;
}
Boy::operator int() const
{
return power();
}
//ostream& Boy::operator<<(ostream& os) const
//{
// os << "ID:" << id << "\t姓名:" << name << "\t年龄:" << age << "\t薪资:"
// << salary << "\t黑马系数:" << darkHorse;
// return os;
//}
std::string Boy::description(void)
{
std::stringstream ret;
ret << "ID:" << id << "\t姓名:" << name << "\t年龄:" << age << "\t薪资:"
<< salary << "\t黑马系数:" << darkHorse;
return ret.str();
}
int Boy::power() const
{
// 薪资* 黑马系数 + (100 - 年龄) * 1000
int value = salary * darkHorse + (100 - age) * 100;
return value;
}main.cpp
#include <iostream>
#include "Boy.h"
using namespace std;
ostream& operator<<(ostream& os, const Boy& boy) {
os << "ID:" << boy.id << "\t姓名:" << boy.name << "\t年龄:" << boy.age << "\t薪资:"
<< boy.salary << "\t黑马系数:" << boy.darkHorse;
return os;
}
istream& operator>>(istream& is, Boy& boy)
{
string name2;
is >> name2 >> boy.age >> boy.salary >> boy.darkHorse;
boy.name = (char*)malloc((name2.length() + 1) * sizeof(char));
strcpy_s(boy.name, name2.length() + 1, name2.c_str());
return is;
}
int main(void) {
Boy boy1("Rock", 38, 58000, 5);
int power = boy1;
char* name = boy1;
system("pause");
return 0;
}类类型之间的转换 类类型A=> 类类型B
调用对应的只有一个参数【参数的类型就是类类型A】的构造函数
也可以使用类型转换函数,但是使用对应的构造函数更合适
实例:
把Boy类型,转换为Man类型
Boy.h
#pragma once
#include <string>
#include <iostream>
#include <ostream>
#include <istream>
#include <fstream>
#define AGE_KEY "age"
#define SALARY_KEY "salary"
#define DARK_HORSE_KEY "darkHorse"
#define POWER_KEY "power"
typedef enum {
AGE,
SALARY,
DARK_HORSE,
POWER
}BOY_KEY_TYPE;
using namespace std;
class Man;
class Boy
{
public:
Boy(const char* name , int age, int , int darkHorse);
Boy(int salary);
Boy(const char*);
~Boy();
char* getname()const;
Boy& operator=(const Boy& boy);
bool operator>(const Boy& boy);
bool operator<(const Boy& boy);
bool operator==(const Boy& boy);
// 下标运算符的重载
int operator[](std::string index)const;
int operator[](int index)const;
//类型运算符重载 不需要返回类型
operator char* ()const;
operator int()const;
// 该方式不适合
//ostream& operator<<(ostream& os) const;
friend ostream& operator<<(ostream& os, const Boy& boy);
friend istream& operator>>(istream& is, Boy& boy);
std::string description(void);
private:
char* name;
int age;
int salary;
int darkHorse; //黑马值,潜力系数
unsigned int id; // 编号
static int LAST_ID;
int power() const; //综合能力值
};
//istream& operator>>(istream& is, Boy& boy);
//ostream& operator<<(ostream& os, const Boy& boy);Boy.cpp
#include "Boy.h"
#include <string.h>
#include <sstream>
int Boy::LAST_ID = 0; //初始值是0
ostream& operator<<(ostream& os, const Boy& boy) {
os << "ID:" << boy.id << "\t姓名:" << boy.name << "\t年龄:" << boy.age << "\t薪资:"
<< boy.salary << "\t黑马系数:" << boy.darkHorse;
return os;
}
istream& operator>>(istream& is, Boy& boy)
{
string name2;
is >> name2 >> boy.age >> boy.salary >> boy.darkHorse;
boy.name = (char*)malloc((name2.length() + 1) * sizeof(char));
strcpy_s(boy.name, name2.length() + 1, name2.c_str());
return is;
}
Boy::Boy(const char* name, int age, int salary, int darkHorse)
{
if (!name) {
name = "未命名";
}
this->name = new char[strlen(name) + 1];
strcpy_s(this->name, strlen(name) + 1, name);
this->age = age;
this->salary = salary;
this->darkHorse = darkHorse;
this->id = ++LAST_ID;
}
Boy::Boy(int salary)
{
const char* defaultName = "Unknow";
this->name = new char[strlen(defaultName) + 1];
strcpy_s(this->name, strlen(defaultName) + 1, defaultName);
this->age =0;
this->salary = salary;
this->darkHorse = 0;
this->id = ++LAST_ID;
}
Boy::Boy(const char* name)
{
this->name = new char[strlen(name) + 1];
strcpy_s(this->name, strlen(name) + 1, name);
this->age = 0;
this->salary = 0;
this->darkHorse = 0;
this->id = ++LAST_ID;
}
Boy::~Boy()
{
if (name) {
delete name;
}
}
char* Boy::getname() const
{
return name;
}
Boy& Boy::operator=(const Boy& boy)
{
if (name) {
delete name; //释放原来的内存
}
name = new char[strlen(boy.name) + 1]; //分配新的内存
strcpy_s(name, strlen(boy.name) + 1, boy.name);
this->age = boy.age;
this->salary = boy.salary;
this->darkHorse = boy.darkHorse;
//this->id = boy.id; //根据需求来确定是否要拷贝id
return *this;
}
bool Boy::operator>(const Boy& boy)
{
// 设置比较规则:
// 薪资 * 黑马系数 + (100-年龄)*100
if (power() > boy.power()) {
return true;
}
else {
return false;
}
}
bool Boy::operator<(const Boy& boy)
{
if (power() < boy.power()) {
return true;
}
else {
return false;
}
}
bool Boy::operator==(const Boy& boy)
{
if (power() == boy.power()) {
return true;
}
else {
return false;
}
}
int Boy::operator[](std::string index)const
{
if (index == AGE_KEY) {
return age;
}
else if (index == SALARY_KEY) {
return salary;
}
else if (index == DARK_HORSE_KEY) {
return darkHorse;
}
else if (index == POWER_KEY) {
return power();
}
else {
return -1;
}
}
int Boy::operator[](int index)const
{
if (index == 0) {
return age;
}
else if (index == 1) {
return salary;
}
else if (index == 2) {
return darkHorse;
}
else if (index == 3) {
return power();
}
else {
return -1;
}
}
Boy::operator char* () const
{
return name;
}
Boy::operator int() const
{
return power();
}
//ostream& Boy::operator<<(ostream& os) const
//{
// os << "ID:" << id << "\t姓名:" << name << "\t年龄:" << age << "\t薪资:"
// << salary << "\t黑马系数:" << darkHorse;
// return os;
//}
std::string Boy::description(void)
{
std::stringstream ret;
ret << "ID:" << id << "\t姓名:" << name << "\t年龄:" << age << "\t薪资:"
<< salary << "\t黑马系数:" << darkHorse;
return ret.str();
}
int Boy::power() const
{
// 薪资* 黑马系数 + (100 - 年龄) * 1000
int value = salary * darkHorse + (100 - age) * 100;
return value;
}Man.h
#pragma once
#include <iostream>
#include <ostream>
#include <istream>
#include <fstream>
class Boy;
using namespace std;
class Man
{
public:
Man(const char* name, int age, int salary);
Man(const Boy& boy);
~Man();
friend ostream&operator<<(ostream& os, const Man& man);
friend istream&operator>>(istream& is, Man& man);
private:
int age;
int salary;
char* name;
};
//ostream& operator<<(ostream& os, const Man& man);
//istream& operator<<(istream& is, const Man& man);Man.cpp
#include <iostream>
#include <fstream>
#include <ostream>
#include <istream>
#include "Boy.h"
#include "Man.h"
using namespace std;
Man::Man(const char* name, int age, int salary)
{
if (!name) {
name = "未命名";
}
this->name = new char[strlen(name)+1];
strcpy_s(this->name, strlen(name) + 1, name);
this->age = age;
this->salary = salary;
}
Man::Man(const Boy& boy)
{
int len = strlen((char*)boy) + 1;
this->name = new char[len];
strcpy_s(name, len, (char*)boy);
age = boy[AGE];
salary = boy[SALARY];
}
Man::~Man()
{
delete name;
}
ostream& operator<<(ostream& os, const Man& man)
{
os <<"[男人]"<<"\t姓名:"<< man.name <<"\t年龄:" << man.age << "\t薪资:"
<< man.salary;
return os;
}
istream& operator>>(istream& is, Man& man)
{
// TODO: 在此处插入 return 语句
string name2;
is >> name2 >> man.salary;
man.name = (char*)malloc((name2.length() + 1) * sizeof(char));
strcpy_s(man.name, name2.length() + 1, name2.c_str());
return is;
}
//istream& operator>>(istream& is,const Man& man)
//{
// string name2;
// //is >> name2 >>man.salary ;
// is >> name2 >> man.salary;
// man.name = (char*)malloc((name2.length() + 1) * sizeof(char));
// strcpy_s(man.name, name2.length() + 1, name2.c_str());
// return is;
//}
Main.cpp
#include <iostream>
#include "Boy.h"
#include "Man.h"
using namespace std;
int main(void) {
Boy boy("Rock", 38, 58000, 5);
Man man = boy;
cout << boy << endl;
cout << man << endl;
system("pause");
return 0;
}注意类型转换中的const const只能调用const方法 (operator函数)
常见错误总结-
const异常导致的BUG
小结:
const对象,只能调用对应的const方法
所以:
类的成员函数,如果已经确定不会修改任何数据成员,
那么,最好把这个成员函数,定义为const函数(在函数体的前面,参数列表的后面添加const)
main.cpp
#include <iostream>
#include "Human.h"
using namespace std;
int main()
{
const Human lucifer("lucifer", 16, 10000);
cout << lucifer[0] << endl;
return 0;
}
Human.cpp
#include "Human.h"
#include <string.h>
Human::Human(const char* name, int age, int salary) {
int len = strlen(name) + 1;
this->name = new char[len];
strcpy_s(this->name, len, name);
this->age = age;
this->salary = salary;
}
Human::~Human()
{
if (name) {
delete name;
}
}
int Human::operator[](std::string index)const
{
/*if (index == NAME) {
}*/
if (index == AGE_KEY) {
return age;
}
else if (index == SALARY_KEY) {
return salary;
}
else {
return -1;
}
return 0;
}
int Human::operator[](int index)
{
if (index == AGE) {
return age;
}
else if(index == SALARY)
{
return salary;
}
else {
return -1;
}
}Human.h
#pragma once
#include <string>
#define AGE_KEY "age"
#define SALARY_KEY "salary"
#define DARK_HORSE_KEY "darkHorse"
#define POWER_KEY "power"
typedef enum {
AGE,
SALARY,
POWER
}BOY_KEY_TYPE;
class Human
{
public:
Human(const char* name, int age,int salary);
~Human();
int operator[](std::string index)const;
int operator[](int index);
private:
char* name;
int age;
int salary;
};
如果此时调用main函数,那么此时的执行结果是
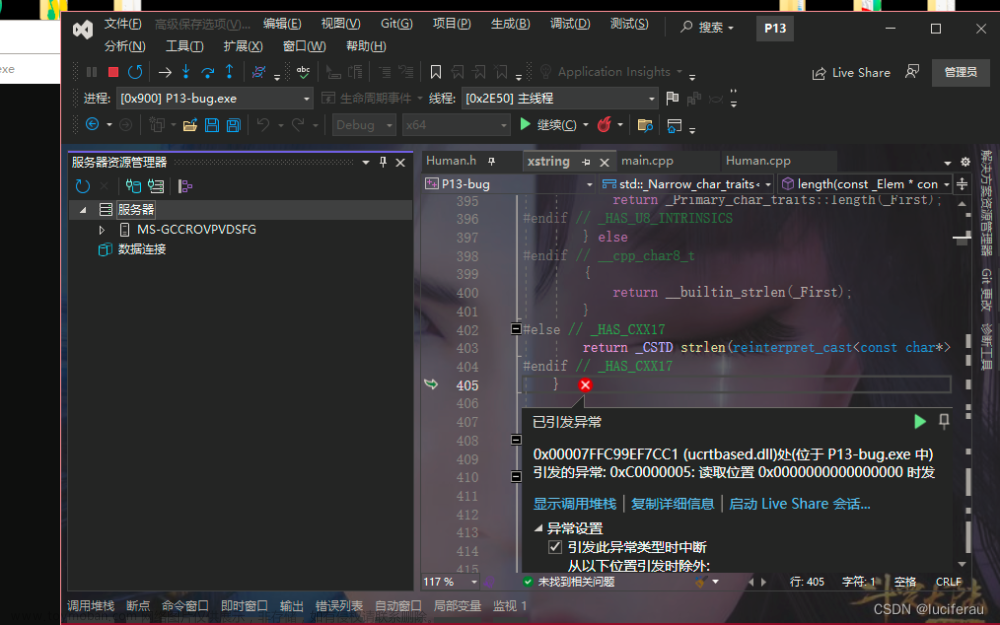
报错原因 const对象只能调用cosnt方法
operator= 的参数问题
赋值运算符的重载,应该使用这种方式:
Boy& operator=(const Boy &boy);
就是:参数要使用引用!
如果定义成:
Boy& operator=(const Boy *boy);
将会没有效果,编译器不会识别为赋值运算符的重载,
也就是:boy2 = boy1时不会调用这个函数
如果定义:
Boy& operator=(const Boy boy);
有效果,但是在调用时,会执行参数的传递:
比如:boy2 = boy1;
就会执行: boy2.operator=(boy1);
就会执行: const Boy boy = boy1;
就会执行: Boy类的赋值构造函数
有两个影响:
1) 浪费性能
2) 如果没有自定义的拷贝构造函数,而且这个类又有指针成员时,就会调用自动生成的拷贝构造函数,导致浅拷贝
如果析构函数中,对这个指针指向的内存做了释放,那就导致数据损坏或崩溃!
小结:
1)赋值·运算符的重载,一定要使用引用参数
2)如果一个类有指针成员,而且使用了动态内存分配,那么一定要定义自己的拷贝构造函数【要使用深拷贝】,避免调用自动生成的拷贝构造函数文章来源:https://www.toymoban.com/news/detail-666999.html
因为自动生成的拷贝构造函数,是浅拷贝!文章来源地址https://www.toymoban.com/news/detail-666999.html
到了这里,关于c++ 友元 运算符重载详解的文章就介绍完了。如果您还想了解更多内容,请在右上角搜索TOY模板网以前的文章或继续浏览下面的相关文章,希望大家以后多多支持TOY模板网!