在使用Spring框架进行Java开发时,对于JavaBean的管理是一个重要而又常见的问题。同时,在JavaBean的管理中,单例模式和原型模式也是必须深入了解的概念。本文将带你全方位探讨Spring框架中JavaBean的管理过程,并深入拓展单例模式和原型模式在JavaBean管理中的应用。
1. Spring框架中JavaBean的管理过程
在Spring框架中,JavaBean的管理主要是通过IOC(Inversion of Control)容器实现的。IOC容器负责创建、管理和注入JavaBean对象,使得开发者能够更加专注于业务逻辑的实现。JavaBean的管理过程包括以下几个步骤:
1.1 #定义Bean
首先,我们需要在配置文件或者通过注解明确定义需要被Spring容器管理的JavaBean。定义Bean时,需要指定Bean的名称、类型、作用域以及其他属性信息。
1.2 Bean的实例化
当Spring容器启动时,会根据配置文件中的定义信息,实例化相应的Bean对象。通过反射机制和工厂模式,Spring容器会根据Bean的定义创建对应的JavaBean实例。
1.3 属性注入
在Bean实例化完成后,Spring容器会根据配置文件中的属性信息,将相应的值注入到Bean中。属性注入可以通过构造函数注入、Setter方法注入或字段注入等方式进行。
1.4 初始化方法
当属性注入完成后,Spring容器会调用Bean的初始化方法(如果有定义的话)。初始化方法可以由开发者自定义,在配置文件或注解中进行指定。在这个阶段,我们可以对Bean做一些额外的初始化操作,例如数据加载、资源分配等。
1.5 Bean的使用和引用
初始化完毕后,Bean就可以被其他对象引用和使用了。在应用程序运行过程中,我们可以随时通过Spring容器获取已经初始化的Bean,并调用其方法进行业务处理。
1.6 销毁方法
当应用程序关闭或者不再需要某个Bean时,Spring容器会调用Bean的销毁方法进行清理工作。开发者可以在配置文件或注解中指定销毁方法,以执行一些资源释放、连接关闭等操作。
2. 单例模式与原型模式在JavaBean管理中的应用
除了JavaBean的管理过程外,单例模式和原型模式也是在JavaBean管理中常见的设计模式。它们分别用于控制JavaBean对象的创建方式和作用域。
1.在Spring管理JavaBean的过程中,每个Bean都有一个生命周期,包括以下几个阶段:

2.1 单例模式与多列模式
1.单例模式保证一个类只有一个实例,并且提供一个全局访问点。在Spring框架中,单例模式广泛应用于Bean的管理中,默认情况下,Spring容器会将所有的Bean都注册为单例对象。这意味着每次从容器中获取Bean时,都会返回同一个实例。
1.在Spring中,bean可以被定义为两种模式:prototype(多例)和singleton(单例)
singleton(单例):只有一个共享的实例存在,所有对这个bean的请求都会返回这个唯一的实例。单例的优点在于可以节约内存,弊端在于会有变量污染。
prototype(多例):对这个bean的每次请求都会创建一个新的bean实例,类似于new。多例的优劣则与单例相反,不会有变量污染,但却非常消耗内存。
代码论证
ParamAction
package com.zking.beanlife;
import java.util.List;
public class ParamAction {
private int age;
private String name;
private List<String> hobby;
private int num = 1;
// private UserBiz userBiz = new UserBizImpl1();
public ParamAction() {
super();
}
public ParamAction(int age, String name, List<String> hobby) {
super();
this.age = age;
this.name = name;
this.hobby = hobby;
}
public void execute() {
// userBiz.upload();
// userBiz = new UserBizImpl2();
System.out.println("this.num=" + this.num++);
System.out.println(this.name);
System.out.println(this.age);
System.out.println(this.hobby);
}
}
demo
package com.zking.beanlife;
import org.junit.Test;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.BeanFactory;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.xml.XmlBeanFactory;
import org.springframework.context.ApplicationContext;
import org.springframework.context.support.ClassPathXmlApplicationContext;
import org.springframework.core.io.ClassPathResource;
import org.springframework.core.io.Resource;
/*
* spring bean的生命週期
* spring bean的單例多例
*/
public class Demo2 {
// 体现单例与多例的区别
@Test
public void test1() {
ClassPathXmlApplicationContext applicationContext = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("/sping-context.xml");
// ApplicationContext applicationContext = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("/spring-context.xml");
ParamAction p1 = (ParamAction) applicationContext.getBean("paramAction");
ParamAction p2 = (ParamAction) applicationContext.getBean("paramAction");
// System.out.println(p1==p2);
p1.execute();
p2.execute();
// 单例时,容器销毁instanceFactory对象也销毁;多例时,容器销毁对象不一定销毁;
applicationContext.close();
}
// 体现单例与多例的初始化的时间点 instanceFactory
@Test
public void test2() {
ApplicationContext applicationContext = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("/sping-context.xml");
}
// BeanFactory会初始化bean对象,但会根据不同的实现子类采取不同的初始化方式
// 默认情况下bean的初始化,单例模式立马会执行,但是此时XmlBeanFactory作为子类,单例模式下容器创建,bean依赖没有初始化,只有要获取使用bean对象才进行初始化
@Test
public void test3() {
// ClassPathXmlApplicationContext applicationContext = new
// ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("/spring-context.xml");
Resource resource = new ClassPathResource("/spring-context.xml");
BeanFactory beanFactory = new XmlBeanFactory(resource);
// InstanceFactory i1 = (InstanceFactory) beanFactory.getBean("instanceFactory");
}
}
spring-context.xml
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"
default-autowire="byType"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd">
<bean class="com.zking.ioc.web.UserAction" id="userAction">
<!-- <property name="userService" ref="userService"></property>-->
<!--<constructor-arg name="uname" value="袁辉sb"></constructor-arg>-->
<!-- <constructor-arg name="age" value="11"></constructor-arg>-->
<!-- <constructor-arg name="hobby" >-->
<!-- <list>-->
<!-- <value>-->
<!-- 农村-->
<!-- </value>-->
<!-- <value>-->
<!-- 农村-->
<!-- </value>-->
<!-- <value>-->
<!-- 农村-->
<!-- </value>-->
<!-- </list>-->
<!-- </constructor-arg>-->
</bean>
<bean class="com.zking.ioc.web.GoodsAction" id="goodsAction">
<!-- <property name="userService" ref="userService"></property>-->
<!-- <property name="gname" value="雨伞"></property>-->
<!-- <property name="age" value="1"></property>-->
<!-- <property name="peoples" >-->
<!-- <list>-->
<!-- <value>男的</value>-->
<!-- <value>女的</value>-->
<!-- </list>-->
<!-- </property>-->
</bean>
<bean class="com.zking.ioc.impl.UserServiceImpl1" id="userService"></bean>
<bean class="com.zking.aop.biz.impl.BookBizImpl" id="bookBiz"></bean>
<bean class="com.zking.aop.advice.MyMethodBeforeAdvice" id="methodBeforeAdvice"></bean>
<bean class="com.zking.aop.advice.MyAfterReturningAdvice" id="myAfterReturningAdvice"></bean>
<bean class="com.zking.aop.advice.MyMethodInterceptor" id="methodInterceptor"></bean>
<bean class="com.zking.aop.advice.MyThrowsAdvice" id="myThrowsAdvice"></bean>
<bean class="org.springframework.aop.support.RegexpMethodPointcutAdvisor" id="methodPointcutAdvisor">
<property name="advice" ref="myAfterReturningAdvice"></property>
<property name="pattern" value=".*buy"></property>
</bean>
<bean class="org.springframework.aop.framework.ProxyFactoryBean" id="bookProxy">
<property name="target" ref="bookBiz"></property>
<property name="proxyInterfaces">
<list>
<value>com.zking.aop.biz.IBookBiz</value>
</list>
</property>
<property name="interceptorNames">
<list>
<value>methodBeforeAdvice</value>
<!-- <value>myAfterReturningAdvice</value>-->
<value>methodPointcutAdvisor</value>
<value>methodInterceptor</value>
<value>myThrowsAdvice</value>
</list>
</property>
</bean>
<bean class="com.zking.beanlife.ParamAction" id="paramAction" scope="prototype">
<constructor-arg name="name" value="三丰"></constructor-arg>
<constructor-arg name="age" value="21"></constructor-arg>
<constructor-arg name="hobby">
<list>
<value>抽烟</value>
<value>烫头</value>
<value>大保健</value>
</list>
</constructor-arg>
</bean>
<bean id="instanceFactory" class="com.zking.beanlife.InstanceFactory"
scope="singleton" init-method="init" destroy-method="destroy"></bean>
</beans>

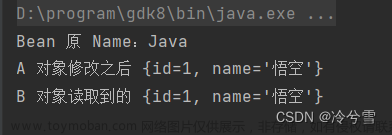
在单列模式下可以看到变量已经被污染从一变为2
然后我们吧spring-context.xml
文件变为多列
然后可以看到污染已经消失
2.在单例模式中,JavaBean是跟着spring上下文初始化的:
package com.zking.beanlife;
public class InstanceFactory {
public void init() {
System.out.println("初始化方法");
}
public void destroy() {
System.out.println("销毁方法");
}
public void service() {
System.out.println("业务方法");
}
}
 文章来源:https://www.toymoban.com/news/detail-667467.html
文章来源:https://www.toymoban.com/news/detail-667467.html
4.我们使用单例一定会初始化JavaBean吗
BeanFactory会初始化bean对象,但会根据不同的实现子类采取不同的初始化方式,默认情况下bean的初始化,单例模式立马会执行,但是此时XmlBeanFactory作为子类,单例模式下容器创建,bean依赖没有初始化,只有要获取使用bean对象才进行初始化。文章来源地址https://www.toymoban.com/news/detail-667467.html
到了这里,关于Spring框架中JavaBean的生命周期及单例模式与多列模式的文章就介绍完了。如果您还想了解更多内容,请在右上角搜索TOY模板网以前的文章或继续浏览下面的相关文章,希望大家以后多多支持TOY模板网!