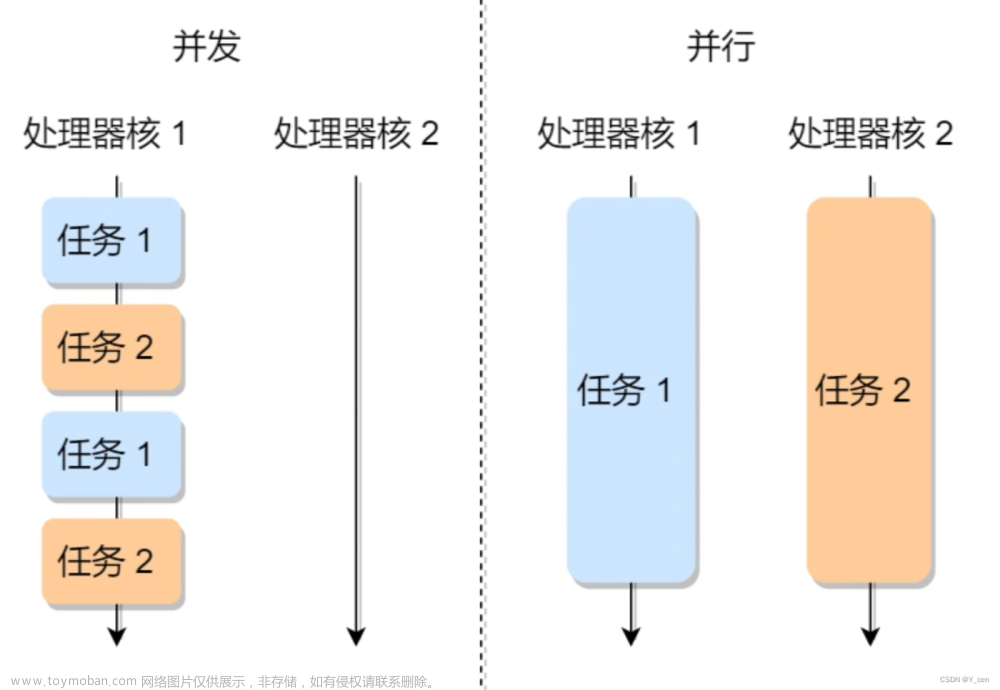
一、程序提速的方法

二、python对并发编程的支持
- 多线程:threading,利用CPU和IO可以同时执行的原理,让CPU不会干巴巴等待IO完成;
- 多进程:multiprocess,利用多核CPU的能力,真正的并行执行任务;
- 异步IO:asyncio,当线程比较多时,切换线程也会占用CPU资源,可在单线程中利用CPU和IO同时执行的原理,实现函数异步执行;
- 使用Lock对资源加锁,防止冲突访问;
- 使用Queue实现不同线程/进程之间的数据通信,实现生产者-消费者模式;
- 使用线程池Pool/进程池Pool,简化线程/进程的任务提交,等待结果、获取结果;
- 使用subprocess启动外部程序的进程,并进行输入输出交互;
python子进程的启动方法:fork与spawn,参考子进程启动方式
三、python并发编程的三种方式
3.1 3种方式的区别和选择
多线程Thread,多进程Process,多协程Coroutine。

3.2 GIL

四、实战
4.1 多线程

4.1.1 多线程网页爬虫示例代码
- blog_spider.py
import requests
from bs4 import BeautifulSoup
urls = [
f"https://www.cnblogs.com/sitehome/p/{page}"
for page in range(1, 50 + 1)
]
def craw(url):
#print("craw url: ", url)
r = requests.get(url)
return r.text
def parse(html):
# class="post-item-title"
soup = BeautifulSoup(html, "html.parser")
links = soup.find_all("a", class_="post-item-title")
return [(link["href"], link.get_text()) for link in links]
if __name__ == "__main__":
for result in parse(craw(urls[2])):
print(result)
- producer_consumer_spider.py
import queue
import blog_spider
import time
import random
import threading
# 生产者
def do_craw(url_queue: queue.Queue, html_queue: queue.Queue):
while True:
url = url_queue.get()
html = blog_spider.craw(url)
html_queue.put(html)
print(threading.current_thread().name, f"craw {url}",
"url_queue.size=", url_queue.qsize())
time.sleep(random.randint(1, 2))
# 消费者
def do_parse(html_queue: queue.Queue, fout):
while True:
html = html_queue.get()
results = blog_spider.parse(html)
for result in results:
fout.write(str(result) + "\n")
print(threading.current_thread().name, f"results.size", len(results),
"html_queue.size=", html_queue.qsize())
time.sleep(random.randint(1, 2))
if __name__ == "__main__":
url_queue = queue.Queue()
html_queue = queue.Queue()
for url in blog_spider.urls:
url_queue.put(url)
#创建生产者线程
for idx in range(3):
t = threading.Thread(target=do_craw, args=(url_queue, html_queue),
name=f"craw{idx}")
t.start()
fout = open("02.data.txt", "w")
# 创建消费者线程
for idx in range(2):
t = threading.Thread(target=do_parse, args=(html_queue, fout),
name=f"parse{idx}")
t.start()
4.1.2 线程安全问题
线程安全指某个函数在多线程环境中被调用时,能够正确的处理多个线程之间的共享变量,使程序功能正确完成。由于线程的执行随时会发生切换,就造成了不可预料的结果,出现线程不安全。
使用Lock解决线程安全:
import threading
import time
lock = threading.Lock()
class Account:
def __init__(self, balance):
self.balance = balance
def draw(account, amount):
with lock:
if account.balance >= amount:
time.sleep(0.1)
print(threading.current_thread().name,
"取钱成功")
account.balance -= amount
print(threading.current_thread().name,
"余额", account.balance)
else:
print(threading.current_thread().name,
"取钱失败,余额不足")
if __name__ == "__main__":
account = Account(1000)
ta = threading.Thread(name="ta", target=draw, args=(account, 800))
tb = threading.Thread(name="tb", target=draw, args=(account, 800))
ta.start()
tb.start()
4.2 多进程

python 线程池实线原理文章来源:https://www.toymoban.com/news/detail-669014.html
4.3 异步IO(协程)

使用协程的时候,要确保使用的库要支持协程,比如requests库不支持协程,可使用aiohttp.文章来源地址https://www.toymoban.com/news/detail-669014.html
import asyncio
import aiohttp
import blog_spider
# 信号量控制协程的并发度
semaphore = asyncio.Semaphore(10)
async def async_craw(url):
async with semaphore:
print("craw url: ", url)
async with aiohttp.ClientSession() as session:
async with session.get(url) as resp:
result = await resp.text()
await asyncio.sleep(5)
print(f"craw url: {url}, {len(result)}")
# 创建时间循环
loop = asyncio.get_event_loop()
tasks = [
loop.create_task(async_craw(url))
for url in blog_spider.urls]
import time
start = time.time()
loop.run_until_complete(asyncio.wait(tasks))
end = time.time()
print("use time seconds: ", end - start)
到了这里,关于python并发编程的文章就介绍完了。如果您还想了解更多内容,请在右上角搜索TOY模板网以前的文章或继续浏览下面的相关文章,希望大家以后多多支持TOY模板网!