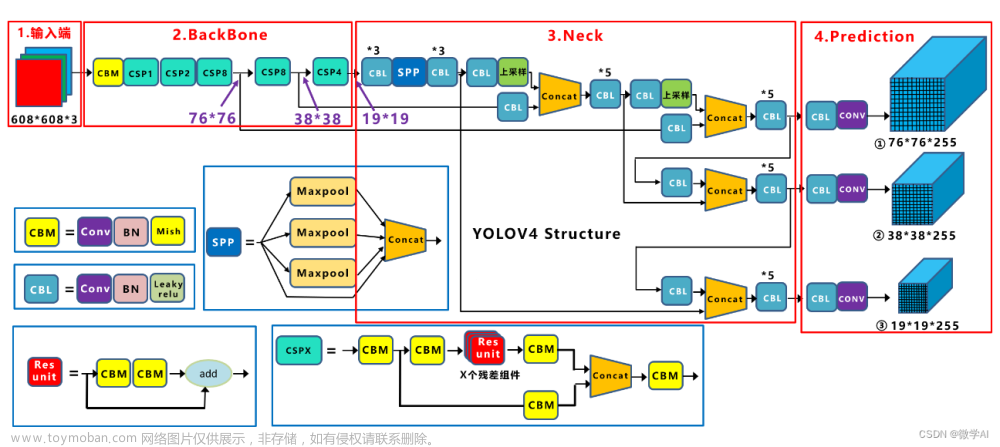
自我记录:代码是根据自己的项目需求,进行了修改,主要是需要检测的图片非常大,目标小,所以对图片进行了分割再检测。下载完配置好环境之后可以直接跑。
我的环境是:windows+vs2019+openvino2022.2+opencv4.5.5+cmake3.14.0
步骤:
1、下载openvino,我用的版本是2022.2
官网网址:https://docs.openvino.ai/latest/index.html



就是这个链接:https://www.intel.com/content/www/us/en/developer/tools/openvino-toolkit/download.html

解压之前记得给电脑设置一下,启动长路径,很简单,教程在这儿:https://blog.csdn.net/weixin_46356818/article/details/121029550
解压后,配置电脑系统变量,下面是我的:

下面是代码:
h文件
#pragma once
#include <opencv2/dnn.hpp>
#include <openvino/openvino.hpp>
#include <opencv2/opencv.hpp>
using namespace std;
class YOLO_OPENVINO
{
public:
YOLO_OPENVINO();
~YOLO_OPENVINO();
public:
struct Detection
{
int class_id;
float confidence;
cv::Rect box;
};
struct Resize
{
cv::Mat resized_image;
int dw;
int dh;
};
Resize resize_and_pad(cv::Mat& img, cv::Size new_shape);
void yolov5_compiled(std::string xml_path, ov::CompiledModel &compiled_model);
void yolov5_detector(ov::CompiledModel compiled_model, cv::Mat input_detect_img, cv::Mat output_detect_img, vector<cv::Rect>& nms_box);
private:
const float SCORE_THRESHOLD = 0.4;
const float NMS_THRESHOLD = 0.4;
const float CONFIDENCE_THRESHOLD = 0.4;
vector<cv::Mat>images;//图像容器
vector<cv::Rect> boxes;
vector<int> class_ids;
vector<float> confidences;
vector<cv::Rect>output_box;
Resize resize;
};
cpp文件
#include"yolo_openvino.h"
YOLO_OPENVINO::YOLO_OPENVINO()
{
}
YOLO_OPENVINO::~YOLO_OPENVINO()
{
}
YOLO_OPENVINO::Resize YOLO_OPENVINO::resize_and_pad(cv::Mat& img, cv::Size new_shape)
{
float width = img.cols;
float height = img.rows;
float r = float(new_shape.width / max(width, height));
int new_unpadW = int(round(width * r));
int new_unpadH = int(round(height * r));
cv::resize(img, resize.resized_image, cv::Size(new_unpadW, new_unpadH), 0, 0, cv::INTER_AREA);
resize.dw = new_shape.width - new_unpadW;//w方向padding值
resize.dh = new_shape.height - new_unpadH;//h方向padding值
cv::Scalar color = cv::Scalar(100, 100, 100);
cv::copyMakeBorder(resize.resized_image, resize.resized_image, 0, resize.dh, 0, resize.dw, cv::BORDER_CONSTANT, color);
return resize;
}
void YOLO_OPENVINO::yolov5_compiled(std::string xml_path, ov::CompiledModel& compiled_model)
{
// Step 1. Initialize OpenVINO Runtime core
ov::Core core;
// Step 2. Read a model
//std::shared_ptr<ov::Model> model = core.read_model("best.xml");
std::shared_ptr<ov::Model> model = core.read_model(xml_path);
// Step 4. Inizialize Preprocessing for the model 初始化模型的预处理
ov::preprocess::PrePostProcessor ppp = ov::preprocess::PrePostProcessor(model);
// Specify input image format 指定输入图像格式
ppp.input().tensor().set_element_type(ov::element::u8).set_layout("NHWC").set_color_format(ov::preprocess::ColorFormat::BGR);
// Specify preprocess pipeline to input image without resizing 指定输入图像的预处理管道而不调整大小
ppp.input().preprocess().convert_element_type(ov::element::f32).convert_color(ov::preprocess::ColorFormat::RGB).scale({ 255., 255., 255. });
// Specify model's input layout 指定模型的输入布局
ppp.input().model().set_layout("NCHW");
// Specify output results format 指定输出结果格式
ppp.output().tensor().set_element_type(ov::element::f32);
// Embed above steps in the graph 在图形中嵌入以上步骤
model = ppp.build();
compiled_model = core.compile_model(model, "CPU");
}
void YOLO_OPENVINO::yolov5_detector(ov::CompiledModel compiled_model, cv::Mat input_detect_img, cv::Mat output_detect_img, vector<cv::Rect>& nms_box)
{
// Step 3. Read input image
cv::Mat img = input_detect_img.clone();
int img_height = img.rows;
int img_width = img.cols;
if (img_height < 5000 && img_width < 5000)
{
images.push_back(img);
}
else
{
images.push_back(img(cv::Range(0, 0.6 * img_height), cv::Range(0, 0.6 * img_width)));
images.push_back(img(cv::Range(0, 0.6 * img_height), cv::Range(0.4 * img_width, img_width)));
images.push_back(img(cv::Range(0.4 * img_height, img_height), cv::Range(0, 0.6 * img_width)));
images.push_back(img(cv::Range(0.4 * img_height, img_height), cv::Range(0.4 * img_width, img_width)));
}
for (int m = 0; m < images.size(); m++)
{
// resize image
Resize res = resize_and_pad(images[m], cv::Size(1280, 1280));
// Step 5. Create tensor from image
float* input_data = (float*)res.resized_image.data;//缩放后图像数据
ov::Tensor input_tensor = ov::Tensor(compiled_model.input().get_element_type(), compiled_model.input().get_shape(), input_data);
// Step 6. Create an infer request for model inference
ov::InferRequest infer_request = compiled_model.create_infer_request();
infer_request.set_input_tensor(input_tensor);
infer_request.infer();
//Step 7. Retrieve inference results
const ov::Tensor& output_tensor = infer_request.get_output_tensor();
ov::Shape output_shape = output_tensor.get_shape();
float* detections = output_tensor.data<float>();
for (int i = 0; i < output_shape[1]; i++)//遍历所有框
{
float* detection = &detections[i * output_shape[2]];//bbox(x y w h obj cls)
float confidence = detection[4];//当前bbox的obj
if (confidence >= CONFIDENCE_THRESHOLD) //判断是否为前景
{
float* classes_scores = &detection[5];
cv::Mat scores(1, output_shape[2] - 5, CV_32FC1, classes_scores);
cv::Point class_id;
double max_class_score;
cv::minMaxLoc(scores, 0, &max_class_score, 0, &class_id);//返回最大得分和最大类别
if (max_class_score > SCORE_THRESHOLD)//满足得分
{
confidences.push_back(confidence);
class_ids.push_back(class_id.x);
float x = detection[0];//框中心x
float y = detection[1];//框中心y
float w = detection[2];//49
float h = detection[3];//50
float rx = (float)images[m].cols / (float)(res.resized_image.cols - res.dw);//x方向映射比例
float ry = (float)images[m].rows / (float)(res.resized_image.rows - res.dh);//y方向映射比例
x = rx * x;
y = ry * y;
w = rx * w;
h = ry * h;
if (m == 0)
{
x = x;
y = y;
}
else if (m == 1)
{
x = x + 0.4 * img_width;
y = y;
}
else if (m == 2)
{
x = x;
y = y + 0.4 * img_height;
}
else if (m == 3)
{
x = x + 0.4 * img_width;
y = y + 0.4 * img_height;
}
float xmin = x - (w / 2);//bbox左上角x
float ymin = y - (h / 2);//bbox左上角y
boxes.push_back(cv::Rect(xmin, ymin, w, h));
}
}
}
}
std::vector<int> nms_result;
cv::dnn::NMSBoxes(boxes, confidences, SCORE_THRESHOLD, NMS_THRESHOLD, nms_result);
std::vector<Detection> output;
for (int i = 0; i < nms_result.size(); i++)
{
Detection result;
int idx = nms_result[i];
result.class_id = class_ids[idx];
result.confidence = confidences[idx];
result.box = boxes[idx];
nms_box.push_back(result.box);//传给Qt NMS后的box
output.push_back(result);
}
// Step 9. Print results and save Figure with detections
for (int i = 0; i < output.size(); i++)
{
auto detection = output[i];
auto box = detection.box;
auto classId = detection.class_id;
auto confidence = detection.confidence;
/*cout << "Bbox" << i + 1 << ": Class: " << classId << " "
<< "Confidence: " << confidence << " Scaled coords: [ "
<< "cx: " << (float)(box.x + (box.width / 2)) / img.cols << ", "
<< "cy: " << (float)(box.y + (box.height / 2)) / img.rows << ", "
<< "w: " << (float)box.width / img.cols << ", "
<< "h: " << (float)box.height / img.rows << " ]" << endl;*/
float xmax = box.x + box.width;
float ymax = box.y + box.height;
cv::rectangle(img, cv::Point(box.x, box.y), cv::Point(xmax, ymax), cv::Scalar(0, 255, 0), 3);
cv::rectangle(img, cv::Point(box.x, box.y - 20), cv::Point(xmax, box.y), cv::Scalar(0, 255, 0), cv::FILLED);
cv::putText(img, std::to_string(classId), cv::Point(box.x, box.y - 5), cv::FONT_HERSHEY_SIMPLEX, 0.5, cv::Scalar(0, 0, 0));
img.copyTo(output_detect_img);
}
cv::imwrite("./fz.jpg", output_detect_img);
}
main.cpp
#include"yolo_openvino.h"
using namespace std;
YOLO_OPENVINO yolo_openvino;
std::string path = "./best.xml";
ov::CompiledModel model;
cv::Mat input_img, output_img;
vector<cv::Rect>output_box;
int main()
{
input_img = cv::imread("140_0_0.jpg");
yolo_openvino.yolov5_compiled(path, model);
yolo_openvino.yolov5_detector(model, input_img, output_img, output_box);
/* for (int i = 0; i < output_box.size(); i++)
{
cv::rectangle(input_img, cv::Point(output_box[i].x, output_box[i].y), cv::Point(output_box[i].x + output_box[i].width, output_box[i].y + output_box[i].height), cv::Scalar(0, 255, 0), 3);
}
cv::imshow("a", input_img);
cv::waitKey(0)*/;
return 0;
}接下来配置项目的包含目录、库目录、附加依赖项


2、下载cmake3.14.0
这个下完之后解压,然后配置个环境变量就行,不下cmake应该也是可以的。

3、跑代码:
放一个onnx转xml、bin文件的方法,现在可以直接从Yolov5中用export_openvino直接导出,其导出函数定义为:
def export_openvino(model, im, file, prefix=colorstr('OpenVINO:')):
# YOLOv5 OpenVINO export
try:
check_requirements(('openvino-dev',)) # requires openvino-dev: https://pypi.org/project/openvino-dev/
import openvino.inference_engine as ie
LOGGER.info(f'\n{prefix} starting export with openvino {ie.__version__}...')
f = str(file).replace('.pt', '_openvino_model' + os.sep)
cmd = f"mo --input_model {file.with_suffix('.onnx')} --output_dir {f}"
subprocess.check_output(cmd, shell=True)
LOGGER.info(f'{prefix} export success, saved as {f} ({file_size(f):.1f} MB)')
except Exception as e:
LOGGER.info(f'\n{prefix} export failure: {e}')所以只需要在yolov5里面运行下面命令:
“mo --input_model {file.with_suffix('.onnx')} --output_dir {f}”文章来源:https://www.toymoban.com/news/detail-670272.html
///然后代码里的模型路径改成你自己的,就可以跑了。文章来源地址https://www.toymoban.com/news/detail-670272.html
到了这里,关于c++windows+yolov5-6.2+openvino模型部署超详细的文章就介绍完了。如果您还想了解更多内容,请在右上角搜索TOY模板网以前的文章或继续浏览下面的相关文章,希望大家以后多多支持TOY模板网!

![[C#]winform部署yolov8图像分类的openvino格式的模型](https://imgs.yssmx.com/Uploads/2024/01/810561-1.jpeg)