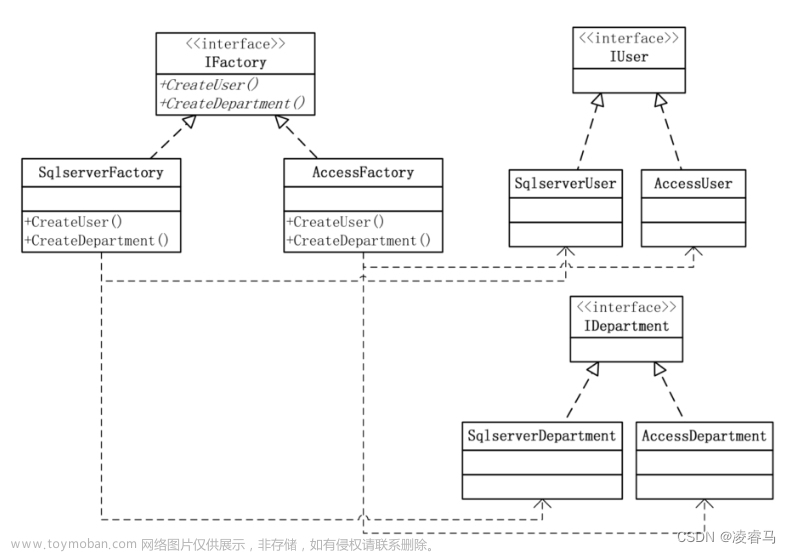
在抽象工厂模式中,接口是负责创建一个相关对象的工厂,不需要显式指定它们的类。每个生成的工厂都能按照工厂模式提供对象。
抽象工厂模式提供了一种创建一系列相关或相互依赖对象的接口,而无需指定具体实现类。通过使用抽象工厂模式,可以将客户端与具体产品的创建过程解耦,使得客户端可以通过工厂接口来创建一族产品。文章来源:https://www.toymoban.com/news/detail-670754.html
意图:提供一个创建一系列相关或相互依赖对象的接口,而无需指定它们具体的类。
主要解决:主要解决接口选择的问题。
何时使用:系统的产品有多于一个的产品族,而系统只消费其中某一族的产品。
如何解决:在一个产品族里面,定义多个产品。文章来源地址https://www.toymoban.com/news/detail-670754.html
public interface Shape {
void draw();
}
public class Circle implements Shape{
@Override
public void draw() {
System.out.println("this is Circle");
}
}
public class Rectangle implements Shape{
@Override
public void draw() {
System.out.println("this is Rectangle");
}
}
public class Square implements Shape {
@Override
public void draw() {
System.out.println("this is Square");
}
}
public interface Color {
void fill();
}
public class Blue implements Color{
@Override
public void fill() {
System.out.println("this is blue");
}
}
public class Green implements Color{
@Override
public void fill() {
System.out.println("this is green");
}
}
public class Red implements Color{
@Override
public void fill() {
System.out.println("this is red");
}
}
public abstract class AbstractFactory {
public abstract Color getColor(String color);
public abstract Shape getShape(String shape);
}
public class ColorFactory extends AbstractFactory{
@Override
public Color getColor(String color) {
if(color == null){
return null;
}
if(color.equalsIgnoreCase("RED")){
return new Red();
} else if(color.equalsIgnoreCase("GREEN")){
return new Green();
} else if(color.equalsIgnoreCase("BLUE")){
return new Blue();
}
return null;
}
@Override
public Shape getShape(String shape) {
return null;
}
}
public class ShapeFactory extends AbstractFactory{
@Override
public Color getColor(String color) {
return null;
}
public Shape getShape(String shapeType){
if (shapeType == null){
return null;
}
if (shapeType.equalsIgnoreCase("CIRCLE")){
return new Circle();
}
if (shapeType.equalsIgnoreCase("RECTANGLE")){
return new Rectangle();
}
if (shapeType.equalsIgnoreCase("SQUARE")){
return new Square();
}
return null;
}
}
public class FactoryProducer {
public static AbstractFactory getFactory(String choice){
if (choice.equalsIgnoreCase("SHAPE")){
return new ShapeFactory();
}else if (choice.equalsIgnoreCase("COLOR")){
return new ColorFactory();
}
return null;
}
}
@Test
public void test7(){
AbstractFactory shapeFactory = FactoryProducer.getFactory("SHAPE");
Shape shape1 = shapeFactory.getShape("CIRCLE");
shape1.draw();
Shape shape2 = shapeFactory.getShape("RECTANGLE");
shape2.draw();
Shape shape3 = shapeFactory.getShape("SQUARE");
shape3.draw();
AbstractFactory colorFactory = FactoryProducer.getFactory("COLOR");
Color color1 = colorFactory.getColor("RED");
color1.fill();
Color color2 = colorFactory.getColor("GREEN");
color2.fill();
Color color3 = colorFactory.getColor("BLUE");
color3.fill();
}
/**
this is Circle
this is Rectangle
this is Square
this is red
this is green
this is blue
**/
工厂模式和抽象工厂模式有什么区别
- 工厂模式是创建单个类型的对象的工厂,而抽象工厂是创建不同但相关或依赖对象的工厂。
- 工厂模式是一个(单个)方法,而抽象工厂模式是一个对象。
- 工厂模式创建一个对象,而抽象工厂创建一系列相关的对象。
到了这里,关于创建型模式-抽象工厂模式的文章就介绍完了。如果您还想了解更多内容,请在右上角搜索TOY模板网以前的文章或继续浏览下面的相关文章,希望大家以后多多支持TOY模板网!