TASK系列解析文章
1.【Apollo学习笔记】——规划模块TASK之LANE_CHANGE_DECIDER
2.【Apollo学习笔记】——规划模块TASK之PATH_REUSE_DECIDER
3.【Apollo学习笔记】——规划模块TASK之PATH_BORROW_DECIDER
4.【Apollo学习笔记】——规划模块TASK之PATH_BOUNDS_DECIDER
5.【Apollo学习笔记】——规划模块TASK之PIECEWISE_JERK_PATH_OPTIMIZER
6.【Apollo学习笔记】——规划模块TASK之PATH_ASSESSMENT_DECIDER
7.【Apollo学习笔记】——规划模块TASK之PATH_DECIDER
8.【Apollo学习笔记】——规划模块TASK之RULE_BASED_STOP_DECIDER
9.【Apollo学习笔记】——规划模块TASK之SPEED_BOUNDS_PRIORI_DECIDER&&SPEED_BOUNDS_FINAL_DECIDER
10.【Apollo学习笔记】——规划模块TASK之SPEED_HEURISTIC_OPTIMIZER
11.【Apollo学习笔记】——规划模块TASK之SPEED_DECIDER
12.【Apollo学习笔记】——规划模块TASK之PIECEWISE_JERK_SPEED_OPTIMIZER
13.【Apollo学习笔记】——规划模块TASK之PIECEWISE_JERK_NONLINEAR_SPEED_OPTIMIZER(一)
14.【Apollo学习笔记】——规划模块TASK之PIECEWISE_JERK_NONLINEAR_SPEED_OPTIMIZER(二)
前言
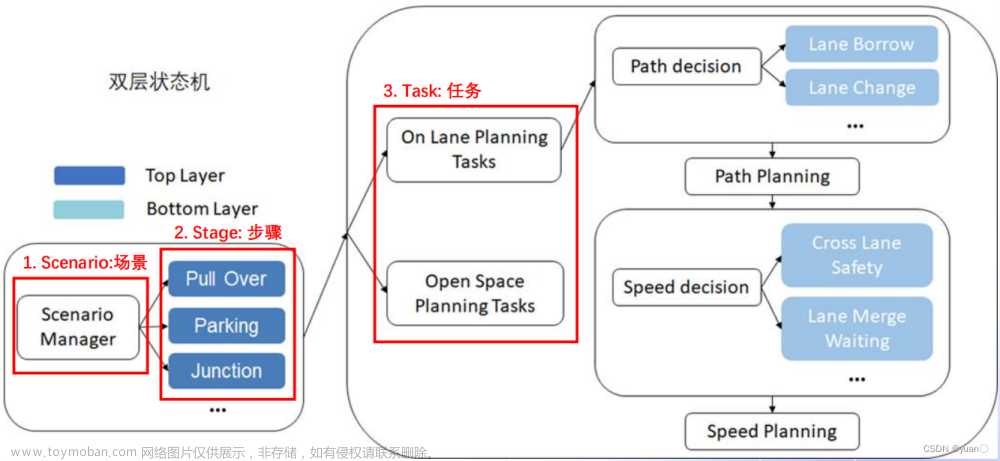
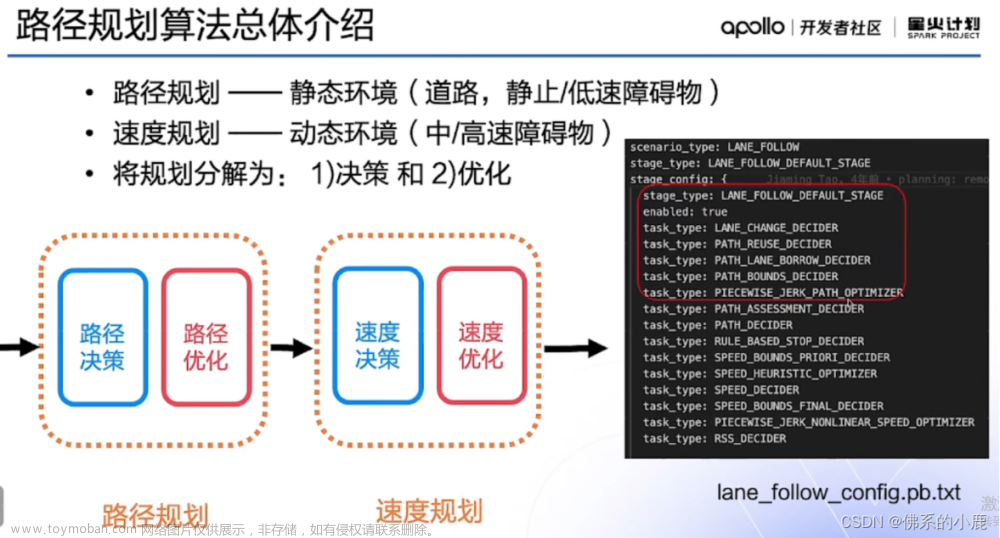
在Apollo星火计划学习笔记——Apollo路径规划算法原理与实践与【Apollo学习笔记】——Planning模块讲到……Stage::Process的PlanOnReferenceLine函数会依次调用task_list中的TASK,本文将会继续以LaneFollow为例依次介绍其中的TASK部分究竟做了哪些工作。由于个人能力所限,文章可能有纰漏的地方,还请批评斧正。
在modules/planning/conf/scenario/lane_follow_config.pb.txt配置文件中,我们可以看到LaneFollow所需要执行的所有task。
stage_config: {
stage_type: LANE_FOLLOW_DEFAULT_STAGE
enabled: true
task_type: LANE_CHANGE_DECIDER
task_type: PATH_REUSE_DECIDER
task_type: PATH_LANE_BORROW_DECIDER
task_type: PATH_BOUNDS_DECIDER
task_type: PIECEWISE_JERK_PATH_OPTIMIZER
task_type: PATH_ASSESSMENT_DECIDER
task_type: PATH_DECIDER
task_type: RULE_BASED_STOP_DECIDER
task_type: SPEED_BOUNDS_PRIORI_DECIDER
task_type: SPEED_HEURISTIC_OPTIMIZER
task_type: SPEED_DECIDER
task_type: SPEED_BOUNDS_FINAL_DECIDER
task_type: PIECEWISE_JERK_SPEED_OPTIMIZER
# task_type: PIECEWISE_JERK_NONLINEAR_SPEED_OPTIMIZER
task_type: RSS_DECIDER
本文将继续介绍LaneFollow的第四个TASK——PATH_BOUNDS_DECIDER
PATH_BOUNDS_DECIDER功能简介
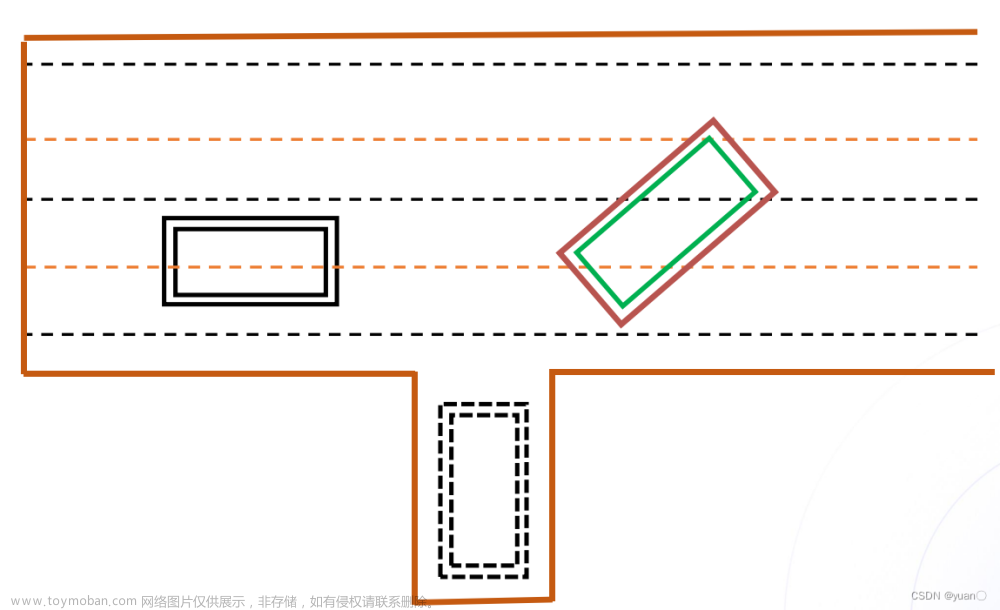
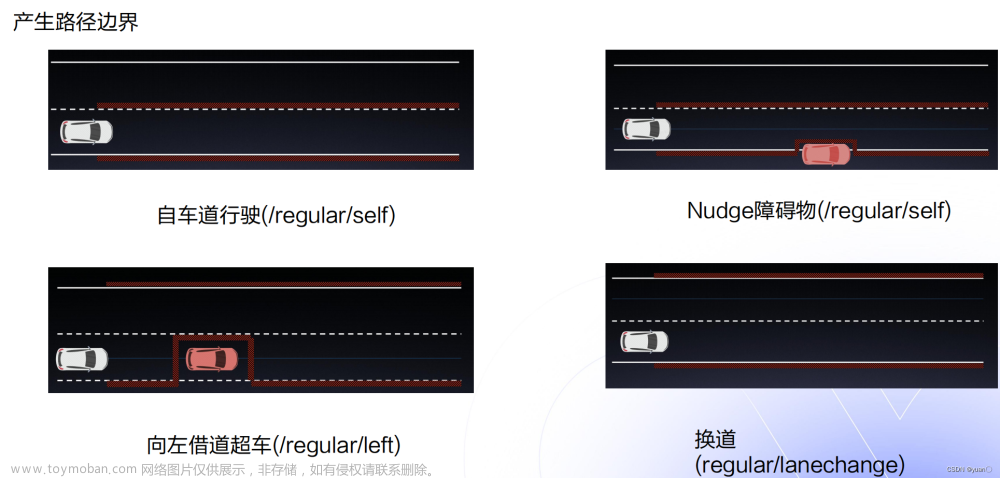 利用前几个决策器,根据相应条件,产生相应的SL边界。这里说明以下Nudge障碍物的概念——主车旁边的障碍物未完全阻挡主车,主车可以通过绕行避过障碍物(注意图中的边界)。
利用前几个决策器,根据相应条件,产生相应的SL边界。这里说明以下Nudge障碍物的概念——主车旁边的障碍物未完全阻挡主车,主车可以通过绕行避过障碍物(注意图中的边界)。
PATH_BOUNDS_DECIDER相关配置
在modules/planning/conf/planning_config.pb.txt中有相关配置。
default_task_config: {
task_type: PATH_BOUNDS_DECIDER
path_bounds_decider_config {
is_lane_borrowing: false
is_pull_over: false
is_extend_lane_bounds_to_include_adc: false
pull_over_destination_to_adc_buffer: 25.0
pull_over_destination_to_pathend_buffer: 4.0
pull_over_road_edge_buffer: 0.15
pull_over_approach_lon_distance_adjust_factor: 1.5
}
}
modules/planning/proto/task_config.proto中也有相关参数
// PathBoundsDeciderConfig
message PathBoundsDeciderConfig {
optional bool is_lane_borrowing = 1;
optional bool is_pull_over = 2;
// not search pull-over position if the destination is within this distance
// from ADC
optional double pull_over_destination_to_adc_buffer = 3 [default = 25.0];
// not search pull-over position if the destination is within this distance to
// path-end
optional double pull_over_destination_to_pathend_buffer = 4 [default = 10.0];
// disquality a pull-over position if the available path boundary's edge is
// not within this distance from the road edge
optional double pull_over_road_edge_buffer = 5 [default = 0.15];
optional double pull_over_approach_lon_distance_adjust_factor = 6
[default = 1.5];
optional double adc_buffer_coeff = 7 [default = 1.0];
optional bool is_extend_lane_bounds_to_include_adc = 8 [default = true];
}
数据结构
// modules/planning/tasks/deciders/path_bounds_decider/path_bounds_decider.cc
namespace {
// PathBoundPoint contains: (s, l_min, l_max).路径边界点
using PathBoundPoint = std::tuple<double, double, double>;
// PathBound contains a vector of PathBoundPoints.路径边界
using PathBound = std::vector<PathBoundPoint>;
// ObstacleEdge contains: (is_start_s, s, l_min, l_max, obstacle_id).障碍物的边
using ObstacleEdge = std::tuple<int, double, double, double, std::string>;
} // namespace
参数设置
// modules/planning/tasks/deciders/path_bounds_decider/path_bounds_decider.h
// s方向的距离
constexpr double kPathBoundsDeciderHorizon = 100.0;
// s方向的间隔
constexpr double kPathBoundsDeciderResolution = 0.5;
// Lane宽度
constexpr double kDefaultLaneWidth = 5.0;
// Road的道路
constexpr double kDefaultRoadWidth = 20.0;
// TODO(all): Update extra tail point base on vehicle speed.
constexpr int kNumExtraTailBoundPoint = 20;
constexpr double kPulloverLonSearchCoeff = 1.5;
constexpr double kPulloverLatSearchCoeff = 1.25;
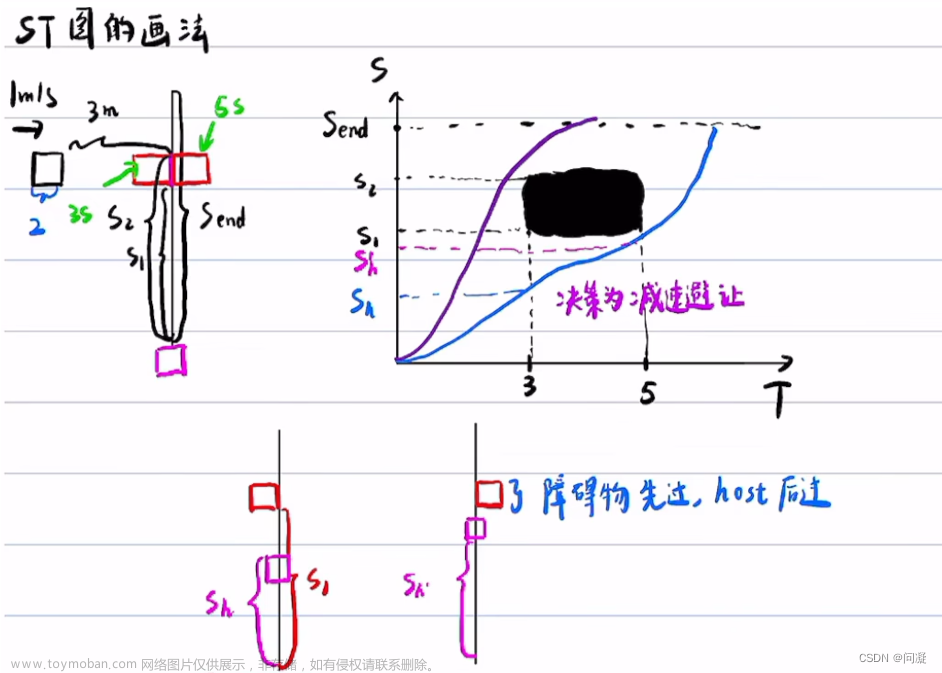
PATH_BOUNDS_DECIDER总体流程
总体流程依然先看Process部分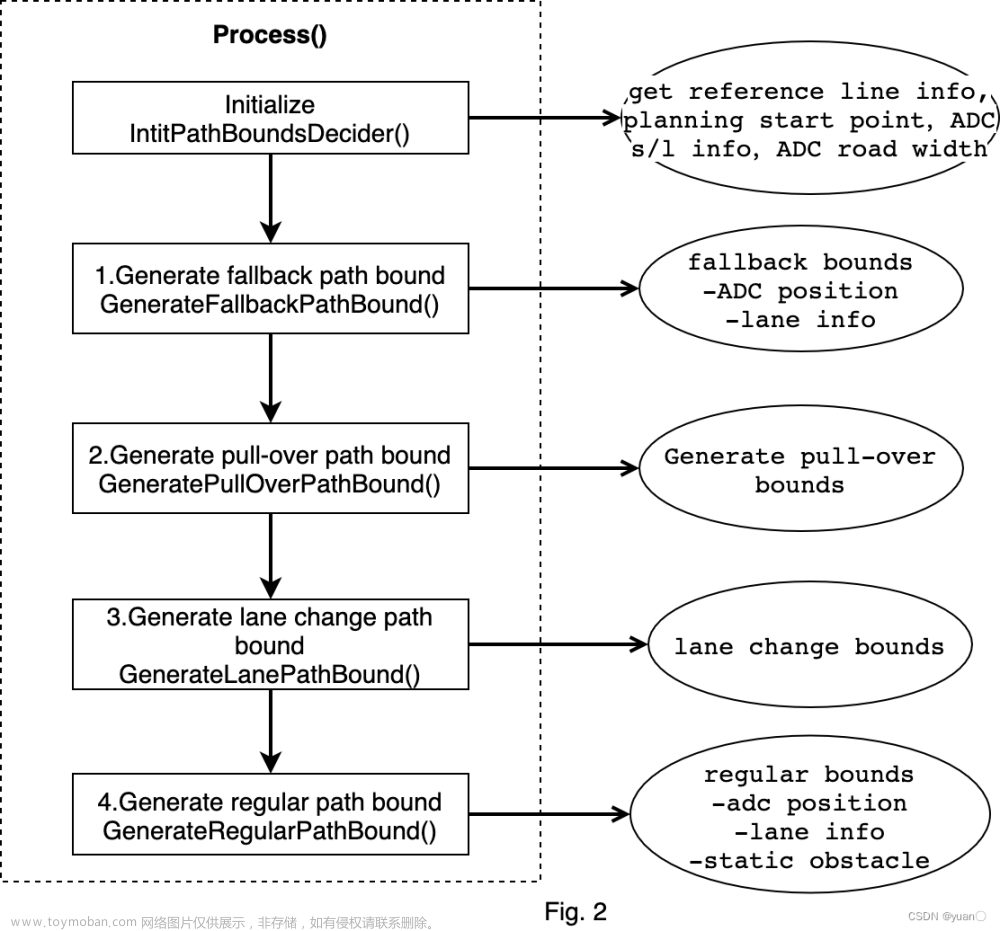
在Process方法中,分四种场景对路径边界进行计算,按照处理的顺序分别是:fallback,pull-over,lane-change,regular。 其中regular场景根据是否借道又分为LEFT_BORROW, NO_BORROW, RIGHT_BORROW。
fallback场景的path bounds一定会生成,另外三种看情况,都是需要if判断。
Status PathBoundsDecider::Process(
Frame* const frame, ReferenceLineInfo* const reference_line_info) {
// Sanity checks.
CHECK_NOTNULL(frame);
CHECK_NOTNULL(reference_line_info);
// 如果道路重用置位,则跳过PathBoundsDecider
// Skip the path boundary decision if reusing the path.
if (FLAGS_enable_skip_path_tasks && reference_line_info->path_reusable()) {
return Status::OK();
}
std::vector<PathBoundary> candidate_path_boundaries;
// const TaskConfig& config = Decider::config_;
// Initialization.
// 用规划起始点自车道的lane width去初始化 path boundary
// 如果无法获取规划起始点的道路宽度,则用默认值目前是5m,来初始化
InitPathBoundsDecider(*frame, *reference_line_info);
// Generate the fallback path boundary.
// 生成fallback_path_bound,无论何种场景都会生成fallback_path_bound
// 生成fallback_path_bound时,会考虑借道场景,向哪个方向借道,对应方向的path_bound会叠加这个方向相邻车道宽度
PathBound fallback_path_bound;
// 生成fallback_path_bound,
// 首先获取当前车道的宽度
// 再根据是否发生借道的决策,获取相邻车道的宽度(包括对向车道以及同向相邻车道);
// 再根据ADC的位置和速度计算边界;
// 最后更新边界。
Status ret =
GenerateFallbackPathBound(*reference_line_info, &fallback_path_bound);
if (!ret.ok()) {
ADEBUG << "Cannot generate a fallback path bound.";
return Status(ErrorCode::PLANNING_ERROR, ret.error_message());
}
if (fallback_path_bound.empty()) {
const std::string msg = "Failed to get a valid fallback path boundary";
AERROR << msg;
return Status(ErrorCode::PLANNING_ERROR, msg);
}
if (!fallback_path_bound.empty()) {
CHECK_LE(adc_frenet_l_, std::get<2>(fallback_path_bound[0]));
CHECK_GE(adc_frenet_l_, std::get<1>(fallback_path_bound[0]));
}
// Update the fallback path boundary into the reference_line_info.
std::vector<std::pair<double, double>> fallback_path_bound_pair;
for (size_t i = 0; i < fallback_path_bound.size(); ++i) {
fallback_path_bound_pair.emplace_back(std::get<1>(fallback_path_bound[i]),
std::get<2>(fallback_path_bound[i]));
}
//生成fallback边界,存入candidate_path_boundaries,并标记为“fallback”
candidate_path_boundaries.emplace_back(std::get<0>(fallback_path_bound[0]),
kPathBoundsDeciderResolution,
fallback_path_bound_pair);
candidate_path_boundaries.back().set_label("fallback");
// 根据场景生成另外一条path_bound
// 依次判断是否处于pull_over、lane_change、regular;当处于其中一个场景,计算对应的path_bound并返回结果;
// 即以上3种场景,只会选一种生成对应的根据场景生成另外一条path_bound
// 判断是否为pull_over_status
// If pull-over is requested, generate pull-over path boundary.
auto* pull_over_status = injector_->planning_context()
->mutable_planning_status()
->mutable_pull_over();
const bool plan_pull_over_path = pull_over_status->plan_pull_over_path();
if (plan_pull_over_path) {
PathBound pull_over_path_bound;
Status ret = GeneratePullOverPathBound(*frame, *reference_line_info,
&pull_over_path_bound);
if (!ret.ok()) {
AWARN << "Cannot generate a pullover path bound, do regular planning.";
} else {
ACHECK(!pull_over_path_bound.empty());
CHECK_LE(adc_frenet_l_, std::get<2>(pull_over_path_bound[0]));
CHECK_GE(adc_frenet_l_, std::get<1>(pull_over_path_bound[0]));
// Update the fallback path boundary into the reference_line_info.
std::vector<std::pair<double, double>> pull_over_path_bound_pair;
for (size_t i = 0; i < pull_over_path_bound.size(); ++i) {
pull_over_path_bound_pair.emplace_back(
std::get<1>(pull_over_path_bound[i]),
std::get<2>(pull_over_path_bound[i]));
}
candidate_path_boundaries.emplace_back(
std::get<0>(pull_over_path_bound[0]), kPathBoundsDeciderResolution,
pull_over_path_bound_pair);
candidate_path_boundaries.back().set_label("regular/pullover");
reference_line_info->SetCandidatePathBoundaries(
std::move(candidate_path_boundaries));
ADEBUG << "Completed pullover and fallback path boundaries generation.";
// set debug info in planning_data
auto* pull_over_debug = reference_line_info->mutable_debug()
->mutable_planning_data()
->mutable_pull_over();
pull_over_debug->mutable_position()->CopyFrom(
pull_over_status->position());
pull_over_debug->set_theta(pull_over_status->theta());
pull_over_debug->set_length_front(pull_over_status->length_front());
pull_over_debug->set_length_back(pull_over_status->length_back());
pull_over_debug->set_width_left(pull_over_status->width_left());
pull_over_debug->set_width_right(pull_over_status->width_right());
return Status::OK();
}
}
// 判断是否满足lane_change场景
// 首先FLAGS_enable_smarter_lane_change 要置位
// 通过判断当前reference_line 是否为目标车道,来进行判断
// If it's a lane-change reference-line, generate lane-change path boundary.
if (FLAGS_enable_smarter_lane_change &&
reference_line_info->IsChangeLanePath()) {
PathBound lanechange_path_bound;
Status ret = GenerateLaneChangePathBound(*reference_line_info,
&lanechange_path_bound);
if (!ret.ok()) {
ADEBUG << "Cannot generate a lane-change path bound.";
return Status(ErrorCode::PLANNING_ERROR, ret.error_message());
}
if (lanechange_path_bound.empty()) {
const std::string msg = "Failed to get a valid fallback path boundary";
AERROR << msg;
return Status(ErrorCode::PLANNING_ERROR, msg);
}
// disable this change when not extending lane bounds to include adc
if (config_.path_bounds_decider_config()
.is_extend_lane_bounds_to_include_adc()) {
CHECK_LE(adc_frenet_l_, std::get<2>(lanechange_path_bound[0]));
CHECK_GE(adc_frenet_l_, std::get<1>(lanechange_path_bound[0]));
}
// Update the fallback path boundary into the reference_line_info.
std::vector<std::pair<double, double>> lanechange_path_bound_pair;
for (size_t i = 0; i < lanechange_path_bound.size(); ++i) {
lanechange_path_bound_pair.emplace_back(
std::get<1>(lanechange_path_bound[i]),
std::get<2>(lanechange_path_bound[i]));
}
candidate_path_boundaries.emplace_back(
std::get<0>(lanechange_path_bound[0]), kPathBoundsDeciderResolution,
lanechange_path_bound_pair);
candidate_path_boundaries.back().set_label("regular/lanechange");
RecordDebugInfo(lanechange_path_bound, "", reference_line_info);
reference_line_info->SetCandidatePathBoundaries(
std::move(candidate_path_boundaries));
ADEBUG << "Completed lanechange and fallback path boundaries generation.";
return Status::OK();
}
// Generate regular path boundaries.
// 生成regular path boundaries
std::vector<LaneBorrowInfo> lane_borrow_info_list;
lane_borrow_info_list.push_back(LaneBorrowInfo::NO_BORROW);
if (reference_line_info->is_path_lane_borrow()) {
const auto& path_decider_status =
injector_->planning_context()->planning_status().path_decider();
for (const auto& lane_borrow_direction :
path_decider_status.decided_side_pass_direction()) {
if (lane_borrow_direction == PathDeciderStatus::LEFT_BORROW) {
lane_borrow_info_list.push_back(LaneBorrowInfo::LEFT_BORROW);
} else if (lane_borrow_direction == PathDeciderStatus::RIGHT_BORROW) {
lane_borrow_info_list.push_back(LaneBorrowInfo::RIGHT_BORROW);
}
}
}
// Try every possible lane-borrow option:
// PathBound regular_self_path_bound;
// bool exist_self_path_bound = false;
for (const auto& lane_borrow_info : lane_borrow_info_list) {
PathBound regular_path_bound;
std::string blocking_obstacle_id = "";
std::string borrow_lane_type = "";
Status ret = GenerateRegularPathBound(
*reference_line_info, lane_borrow_info, ®ular_path_bound,
&blocking_obstacle_id, &borrow_lane_type);
if (!ret.ok()) {
continue;
}
if (regular_path_bound.empty()) {
continue;
}
// disable this change when not extending lane bounds to include adc
if (config_.path_bounds_decider_config()
.is_extend_lane_bounds_to_include_adc()) {
CHECK_LE(adc_frenet_l_, std::get<2>(regular_path_bound[0]));
CHECK_GE(adc_frenet_l_, std::get<1>(regular_path_bound[0]));
}
// Update the path boundary into the reference_line_info.
std::vector<std::pair<double, double>> regular_path_bound_pair;
for (size_t i = 0; i < regular_path_bound.size(); ++i) {
regular_path_bound_pair.emplace_back(std::get<1>(regular_path_bound[i]),
std::get<2>(regular_path_bound[i]));
}
candidate_path_boundaries.emplace_back(std::get<0>(regular_path_bound[0]),
kPathBoundsDeciderResolution,
regular_path_bound_pair);
std::string path_label = "";
switch (lane_borrow_info) {
case LaneBorrowInfo::LEFT_BORROW:
path_label = "left";
break;
case LaneBorrowInfo::RIGHT_BORROW:
path_label = "right";
break;
default:
path_label = "self";
// exist_self_path_bound = true;
// regular_self_path_bound = regular_path_bound;
break;
}
// RecordDebugInfo(regular_path_bound, "", reference_line_info);
candidate_path_boundaries.back().set_label(
absl::StrCat("regular/", path_label, "/", borrow_lane_type));
candidate_path_boundaries.back().set_blocking_obstacle_id(
blocking_obstacle_id);
}
// Remove redundant boundaries.
// RemoveRedundantPathBoundaries(&candidate_path_boundaries);
// Success
reference_line_info->SetCandidatePathBoundaries(
std::move(candidate_path_boundaries));
ADEBUG << "Completed regular and fallback path boundaries generation.";
return Status::OK();
}
InitPathBoundsDecider
InitPathBoundsDecider初始化planning_start_point、获取ADC S/L坐标信息、获取ADC当前所在的车道线宽度。
void PathBoundsDecider::InitPathBoundsDecider(
const Frame& frame, const ReferenceLineInfo& reference_line_info) {
const ReferenceLine& reference_line = reference_line_info.reference_line();
common::TrajectoryPoint planning_start_point = frame.PlanningStartPoint();
if (FLAGS_use_front_axe_center_in_path_planning) {
planning_start_point =
InferFrontAxeCenterFromRearAxeCenter(planning_start_point);
}
ADEBUG << "Plan at the starting point: x = "
<< planning_start_point.path_point().x()
<< ", y = " << planning_start_point.path_point().y()
<< ", and angle = " << planning_start_point.path_point().theta();
// Initialize some private variables.
// ADC s/l info.
auto adc_sl_info = reference_line.ToFrenetFrame(planning_start_point);
adc_frenet_s_ = adc_sl_info.first[0];
adc_frenet_l_ = adc_sl_info.second[0];
adc_frenet_sd_ = adc_sl_info.first[1];
adc_frenet_ld_ = adc_sl_info.second[1] * adc_frenet_sd_;
double offset_to_map = 0.0;
reference_line.GetOffsetToMap(adc_frenet_s_, &offset_to_map);
adc_l_to_lane_center_ = adc_frenet_l_ + offset_to_map;
// ADC's lane width.
double lane_left_width = 0.0;
double lane_right_width = 0.0;
if (!reference_line.GetLaneWidth(adc_frenet_s_, &lane_left_width,
&lane_right_width)) {
AWARN << "Failed to get lane width at planning start point.";
adc_lane_width_ = kDefaultLaneWidth;
} else {
adc_lane_width_ = lane_left_width + lane_right_width;
}
}
1. fallback
无论当前处于何种场景,都会调用GenerateFallbackPathBound() 来生成备用的path bound,在计算FallbackPathBound时不考虑障碍物边界,仅使用道路边界,并考虑借道信息来进行计算。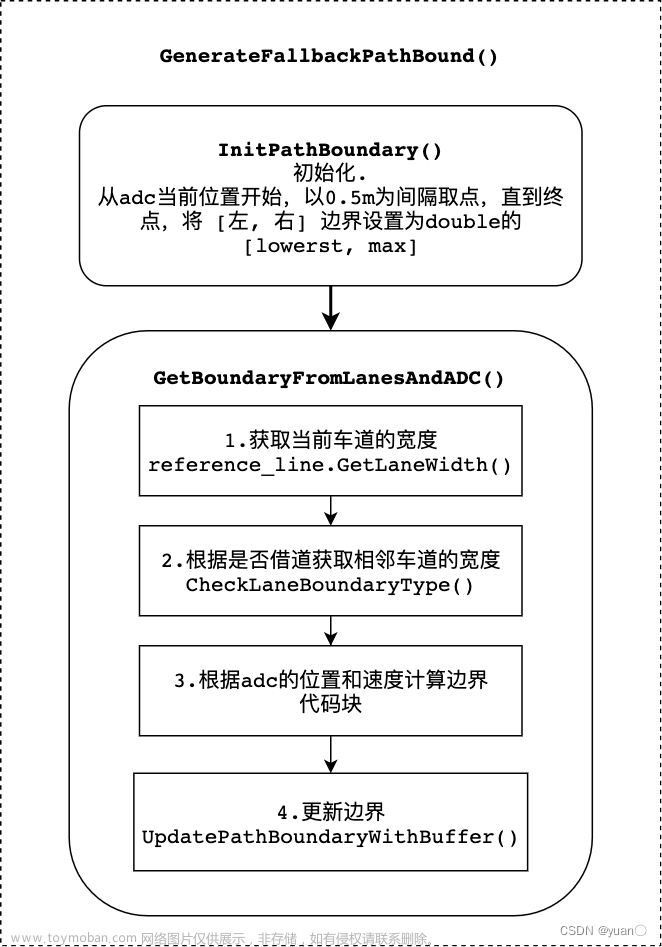
fallback部分主要包含两个函数,InitPathBoundary 和GetBoundaryFromLanesAndADC。fallback是备选的方案,只考虑adc信息和静态道路信息。
GenerateFallbackPathBound
Status PathBoundsDecider::GenerateFallbackPathBound(
const ReferenceLineInfo& reference_line_info, PathBound* const path_bound) {
// 1. Initialize the path boundaries to be an indefinitely large area.
if (!InitPathBoundary(reference_line_info, path_bound)) {...
// PathBoundsDebugString(*path_bound);
// 2. Decide a rough boundary based on lane info and ADC's position
std::string dummy_borrow_lane_type;
if (!GetBoundaryFromLanesAndADC(reference_line_info,
LaneBorrowInfo::NO_BORROW, 0.5, path_bound,
&dummy_borrow_lane_type, true)) {...
// PathBoundsDebugString(*path_bound);
ADEBUG << "Completed generating fallback path boundaries.";
return Status::OK();
}
InitPathBoundary
InitPathBoundary从adc当前位置开始,以0.5m为间隔取点,直到终点,将 [左, 右] 边界设置为double的 [lowerst, max]。
bool PathBoundsDecider::InitPathBoundary(
...
// Starting from ADC's current position, increment until the horizon, and
// set lateral bounds to be infinite at every spot.
// 从adc当前位置开始,以0.5m为间隔取点,直到终点,将 [左, 右] 边界设置为double的 [lowerst, max]
for (double curr_s = adc_frenet_s_;
curr_s < std::fmin(adc_frenet_s_ +
std::fmax(kPathBoundsDeciderHorizon,
reference_line_info.GetCruiseSpeed() *
FLAGS_trajectory_time_length),
reference_line.Length());
curr_s += kPathBoundsDeciderResolution) {
path_bound->emplace_back(curr_s, std::numeric_limits<double>::lowest(),
std::numeric_limits<double>::max());
}
...}
GetBoundaryFromLanesAndADC
GetBoundaryFromLanesAndADC首先获取当前车道的宽度;再根据是否发生借道的决策,获取相邻车道的宽度(包括对向车道以及同向相邻车道);再根据ADC的位置和速度计算边界;最后更新边界。
// TODO(jiacheng): this function is to be retired soon.
bool PathBoundsDecider::GetBoundaryFromLanesAndADC(
...
for (size_t i = 0; i < path_bound->size(); ++i) {
double curr_s = std::get<0>((*path_bound)[i]);
// 1. Get the current lane width at current point.获取当前点车道的宽度
if (!reference_line.GetLaneWidth(curr_s, &curr_lane_left_width,
&curr_lane_right_width)) {
AWARN << "Failed to get lane width at s = " << curr_s;
curr_lane_left_width = past_lane_left_width;
curr_lane_right_width = past_lane_right_width;
} else {...}
// 2. Get the neighbor lane widths at the current point.获取当前点相邻车道的宽度
double curr_neighbor_lane_width = 0.0;
if (CheckLaneBoundaryType(reference_line_info, curr_s, lane_borrow_info)) {
hdmap::Id neighbor_lane_id;
if (lane_borrow_info == LaneBorrowInfo::LEFT_BORROW) {
// 借左车道
...
} else if (lane_borrow_info == LaneBorrowInfo::RIGHT_BORROW) {
// 借右车道
...
}
}
// 3. 根据道路宽度,adc的位置和速度计算合适的边界。
static constexpr double kMaxLateralAccelerations = 1.5;
double offset_to_map = 0.0;
reference_line.GetOffsetToMap(curr_s, &offset_to_map);
double ADC_speed_buffer = (adc_frenet_ld_ > 0 ? 1.0 : -1.0) *
adc_frenet_ld_ * adc_frenet_ld_ /
kMaxLateralAccelerations / 2.0;
// 向左车道借到,左边界会变成左侧车道左边界
double curr_left_bound_lane =
curr_lane_left_width + (lane_borrow_info == LaneBorrowInfo::LEFT_BORROW
? curr_neighbor_lane_width
: 0.0);
// 和上面类似
double curr_right_bound_lane =
-curr_lane_right_width -
(lane_borrow_info == LaneBorrowInfo::RIGHT_BORROW
? curr_neighbor_lane_width
: 0.0);
double curr_left_bound = 0.0; // 左边界
double curr_right_bound = 0.0; // 右边界
// 计算左边界和右边界
if (config_.path_bounds_decider_config()
.is_extend_lane_bounds_to_include_adc() ||
is_fallback_lanechange) {
// extend path bounds to include ADC in fallback or change lane path
// bounds.
double curr_left_bound_adc =
std::fmax(adc_l_to_lane_center_,
adc_l_to_lane_center_ + ADC_speed_buffer) +
GetBufferBetweenADCCenterAndEdge() + ADC_buffer;
curr_left_bound =
std::fmax(curr_left_bound_lane, curr_left_bound_adc) - offset_to_map;
double curr_right_bound_adc =
std::fmin(adc_l_to_lane_center_,
adc_l_to_lane_center_ + ADC_speed_buffer) -
GetBufferBetweenADCCenterAndEdge() - ADC_buffer;
curr_right_bound =
std::fmin(curr_right_bound_lane, curr_right_bound_adc) -
offset_to_map;
} else {
curr_left_bound = curr_left_bound_lane - offset_to_map;
curr_right_bound = curr_right_bound_lane - offset_to_map;
}
// 4. 更新边界.
if (!UpdatePathBoundaryWithBuffer(i, curr_left_bound, curr_right_bound,
path_bound, is_left_lane_boundary,
is_right_lane_boundary)) {
path_blocked_idx = static_cast<int>(i);
}
... }
PS:
涉及到的几个参数:
(1)ADC_speed_buffer,我的理解是车辆以最大横向加速度将横向速度降为0所经过的距离。
l
a
t
=
V
l
a
t
2
2
a
lat=\frac {{V_{lat}}^2} {2a}
lat=2aVlat2
double ADC_speed_buffer = (adc_frenet_ld_ > 0 ? 1.0 : -1.0) *
adc_frenet_ld_ * adc_frenet_ld_ /
kMaxLateralAccelerations / 2.0;
(2) curr_left_bound_lane、curr_right_bound_lane基于车道线的左右边界,如果产生变道,则加上相邻车道的宽度。
double curr_left_bound_lane =
curr_lane_left_width + (lane_borrow_info == LaneBorrowInfo::LEFT_BORROW
? curr_neighbor_lane_width
: 0.0);
double curr_right_bound_lane =
-curr_lane_right_width -
(lane_borrow_info == LaneBorrowInfo::RIGHT_BORROW
? curr_neighbor_lane_width
: 0.0);
(3)curr_left_bound_adc基于自车产生的边界。根据ADC_speed_buffer,ADC_buffer(0.5,可以认为是横向安全区间),半车宽,adc_l_to_lane_center_(自车相对于车道中心的偏移量)计算。
double curr_left_bound_adc =
std::fmax(adc_l_to_lane_center_,
adc_l_to_lane_center_ + ADC_speed_buffer) +
GetBufferBetweenADCCenterAndEdge() + ADC_buffer;
计算示意图大致如下: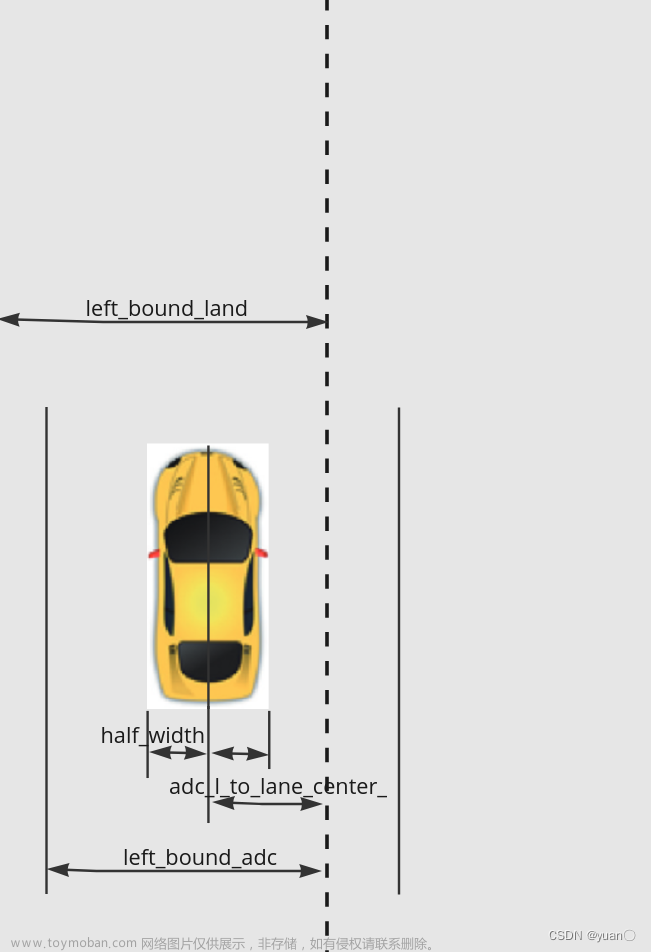
(4)offset_to_map:相对地图的偏移量。
UpdatePathBoundaryWithBuffer
UpdatePathBoundaryWithBuffer首先计算缓冲边界(实际意义就是将左右边界各收缩半个车宽),若(l_min > l_max),即右边界大于左边界,则发生block,不更新。
bool PathBoundsDecider::UpdatePathBoundaryWithBuffer(
size_t idx, double left_bound, double right_bound,
PathBound* const path_boundaries, bool is_left_lane_bound,
bool is_right_lane_bound) {
// substract vehicle width when bound does not come from the lane boundary
// 计算缓冲边界,默认是1.0
const double default_adc_buffer_coeff = 1.0;
double left_adc_buffer_coeff =
(is_left_lane_bound
? config_.path_bounds_decider_config().adc_buffer_coeff()
: default_adc_buffer_coeff);
double right_adc_buffer_coeff =
(is_right_lane_bound
? config_.path_bounds_decider_config().adc_buffer_coeff()
: default_adc_buffer_coeff);
// Update the right bound (l_min):
double new_l_min =
std::fmax(std::get<1>((*path_boundaries)[idx]),
right_bound + right_adc_buffer_coeff *
GetBufferBetweenADCCenterAndEdge());
// Update the left bound (l_max):
double new_l_max = std::fmin(
std::get<2>((*path_boundaries)[idx]),
left_bound - left_adc_buffer_coeff * GetBufferBetweenADCCenterAndEdge());
// Check if ADC is blocked.
// If blocked, don't update anything, return false.
if (new_l_min > new_l_max) {
ADEBUG << "Path is blocked at idx = " << idx;
return false;
}
// Otherwise, update path_boundaries and center_line; then return true.
std::get<1>((*path_boundaries)[idx]) = new_l_min;
std::get<2>((*path_boundaries)[idx]) = new_l_max;
return true;
}
TrimPathBounds
TrimPathBounds截断block之后的边界点。
2. pull over
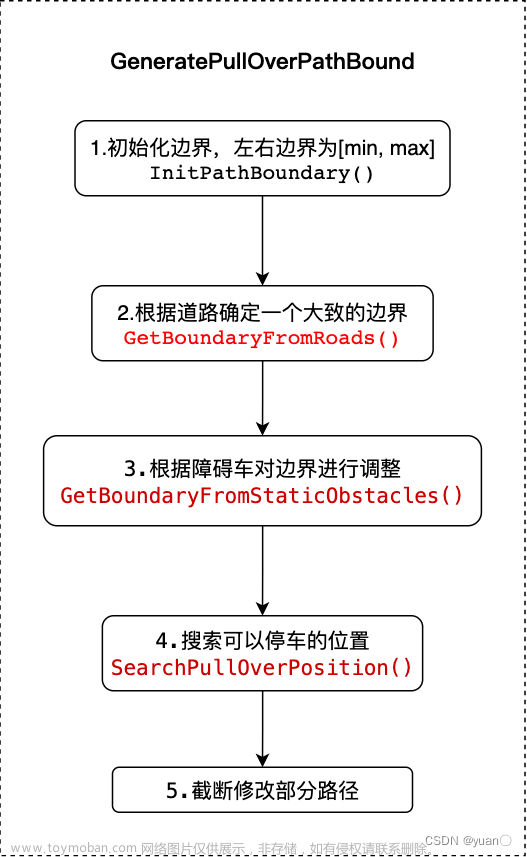
GeneratePullOverPathBound
核心逻辑在GeneratePullOverPathBound中。InitPathBoundary在fallback部分已经讨论过了,接着来看GetBoundaryFromRoads。
GetBoundaryFromRoads
GetBoundaryFromRoads主要完成:获取道路边界;更新道路边界;裁剪block之后的边界点。
GetBoundaryFromRoads根据道路信息确定一个大致的边界。返回的边界是相对于车道中心(而不是reference_line)的,尽管在大多数情况下reference_line与车道中心的偏差可以忽略不计。
UpdatePullOverBoundaryByLaneBoundary
之后调用UpdatePullOverBoundaryByLaneBoundary更新pull over的边界。pull over有两种状态:PULL_OVER和EMERGENCY_PULL_OVER。
对于PULL_OVER,选取车道左边界作为边界。对于EMERGENCY_PULL_OVER,选取左/右车道边界作为边界,因为可能会在对向车道停车。
GetBoundaryFromStaticObstacles
根据静态障碍物对边界进行调整。它将确保边界不包含任何静态障碍,这样之后优化时生成的路径就不会与任何静态障碍碰撞。
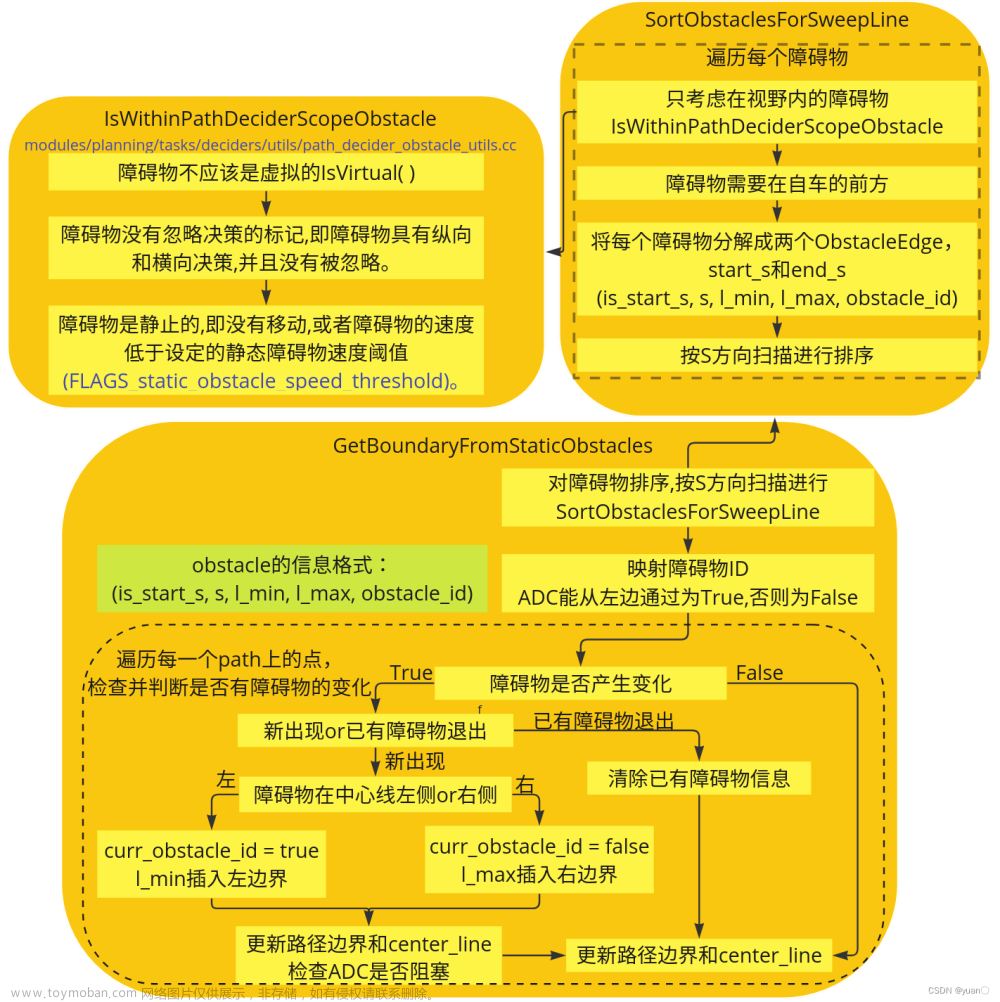
SearchPullOverPosition
它的目的是搜索停车点,为了能够容纳车的尺寸,因为要先搜索可以停车的区域,然后在该区域内取一点作为停车点。搜索区域时,要先确定一个端点,然后向前或向后考察另一个端点,以及考察两端点之间的区域是否符合要求。
搜索pull over位置的过程:
- 根据pull_over_status.pull_over_type()判断是前向搜索(pull
over开头第一个点),还是后向搜索(pull over末尾后一个点) - 两层循环,外层控制搜索的索引idx,内层控制进一步的索引(前向idx+1,后向idx-1)。
- 根据内外两层循环的索引,判断搜索到的空间是否满足宽度和长度要求,判断是否可以pull over
bool PathBoundsDecider::SearchPullOverPosition(
const Frame& frame, const ReferenceLineInfo& reference_line_info,
const std::vector<std::tuple<double, double, double>>& path_bound,
std::tuple<double, double, double, int>* const pull_over_configuration) {
const auto& pull_over_status =
injector_->planning_context()->planning_status().pull_over();
// 搜索方向,默认前向搜索
bool search_backward = false; // search FORWARD by default
double pull_over_s = 0.0;
if (pull_over_status.pull_over_type() ==
PullOverStatus::EMERGENCY_PULL_OVER) {...}
int idx = 0;
if (search_backward) {
// 后向搜索,定位pull over末尾的一个点.
idx = static_cast<int>(path_bound.size()) - 1;
while (idx >= 0 && std::get<0>(path_bound[idx]) > pull_over_s) {
--idx;
}
} else {
// 前向搜索,定位emergency pull over开头后的第一个点.
while (idx < static_cast<int>(path_bound.size()) &&
std::get<0>(path_bound[idx]) < pull_over_s) {
++idx;
}
}
// 为pull over搜索到一个可行的位置,主要是确定该区域的宽度和长度
const double pull_over_space_length =
kPulloverLonSearchCoeff *
VehicleConfigHelper::GetConfig().vehicle_param().length() -
FLAGS_obstacle_lon_start_buffer - FLAGS_obstacle_lon_end_buffer;
const double pull_over_space_width =
(kPulloverLatSearchCoeff - 1.0) *
VehicleConfigHelper::GetConfig().vehicle_param().width();
const double adc_half_width =
VehicleConfigHelper::GetConfig().vehicle_param().width() / 2.0;
// 2. Find a window that is close to road-edge.
/*
这里用了内外两层循环进行搜索,外层循环控制搜索的开始的端点idx。
内层控制另一个端点。根据找到的两个端点,判断区域是否可以pull over
*/
bool has_a_feasible_window = false;
while ((search_backward && idx >= 0 &&
std::get<0>(path_bound[idx]) - std::get<0>(path_bound.front()) >
pull_over_space_length) ||
(!search_backward && idx < static_cast<int>(path_bound.size()) &&
std::get<0>(path_bound.back()) - std::get<0>(path_bound[idx]) >
pull_over_space_length)) {
while ((search_backward && j >= 0 &&
std::get<0>(path_bound[idx]) - std::get<0>(path_bound[j]) <
pull_over_space_length) ||
(!search_backward && j < static_cast<int>(path_bound.size()) &&
std::get<0>(path_bound[j]) - std::get<0>(path_bound[idx]) <
pull_over_space_length)) {...}
// 找到可行区域,获取停车区域的位置和姿态
if (is_feasible_window) {
...
break;}
...} // 外层while
...
}
3. lane change

核心逻辑在GenerateLaneChangePathBound函数中,与前面的场景计算流程大同小异。主要核心部分在GetBoundaryFromLaneChangeForbiddenZone部分。
GenerateLaneChangePathBound
Status PathBoundsDecider::GenerateLaneChangePathBound(
const ReferenceLineInfo& reference_line_info,
std::vector<std::tuple<double, double, double>>* const path_bound) {
// 1.初始化,和前面的步骤类似
if (!InitPathBoundary(reference_line_info, path_bound)) {...}
// 2. 根据道路和adc的信息获取一个大致的路径边界
std::string dummy_borrow_lane_type;
if (!GetBoundaryFromLanesAndADC(reference_line_info,
LaneBorrowInfo::NO_BORROW, 0.1, path_bound,
&dummy_borrow_lane_type, true)) {...}
// 3. Remove the S-length of target lane out of the path-bound.
GetBoundaryFromLaneChangeForbiddenZone(reference_line_info, path_bound);
// 根据静态障碍物调整边界.
if (!GetBoundaryFromStaticObstacles(reference_line_info.path_decision(),
path_bound, &blocking_obstacle_id)) {...}
...
}
GetBoundaryFromLaneChangeForbiddenZone
GetBoundaryFromLaneChangeForbiddenZone函数运行流程如下:
- 如果当前位置可以变道,则直接变道
- 如果有一个lane-change的起点,则直接使用它
- 逐个检查变道前的点的边界,改变边界的值(如果已经过了变道点,则返回)
void PathBoundsDecider::GetBoundaryFromLaneChangeForbiddenZone(
const ReferenceLineInfo& reference_line_info, PathBound* const path_bound) {
// Sanity checks.
CHECK_NOTNULL(path_bound);
const ReferenceLine& reference_line = reference_line_info.reference_line();
// If there is a pre-determined lane-change starting position, then use it;
// otherwise, decide one.
auto* lane_change_status = injector_->planning_context()
->mutable_planning_status()
->mutable_change_lane();
// 1.当前位置直接变道。
if (lane_change_status->is_clear_to_change_lane()) {
ADEBUG << "Current position is clear to change lane. No need prep s.";
lane_change_status->set_exist_lane_change_start_position(false);
return;
}
double lane_change_start_s = 0.0;
// 2.如果已经有一个lane-change的起点,就直接使用它,否则再找一个
if (lane_change_status->exist_lane_change_start_position()) {
common::SLPoint point_sl;
reference_line.XYToSL(lane_change_status->lane_change_start_position(),
&point_sl);
lane_change_start_s = point_sl.s();
} else {
// TODO(jiacheng): train ML model to learn this.
// 设置为adc前方一段距离为变道起始点
lane_change_start_s = FLAGS_lane_change_prepare_length + adc_frenet_s_;
// Update the decided lane_change_start_s into planning-context.
// 更新变道起始点的信息
common::SLPoint lane_change_start_sl;
lane_change_start_sl.set_s(lane_change_start_s);
lane_change_start_sl.set_l(0.0);
common::math::Vec2d lane_change_start_xy;
reference_line.SLToXY(lane_change_start_sl, &lane_change_start_xy);
lane_change_status->set_exist_lane_change_start_position(true);
lane_change_status->mutable_lane_change_start_position()->set_x(
lane_change_start_xy.x());
lane_change_status->mutable_lane_change_start_position()->set_y(
lane_change_start_xy.y());
}
// Remove the target lane out of the path-boundary, up to the decided S.
if (lane_change_start_s < adc_frenet_s_) {
// If already passed the decided S, then return.
// lane_change_status->set_exist_lane_change_start_position(false);
return;
}
// 逐个检查变道前的点的边界,改变边界的值
for (size_t i = 0; i < path_bound->size(); ++i) {
double curr_s = std::get<0>((*path_bound)[i]);
if (curr_s > lane_change_start_s) {
break;
}
double curr_lane_left_width = 0.0;
double curr_lane_right_width = 0.0;
double offset_to_map = 0.0;
reference_line.GetOffsetToMap(curr_s, &offset_to_map);
if (reference_line.GetLaneWidth(curr_s, &curr_lane_left_width,
&curr_lane_right_width)) {
double offset_to_lane_center = 0.0;
reference_line.GetOffsetToMap(curr_s, &offset_to_lane_center);
curr_lane_left_width += offset_to_lane_center;
curr_lane_right_width -= offset_to_lane_center;
}
curr_lane_left_width -= offset_to_map;
curr_lane_right_width += offset_to_map;
std::get<1>((*path_bound)[i]) =
adc_frenet_l_ > curr_lane_left_width //右变道已跨过车道线,设定右界限
? curr_lane_left_width + GetBufferBetweenADCCenterAndEdge()
: std::get<1>((*path_bound)[i]);
std::get<1>((*path_bound)[i]) =
std::fmin(std::get<1>((*path_bound)[i]), adc_frenet_l_ - 0.1);
std::get<2>((*path_bound)[i]) =
adc_frenet_l_ < -curr_lane_right_width
? -curr_lane_right_width - GetBufferBetweenADCCenterAndEdge()
: std::get<2>((*path_bound)[i]); //左变道已跨过车道线,设定左界限
std::get<2>((*path_bound)[i]) =
std::fmax(std::get<2>((*path_bound)[i]), adc_frenet_l_ + 0.1);
}
}
PS:变道时是以相邻车道的参考线作为参考线。以向右变道为例,变道前(指跨过车道线线前adc_frenet_l_ > curr_lane_left_width),使用原先的path bound,不给右侧留空间;变道之后,再进行更新。
4. regular

代码流程如下:文章来源:https://www.toymoban.com/news/detail-672521.html
Status PathBoundsDecider::GenerateRegularPathBound(
const ReferenceLineInfo& reference_line_info,
const LaneBorrowInfo& lane_borrow_info, PathBound* const path_bound,
std::string* const blocking_obstacle_id,
std::string* const borrow_lane_type) {
// 1.初始化边界.
if (!InitPathBoundary(reference_line_info, path_bound)) {...}
// 2.根据adc位置和lane信息确定大致的边界
if (!GetBoundaryFromLanesAndADC(reference_line_info, lane_borrow_info, 0.1,
path_bound, borrow_lane_type)) {...}
// PathBoundsDebugString(*path_bound);
// 3.根据障碍物调整道路边界
if (!GetBoundaryFromStaticObstacles(reference_line_info.path_decision(),
path_bound, blocking_obstacle_id)) {...}
...
}
流程和上面的几个基本类似,借道有三种类型文章来源地址https://www.toymoban.com/news/detail-672521.html
enum class LaneBorrowInfo {
LEFT_BORROW,
NO_BORROW,
RIGHT_BORROW,
};
到了这里,关于【Apollo学习笔记】——规划模块TASK之PATH_BOUNDS_DECIDER的文章就介绍完了。如果您还想了解更多内容,请在右上角搜索TOY模板网以前的文章或继续浏览下面的相关文章,希望大家以后多多支持TOY模板网!