TASK系列解析文章
1.【Apollo学习笔记】——规划模块TASK之LANE_CHANGE_DECIDER
2.【Apollo学习笔记】——规划模块TASK之PATH_REUSE_DECIDER
3.【Apollo学习笔记】——规划模块TASK之PATH_BORROW_DECIDER
4.【Apollo学习笔记】——规划模块TASK之PATH_BOUNDS_DECIDER
5.【Apollo学习笔记】——规划模块TASK之PIECEWISE_JERK_PATH_OPTIMIZER
6.【Apollo学习笔记】——规划模块TASK之PATH_ASSESSMENT_DECIDER
7.【Apollo学习笔记】——规划模块TASK之PATH_DECIDER
8.【Apollo学习笔记】——规划模块TASK之RULE_BASED_STOP_DECIDER
9.【Apollo学习笔记】——规划模块TASK之SPEED_BOUNDS_PRIORI_DECIDER&&SPEED_BOUNDS_FINAL_DECIDER
10.【Apollo学习笔记】——规划模块TASK之SPEED_HEURISTIC_OPTIMIZER
11.【Apollo学习笔记】——规划模块TASK之SPEED_DECIDER
12.【Apollo学习笔记】——规划模块TASK之PIECEWISE_JERK_SPEED_OPTIMIZER
13.【Apollo学习笔记】——规划模块TASK之PIECEWISE_JERK_NONLINEAR_SPEED_OPTIMIZER(一)
14.【Apollo学习笔记】——规划模块TASK之PIECEWISE_JERK_NONLINEAR_SPEED_OPTIMIZER(二)
前言
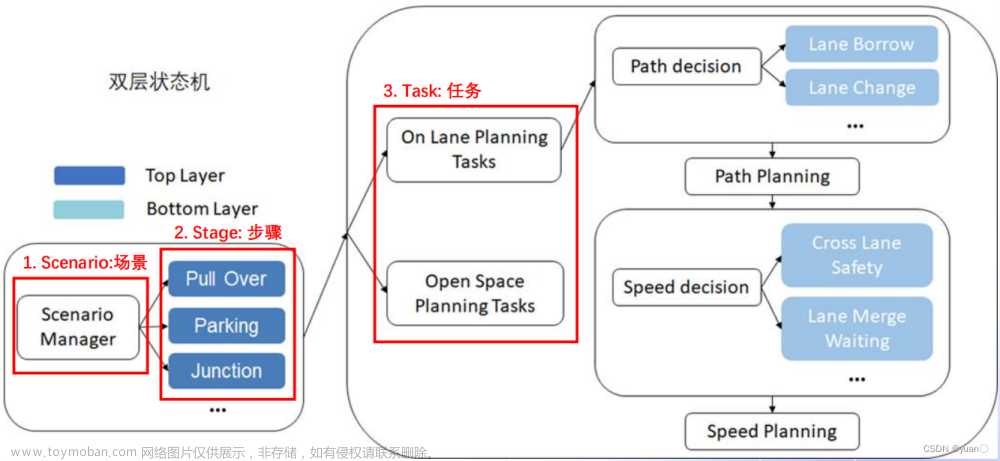
在Apollo星火计划学习笔记——Apollo路径规划算法原理与实践与【Apollo学习笔记】——Planning模块讲到……Stage::Process的PlanOnReferenceLine函数会依次调用task_list中的TASK,本文将会继续以LaneFollow为例依次介绍其中的TASK部分究竟做了哪些工作。由于个人能力所限,文章可能有纰漏的地方,还请批评斧正。
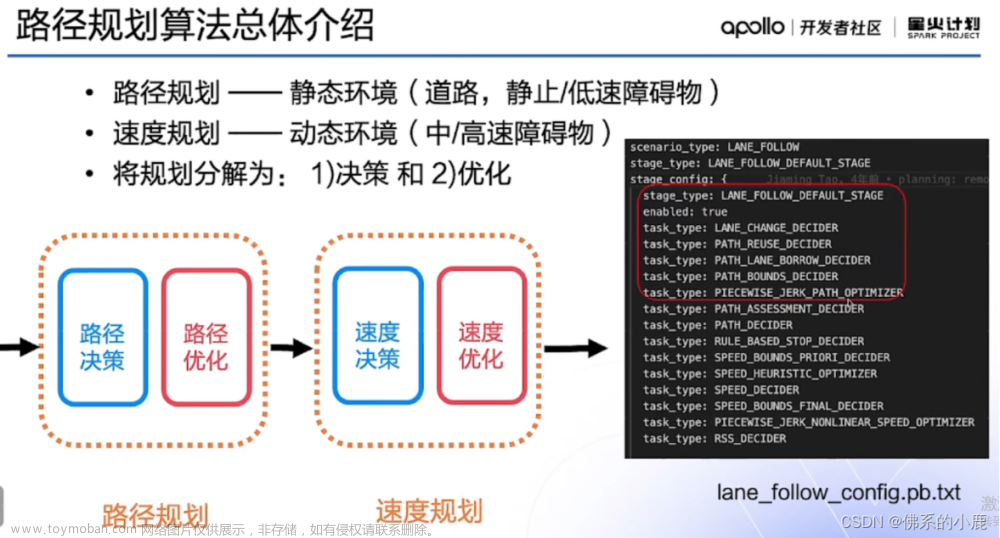
在modules/planning/conf/scenario/lane_follow_config.pb.txt配置文件中,我们可以看到LaneFollow所需要执行的所有task。
stage_config: {
stage_type: LANE_FOLLOW_DEFAULT_STAGE
enabled: true
task_type: LANE_CHANGE_DECIDER
task_type: PATH_REUSE_DECIDER
task_type: PATH_LANE_BORROW_DECIDER
task_type: PATH_BOUNDS_DECIDER
task_type: PIECEWISE_JERK_PATH_OPTIMIZER
task_type: PATH_ASSESSMENT_DECIDER
task_type: PATH_DECIDER
task_type: RULE_BASED_STOP_DECIDER
task_type: SPEED_BOUNDS_PRIORI_DECIDER
task_type: SPEED_HEURISTIC_OPTIMIZER
task_type: SPEED_DECIDER
task_type: SPEED_BOUNDS_FINAL_DECIDER
task_type: PIECEWISE_JERK_SPEED_OPTIMIZER
# task_type: PIECEWISE_JERK_NONLINEAR_SPEED_OPTIMIZER
task_type: RSS_DECIDER
本文将继续介绍LaneFollow的第6个TASK——PATH_ASSESSMENT_DECIDER
PATH_ASSESSMENT_DECIDER功能简介
路径评价,选出最优路径

由PATH_BOUNDS_DECIDER可以知道会产生以下几种类型的路径边界:
fallback-
fallback+lanechange -
fallback+pullover -
fallback+regular
依据不同的边界会产生不同的路径,接着便需要筛选出一条最优的路径。依据以下规则,进行评价:
- 路径是否和障碍物碰撞
- 路径长度
- 路径是否会停在对向车道
- 路径离自车远近
- 哪个路径更早回自车道
- …
PATH_ASSESSMENT_DECIDER相关信息
- 输入:
Status PathAssessmentDecider::Process(Frame* const frame, ReferenceLineInfo* const reference_line_info)
输入Frame,reference_line_info。 - 输出:路径排序之后,选择第一个路径。结果保存在reference_line_info中
PATH_ASSESSMENT_DECIDER总体流程


首先来看看PathAssessmentDecider::Process流程部分:
Process部分主要完成路径重复使用判断、去除无效路径、分析路径并加入重要信息提供给速度决策部分、排序选择最优的路径以及最后的更新必要的信息。
1. 去除无效路径
// 1. Remove invalid path.
// 1. 删掉无效路径.
std::vector<PathData> valid_path_data;
for (const auto& curr_path_data : candidate_path_data) {
// RecordDebugInfo(curr_path_data, curr_path_data.path_label(),
// reference_line_info);
if (curr_path_data.path_label().find("fallback") != std::string::npos) {
// fallback的无效路径是偏离参考线以及道路的路径
if (IsValidFallbackPath(*reference_line_info, curr_path_data)) {
valid_path_data.push_back(curr_path_data);
}
} else {
// regular的无效路径是偏离参考线、道路,碰撞,停在相邻的逆向车道的路径。
if (IsValidRegularPath(*reference_line_info, curr_path_data)) {
valid_path_data.push_back(curr_path_data);
}
}
}
const auto& end_time1 = std::chrono::system_clock::now();
std::chrono::duration<double> diff = end_time1 - end_time0;
ADEBUG << "Time for path validity checking: " << diff.count() * 1000
<< " msec.";
其中fallback的无效路径是偏离参考线以及道路的路径。regular的无效路径是偏离参考线、道路,碰撞,停在相邻的逆向车道的路径。
2. 分析并加入重要信息给speed决策
// 2. Analyze and add important info for speed decider to use
// 2. 分析并加入重要信息给speed决策
size_t cnt = 0;
const Obstacle* blocking_obstacle_on_selflane = nullptr;
for (size_t i = 0; i != valid_path_data.size(); ++i) {
auto& curr_path_data = valid_path_data[i];
if (curr_path_data.path_label().find("fallback") != std::string::npos) {
// remove empty path_data.
if (!curr_path_data.Empty()) {
if (cnt != i) {
valid_path_data[cnt] = curr_path_data;
}
++cnt;
}
continue;
}
// 添加相关信息
SetPathInfo(*reference_line_info, &curr_path_data);
// Trim all the lane-borrowing paths so that it ends with an in-lane
// position.
// 修剪所有路径(只要不是pull-over),使其能够以in-lane结尾
if (curr_path_data.path_label().find("pullover") == std::string::npos) {
TrimTailingOutLanePoints(&curr_path_data);
}
// find blocking_obstacle_on_selflane, to be used for lane selection later
// 找到self_lane上的阻塞障碍物, 为下一步选择车道做准备
if (curr_path_data.path_label().find("self") != std::string::npos) {
const auto blocking_obstacle_id = curr_path_data.blocking_obstacle_id();
blocking_obstacle_on_selflane =
reference_line_info->path_decision()->Find(blocking_obstacle_id);
}
// remove empty path_data.
if (!curr_path_data.Empty()) {
if (cnt != i) {
valid_path_data[cnt] = curr_path_data;
}
++cnt;
}
// RecordDebugInfo(curr_path_data, curr_path_data.path_label(),
// reference_line_info);
ADEBUG << "For " << curr_path_data.path_label() << ", "
<< "path length = " << curr_path_data.frenet_frame_path().size();
}
valid_path_data.resize(cnt);
// If there is no valid path_data, exit.
// 如果没有有效路径,退出
if (valid_path_data.empty()) {
const std::string msg = "Neither regular nor fallback path is valid.";
AERROR << msg;
return Status(ErrorCode::PLANNING_ERROR, msg);
}
ADEBUG << "There are " << valid_path_data.size() << " valid path data.";
const auto& end_time2 = std::chrono::system_clock::now();
diff = end_time2 - end_time1;
ADEBUG << "Time for path info labeling: " << diff.count() * 1000 << " msec.";
SetPathInfo
void PathAssessmentDecider::SetPathInfo(
const ReferenceLineInfo& reference_line_info, PathData* const path_data) {
// Go through every path_point, and label its:
// - in-lane/out-of-lane info (side-pass or lane-change)
// - distance to the closest obstacle.
std::vector<PathPointDecision> path_decision;
// 0. Initialize the path info.
InitPathPointDecision(*path_data, &path_decision);
// 1. Label caution types, differently for side-pass or lane-change.
if (reference_line_info.IsChangeLanePath()) {
// If lane-change, then label the lane-changing part to
// be out-on-forward lane.
SetPathPointType(reference_line_info, *path_data, true, &path_decision);
} else {
// Otherwise, only do the label for borrow-lane generated paths.
// 仅仅对借道进行标记
if (path_data->path_label().find("fallback") == std::string::npos &&
path_data->path_label().find("self") == std::string::npos) {
SetPathPointType(reference_line_info, *path_data, false, &path_decision);
}
}
// SetObstacleDistance(reference_line_info, *path_data, &path_decision);
path_data->SetPathPointDecisionGuide(std::move(path_decision));
}
这一部分中函数SetPathInfo完成以下功能:初始化path info;根据是lane-change还是side-pass,设置路径点的类型;添加相关决策引导信息等信息。
SetPathPointType
在设置路径点的类型时涉及到SetPathPointType这一个函数。
流程如下图所示:

void PathAssessmentDecider::SetPathPointType(
const ReferenceLineInfo& reference_line_info, const PathData& path_data,
const bool is_lane_change_path,
std::vector<PathPointDecision>* const path_point_decision) {
// Sanity checks.
CHECK_NOTNULL(path_point_decision);
// Go through every path_point, and add in-lane/out-of-lane info.
const auto& discrete_path = path_data.discretized_path();
const auto& vehicle_config =
common::VehicleConfigHelper::Instance()->GetConfig();
const double ego_length = vehicle_config.vehicle_param().length();
const double ego_width = vehicle_config.vehicle_param().width();
const double ego_back_to_center =
vehicle_config.vehicle_param().back_edge_to_center();
// 车辆几何中心点与车辆后轴的偏移距离
const double ego_center_shift_distance =
ego_length / 2.0 - ego_back_to_center;
bool is_prev_point_out_lane = false;
for (size_t i = 0; i < discrete_path.size(); ++i) {
// 以车辆后轴中心获取boundingbox
const auto& rear_center_path_point = discrete_path[i];
const double ego_theta = rear_center_path_point.theta();
Box2d ego_box({rear_center_path_point.x(), rear_center_path_point.y()},
ego_theta, ego_length, ego_width);
Vec2d shift_vec{ego_center_shift_distance * std::cos(ego_theta),
ego_center_shift_distance * std::sin(ego_theta)};
// 将boundingbox从车辆后轴中心变换到几何中心(apollo在这里采用的是AABB的boundingbox,其中有些细节等之后再细看)
ego_box.Shift(shift_vec);
// 得到SL坐标系下的boundary
SLBoundary ego_sl_boundary;
if (!reference_line_info.reference_line().GetSLBoundary(ego_box,
&ego_sl_boundary)) {
ADEBUG << "Unable to get SL-boundary of ego-vehicle.";
continue;
}
double lane_left_width = 0.0;
double lane_right_width = 0.0;
double middle_s =
(ego_sl_boundary.start_s() + ego_sl_boundary.end_s()) / 2.0;
if (reference_line_info.reference_line().GetLaneWidth(
middle_s, &lane_left_width, &lane_right_width)) {
// Rough sl boundary estimate using single point lane width
double back_to_inlane_extra_buffer = 0.2;
double in_and_out_lane_hysteresis_buffer =
is_prev_point_out_lane ? back_to_inlane_extra_buffer : 0.0;
// Check for lane-change and lane-borrow differently:
if (is_lane_change_path) {
// For lane-change path, only transitioning part is labeled as
// out-of-lane.
if (ego_sl_boundary.start_l() > lane_left_width ||
ego_sl_boundary.end_l() < -lane_right_width) {
// This means that ADC hasn't started lane-change yet.
// 再次重申,变道时是以要变道的目标车道作为参考线
std::get<1>((*path_point_decision)[i]) =
PathData::PathPointType::IN_LANE;
} else if (ego_sl_boundary.start_l() >
-lane_right_width + back_to_inlane_extra_buffer &&
ego_sl_boundary.end_l() <
lane_left_width - back_to_inlane_extra_buffer) {
// This means that ADC has safely completed lane-change with margin.
std::get<1>((*path_point_decision)[i]) =
PathData::PathPointType::IN_LANE;
} else {
// ADC is right across two lanes.
std::get<1>((*path_point_decision)[i]) =
PathData::PathPointType::OUT_ON_FORWARD_LANE;
}
} else {
// For lane-borrow path, as long as ADC is not on the lane of
// reference-line, it is out on other lanes. It might even be
// on reverse lane!
if (ego_sl_boundary.end_l() >
lane_left_width + in_and_out_lane_hysteresis_buffer ||
ego_sl_boundary.start_l() <
-lane_right_width - in_and_out_lane_hysteresis_buffer) {
if (path_data.path_label().find("reverse") != std::string::npos) {
std::get<1>((*path_point_decision)[i]) =
PathData::PathPointType::OUT_ON_REVERSE_LANE;
} else if (path_data.path_label().find("forward") !=
std::string::npos) {
std::get<1>((*path_point_decision)[i]) =
PathData::PathPointType::OUT_ON_FORWARD_LANE;
} else {
std::get<1>((*path_point_decision)[i]) =
PathData::PathPointType::UNKNOWN;
}
if (!is_prev_point_out_lane) {
if (ego_sl_boundary.end_l() >
lane_left_width + back_to_inlane_extra_buffer ||
ego_sl_boundary.start_l() <
-lane_right_width - back_to_inlane_extra_buffer) {
is_prev_point_out_lane = true;
}
}
} else {
// The path point is within the reference_line's lane.
std::get<1>((*path_point_decision)[i]) =
PathData::PathPointType::IN_LANE;
if (is_prev_point_out_lane) {
is_prev_point_out_lane = false;
}
}
}
} else {
AERROR << "reference line not ready when setting path point guide";
return;
}
}
}
PS:关于ego_box.Shift(shift_vec);这一步是如何实现的,可以关注这篇博客:Apollo EM中path_assesment_task相关细节的讨论
3. 排序选择最优的路径
... ...
// 3. Pick the optimal path.
// 3. 选择最优路径,两两比较路径。排序是根据 ComparePathData 函数的返回值进行的。
std::sort(valid_path_data.begin(), valid_path_data.end(),
std::bind(ComparePathData, std::placeholders::_1,
std::placeholders::_2, blocking_obstacle_on_selflane));
ADEBUG << "Using '" << valid_path_data.front().path_label()
<< "' path out of " << valid_path_data.size() << " path(s)";
if (valid_path_data.front().path_label().find("fallback") !=
std::string::npos) {
FLAGS_static_obstacle_nudge_l_buffer = 0.8;
}
*(reference_line_info->mutable_path_data()) = valid_path_data.front();
reference_line_info->SetBlockingObstacle(
valid_path_data.front().blocking_obstacle_id());
const auto& end_time3 = std::chrono::system_clock::now();
diff = end_time3 - end_time2;
ADEBUG << "Time for optimal path selection: " << diff.count() * 1000
<< " msec.";
... ...
主要排序规则在ComparePathData函数中。
bool ComparePathData(const PathData& lhs, const PathData& rhs,
const Obstacle* blocking_obstacle) {
ADEBUG << "Comparing " << lhs.path_label() << " and " << rhs.path_label();
// Empty path_data is never the larger one.
// 空的路径永远排在后面
if (lhs.Empty()) {
ADEBUG << "LHS is empty.";
return false;
}
if (rhs.Empty()) {
ADEBUG << "RHS is empty.";
return true;
}
// Regular path goes before fallback path.regular > fallback
// 如果lhs是regular路径而rhs是fallback路径,那么lhs会被认为更好,返回true。
bool lhs_is_regular = lhs.path_label().find("regular") != std::string::npos;
bool rhs_is_regular = rhs.path_label().find("regular") != std::string::npos;
if (lhs_is_regular != rhs_is_regular) {
return lhs_is_regular;
}
// Select longer path.
// If roughly same length, then select self-lane path.
bool lhs_on_selflane = lhs.path_label().find("self") != std::string::npos;
bool rhs_on_selflane = rhs.path_label().find("self") != std::string::npos;
static constexpr double kSelfPathLengthComparisonTolerance = 15.0;
static constexpr double kNeighborPathLengthComparisonTolerance = 25.0;
double lhs_path_length = lhs.frenet_frame_path().back().s();
double rhs_path_length = rhs.frenet_frame_path().back().s();
// 至少其中有一条是self_lane
if (lhs_on_selflane || rhs_on_selflane) {
// 如果两条路径的长度相差超过了kSelfPathLengthComparisonTolerance(在这里是15.0),那么较长的路径将被认为更好。
if (std::fabs(lhs_path_length - rhs_path_length) >
kSelfPathLengthComparisonTolerance) {
return lhs_path_length > rhs_path_length;
} else {
// 如果两条路径的长度相差在这个容差范围内,并且其中一条路径在"self"车道上,那么"self"车道上的路径将被认为更好。
return lhs_on_selflane;
}
} else {
// 没有一条是self_lane
if (std::fabs(lhs_path_length - rhs_path_length) >
kNeighborPathLengthComparisonTolerance) {
return lhs_path_length > rhs_path_length;
}
}
// If roughly same length, and must borrow neighbor lane,
// then prefer to borrow forward lane rather than reverse lane.
int lhs_on_reverse =
ContainsOutOnReverseLane(lhs.path_point_decision_guide());
int rhs_on_reverse =
ContainsOutOnReverseLane(rhs.path_point_decision_guide());
// TODO(jiacheng): make this a flag.
// 如果需要借用逆向车道的次数差超过了6次,那么次数较少的路径将被认为更好(相当于选择逆向距离短的)。
if (std::abs(lhs_on_reverse - rhs_on_reverse) > 6) {
return lhs_on_reverse < rhs_on_reverse;
}
// For two lane-borrow directions, based on ADC's position,
// select the more convenient one.
if ((lhs.path_label().find("left") != std::string::npos &&
rhs.path_label().find("right") != std::string::npos) ||
(lhs.path_label().find("right") != std::string::npos &&
rhs.path_label().find("left") != std::string::npos)) {
if (blocking_obstacle) {
// select left/right path based on blocking_obstacle's position
// 有障碍物,选择合适的方向,左或右借道
const double obstacle_l =
(blocking_obstacle->PerceptionSLBoundary().start_l() +
blocking_obstacle->PerceptionSLBoundary().end_l()) /
2;
ADEBUG << "obstacle[" << blocking_obstacle->Id() << "] l[" << obstacle_l
<< "]";
// 如果阻挡障碍物的横向位置大于0(在障碍物的右侧),那么含有"right"的路径将被认为更好;否则,含有"left"的路径将被认为更好。
return (obstacle_l > 0.0
? (lhs.path_label().find("right") != std::string::npos)
: (lhs.path_label().find("left") != std::string::npos));
} else {
// select left/right path based on ADC's position
// 无障碍物,根据adc的位置选择借道方向
double adc_l = lhs.frenet_frame_path().front().l();
if (adc_l < -1.0) {
return lhs.path_label().find("right") != std::string::npos;
} else if (adc_l > 1.0) {
return lhs.path_label().find("left") != std::string::npos;
}
}
}
// If same length, both neighbor lane are forward,
// then select the one that returns to in-lane earlier.
// 路径长度相同,相邻车道都是前向的,选择较早返回自车道的路径
static constexpr double kBackToSelfLaneComparisonTolerance = 20.0;
int lhs_back_idx = GetBackToInLaneIndex(lhs.path_point_decision_guide());
int rhs_back_idx = GetBackToInLaneIndex(rhs.path_point_decision_guide());
double lhs_back_s = lhs.frenet_frame_path()[lhs_back_idx].s();
double rhs_back_s = rhs.frenet_frame_path()[rhs_back_idx].s();
if (std::fabs(lhs_back_s - rhs_back_s) > kBackToSelfLaneComparisonTolerance) {
return lhs_back_idx < rhs_back_idx;
}
// If same length, both forward, back to inlane at same time,
// select the left one to side-pass.
// 如果路径长度相同,前向借道,返回自车道时间相同,选择从左侧借道的路径
bool lhs_on_leftlane = lhs.path_label().find("left") != std::string::npos;
bool rhs_on_leftlane = rhs.path_label().find("left") != std::string::npos;
if (lhs_on_leftlane != rhs_on_leftlane) {
ADEBUG << "Select " << (lhs_on_leftlane ? "left" : "right") << " lane over "
<< (!lhs_on_leftlane ? "left" : "right") << " lane.";
return lhs_on_leftlane;
}
// Otherwise, they are the same path, lhs is not < rhs.
// 最后如果两条路径相同,则 lhs is not < rhl
return false;
}
路径排序规则如下:(道路评估的优劣通过排序获得)
1.空的路径永远排在后面
2.regular > fallback
3.如果self-lane有一个存在,选择那个。如果都存在,选择较长的.如果长度接近,选择self-lane如果self-lane都不存在,选择较长的路径
4.如果路径长度接近,且都要借道:
- (1) 都要借逆向车道,选择距离短的
- (2) 针对具有两个借道方向的情况:
- 有障碍物,选择合适的方向,左或右借道
- 无障碍物,根据adc的位置选择借道方向
- (3) 路径长度相同,相邻车道都是前向的,选择较早返回自车道的路径
- (4) 如果路径长度相同,前向借道,返回自车道时间相同,选择从左侧借道的路径
5.最后如果两条路径相同,则 lhs is not < rhl
排序之后:选择最优路径,即第一个路径
4. 更新必要的信息
// 4. Update necessary info for lane-borrow decider's future uses.
// Update front static obstacle's info.
auto* mutable_path_decider_status = injector_->planning_context()
->mutable_planning_status()
->mutable_path_decider();
if (reference_line_info->GetBlockingObstacle() != nullptr) {
int front_static_obstacle_cycle_counter =
mutable_path_decider_status->front_static_obstacle_cycle_counter();
mutable_path_decider_status->set_front_static_obstacle_cycle_counter(
std::max(front_static_obstacle_cycle_counter, 0));
mutable_path_decider_status->set_front_static_obstacle_cycle_counter(
std::min(front_static_obstacle_cycle_counter + 1, 10));
mutable_path_decider_status->set_front_static_obstacle_id(
reference_line_info->GetBlockingObstacle()->Id());
} else {
int front_static_obstacle_cycle_counter =
mutable_path_decider_status->front_static_obstacle_cycle_counter();
mutable_path_decider_status->set_front_static_obstacle_cycle_counter(
std::min(front_static_obstacle_cycle_counter, 0));
mutable_path_decider_status->set_front_static_obstacle_cycle_counter(
std::max(front_static_obstacle_cycle_counter - 1, -10));
}
// Update self-lane usage info.
if (reference_line_info->path_data().path_label().find("self") !=
std::string::npos) {
// && std::get<1>(reference_line_info->path_data()
// .path_point_decision_guide()
// .front()) == PathData::PathPointType::IN_LANE)
int able_to_use_self_lane_counter =
mutable_path_decider_status->able_to_use_self_lane_counter();
if (able_to_use_self_lane_counter < 0) {
able_to_use_self_lane_counter = 0;
}
mutable_path_decider_status->set_able_to_use_self_lane_counter(
std::min(able_to_use_self_lane_counter + 1, 10));
} else {
mutable_path_decider_status->set_able_to_use_self_lane_counter(0);
}
// Update side-pass direction.
if (mutable_path_decider_status->is_in_path_lane_borrow_scenario()) {
bool left_borrow = false;
bool right_borrow = false;
const auto& path_decider_status =
injector_->planning_context()->planning_status().path_decider();
for (const auto& lane_borrow_direction :
path_decider_status.decided_side_pass_direction()) {
if (lane_borrow_direction == PathDeciderStatus::LEFT_BORROW &&
reference_line_info->path_data().path_label().find("left") !=
std::string::npos) {
left_borrow = true;
}
if (lane_borrow_direction == PathDeciderStatus::RIGHT_BORROW &&
reference_line_info->path_data().path_label().find("right") !=
std::string::npos) {
right_borrow = true;
}
}
mutable_path_decider_status->clear_decided_side_pass_direction();
if (right_borrow) {
mutable_path_decider_status->add_decided_side_pass_direction(
PathDeciderStatus::RIGHT_BORROW);
}
if (left_borrow) {
mutable_path_decider_status->add_decided_side_pass_direction(
PathDeciderStatus::LEFT_BORROW);
}
}
const auto& end_time4 = std::chrono::system_clock::now();
diff = end_time4 - end_time3;
ADEBUG << "Time for FSM state updating: " << diff.count() * 1000 << " msec.";
// Plot the path in simulator for debug purpose.
RecordDebugInfo(reference_line_info->path_data(), "Planning PathData",
reference_line_info);
return Status::OK();
更新必要信息:文章来源:https://www.toymoban.com/news/detail-679223.html
1.更新adc前方静态障碍物的信息
2.更新自车道使用信息
3.更新旁车道的方向根据:PathDeciderStatus是RIGHT_BORROW或LEFT_BORROW判断是从左侧借道,还是从右侧借道文章来源地址https://www.toymoban.com/news/detail-679223.html
到了这里,关于【Apollo学习笔记】——规划模块TASK之PATH_ASSESSMENT_DECIDER的文章就介绍完了。如果您还想了解更多内容,请在右上角搜索TOY模板网以前的文章或继续浏览下面的相关文章,希望大家以后多多支持TOY模板网!