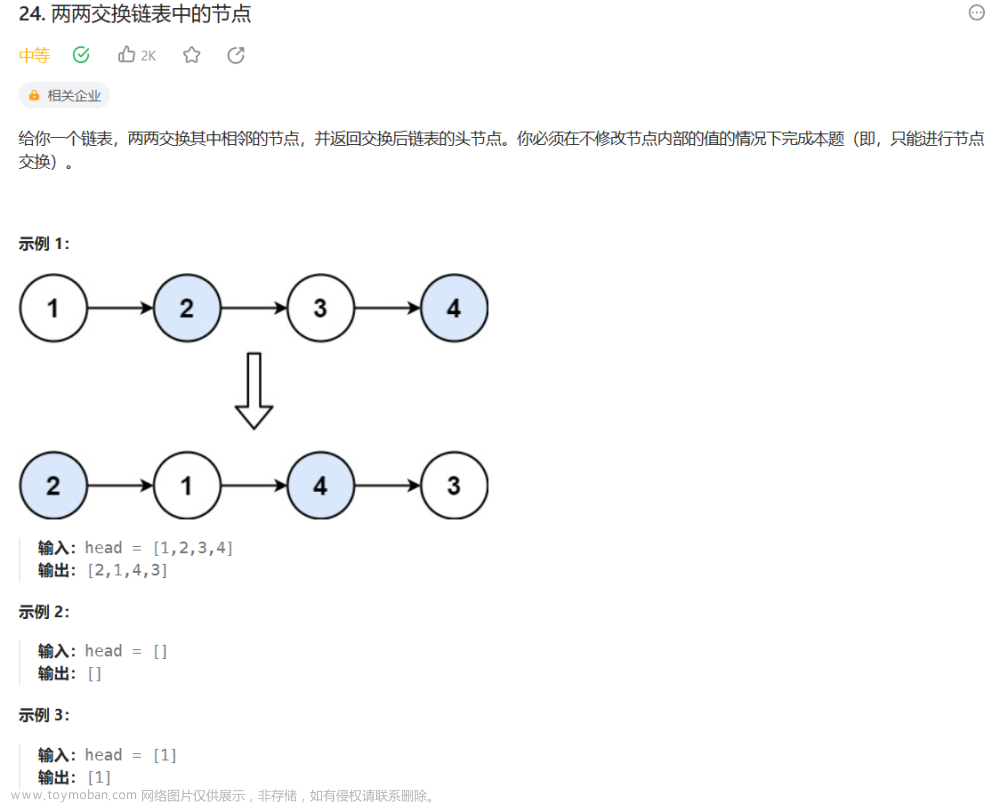
题目

方法一:集合排序(核心是内部的排序)
把链表放到List集合,排好序,再依据List集合创建一个新有序链表返回就行了
//方法一 集合倒序 (存.val值在转换为ListNode)
public ListNode sortList(ListNode head) {
if(head == null) return head;
List<Integer> list = new ArrayList<>();
ListNode node = head;
while(node != null){
list.add(node.val);
node = node.next;
}
Collections.sort(list);//升序排列
ListNode min = new ListNode(list.get(0));//直接找出小值记录头结点
node = min;
for(int i = 1; i<list.size(); i++){
ListNode h = new ListNode(list.get(i));
node.next = h;
node = node.next;
}
return min;
}
// 方法一 集合倒序(存ListNode值直接调用Comparator接口进行值排序)
// public ListNode sortList(ListNode head) {
// if(head == null){
// return null;
// }
// List<ListNode> list = new ArrayList<>();
// while(head !=null){
// list.add(head);
// head = head.next;
// }
// list.sort(new Comparator<ListNode>(){
// @Override
// public int compare(ListNode o1, ListNode o2) {
// return o1.val - o2.val;
// }
// });
// for(int i = 0 ; i < list.size() - 1;i++){
// list.get(i).next = list.get(i + 1);
// }
// list.get(list.size() - 1).next = null;
// return list.get(0);
方法二: 优先队列(核心也是内部的排序)
优先队列 往这个优先队列中插入元素时,会按照节点 val 属性的大小顺序进行排序,即小的节点排在前面,大的节点排在后面。依次谈栈再创建新链表
优先队列声明
PriorityQueue<ListNode> queue = new PriorityQueue<>((node1, node2) -> node1.val - node2.val);
((node1, node2) -> node1.val - node2.val) 升序排列
((node1, node2) -> node2.val - node1.val) 降序排列
public ListNode sortList(ListNode head) {
PriorityQueue<ListNode> queue = new PriorityQueue<>((node1, node2) -> node1.val - node2.val);
ListNode cur = head;
while (cur != null) {
queue.offer(cur);
cur = cur.next;
}
ListNode dummy = new ListNode(0);
cur = dummy;
while (!queue.isEmpty()) {
cur.next = queue.poll();
cur = cur.next;
}
cur.next = null;
return dummy.next;
}
方法三:归并排序(带递归) 从上往下
先找到中间点 按中间点切割链表 然后排序好切割好的两头的链表 再将两个排序好的链表合并起来 (递归终止条件是切割到只有一个节点,直接返回可以排序了)
- 先找到待排序链表的中间节点(快慢指针找)
- 再根据中间节点对两边的链表分别进行归并排序(递归)
- 将排序好的两部分链表进行合并( 双指针法 无需递归)

public ListNode sortList(ListNode head) {
return mergeSort(head);
}
// 归并排序
private ListNode mergeSort(ListNode head){
if(head ==null || head.next==null) return head;// 如果没有结点/只有一个结点,无需排序,直接返回--也是递归的出口
// 快慢指针找出中位点
ListNode fast = head.next;//让fast比slow快1个位置,这样最后solw会停在链表中间点前一个位置
// ListNode fast = head.next.next;//两种方式都可以 最终slow都会停在中间点前一个位置
ListNode slow = head;
//记住这个判断条件,偶数结点会找靠左结点,奇数就是中间节点,能用到很多题上
while(fast !=null && fast.next !=null){
slow =slow.next;
fast = fast.next.next;
}
// 对右半部分进行归并排序
ListNode right = mergeSort(slow.next);
// 对左半部分进行断链操作
slow.next =null;
// 对左半部分进行归并排序
ListNode left = mergeSort(head);
//合并两个有序链表
return mergeList(left,right);
}
// 合并链表 双指针法
private ListNode mergeList(ListNode l,ListNode r){
// 临时头节点
ListNode tmpHead=new ListNode(-1);
ListNode tem = tmpHead;
while( l!=null && r!=null ){ //只循环走到任何一方为null时 后面就不需要再比较了 直接把多的哪一方拼接起来就行
if(l.val < r.val){
tem.next =l;
l = l.next;
}else{
tem.next =r;
r = r.next;
}
tem = tem.next;
}
if(l==null) tem.next = r;//只循环走到任何一方为null时 后面就不需要再比较了 直接不为null的哪一方拼接起来就行
else tem.next =l;
return tmpHead.next;
}
方法四:归并排序(省去递归,用迭代) 从下往上
核心就行直接定义排序的最小单位 也就是一个节点的链表(大for循环从intv = 1(子俩表长度) 开始 在intv >= 大链表的长度停止),然后分别对链表长度为1 2 3 4 进行合并排序,然后拼接到一起,就是排序号的链表文章来源:https://www.toymoban.com/news/detail-680364.html
 文章来源地址https://www.toymoban.com/news/detail-680364.html
文章来源地址https://www.toymoban.com/news/detail-680364.html
public ListNode sortList(ListNode head) {
if(head == null) return head;
int length = 0;//统计链表的长度
ListNode node = head;
while(node != null){
length++;
node = node.next;
}
ListNode preHead = new ListNode(0,head);//创建哑结点 preHead--->head
for(int intv = 1; intv < length ;intv=intv*2){ //每次intv扩大两倍 直到intv 大于等于了链表的长度
ListNode prev = preHead;//prev为拼接点(拼接合并好的链表)
ListNode cur = preHead.next;
while(cur != null){//开始拆分
ListNode head1 = cur;//intv为1 时的 第一段链表的头节点
for(int i = 1 ; i<intv&&cur.next !=null&& cur != null;i++){//找到intv为1 时的 第一段链表的末尾节点 方便找到第二段的头结点
cur=cur.next;//此时循环结束 cur指向的是第一段链表的尾部
}
ListNode head2 = cur.next;//intv为1 时的 第二段链表的头节点
cur.next = null; //端链操作 将两部分链表断开
cur = head2; //更新cur到第二段链表的首节点
for(int i = 1 ; i<intv && cur != null && cur.next != null ; i++){
cur=cur.next;//此时 cur指向的是第二段链表的尾部
}
ListNode next = null;
if(cur != null){ //记录第二次进行 比较的 第一段链表的第一个节点
next = cur.next;
cur.next = null;//对第一次比较的第二个链表进行断链
}
ListNode merged = mergeList(head1,head2);//对第一次的两个链表进行合并排序
prev.next = merged;//将合并好的链表 拼接到prev后面
while(prev.next != null){
prev = prev.next; //把prev移动到拼接好的链表的尾部,方便下次再拼接合并排序好的链表
}
cur = next;//将cur更新到下一批次合并排序的第一个俩表的头结点
}
}
return preHead.next;
}
// // 合并两个有序链表 双指针法
private ListNode mergeList(ListNode l,ListNode r){
// 临时头节点
ListNode tmpHead= new ListNode(-1);
ListNode tem = tmpHead;
while( l!=null && r!=null ){ //只循环走到任何一方为null时 后面就不需要再比较了 直接把多的哪一方拼接起来就行
if(l.val < r.val){
tem.next =l;
l = l.next;
}else{
tem.next =r;
r = r.next;
}
tem = tem.next;
}
if(l==null) tem.next = r;//只循环走到任何一方为null时 后面就不需要再比较了 直接不为null的哪一方拼接起来就行
else tem.next =l;
return tmpHead.next;
}
到了这里,关于【LeetCode-中等题】148. 排序链表的文章就介绍完了。如果您还想了解更多内容,请在右上角搜索TOY模板网以前的文章或继续浏览下面的相关文章,希望大家以后多多支持TOY模板网!