List是有序、可重复的容器。
有序:
List中每个元素都有索引标记。可以根据元素的索引标记(在List中的位置)访问 元素,从而精确控制这些元素。
可重复:
List允许加入重复的元素。更确切地讲,List通常允许满足 e1.equals(e2) 的元素重复加入容器。
List接口常用的实现类有3个:ArrayList、LinkedList和Vector。
1.ArrayList:
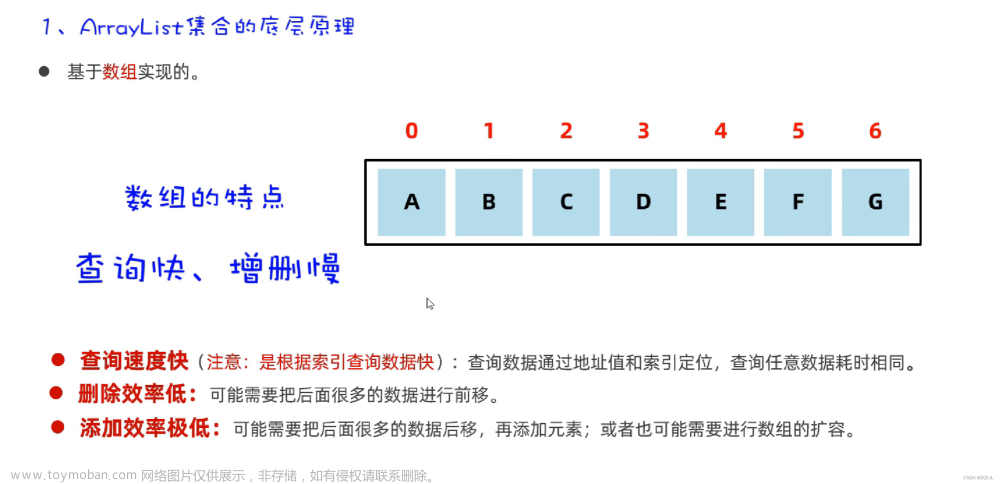
ArrayList底层是用数组实现的存储。 特点:查询效率高,增删效率低,线程不安全。我们一般使用它。
ArrayList底层使用Object数组来存储元素数据。所有的方法,都围绕这个核心的Object数组来开展。
2.LinkedList:
LinkedList底层用双向链表实现的存储。特点:查询效率低,增删效率高,线程不安全。
双向链表也叫双链表,是链表的一种,它的每个数据节点中都有两个指针,分别指向前一个节点和后一个节点。 所以,从双向链表中的任意一个节点开始,都可以很方便地找到所有节点。
3.Vector:
Vector底层是用数组实现的List,相关的方法都加了同步检查,因此“线程安全,效率低”。 比如,copyInto方法就增加了synchronized同步标记。
使用原则:ArrayList、LinkedList、Vector
- 需要线程安全时,用Vector。
- 不存在线程安全问题时,并且查找较多用ArrayList(一般使用它)。
- 不存在线程安全问题时,增加或删除元素较多用LinkedList。
测试案例:文章来源:https://www.toymoban.com/news/detail-682304.html
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.Arrays;
import java.util.LinkedList;
import java.util.List;
import java.util.Vector;
public class day17 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
List<String> arrayList = new ArrayList<>();
List<String> linkedList = new LinkedList<>();
List<String> vector = new Vector<>();
List<Integer> arrayList2 = new ArrayList<>();
List<Integer> linkedList2 = new LinkedList<>();
List<Integer> vector2 = new Vector<>();
List<String> arrayList3 = new ArrayList<>();
List<String> linkedList3 = new LinkedList<>();
List<String> vector3 = new Vector<>();
List<String> list1 = Arrays.asList("黄","河","之","水","天","上","来","奔","流","到","海","不","复","回",
"黄","河","之","水","天","上","来","奔","流","到","海","不","复","回");
List<Integer> list2 = Arrays.asList(2 , 1 , 4 , 3 , 6 , 5 ,7 , 14, 13 ,12 , 11 ,10 , 9 , 8,
2 , 1 , 4 , 3 , 6 , 5 ,7 , 8 , 9 ,10 , 11 ,12 , 13 , 14);
List<String> list3 = Arrays.asList("2" , "1" , "4" , "3" , "6" , "5" ,"7" , "14", "13" ,"12" , "11" ,"10" , "9" , "8",
"2" , "1" , "4" , "3" , "6" , "5" ,"7" , "8" , "9" ,"10" , "11" ,"12" , "13" , "14");
arrayList.addAll(list1);
System.out.println("arrayList:"+arrayList);
arrayList2.addAll(list2);
System.out.println("arrayList2:"+arrayList2);
arrayList3.addAll(list3);
System.out.println("arrayList3:"+arrayList3);
System.out.println("-------------------------------------------");
linkedList.addAll(list1);
System.out.println("linkedList:"+linkedList);
linkedList2.addAll(list2);
System.out.println("linkedList2:"+linkedList2);
linkedList3.addAll(list3);
System.out.println("linkedList3:"+linkedList3);
System.out.println("-------------------------------------------");
vector.addAll(list1);
System.out.println("vector:"+vector);
vector2.addAll(list2);
System.out.println("vector2:"+vector2);
vector3.addAll(list3);
System.out.println("vector3:"+vector3);
System.out.println("-------------------------------------------");
}
}
测试输出:文章来源地址https://www.toymoban.com/news/detail-682304.html
arrayList:[黄, 河, 之, 水, 天, 上, 来, 奔, 流, 到, 海, 不, 复, 回, 黄, 河, 之, 水, 天, 上, 来, 奔, 流, 到, 海, 不, 复, 回]
arrayList2:[2, 1, 4, 3, 6, 5, 7, 14, 13, 12, 11, 10, 9, 8, 2, 1, 4, 3, 6, 5, 7, 8, 9, 10, 11, 12, 13, 14]
arrayList3:[2, 1, 4, 3, 6, 5, 7, 14, 13, 12, 11, 10, 9, 8, 2, 1, 4, 3, 6, 5, 7, 8, 9, 10, 11, 12, 13, 14]
-------------------------------------------
linkedList:[黄, 河, 之, 水, 天, 上, 来, 奔, 流, 到, 海, 不, 复, 回, 黄, 河, 之, 水, 天, 上, 来, 奔, 流, 到, 海, 不, 复, 回]
linkedList2:[2, 1, 4, 3, 6, 5, 7, 14, 13, 12, 11, 10, 9, 8, 2, 1, 4, 3, 6, 5, 7, 8, 9, 10, 11, 12, 13, 14]
linkedList3:[2, 1, 4, 3, 6, 5, 7, 14, 13, 12, 11, 10, 9, 8, 2, 1, 4, 3, 6, 5, 7, 8, 9, 10, 11, 12, 13, 14]
-------------------------------------------
vector:[黄, 河, 之, 水, 天, 上, 来, 奔, 流, 到, 海, 不, 复, 回, 黄, 河, 之, 水, 天, 上, 来, 奔, 流, 到, 海, 不, 复, 回]
vector2:[2, 1, 4, 3, 6, 5, 7, 14, 13, 12, 11, 10, 9, 8, 2, 1, 4, 3, 6, 5, 7, 8, 9, 10, 11, 12, 13, 14]
vector3:[2, 1, 4, 3, 6, 5, 7, 14, 13, 12, 11, 10, 9, 8, 2, 1, 4, 3, 6, 5, 7, 8, 9, 10, 11, 12, 13, 14]
-------------------------------------------
到了这里,关于【List】List集合有序测试案例:ArrayList,LinkedList,Vector(123)的文章就介绍完了。如果您还想了解更多内容,请在右上角搜索TOY模板网以前的文章或继续浏览下面的相关文章,希望大家以后多多支持TOY模板网!