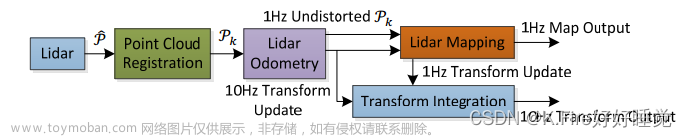
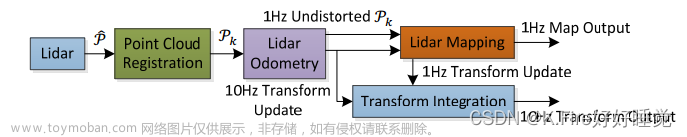
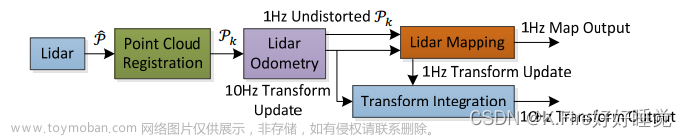
1.常用的几种loam算法
aloam 纯激光
lego_loam 纯激光 去除了地面
lio_sam imu+激光紧耦合
lvi_sam 激光+视觉
2.代码思路
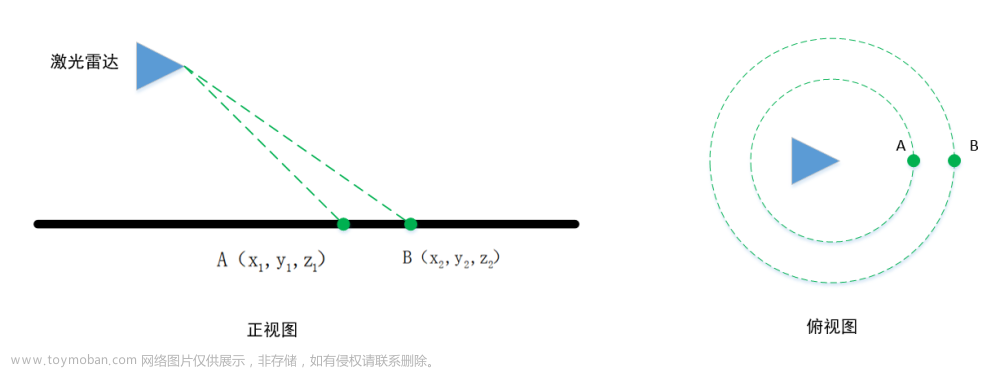
2.1.特征点提取scanRegistration.cpp,这个文件的目的是为了根据曲率提取4种特征点和对当前点云进行预处理
输入是雷达点云话题
输出是 4种特征点点云和预处理后的当前点云
(1)带有点云线束id+在角度范围所处进度的全部有效点点云(因为雷达是旋转的,雷达旋转的进度)
(2)曲率比较大的特征点点云,对每条线6等分之后每段2个点
(3)曲率一般大的特征点点云,对每条线6等分之后每段20个点
(4)曲率比较小的面点点云
(5)一般面点点云,角点提取剩下的那些点
当输入雷达是16线雷达,去计算是哪条线id是通过计算俯仰角每2度算一根线去计算的
角度所处的进度,是根据水平角计算获得的
2.1.1选择雷达扫描半径范围内的点
pcl::PointCloud<pcl::PointXYZ> narrowed_scan;
narrowed_scan.header = scan.header;
if (min_range >= max_range)
{
ROS_ERROR_ONCE("min_range>=max_range @(%lf, %lf)", min_range, max_range);
return scan;
}
double square_min_range = min_range * min_range;
double square_max_range = max_range * max_range;
for (pcl::PointCloud<pcl::PointXYZ>::const_iterator iter = scan.begin(); iter != scan.end(); ++iter)
{
const pcl::PointXYZ &p = *iter;
// 点云点到原点的位置的欧式距离
double square_distance = p.x * p.x + p.y * p.y;
if (square_min_range <= square_distance && square_distance <= square_max_range)
{
narrowed_scan.points.push_back(p);
}
}
return narrowed_scan;
2.1.2计算水平角角度范围
int cloudSize = laserCloudIn.points.size();
// 起始点角度 atan2范围是-pi~pi
float startOri = -atan2(laserCloudIn.points[0].y, laserCloudIn.points[0].x);
// 终止点角度
float endOri = -atan2(laserCloudIn.points[cloudSize - 1].y,
laserCloudIn.points[cloudSize - 1].x) +
2 * M_PI;
// 总有些例外 ,比如这里大于3pi 和小于pi 就要做一些调整到合理的范围
if (endOri - startOri > 3 * M_PI)
{
endOri -= 2 * M_PI;
}
else if (endOri - startOri < M_PI)
{
endOri += 2 * M_PI;
}
Eigen::Vector2f anglerange;
anglerange[0] = startOri;
anglerange[1] = endOri;
return anglerange;
2.1.3每条线上点的计算范围
// 计算的范围 起始点是从第5个点开始 终止点是倒数第6个点
for (int i = 0; i < N_SCANS; i++)
{
// 第一根线就是 0+5
scanStartInd[i] = laserCloud->size() + 5;
*laserCloud += laserCloudScans[i];
// 第一根线就是第一根线的点数量-6
scanEndInd[i] = laserCloud->size() - 6;
}
2.1.4计算每个点的曲率
// 开始计算曲率
for (int i = 5; i < cloudSize - 5; i++)
{
// 每一小段计算了弧长
float diffX = laserCloud->points[i - 5].x + laserCloud->points[i - 4].x + laserCloud->points[i - 3].x + laserCloud->points[i - 2].x + laserCloud->points[i - 1].x - 10 * laserCloud->points[i].x + laserCloud->points[i + 1].x + laserCloud->points[i + 2].x + laserCloud->points[i + 3].x + laserCloud->points[i + 4].x + laserCloud->points[i + 5].x;
float diffY = laserCloud->points[i - 5].y + laserCloud->points[i - 4].y + laserCloud->points[i - 3].y + laserCloud->points[i - 2].y + laserCloud->points[i - 1].y - 10 * laserCloud->points[i].y + laserCloud->points[i + 1].y + laserCloud->points[i + 2].y + laserCloud->points[i + 3].y + laserCloud->points[i + 4].y + laserCloud->points[i + 5].y;
float diffZ = laserCloud->points[i - 5].z + laserCloud->points[i - 4].z + laserCloud->points[i - 3].z + laserCloud->points[i - 2].z + laserCloud->points[i - 1].z - 10 * laserCloud->points[i].z + laserCloud->points[i + 1].z + laserCloud->points[i + 2].z + laserCloud->points[i + 3].z + laserCloud->points[i + 4].z + laserCloud->points[i + 5].z;
// 存储起始+5到终止-6每个点对应的曲率
cloudCurvature[i] = diffX * diffX + diffY * diffY + diffZ * diffZ;
// 每个点的索引
cloudSortInd[i] = i;
// 标记
cloudNeighborPicked[i] = 0;
cloudLabel[i] = 0;
}
2.1.4对每个点的曲率进行排序
float t_q_sort = 0;
// 遍历每个scan
for (int i = 0; i < N_SCANS; i++)
{
// 点云点数小于6个就认为 没有有效的点 就进行continue
if (scanEndInd[i] - scanStartInd[i] < 6)
{
continue;
}
// 用来存储不太平整的点
pcl::PointCloud<PointType>::Ptr surfPointsLessFlatScan(new pcl::PointCloud<PointType>);
// 将每个scan分成6等分
for (int j = 0; j < 6; j++)
{
// 每个等分的起点和结束点
// 起点id
int sp = scanStartInd[i] + (scanEndInd[i] - scanStartInd[i]) * j / 6;
// 结束点id
int ep = scanStartInd[i] + (scanEndInd[i] - scanStartInd[i]) * (j + 1) / 6 - 1;
TicToc t_tmp;
// 对点云曲率进行索引排序,小的在前,大的在后
std::sort(cloudSortInd + sp, cloudSortInd + ep + 1, comp);
t_q_sort += t_tmp.toc();
int largestPickedNum = 0;
// 挑选曲率比较大的部分
for (int k = ep; k >= sp; k--)
{
// 排序后顺序就乱了,这个时候索引的作用就体现出来了
int ind = cloudSortInd[k];
// 看看这个点是否是有效点,同时曲率是否大于阈值
if (cloudNeighborPicked[ind] == 0 &&
cloudCurvature[ind] > 0.1)
{
largestPickedNum++;
// //目的是为了当前帧大曲率的点和上一帧小一点曲率的点建立约束
// 每段选两个曲率大的点
if (largestPickedNum <= 2)
{
cloudLabel[ind] = 2;
// cornerPointsSharp存放大曲率的点
cornerPointsSharp.push_back(laserCloud->points[ind]);
cornerPointsLessSharp.push_back(laserCloud->points[ind]);
}
// 以及20个曲率稍微大一点的点
else if (largestPickedNum <= 20)
{
// label置1表示曲率稍微大一点的点
cloudLabel[ind] = 1;
cornerPointsLessSharp.push_back(laserCloud->points[ind]);
}
// 超过20个就算了
else
{
break;
}
// 这个点被选中了,pick标志位置1
cloudNeighborPicked[ind] = 1;
// 为了保证特征点不过渡集中,将选中的点周围5个点都置为1,避免后续会选到
for (int l = 1; l <= 5; l++)
{
// 查看相邻点距离是否差异过大,如果差异过大说明点云在此不连续,是特征边缘,就会是新的特征,因此就不置位了
float diffX = laserCloud->points[ind + l].x - laserCloud->points[ind + l - 1].x;
float diffY = laserCloud->points[ind + l].y - laserCloud->points[ind + l - 1].y;
float diffZ = laserCloud->points[ind + l].z - laserCloud->points[ind + l - 1].z;
if (diffX * diffX + diffY * diffY + diffZ * diffZ > 0.05)
{
break;
}
cloudNeighborPicked[ind + l] = 1;
}
// 下面同理
for (int l = -1; l >= -5; l--)
{
float diffX = laserCloud->points[ind + l].x - laserCloud->points[ind + l + 1].x;
float diffY = laserCloud->points[ind + l].y - laserCloud->points[ind + l + 1].y;
float diffZ = laserCloud->points[ind + l].z - laserCloud->points[ind + l + 1].z;
if (diffX * diffX + diffY * diffY + diffZ * diffZ > 0.05)
{
break;
}
cloudNeighborPicked[ind + l] = 1;
}
}
}
// 下面开始挑选面点
int smallestPickedNum = 0;
for (int k = sp; k <= ep; k++)
{
int ind = cloudSortInd[k];
// 确定这个点没有被pack 并且曲率小于阈值
if (cloudNeighborPicked[ind] == 0 &&
cloudCurvature[ind] < 0.1)
{
// -1是认为平坦的点
cloudLabel[ind] = -1;
surfPointsFlat.push_back(laserCloud->points[ind]);
smallestPickedNum++;
// 每个等分取4个比较平坦的面点
// 这里不区分平坦和比较平坦,因为剩下的点label默认是0就是比较平坦
if (smallestPickedNum >= 4)
{
break;
}
cloudNeighborPicked[ind] = 1;
// 下面同理 除非曲率在0.05-0.1之间的点 否则就要标记后5个点
for (int l = 1; l <= 5; l++)
{
float diffX = laserCloud->points[ind + l].x - laserCloud->points[ind + l - 1].x;
float diffY = laserCloud->points[ind + l].y - laserCloud->points[ind + l - 1].y;
float diffZ = laserCloud->points[ind + l].z - laserCloud->points[ind + l - 1].z;
if (diffX * diffX + diffY * diffY + diffZ * diffZ > 0.05)
{
break;
}
cloudNeighborPicked[ind + l] = 1;
}
// 标记前5个点
for (int l = -1; l >= -5; l--)
{
float diffX = laserCloud->points[ind + l].x - laserCloud->points[ind + l + 1].x;
float diffY = laserCloud->points[ind + l].y - laserCloud->points[ind + l + 1].y;
float diffZ = laserCloud->points[ind + l].z - laserCloud->points[ind + l + 1].z;
if (diffX * diffX + diffY * diffY + diffZ * diffZ > 0.05)
{
break;
}
cloudNeighborPicked[ind + l] = 1;
}
}
}
for (int k = sp; k <= ep; k++)
{
// 除了角点 其它的点都是一般平坦的点云
if (cloudLabel[k] <= 0)
{
surfPointsLessFlatScan->push_back(laserCloud->points[k]);
}
}
}
pcl::PointCloud<PointType> surfPointsLessFlatScanDS;
pcl::VoxelGrid<PointType> downSizeFilter;
// 一般平坦的点比较多,所以这里做一个体素滤波
downSizeFilter.setInputCloud(surfPointsLessFlatScan);
downSizeFilter.setLeafSize(0.2, 0.2, 0.2);
downSizeFilter.filter(surfPointsLessFlatScanDS);
surfPointsLessFlat += surfPointsLessFlatScanDS;
}
printf("sort q time %f \n", t_q_sort);
2.1.5 发布4种特征点及插入标志的整体点云
// 分别将当前点云 四种特征的点云发布出去
sensor_msgs::PointCloud2 laserCloudOutMsg;
// 1.整体的点云 对每个点打了标签(哪一根线id+在角度范围所处的一个进度)
pcl::toROSMsg(*laserCloud, laserCloudOutMsg);
laserCloudOutMsg.header.stamp = laserCloudMsg->header.stamp;
laserCloudOutMsg.header.frame_id = "/map";
pubLaserCloud.publish(laserCloudOutMsg);
sensor_msgs::PointCloud2 cornerPointsSharpMsg;
// 2.大曲率特征点
pcl::toROSMsg(cornerPointsSharp, cornerPointsSharpMsg);
cornerPointsSharpMsg.header.stamp = laserCloudMsg->header.stamp;
cornerPointsSharpMsg.header.frame_id = "/map";
pubCornerPointsSharp.publish(cornerPointsSharpMsg);
sensor_msgs::PointCloud2 cornerPointsLessSharpMsg;
// 3.曲率稍微大一点的特征点
pcl::toROSMsg(cornerPointsLessSharp, cornerPointsLessSharpMsg);
cornerPointsLessSharpMsg.header.stamp = laserCloudMsg->header.stamp;
cornerPointsLessSharpMsg.header.frame_id = "/map";
pubCornerPointsLessSharp.publish(cornerPointsLessSharpMsg);
sensor_msgs::PointCloud2 surfPointsFlat2;
// 4.平坦的点
pcl::toROSMsg(surfPointsFlat, surfPointsFlat2);
surfPointsFlat2.header.stamp = laserCloudMsg->header.stamp;
surfPointsFlat2.header.frame_id = "/map";
pubSurfPointsFlat.publish(surfPointsFlat2);
// 5.一般平坦的点
sensor_msgs::PointCloud2 surfPointsLessFlat2;
pcl::toROSMsg(surfPointsLessFlat, surfPointsLessFlat2);
surfPointsLessFlat2.header.stamp = laserCloudMsg->header.stamp;
surfPointsLessFlat2.header.frame_id = "/map";
pubSurfPointsLessFlat.publish(surfPointsLessFlat2);
2.2.激光里程计laserOdometry.cpp
(1)对特征点提取后的5个点云进行回调并存放到队列里,并同时转成pcl点云格式
(2)两次迭代,寻找角点约束和面点约束
(3)角点约束,首先进行雷达运动补偿,通过kdtee从上一帧中寻找距离当前帧角点最近的一个点p1,根据p1去找不同线上距离最近的点p2, 根据点到直线的垂线距离,构建残差方程给到ceres,可以求解出点到线的约束
(4)面点约束,首先进行雷达运动补偿,通过kdtee从上一帧中寻找距离当前帧角点最近的一个点p1,根据p1去找相同线上距离最近的点p2,根据p1去找不同线上距离最近的点p3,根据点到平面的距离,构建残差方程给到ceres,可以求解出点到面的约束
(5)通过两次迭代,进行ceres求解 得到最终的帧间约束结果,与之前的坐标约束进行求解,就得到了前端激光里程计
2.2.1运动补偿部分
激光雷达运动补偿:就是把所有的点补偿到某一时刻,这样就可以把本身过去100ms的点收集到一个时间点上去
void TransformToStart(PointType const *const pi, PointType *const po)
{
// interpolation ratio
double s;
// 由于kitti数据集上的lidar已经做过了运动补偿,因此这里就不做具体补偿了
if (DISTORTION)
s = (pi->intensity - int(pi->intensity)) / SCAN_PERIOD;
else
s = 1.0; // s=1s说明全部补偿到点云结束的时刻
// s = 1;
// 所有点的操作方式都是一致的,相当于从结束时刻补偿到起始时刻
// 这里相当于是一个匀速模型的假设
Eigen::Quaterniond q_point_last = Eigen::Quaterniond::Identity().slerp(s, q_last_curr);
Eigen::Vector3d t_point_last = s * t_last_curr;
Eigen::Vector3d point(pi->x, pi->y, pi->z);
Eigen::Vector3d un_point = q_point_last * point + t_point_last;
po->x = un_point.x();
po->y = un_point.y();
po->z = un_point.z();
po->intensity = pi->intensity;
}
根据反变换求出结束时刻的点坐标,附公式推解
void TransformToEnd(PointType const *const pi, PointType *const po)
{
// undistort point first
pcl::PointXYZI un_point_tmp;
// 把所有点补偿到起始时刻
TransformToStart(pi, &un_point_tmp);
//再 通过反变换的方式 将起始时刻坐标系下的点 转到 结束时刻坐标系下
Eigen::Vector3d un_point(un_point_tmp.x, un_point_tmp.y, un_point_tmp.z);//取出起始时刻坐标系下的点
//q_last_curr \ t_last_curr 是结束时刻坐标系转到起始时刻坐标系 的 旋转 和 平移
Eigen::Vector3d point_end = q_last_curr.inverse() * (un_point - t_last_curr);//通过反变换,求得转到 结束时刻坐标系下 的点坐标
po->x = point_end.x();
po->y = point_end.y();
po->z = point_end.z();
// Remove distortion time info
po->intensity = int(pi->intensity);
}

2.2.2确保5个点云都不为空
// 首先确保5个消息都有,有一个队列为空都不行
if (!cornerSharpBuf.empty() && !cornerLessSharpBuf.empty() &&
!surfFlatBuf.empty() && !surfLessFlatBuf.empty() &&
!fullPointsBuf.empty())
{
return false;
}
else
{
return true;
}
2.2.3通过比较时间戳,判断是否是同一帧
// 分别求出队列第一个时间
timeCornerPointsSharp = cornerSharpBuf.front()->header.stamp.toSec();
timeCornerPointsLessSharp = cornerLessSharpBuf.front()->header.stamp.toSec();
timeSurfPointsFlat = surfFlatBuf.front()->header.stamp.toSec();
timeSurfPointsLessFlat = surfLessFlatBuf.front()->header.stamp.toSec();
timeLaserCloudFullRes = fullPointsBuf.front()->header.stamp.toSec();
// 因为同一帧时间戳是相同的,因此这里比较是否是同一帧
if (timeCornerPointsSharp != timeLaserCloudFullRes ||
timeCornerPointsLessSharp != timeLaserCloudFullRes ||
timeSurfPointsFlat != timeLaserCloudFullRes ||
timeSurfPointsLessFlat != timeLaserCloudFullRes)
{
printf("点云消息时间戳不同步!");
return true;
}
else
{
return false;
}
2.2.4传感器格式转换成点云格式
// 分别将5个消息取出来,同时转成pcl的点云格式
mBuf.lock();
cornerPointsSharp->clear();
// 将第一根元素存放到cornerPointsSharp 就是当前的点云
pcl::fromROSMsg(*cornerSharpBuf.front(), *cornerPointsSharp);
// 移除前端的第一个元素 当前待处理的点云
cornerSharpBuf.pop();
cornerPointsLessSharp->clear();
pcl::fromROSMsg(*cornerLessSharpBuf.front(), *cornerPointsLessSharp);
cornerLessSharpBuf.pop();
surfPointsFlat->clear();
pcl::fromROSMsg(*surfFlatBuf.front(), *surfPointsFlat);
surfFlatBuf.pop();
surfPointsLessFlat->clear();
pcl::fromROSMsg(*surfLessFlatBuf.front(), *surfPointsLessFlat);
surfLessFlatBuf.pop();
laserCloudFullRes->clear();
pcl::fromROSMsg(*fullPointsBuf.front(), *laserCloudFullRes);
fullPointsBuf.pop();
mBuf.unlock();
2.2.5 点到线残差构建
for (int i = 0; i < cornerPointsSharpNum; ++i)
{
// 运动补偿
TransformToStart(&(cornerPointsSharp->points[i]), &pointSel);
// 在上一帧所有角点构成的kdtee中寻找距离当前帧最近的一个点
kdtreeCornerLast->nearestKSearch(pointSel, 1, pointSearchInd, pointSearchSqDis);
int closestPointInd = -1, minPointInd2 = -1;
// 只有小于给定界限才认为是有效约束
if (pointSearchSqDis[0] < DISTANCE_SQ_THRESHOLD)
{
closestPointInd = pointSearchInd[0]; // 对应的最近距离约束的索引取出来
// 找到其所对应的线束id 线束信息隐藏在intensity中
int closestPointScanID = int(laserCloudCornerLast->points[closestPointInd].intensity);
double minPointSqDis2 = DISTANCE_SQ_THRESHOLD;
// 寻找角点,在刚刚角点的id上下分别继续寻找,目的是找到最近的角点,由于其按照约束进行排序,所以就是向上找
for (int j = closestPointInd + 1; j < (int)laserCloudCornerLast->points.size(); ++j)
{
// 不找同一根线束的
if (int(laserCloudCornerLast->points[j].intensity) <= closestPointScanID)
continue;
// 要求找到的线束距离当前线束不能太远
if (int(laserCloudCornerLast->points[j].intensity) > (closestPointScanID + NEARBY_SCAN))
break;
// 上一帧线的第2个点 到当前帧点的距离
double pointSqDis = (laserCloudCornerLast->points[j].x - pointSel.x) *
(laserCloudCornerLast->points[j].x - pointSel.x) +
(laserCloudCornerLast->points[j].y - pointSel.y) *
(laserCloudCornerLast->points[j].y - pointSel.y) +
(laserCloudCornerLast->points[j].z - pointSel.z) *
(laserCloudCornerLast->points[j].z - pointSel.z);
if (pointSqDis < minPointSqDis2)
{
minPointSqDis2 = pointSqDis;
minPointInd2 = j;
}
}
// 同样另外一个方向寻找角点
for (int j = closestPointInd - 1; j >= 0; --j)
{
if (int(laserCloudCornerLast->points[j].intensity) >= closestPointScanID)
continue;
if (int(laserCloudCornerLast->points[j].intensity) < (closestPointScanID - NEARBY_SCAN))
break;
double pointSqDis = (laserCloudCornerLast->points[j].x - pointSel.x) *
(laserCloudCornerLast->points[j].x - pointSel.x) +
(laserCloudCornerLast->points[j].y - pointSel.y) *
(laserCloudCornerLast->points[j].y - pointSel.y) +
(laserCloudCornerLast->points[j].z - pointSel.z) *
(laserCloudCornerLast->points[j].z - pointSel.z);
if (pointSqDis < minPointSqDis2)
{
// 取出当前点和上一帧的两个角点
minPointSqDis2 = pointSqDis;
minPointInd2 = j;
}
}
}
// 最近点所在的线束
if (minPointInd2 >= 0)
{
// 当前点
Eigen::Vector3d curr_point(cornerPointsSharp->points[i].x,
cornerPointsSharp->points[i].y,
cornerPointsSharp->points[i].z);
// 距离当前点最近的上一帧的点
Eigen::Vector3d last_point_a(laserCloudCornerLast->points[closestPointInd].x,
laserCloudCornerLast->points[closestPointInd].y,
laserCloudCornerLast->points[closestPointInd].z);
// 距离上一帧点最近的不同线束上的第二个点 构成棱
Eigen::Vector3d last_point_b(laserCloudCornerLast->points[minPointInd2].x,
laserCloudCornerLast->points[minPointInd2].y,
laserCloudCornerLast->points[minPointInd2].z);
double s;
if (DISTORTION)
// 点在起始点到结束点一周中的进度
s = (cornerPointsSharp->points[i].intensity - int(cornerPointsSharp->points[i].intensity)) / SCAN_PERIOD;
else
s = 1.0;
// 残差项
ceres::CostFunction *cost_function = LidarEdgeFactor::Create(curr_point, last_point_a, last_point_b, s);
// 添加残差块 残差项 损失函数 待优化的变量
problem.AddResidualBlock(cost_function, loss_function, para_q, para_t);
corner_correspondence++;
}
}
2.2.6 点到面残差构建
for (int i = 0; i < surfPointsFlatNum; ++i)
{
TransformToStart(&(surfPointsFlat->points[i]), &pointSel);
// 先找上一帧距离当前帧最近的面点
kdtreeSurfLast->nearestKSearch(pointSel, 1, pointSearchInd, pointSearchSqDis);
int closestPointInd = -1, minPointInd2 = -1, minPointInd3 = -1;
// 距离必须小于阈值
if (pointSearchSqDis[0] < DISTANCE_SQ_THRESHOLD)
{
// 取出找到的上一帧面点的索引
closestPointInd = pointSearchInd[0];
// 取出最近的面点在上一帧的那一条scan线上
int closestPointScanID = int(laserCloudSurfLast->points[closestPointInd].intensity);
double minPointSqDis2 = DISTANCE_SQ_THRESHOLD, minPointSqDis3 = DISTANCE_SQ_THRESHOLD;
// 额外在寻找两个点,要求一个点和最近点同一个scan线 另一个点不同的scan
// 按照增量方向寻找其它面点
for (int j = closestPointInd + 1; j < (int)laserCloudSurfLast->points.size(); ++j)
{
// 不能和当前找到的上一帧面点线束太远
if (int(laserCloudSurfLast->points[j].intensity) > (closestPointScanID + NEARBY_SCAN))
break;
// 计算和当前帧该点距离
double pointSqDis = (laserCloudSurfLast->points[j].x - pointSel.x) *
(laserCloudSurfLast->points[j].x - pointSel.x) +
(laserCloudSurfLast->points[j].y - pointSel.y) *
(laserCloudSurfLast->points[j].y - pointSel.y) +
(laserCloudSurfLast->points[j].z - pointSel.z) *
(laserCloudSurfLast->points[j].z - pointSel.z);
// 如果是同一根scan且距离最近
if (int(laserCloudSurfLast->points[j].intensity) <= closestPointScanID && pointSqDis < minPointSqDis2)
{
minPointSqDis2 = pointSqDis;
minPointInd2 = j;
}
// 如果是其它的线束点
else if (int(laserCloudSurfLast->points[j].intensity) > closestPointScanID && pointSqDis < minPointSqDis3)
{
minPointSqDis3 = pointSqDis;
minPointInd3 = j;
}
}
// 同样的方式 按照降序的方式去找这两个点
for (int j = closestPointInd - 1; j >= 0; --j)
{
if (int(laserCloudSurfLast->points[j].intensity) < (closestPointScanID - NEARBY_SCAN))
break;
double pointSqDis = (laserCloudSurfLast->points[j].x - pointSel.x) *
(laserCloudSurfLast->points[j].x - pointSel.x) +
(laserCloudSurfLast->points[j].y - pointSel.y) *
(laserCloudSurfLast->points[j].y - pointSel.y) +
(laserCloudSurfLast->points[j].z - pointSel.z) *
(laserCloudSurfLast->points[j].z - pointSel.z);
if (int(laserCloudSurfLast->points[j].intensity) >= closestPointScanID && pointSqDis < minPointSqDis2)
{
minPointSqDis2 = pointSqDis;
minPointInd2 = j;
}
else if (int(laserCloudSurfLast->points[j].intensity) < closestPointScanID && pointSqDis < minPointSqDis3)
{
minPointSqDis3 = pointSqDis;
minPointInd3 = j;
}
}
// 如果找到的另外两个点是有效值,就取出它们的3d坐标
if (minPointInd2 >= 0 && minPointInd3 >= 0)
{
// 当前角点
Eigen::Vector3d curr_point(surfPointsFlat->points[i].x,
surfPointsFlat->points[i].y,
surfPointsFlat->points[i].z);
// 上一帧距离当前焦点最近的点
Eigen::Vector3d last_point_a(laserCloudSurfLast->points[closestPointInd].x,
laserCloudSurfLast->points[closestPointInd].y,
laserCloudSurfLast->points[closestPointInd].z);
Eigen::Vector3d last_point_b(laserCloudSurfLast->points[minPointInd2].x,
laserCloudSurfLast->points[minPointInd2].y,
laserCloudSurfLast->points[minPointInd2].z);
Eigen::Vector3d last_point_c(laserCloudSurfLast->points[minPointInd3].x,
laserCloudSurfLast->points[minPointInd3].y,
laserCloudSurfLast->points[minPointInd3].z);
double s;
if (DISTORTION)
s = (surfPointsFlat->points[i].intensity - int(surfPointsFlat->points[i].intensity)) / SCAN_PERIOD;
else
s = 1.0;
// 构建点到面的约束
ceres::CostFunction *cost_function = LidarPlaneFactor::Create(curr_point, last_point_a, last_point_b, last_point_c, s);
problem.AddResidualBlock(cost_function, loss_function, para_q, para_t);
plane_correspondence++;
}
}
}
2.2.7发布激光里程计和角点面点降频发送给后端
// 发布雷达里程计结果
nav_msgs::Odometry laserOdometry;
laserOdometry.header.frame_id = "/map";
laserOdometry.child_frame_id = "/laser_odom";
laserOdometry.header.stamp = ros::Time().fromSec(timeSurfPointsLessFlat);
// 以四元数和平移向量发布出去
laserOdometry.pose.pose.orientation.x = q_w_curr.x();
laserOdometry.pose.pose.orientation.y = q_w_curr.y();
laserOdometry.pose.pose.orientation.z = q_w_curr.z();
laserOdometry.pose.pose.orientation.w = q_w_curr.w();
laserOdometry.pose.pose.position.x = t_w_curr.x();
laserOdometry.pose.pose.position.y = t_w_curr.y();
laserOdometry.pose.pose.position.z = t_w_curr.z();
pubLaserOdometry.publish(laserOdometry);
// 激光里程计路径
geometry_msgs::PoseStamped laserPose;
nav_msgs::Path laserPath;
laserPose.header = laserOdometry.header;
laserPose.pose = laserOdometry.pose.pose;
laserPath.header.stamp = laserOdometry.header.stamp;
laserPath.poses.push_back(laserPose);
laserPath.header.frame_id = "/map";
pubLaserPath.publish(laserPath);
// 一般角点
pcl::PointCloud<PointType>::Ptr laserCloudTemp = cornerPointsLessSharp;
// 上一帧的一般角点
cornerPointsLessSharp = laserCloudCornerLast;
laserCloudCornerLast = laserCloudTemp;
//
laserCloudTemp = surfPointsLessFlat;
surfPointsLessFlat = laserCloudSurfLast;
laserCloudSurfLast = laserCloudTemp;
laserCloudCornerLastNum = laserCloudCornerLast->points.size();
laserCloudSurfLastNum = laserCloudSurfLast->points.size();
// kdtree设置当前帧,用来下一帧lidar odom使用
kdtreeCornerLast->setInputCloud(laserCloudCornerLast);
kdtreeSurfLast->setInputCloud(laserCloudSurfLast);
// 一定降频后给后端发送
if (frameCount % skipFrameNum == 0)
{
frameCount = 0;
// 一般角点
sensor_msgs::PointCloud2 laserCloudCornerLast2;
pcl::toROSMsg(*laserCloudCornerLast, laserCloudCornerLast2);
laserCloudCornerLast2.header.stamp = ros::Time().fromSec(timeSurfPointsLessFlat);
laserCloudCornerLast2.header.frame_id = "/camera";
pubLaserCloudCornerLast.publish(laserCloudCornerLast2);
// 面点
sensor_msgs::PointCloud2 laserCloudSurfLast2;
pcl::toROSMsg(*laserCloudSurfLast, laserCloudSurfLast2);
laserCloudSurfLast2.header.stamp = ros::Time().fromSec(timeSurfPointsLessFlat);
laserCloudSurfLast2.header.frame_id = "/camera";
pubLaserCloudSurfLast.publish(laserCloudSurfLast2);
// 整体点云
sensor_msgs::PointCloud2 laserCloudFullRes3;
pcl::toROSMsg(*laserCloudFullRes, laserCloudFullRes3);
laserCloudFullRes3.header.stamp = ros::Time().fromSec(timeSurfPointsLessFlat);
laserCloudFullRes3.header.frame_id = "/camera";
pubLaserCloudFullRes.publish(laserCloudFullRes3);
}
2.3 scan-map 后端匹配 点云插入地图laserMapping.cpp
2.3.1 传感器数据类型转换成点云 odom转换为eigen类型
// 点云全部转换为pcl的数据格式
laserCloudCornerLast->clear();
pcl::fromROSMsg(*cornerLastBuf.front(), *laserCloudCornerLast);
cornerLastBuf.pop();
laserCloudSurfLast->clear();
pcl::fromROSMsg(*surfLastBuf.front(), *laserCloudSurfLast);
surfLastBuf.pop();
laserCloudFullRes->clear();
pcl::fromROSMsg(*fullResBuf.front(), *laserCloudFullRes);
fullResBuf.pop();
// lidar odom 的结果转成eigen数据格式
q_wodom_curr.x() = odometryBuf.front()->pose.pose.orientation.x;
q_wodom_curr.y() = odometryBuf.front()->pose.pose.orientation.y;
q_wodom_curr.z() = odometryBuf.front()->pose.pose.orientation.z;
q_wodom_curr.w() = odometryBuf.front()->pose.pose.orientation.w;
t_wodom_curr.x() = odometryBuf.front()->pose.pose.position.x;
t_wodom_curr.y() = odometryBuf.front()->pose.pose.position.y;
t_wodom_curr.z() = odometryBuf.front()->pose.pose.position.z;
odometryBuf.pop();
// 考虑到实时性,就把队列其他的都pop出去,不然可能出现处理延时的情况
while (!cornerLastBuf.empty())
{
cornerLastBuf.pop();
printf("普通面点未清空 \n");
}
mBuf.unlock();
2.3.2 根据前端结果 得到后端的初始位姿
// q_wodom_curr t_wodom_curr 是雷达的odom
// q_w_curr t_w_curr是map坐标系下的位姿
q_w_curr = q_wmap_wodom * q_wodom_curr;
t_w_curr = q_wmap_wodom * t_wodom_curr + t_wmap_wodom;
2.3.3根据位置,获得全局地图的中心格子
// 根据初始估计值计算寻找当前位姿在地图中的索引,一个各自边长是50m
// 后端的地图本质上是一个以当前点为中心的一个栅格地图
// 判断在全局栅格的哪一个栅格里,一个栅格是50m 栅格中心是25m
// t_w_curr 是map坐标系下的位姿 centerCubeI网格中心
centerCubeI = int((t_w_curr.x() + 25.0) / 50.0) + laserCloudCenWidth;
centerCubeJ = int((t_w_curr.y() + 25.0) / 50.0) + laserCloudCenHeight;
centerCubeK = int((t_w_curr.z() + 25.0) / 50.0) + laserCloudCenDepth;
// 由于c语言的取整是向0取整 因此如-1.66 成为了-1 但-2才是正确的,因此这里自减1
if (t_w_curr.x() + 25.0 < 0)
centerCubeI--;
if (t_w_curr.y() + 25.0 < 0)
centerCubeJ--;
if (t_w_curr.z() + 25.0 < 0)
centerCubeK--;
2.3.4 根据机器人位置 更新全局地图范围 其它方向雷同
// 如果当前centerCubeI栅格索引小于3,就说明当前点快接近地图边界了,需要进行调整,相当于地图整体往x正方向移动
while (centerCubeI < 3)
{
for (int j = 0; j < laserCloudHeight; j++)
{
for (int k = 0; k < laserCloudDepth; k++)
{
// laserCloudWidth是widtch方向栅格总大小21 laserCloudHeight 21
int i = laserCloudWidth - 1;
// 从x最大值开始
pcl::PointCloud<PointType>::Ptr laserCloudCubeCornerPointer =
// 角点
laserCloudCornerArray[i + laserCloudWidth * j + laserCloudWidth * laserCloudHeight * k];
pcl::PointCloud<PointType>::Ptr laserCloudCubeSurfPointer =
// 面点
laserCloudSurfArray[i + laserCloudWidth * j + laserCloudWidth * laserCloudHeight * k];
// 整体右移
for (; i >= 1; i--)
{
laserCloudCornerArray[i + laserCloudWidth * j + laserCloudWidth * laserCloudHeight * k] =
laserCloudCornerArray[i - 1 + laserCloudWidth * j + laserCloudWidth * laserCloudHeight * k];
laserCloudSurfArray[i + laserCloudWidth * j + laserCloudWidth * laserCloudHeight * k] =
laserCloudSurfArray[i - 1 + laserCloudWidth * j + laserCloudWidth * laserCloudHeight * k];
}
// 此时i=0,也就是最左边的格子赋值了之前最右边的格子
laserCloudCornerArray[i + laserCloudWidth * j + laserCloudWidth * laserCloudHeight * k] =
laserCloudCubeCornerPointer;
laserCloudSurfArray[i + laserCloudWidth * j + laserCloudWidth * laserCloudHeight * k] =
laserCloudCubeSurfPointer;
// 该点云清零,由于是指针操作,相当于最左边的格子清空了
laserCloudCubeCornerPointer->clear();
laserCloudCubeSurfPointer->clear();
}
}
// 索引右移
centerCubeI++;
laserCloudCenWidth++;
}
2.3.5根据全局地图中心 ,提取局部地图每个格子在全局地图中的位置
// 从当前格子为中心,选出地图中一定范围的点云 5*5*3 75个cube
for (int i = centerCubeI - 2; i <= centerCubeI + 2; i++) // 宽度方向
{
for (int j = centerCubeJ - 2; j <= centerCubeJ + 2; j++) // 高度方向
{
for (int k = centerCubeK - 1; k <= centerCubeK + 1; k++) // 深度方向
{
if (i >= 0 && i < laserCloudWidth &&
j >= 0 && j < laserCloudHeight &&
k >= 0 && k < laserCloudDepth)
{
// 把每个格子序号依次存到对应的索引
// i + laserCloudWidth * j 二维度平面位置
// 每个格子在三维全局地图中的位置
laserCloudValidInd[laserCloudValidNum] = i + laserCloudWidth * j + laserCloudWidth * laserCloudHeight * k;
// 局部地图格子数量
laserCloudValidNum++;
laserCloudSurroundInd[laserCloudSurroundNum] = i + laserCloudWidth * j + laserCloudWidth * laserCloudHeight * k;
laserCloudSurroundNum++;
}
}
}
}
2.3.6当前帧 根据每个格子的在全局地图中的id,将局部地图的每个格子角点和面点分别叠加
laserCloudCornerFromMap->clear();
laserCloudSurfFromMap->clear();
// 开始构建用来这一帧优化的小的局部地图 根据上面得到的索引进行叠加求和
for (int i = 0; i < laserCloudValidNum; i++)
{
// 角点叠加
// laserCloudValidInd[i] 每个格子的在全局地图中的位置
*laserCloudCornerFromMap += *laserCloudCornerArray[laserCloudValidInd[i]];
// 面点叠加
*laserCloudSurfFromMap += *laserCloudSurfArray[laserCloudValidInd[i]];
}
2.3.7对当前帧角点面点下采样
// 角点
downSizeFilterCorner.setInputCloud(laserCloudCornerLast);
downSizeFilterCorner.filter(*laserCloudCornerStack);
// 面点
downSizeFilterSurf.setInputCloud(laserCloudSurfLast);
downSizeFilterSurf.filter(*laserCloudSurfStack);
2.3.8点线残差构建 ,这里和前端有区别 ,通过最邻近的5个地图点进行构建协方差矩阵,通过协方差矩阵最大特征值与次大特征值判断是否存在直线
int corner_num = 0;
// 构建角点相关约束
for (int i = 0; i < laserCloudCornerStackNum; i++)
{
// 实时角点 点坐标
pointOri = laserCloudCornerStack->points[i];
// 把雷达点转换到map坐标系
pointAssociateToMap(&pointOri, &pointSel);
// 局部地图中寻找和该点最近的5个点
// pointSearchInd 5个点在局部地图中的索引
kdtreeCornerFromMap->nearestKSearch(pointSel, 5, pointSearchInd, pointSearchSqDis);
// 判断最远的点距离不能超过1m,否则就是无效约束
if (pointSearchSqDis[4] < 1.0)
{
std::vector<Eigen::Vector3d> nearCorners;
Eigen::Vector3d center(0, 0, 0);
for (int j = 0; j < 5; j++)
{
Eigen::Vector3d tmp(laserCloudCornerFromMap->points[pointSearchInd[j]].x,
laserCloudCornerFromMap->points[pointSearchInd[j]].y,
laserCloudCornerFromMap->points[pointSearchInd[j]].z);
// 5个点坐标的叠加
center = center + tmp;
// 转存这5个点给nearCorners
nearCorners.push_back(tmp);
}
// 计算这5个点的均值
center = center / 5.0;
Eigen::Matrix3d covMat = Eigen::Matrix3d::Zero();
// 构建协方差矩阵,5个变量的变化趋势
for (int j = 0; j < 5; j++)
{
// 每个点与均值之间的偏移量
Eigen::Matrix<double, 3, 1> tmpZeroMean = nearCorners[j] - center;
// 该点与该点转置的外积 当前矩阵与当前矩阵的转置 得到3*3的矩阵,当前点的协方差矩阵
covMat = covMat + tmpZeroMean * tmpZeroMean.transpose();
}
// 进行特征值分解
Eigen::SelfAdjointEigenSolver<Eigen::Matrix3d> saes(covMat);
// 根据特征值分解情况看看是不是真正的线特征
// 特征向量就是线特征的方向
Eigen::Vector3d unit_direction = saes.eigenvectors().col(2);
Eigen::Vector3d curr_point(pointOri.x, pointOri.y, pointOri.z);
// 最大特征值大于次大特征值的3倍认为是线特征
if (saes.eigenvalues()[2] > 3 * saes.eigenvalues()[1])
{
Eigen::Vector3d point_on_line = center;
Eigen::Vector3d point_a, point_b;
// 根据拟合出来的线特征方向,以平均点为中心构建两个虚拟点
//从中心点沿着方向向量向两端移动0.1m,使用两个点代替一条直线,
//这样计算点到直线的距离的形式就跟laserOdometry相似
point_a = 0.1 * unit_direction + point_on_line;
point_b = -0.1 * unit_direction + point_on_line;
// 构建约束 和lidar odom 约束一致
ceres::CostFunction *cost_function = LidarEdgeFactor::Create(curr_point, point_a, point_b, 1.0);
problem.AddResidualBlock(cost_function, loss_function, parameters, parameters + 4);
corner_num++;
}
}
}
2.3.9点面残差构建 这里与前端有区别 面的构建通过 最临近当前角点的5个点 通过构建超定方程 qr分解获得的 法向量与点之间的关系
int surf_num = 0;
// 构建面点的约束
for (int i = 0; i < laserCloudSurfStackNum; i++)
{
// 实时面点坐标
pointOri = laserCloudSurfStack->points[i];
// 把雷达点坐标转到map坐标系
pointAssociateToMap(&pointOri, &pointSel);
// 局部地图中搜索距离该点最近的5个点
kdtreeSurfFromMap->nearestKSearch(pointSel, 5, pointSearchInd, pointSearchSqDis);
Eigen::Matrix<double, 5, 3> matA0;
Eigen::Matrix<double, 5, 1> matB0 = -1 * Eigen::Matrix<double, 5, 1>::Ones();
// 构建面点方程ax+by+cz+d=0
// 通过构建一个超定方程求解这个平面方程
// 判断最远的点距离不能超过1m,否则就是无效约束
if (pointSearchSqDis[4] < 1.0)
{
for (int j = 0; j < 5; j++)
{
matA0(j, 0) = laserCloudSurfFromMap->points[pointSearchInd[j]].x;
matA0(j, 1) = laserCloudSurfFromMap->points[pointSearchInd[j]].y;
matA0(j, 2) = laserCloudSurfFromMap->points[pointSearchInd[j]].z;
}
// 通过eigen接口求解该方程,解就是这个平面的法向量
// 豪斯霍尔德变换
Eigen::Vector3d norm = matA0.colPivHouseholderQr().solve(matB0);
double negative_OA_dot_norm = 1 / norm.norm();
// 法向量归一化
norm.normalize();
bool planeValid = true;
// 根据求出来的平面方程进行校验 看看是不是符合平面约束
for (int j = 0; j < 5; j++)
{
// 这里相当于求解点到平面的距离
if (fabs(norm(0) * laserCloudSurfFromMap->points[pointSearchInd[j]].x +
norm(1) * laserCloudSurfFromMap->points[pointSearchInd[j]].y +
norm(2) * laserCloudSurfFromMap->points[pointSearchInd[j]].z + negative_OA_dot_norm) > 0.2)
{
planeValid = false; // 点如果距离平面过远,就认为这是一个拟合的不好的平面
break;
}
}
Eigen::Vector3d curr_point(pointOri.x, pointOri.y, pointOri.z);
// 如果平面有效就构建平面约束
if (planeValid)
{
// 利用平面方程构建约束 和前端构建形式稍有不同
ceres::CostFunction *cost_function = LidarPlaneNormFactor::Create(curr_point, norm, negative_OA_dot_norm);
problem.AddResidualBlock(cost_function, loss_function, parameters, parameters + 4);
surf_num++;
}
2.3.10通过反变换更新odom-》map的tf关系
// q_wmap_wodom t_wmap_wodom是map到odom之间的关系
q_wmap_wodom = q_w_curr * q_wodom_curr.inverse();
t_wmap_wodom = t_w_curr - q_wmap_wodom * t_wodom_curr;
2.3.11将优化后的当前帧角点加入到局部地图,面点雷同
for (int i = 0; i < laserCloudCornerStackNum; i++)
{
// 该点根据位姿投到地图坐标系
pointAssociateToMap(&laserCloudCornerStack->points[i], &pointSel);
// 算出这个点所在的格子在全局地图中的索引
int cubeI = int((pointSel.x + 25.0) / 50.0) + laserCloudCenWidth;
int cubeJ = int((pointSel.y + 25.0) / 50.0) + laserCloudCenHeight;
int cubeK = int((pointSel.z + 25.0) / 50.0) + laserCloudCenDepth;
// 同样负数做对应的操作
if (pointSel.x + 25.0 < 0)
cubeI--;
if (pointSel.y + 25.0 < 0)
cubeJ--;
if (pointSel.z + 25.0 < 0)
cubeK--;
// 如果超过边界的话就算了
if (cubeI >= 0 && cubeI < laserCloudWidth &&
cubeJ >= 0 && cubeJ < laserCloudHeight &&
cubeK >= 0 && cubeK < laserCloudDepth)
{
// 当前格子在全局地图中的索引
int cubeInd = cubeI + laserCloudWidth * cubeJ + laserCloudWidth * laserCloudHeight * cubeK;
// 将当前帧点云角点插入到角点格子中
laserCloudCornerArray[cubeInd]->push_back(pointSel);
}
}
2.3.12把当前帧涉及到的局部地图下采样
for (int i = 0; i < laserCloudValidNum; i++)
{
int ind = laserCloudValidInd[i];
pcl::PointCloud<PointType>::Ptr tmpCorner(new pcl::PointCloud<PointType>());
downSizeFilterCorner.setInputCloud(laserCloudCornerArray[ind]);
downSizeFilterCorner.filter(*tmpCorner);
laserCloudCornerArray[ind] = tmpCorner;
pcl::PointCloud<PointType>::Ptr tmpSurf(new pcl::PointCloud<PointType>());
downSizeFilterSurf.setInputCloud(laserCloudSurfArray[ind]);
downSizeFilterSurf.filter(*tmpSurf);
laserCloudSurfArray[ind] = tmpSurf;
}
2.3.13局部地图发布
// 每隔5帧对外发布一下
if (frameCount % 5 == 0)
{
laserCloudSurround->clear();
// 把当前帧相关的局部地图发布出去 laserCloudSurroundNum 坐标点的索引数目
for (int i = 0; i < laserCloudSurroundNum; i++)
{
int ind = laserCloudSurroundInd[i];
*laserCloudSurround += *laserCloudCornerArray[ind];
*laserCloudSurround += *laserCloudSurfArray[ind];
}
sensor_msgs::PointCloud2 laserCloudSurround3;
pcl::toROSMsg(*laserCloudSurround, laserCloudSurround3);
laserCloudSurround3.header.stamp = ros::Time().fromSec(timeLaserOdometry);
laserCloudSurround3.header.frame_id = "/map";
pubLaserCloudSurround.publish(laserCloudSurround3);
}
2.3.14全局地图发布文章来源:https://www.toymoban.com/news/detail-682387.html
// 每隔20帧发布一次全局地图
if (frameCount % 20 == 0)
{
// 21*21*11=4851
pcl::PointCloud<PointType> laserCloudMap;
for (int i = 0; i < 4851; i++)
{
laserCloudMap += *laserCloudCornerArray[i];
laserCloudMap += *laserCloudSurfArray[i];
}
sensor_msgs::PointCloud2 laserCloudMsg;
pcl::toROSMsg(laserCloudMap, laserCloudMsg);
laserCloudMsg.header.stamp = ros::Time().fromSec(timeLaserOdometry);
laserCloudMsg.header.frame_id = "/map";
pubLaserCloudMap.publish(laserCloudMsg);
}
2.3.15全局位姿,轨迹 tf 发布文章来源地址https://www.toymoban.com/news/detail-682387.html
// 发布当前位姿
nav_msgs::Odometry odomAftMapped;
odomAftMapped.header.frame_id = "/map";
odomAftMapped.child_frame_id = "/laser_link";
odomAftMapped.header.stamp = ros::Time().fromSec(timeLaserOdometry);
odomAftMapped.pose.pose.orientation.x = q_w_curr.x();
odomAftMapped.pose.pose.orientation.y = q_w_curr.y();
odomAftMapped.pose.pose.orientation.z = q_w_curr.z();
odomAftMapped.pose.pose.orientation.w = q_w_curr.w();
odomAftMapped.pose.pose.position.x = t_w_curr.x();
odomAftMapped.pose.pose.position.y = t_w_curr.y();
odomAftMapped.pose.pose.position.z = t_w_curr.z();
pubOdomAftMapped.publish(odomAftMapped);
// 发布当前轨迹
geometry_msgs::PoseStamped laserAfterMappedPose;
laserAfterMappedPose.header = odomAftMapped.header;
laserAfterMappedPose.pose = odomAftMapped.pose.pose;
laserAfterMappedPath.header.stamp = odomAftMapped.header.stamp;
laserAfterMappedPath.header.frame_id = "/map";
laserAfterMappedPath.poses.push_back(laserAfterMappedPose);
pubLaserAfterMappedPath.publish(laserAfterMappedPath);
// 发布tf
static tf::TransformBroadcaster br;
tf::Transform transform;
tf::Quaternion q;
transform.setOrigin(tf::Vector3(t_w_curr(0),
t_w_curr(1),
t_w_curr(2)));
q.setW(q_w_curr.w());
q.setX(q_w_curr.x());
q.setY(q_w_curr.y());
q.setZ(q_w_curr.z());
transform.setRotation(q);
br.sendTransform(tf::StampedTransform(transform, odomAftMapped.header.stamp, "/map", "/laser_link"));
到了这里,关于3d激光slam建图与定位(2)_aloam代码阅读的文章就介绍完了。如果您还想了解更多内容,请在右上角搜索TOY模板网以前的文章或继续浏览下面的相关文章,希望大家以后多多支持TOY模板网!