目录
1--颜色分类(75)
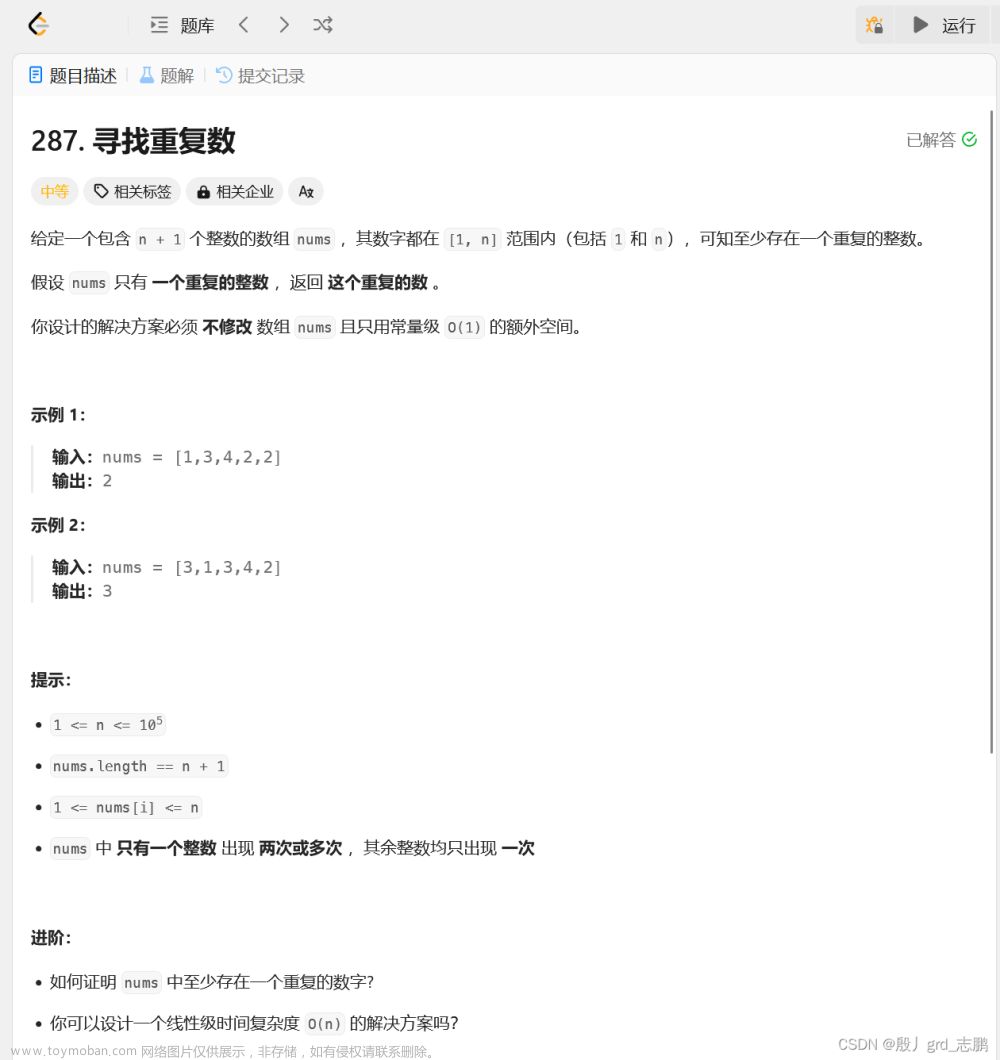
2--最小覆盖子串(76)
3--子集(78)
4--单词搜索(79)
5--柱状图中最大的矩形(84)
6--最大矩形(85)
7--二叉树的中序遍历(94)
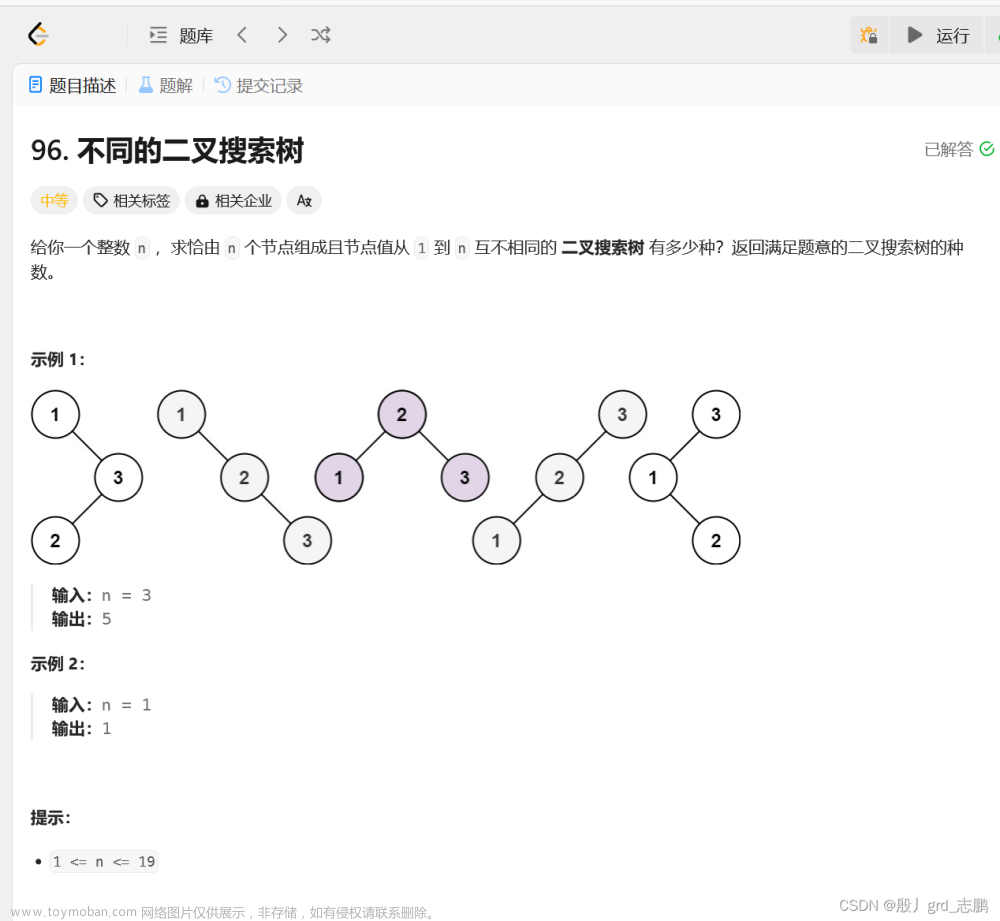
8--不同的二叉搜索数(96)
9--验证二叉搜索树(96)
10--对称二叉树(101)
1--颜色分类(75)

主要思路:文章来源:https://www.toymoban.com/news/detail-683423.html
快排
#include <iostream>
#include <vector>
class Solution {
public:
void sortColors(std::vector<int>& nums) {
quicksort(nums, 0, nums.size()-1);
}
void quicksort(std::vector<int>& nums, int left, int right){
if(left >= right) return;
int pivot = nums[left];
int l = left, r = right;
while(l < r){
while(l < r && nums[r] >= pivot) r--;
nums[l] = nums[r];
while(l < r && nums[l] <= pivot) l++;
nums[r] = nums[l];
}
nums[l] = pivot;
quicksort(nums, left, l-1);
quicksort(nums, l+1, right);
}
};
int main(int argc, char *argv[]){
// nums = [2,0,2,1,1,0]
std::vector<int> test = {2, 0, 2, 1, 1, 0};
Solution S1;
S1.sortColors(test);
for(auto item : test){
std::cout << item << " ";
}
return 0;
}主要思路:
#include <iostream>
#include <vector>
class Solution {
public:
void sortColors(std::vector<int>& nums) {
int n = nums.size();
int p0 = 0, p2 = n - 1;
for (int i = 0; i <= p2; ++i) {
while (i <= p2 && nums[i] == 2) {
std::swap(nums[i], nums[p2]);
--p2;
}
if (nums[i] == 0) {
std::swap(nums[i], nums[p0]);
++p0;
}
}
}
};
int main(int argc, char *argv[]){
// nums = [2,0,2,1,1,0]
std::vector<int> test = {2, 0, 2, 1, 1, 0};
Solution S1;
S1.sortColors(test);
for(auto item : test){
std::cout << item << " ";
}
return 0;
}2--最小覆盖子串(76)

主要思路:
参考思路:视频讲解
#include <iostream>
#include <string>
#include <unordered_map>
class Solution {
public:
std::unordered_map<char, int> t_map;
std::unordered_map<char, int> min_map;
public:
std::string minWindow(std::string s, std::string t) {
if(s.length() < t.length()) return "";
for(int i = 0; i < t.length(); i++){
if(t_map.find(t[i]) == t_map.end()) t_map[t[i]] = 1;
else t_map[t[i]] += 1;
}
int l = 0, r = 0;
int min_l = 0, min_len = s.length() + 1;
while(r < s.length()){
if(min_map.find(s[r]) == min_map.end()) min_map[s[r]] = 1;
else min_map[s[r]] += 1;
while(check()){
if(r - l + 1 < min_len){
min_l = l;
min_len = r - l + 1;
}
min_map[s[l]]--;
l++; // 左指针右移
}
r++;
}
return min_len == s.length() + 1 ? "" : s.substr(min_l, min_len);
}
bool check(){
if(t_map.size() > min_map.size()) return false;
for(auto kv : t_map){
char key = kv.first;
int value = kv.second;
if(min_map.find(key) == min_map.end() || min_map[key] < t_map[key]){
return false;
}
}
return true;
}
};
int main(int argc, char *argv[]){
// s = "ADOBECODEBANC", t = "ABC"
std::string s = "ADOBECODEBANC";
std::string t = "ABC";
Solution S1;
std::string res = S1.minWindow(s, t);
std::cout << res << std::endl;
return 0;
}3--子集(78)

主要思路:
整体思路有点类似全排列,对于数组中的元素,加入(递归)或不加入(回溯)到记录数组中;
不同于全排列的是,本题 dfs 的时候不需要重头遍历所有元素,整个加入过程是前向的;
#include <iostream>
#include <vector>
class Solution {
public:
std::vector<std::vector<int>> subsets(std::vector<int>& nums) {
std::vector<int> tmp;
res.push_back(tmp); // []
dfs(nums, 0, tmp);
return res;
}
void dfs(std::vector<int>& nums, int idx, std::vector<int>& tmp){
if(idx == nums.size()) {
return;
}
tmp.push_back(nums[idx]); // 加入当前的值
res.push_back(tmp);
dfs(nums, idx+1, tmp);
tmp.pop_back(); // 回溯剔出当前加入的值
dfs(nums, idx+1, tmp);
return;
}
private:
std::vector<std::vector<int>> res;
};
int main(int arc, char *argv[]){
std::vector<int> test = {1, 2, 3};
Solution S1;
std::vector<std::vector<int>> res = S1.subsets(test);
for(auto v : res){
std::cout << "[";
for(int item : v){
std::cout << item << " ";
}
std::cout << "]" << std::endl;
}
return 0;
}4--单词搜索(79)

主要思路:
递归+回溯,遍历从board[i][j]出发,能否匹配给定的字符串;
需要使用一个记录数组来标记当前 board[i][j] 是否被访问,回溯时还原访问状态;
#include <iostream>
#include <vector>
#include <string>
class Solution {
public:
bool exist(std::vector<std::vector<char>>& board, std::string word) {
int m = board.size(), n = board[0].size();
std::vector<std::vector<bool>> vis(m, std::vector<bool>(n, false));
bool res;
for(int i = 0; i < m; i++){
for(int j = 0; j < n; j++){
res = dfs(i, j, 0, board, word, vis);
if(res) return true;
}
}
return false;
}
bool dfs(int i, int j, int cur, std::vector<std::vector<char>>& board, std::string word, std::vector<std::vector<bool>>& vis){
if(cur == word.length()) return true;
if(i >= board.size() || j >= board[0].size() || i < 0 || j < 0 || board[i][j] != word[cur] || vis[i][j] == true){
return false;
}
vis[i][j] = true;
bool res = dfs(i+1, j, cur+1, board, word, vis) || dfs(i, j+1, cur+1, board, word, vis)
|| dfs(i-1, j, cur+1, board, word, vis) || dfs(i, j-1, cur+1, board, word, vis);
vis[i][j] = false; // 回溯
return res;
}
};
int main(int arc, char *argv[]){
// board = [["A","B","C","E"],["S","F","C","S"],["A","D","E","E"]]
// word = "ABCCED"
std::vector<std::vector<char>> board = {{'A', 'B', 'C', 'E'},
{'S', 'F', 'C', 'S'},
{'A', 'D', 'E', 'E'}};
std::string word = "ABCCED";
Solution S1;
bool res = S1.exist(board, word);
if(res) std::cout << "true" << std::endl;
else std::cout << "false" << std::endl;
return 0;
}5--柱状图中最大的矩形(84)

主要思路:
对于每一根柱子 i,找到最左边比它高度低的柱子,记为 left[i],同理找到最右边比它高度低的柱子,记为 right[i];则对于该柱子而言,最大面积为(right[i] - left[i] - 1)* height[i];
问题的关键是如何找到左右两边第一个矮柱子,只需要维护一个单调栈即可;
#include <iostream>
#include <vector>
#include <stack>
class Solution {
public:
int largestRectangleArea(std::vector<int>& heights) {
std::vector<int>left(heights.size(), 0), right(heights.size(), 0);
std::stack<int> stk1;
for(int i = 0; i < heights.size(); i++){
// 找到左边第一个比 heights[i] 小的柱子
while(!stk1.empty() && heights[stk1.top()] >= heights[i]){
stk1.pop();
}
left[i] = stk1.empty()? -1 : stk1.top();
stk1.push(i);
}
std::stack<int> stk2;
for(int i = heights.size() - 1; i >= 0; i--){
// 找到右边第一个比 heights[i] 小的柱子
while(!stk2.empty() && heights[stk2.top()] >= heights[i]){
stk2.pop();
}
right[i] = stk2.empty()? heights.size(): stk2.top();
stk2.push(i);
}
// 遍历计算最大面积
int max = 0;
for(int i = 0; i < heights.size(); i++){
max = std::max(max, (right[i] - left[i] - 1)*heights[i]);
}
return max;
}
};
int main(int argc, char* argv[]){
std::vector<int> test = {2, 1, 5, 6, 2, 3};
Solution S1;
int res = S1.largestRectangleArea(test);
std::cout << res << std::endl;
return 0;
}6--最大矩形(85)

主要思路:
遍历每一行,以当前行为底,将列看成柱子,遍历每一根柱子,类似于上题,寻找基于该柱子的最大矩形(利用单调栈向左向右寻找比当前柱子矮的边界);
更新每一行的柱子高度,当当前行的值为1时,当前行的柱子高度为上一行数字高度 + 1;当当前行的值为0时,当前行的柱子高度为0;
#include <iostream>
#include <vector>
#include <stack>
class Solution {
public:
int maximalRectangle(std::vector<std::vector<char>>& matrix) {
int n = matrix.size();
if(n == 0) return 0;
int m = matrix[0].size();
if(m == 0) return 0;
int max = 0;
std::vector<int> pre(m, 0); // 上一行的柱状高度
std::vector<int> cur(m, 0); // 当前行的柱状高度
// 第 r 行为底
for(int r = 0; r < n; r++){
for(int c = 0; c < m; c++){
// 更新当前行的柱子高度
if(matrix[r][c] == '0') cur[c] = 0;
else cur[c] = pre[c] + 1;
}
std::vector<int>left(m, 0), right(m, 0); // 左右边界
// 遍历寻找第c列柱子的左边界,并记录在left数组中
std::stack<int> stk1;
for(int c = 0; c < m; c++){
while(!stk1.empty() && cur[stk1.top()] >= cur[c]){
stk1.pop();
}
left[c] = stk1.empty()? -1 : stk1.top();
stk1.push(c);
}
// 遍历寻找第c列柱子的右边界,并记录在right数组中
std::stack<int> stk2;
for(int c = m - 1; c >= 0; c--){
// 找到右边第一个比 heights[i] 小的柱子
while(!stk2.empty() && cur[stk2.top()] >= cur[c]){
stk2.pop();
}
right[c] = stk2.empty()? m: stk2.top();
stk2.push(c);
}
// 计算最大矩形
for(int c = 0; c < m; c++){
max = std::max(max, (right[c] - left[c] - 1)*cur[c]);
}
pre = cur; // 对于下一行 r + 1来说,上一行的柱子高度 pre 等于第 r 的柱子高度 cur
}
return max;
}
};
int main(int argc, char* argv[]){
// matrix = [["1","0","1","0","0"],["1","0","1","1","1"],
// ["1","1","1","1","1"],["1","0","0","1","0"]]
std::vector<std::vector<char>> test = {{'1', '0', '1', '0', '0'},
{'1', '0', '1', '1', '1'},
{'1', '1', '1', '1', '1'},
{'1', '0', '0', '1', '0'}};
Solution S1;
int res = S1.maximalRectangle(test);
std::cout << res << std::endl;
return 0;
}7--二叉树的中序遍历(94)

主要思路:
经典中序遍历
#include <iostream>
#include <vector>
#include <algorithm>
struct TreeNode {
int val;
TreeNode *left;
TreeNode *right;
TreeNode() : val(0), left(nullptr), right(nullptr) {}
TreeNode(int x) : val(x), left(nullptr), right(nullptr) {}
TreeNode(int x, TreeNode *left, TreeNode *right) : val(x), left(left), right(right) {}
};
class Solution {
public:
std::vector<int> inorderTraversal(TreeNode* root) {
std::vector<int> res;
dfs(root, res);
return res;
}
void dfs(TreeNode* root, std::vector<int>& res){
if(root == nullptr) return;
dfs(root->left, res);
res.push_back(root->val);
dfs(root->right, res);
}
};
int main(int argc, char* argv[]){
TreeNode *Node1 = new TreeNode(1);
TreeNode *Node2 = new TreeNode(2);
TreeNode *Node3 = new TreeNode(3);
Node1->right = Node2;
Node2->left = Node3;
Solution S1;
std::vector<int> res = S1.inorderTraversal(Node1);
for(auto v : res) std::cout << v << " ";
std::cout << std::endl;
return 0;
}8--不同的二叉搜索数(96)

主要思路:
基于动态规划,定义状态 dp[i] 表示由 i 个数字构成的不同二叉搜索树的数目;
对于 i 个数字,选定不同的数字 head 作为根节点,则左子树的节点数为 head - 1,对应的二叉搜索树数目为 dp[head - 1],右子树的节点数为 i - head,对应的二叉搜索树数目为 dp[i - head];
状态转移方程:dp[i] += dp[head - 1] * dp[i - head];
#include <iostream>
#include <vector>
class Solution {
public:
int numTrees(int n) {
// dp[i]表示由i个数字构成的不同二叉搜索树的数目
std::vector<int> dp(n+1, 0);
dp[0] = 1; // 边界条件
for(int i = 1; i <= n; i++){
// 从i个数字中选一个作为根节点
for(int head = 1; head <= i; head++){
// 由于二叉搜索树的左子树节点都比根节点小,则左子树的节点数为head-1
// 由于二叉搜索树的右子树节点都比根节点大,则右子树的节点数为i-head
dp[i] += dp[head - 1] * dp[i - head]; // 不同根节点的二叉搜索树求和
}
}
return dp[n];
}
};
int main(int argc, char* argv[]){
int n = 3;
Solution S1;
int res = S1.numTrees(n);
std::cout << res << std::endl;
return 0;
}9--验证二叉搜索树(96)

主要思路:
深度优先,递归判断子树是否符合二叉搜索树;
这道题的关键是如何确保子树的所有节点都大于根节点或者小于根节点,需要借助两个变量:最大值和最小值,在递归的过程中更新最大值和最小值;
#include <iostream>
#include <limits.h>
struct TreeNode {
int val;
TreeNode *left;
TreeNode *right;
TreeNode() : val(0), left(nullptr), right(nullptr) {}
TreeNode(int x) : val(x), left(nullptr), right(nullptr) {}
TreeNode(int x, TreeNode *left, TreeNode *right) : val(x), left(left), right(right) {}
};
class Solution {
public:
bool isValidBST(TreeNode* root) {
bool res = dfs(root, LONG_MIN, LONG_MAX);
return res;
}
bool dfs(TreeNode* root, long long min, long long max){
if(root == nullptr) return true;
if(root->val <= min || root->val >= max) return false;
return dfs(root->left, min, root->val) && dfs(root->right, root->val, max);
}
};
int main(int argc, char* argv[]){
TreeNode* Node1 = new TreeNode(1);
TreeNode* Node2 = new TreeNode(2);
TreeNode* Node3 = new TreeNode(3);
Node2->left = Node1;
Node2->right = Node3;
Solution S1;
bool res = S1.isValidBST(Node2);
if(res) std::cout << "true" << std::endl;
else std::cout << "false" << std::endl;
return 0;
}10--对称二叉树(101)

主要思路:
递归判断左树的左子树与右树的右子树,以及左树的右子树与右树的左子树是否相等;文章来源地址https://www.toymoban.com/news/detail-683423.html
#include <iostream>
#include <stack>
struct TreeNode {
int val;
TreeNode *left;
TreeNode *right;
TreeNode() : val(0), left(nullptr), right(nullptr) {}
TreeNode(int x) : val(x), left(nullptr), right(nullptr) {}
TreeNode(int x, TreeNode *left, TreeNode *right) : val(x), left(left), right(right) {}
};
class Solution {
public:
bool isSymmetric(TreeNode* root) {
if(root == nullptr) return true;
bool res = dfs(root->left, root->right);
return res;
}
bool dfs(TreeNode *Tree1, TreeNode *Tree2){
if(Tree1 == nullptr && Tree2 == nullptr) return true;
if((Tree1 == nullptr && Tree2 != nullptr) ||
(Tree1 != nullptr && Tree2 == nullptr)) return false;
if(Tree1->val != Tree2->val) return false;
return dfs(Tree1->left, Tree2->right) && dfs(Tree1->right, Tree2->left);
}
};
int main(int argc, char* argv[]){
TreeNode *Node1 = new TreeNode(1);
TreeNode *Node2 = new TreeNode(2);
TreeNode *Node3 = new TreeNode(2);
TreeNode *Node4 = new TreeNode(3);
TreeNode *Node5 = new TreeNode(4);
TreeNode *Node6 = new TreeNode(4);
TreeNode *Node7 = new TreeNode(3);
Node1->left = Node2;
Node1->right = Node3;
Node2->left = Node4;
Node2->right = Node5;
Node3->left = Node6;
Node3->right = Node7;
Solution S1;
bool res = S1.isSymmetric(Node1);
if(res) std::cout << "true" << std::endl;
else std::cout << "false" << std::endl;
return 0;
}到了这里,关于Leetcode刷题笔记--Hot31-40的文章就介绍完了。如果您还想了解更多内容,请在右上角搜索TOY模板网以前的文章或继续浏览下面的相关文章,希望大家以后多多支持TOY模板网!