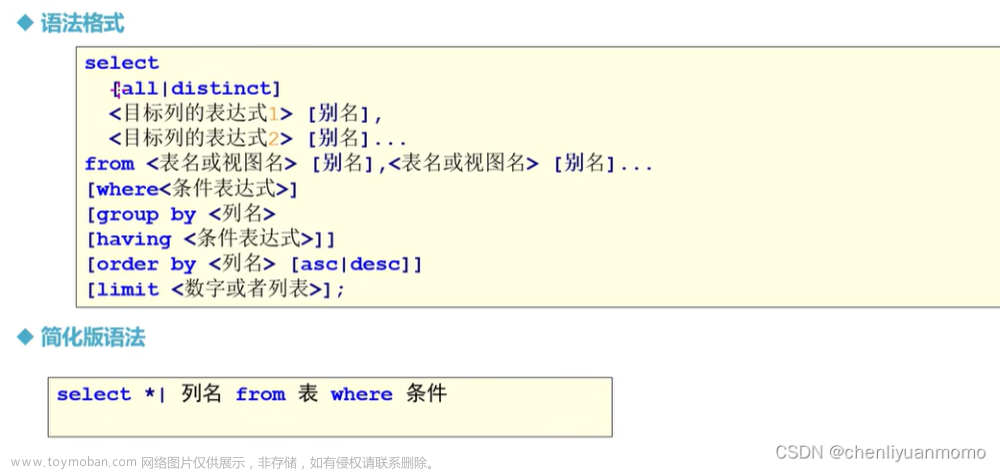
目录
Create
insert
插入跟新 1
插入跟新 2
Retrive
select
where 子句查询
1.查找数学成绩小于 80 的同学。
2.查询数学成绩等于90分的同学。
3.查询总分大于240 的学生
4.查询空值或者非空值
5.查询语文成绩在70~80之间的同学
6.查询英语成绩是99 和 93 和 19 和 30
7.模糊匹配
排序
LIMIT
mysql 的基本操作就是:CURD
-
Create(创建)
-
Retrive(读取)
-
Update(跟新)
-
Delete(删除)
Create
insert
这里就对应的是表数据的操作,而不是表结构的操作,这里的 create 也表示的是插入也就是 insert
insert [into]
table_name [(column, ...)]
values(value_list), [(value_list)], ...
value_list: value, [value, ][... ,]上面就是插入的语法,还是直接看一下插入示例:
mysql> create table exam_result(
-> id int primary key auto_increment,
-> name varchar(12) not null,
-> chinese tinyint unsigned,
-> math tinyint unsigned,
-> engilsh tinyint unsigned
-> );
Query OK, 0 rows affected (0.01 sec)
mysql> desc exam_result;
+---------+---------------------+------+-----+---------+----------------+
| Field | Type | Null | Key | Default | Extra |
+---------+---------------------+------+-----+---------+----------------+
| id | int(11) | NO | PRI | NULL | auto_increment |
| name | varchar(12) | NO | | NULL | |
| chinese | tinyint(3) unsigned | YES | | NULL | |
| math | tinyint(3) unsigned | YES | | NULL | |
| engilsh | tinyint(3) unsigned | YES | | NULL | |
+---------+---------------------+------+-----+---------+----------------+
5 rows in set (0.00 sec)上面是创建一张表,考试成绩表,下面插入数据:
首先介绍一下语法:
-
into 是可以有也可以没有,但是为了语法的完整性,还是带上比较好。
-
表名后面跟的是想要插入的列名,如果没有写表示全列插入。
-
values 后面表示要插入的值,插入值的顺序要和表明后面的顺序相同,如果没有写,那么就要按照表里面的值的顺序来插入。
-
插入不仅可以插入一行记录,也可以插入多行记录,插入插入多行数据的话要用逗号隔开。
mysql> insert into exam_result (id, name, chinese, math, english) values (1, '林黛玉', 98, 90, 99);
Query OK, 1 row affected (0.00 sec)
mysql> select * from exam_result;
+----+-----------+---------+------+---------+
| id | name | chinese | math | english |
+----+-----------+---------+------+---------+
| 1 | 林黛玉 | 98 | 90 | 99 |
+----+-----------+---------+------+---------+
1 row in set (0.00 sec)上面没有省略,插入成功,下面我们省略表明后面的列名,全列插入:
mysql> insert into exam_result values (2, '沙和尚', 77, 87, 72);
Query OK, 1 row affected (0.00 sec)
mysql> select * from exam_result;
+----+-----------+---------+------+---------+
| id | name | chinese | math | english |
+----+-----------+---------+------+---------+
| 1 | 林黛玉 | 98 | 90 | 99 |
| 2 | 沙和尚 | 77 | 87 | 72 |
+----+-----------+---------+------+---------+
2 rows in set (0.00 sec)全列插入就不能省略,这个也插入成功了,下面试一下全列插入:
mysql> insert into exam_result(name, chinese, math, english) values ('薛宝钗', 88, 90, 88), ('赵姨娘', 79, 90, 93), ('唐三藏', 72, 60, 56);
Query OK, 3 rows affected (0.00 sec)
Records: 3 Duplicates: 0 Warnings: 0
mysql> select * from exam_result;
+----+-----------+---------+------+---------+
| id | name | chinese | math | english |
+----+-----------+---------+------+---------+
| 1 | 林黛玉 | 98 | 90 | 99 |
| 2 | 沙和尚 | 77 | 87 | 72 |
| 3 | 薛宝钗 | 88 | 90 | 88 |
| 4 | 赵姨娘 | 79 | 90 | 93 |
| 5 | 唐三藏 | 72 | 60 | 56 |
+----+-----------+---------+------+---------+
5 rows in set (0.00 sec)上面就插入完成了。
插入跟新 1
insert ... on duplicate key update 列名 = value, ...再插入了之后有可能会插入失败,也就是里面的唯一键或者主键有重复等情况所以如果有重复插入失败的话就跟新里面的值。
mysql> insert into exam_result values (2, '沙和尚', 77, 87, 72) on duplicate key update id = 6, name = '沙悟净', chinese = 77, math = 87, english = 72;
Query OK, 2 rows affected (0.00 sec)
mysql> select * from exam_result;
+----+-----------+---------+------+---------+
| id | name | chinese | math | english |
+----+-----------+---------+------+---------+
| 1 | 林黛玉 | 98 | 90 | 99 |
| 3 | 薛宝钗 | 88 | 90 | 88 |
| 4 | 赵姨娘 | 79 | 90 | 93 |
| 5 | 唐三藏 | 72 | 60 | 56 |
| 6 | 沙悟净 | 77 | 87 | 72 |
+----+-----------+---------+------+---------+
5 rows in set (0.00 sec)而跟新后的值也是自己设定的。
插入跟新 2
mysql> replace into exam_result (id, name, chinese, math, english) values(7, '白龙马', 90, 46, 50);
Query OK, 1 row affected (0.00 sec)
mysql> select * from exam_result;
+----+-----------+---------+------+---------+
| id | name | chinese | math | english |
+----+-----------+---------+------+---------+
| 1 | 林黛玉 | 98 | 90 | 99 |
| 3 | 薛宝钗 | 88 | 90 | 88 |
| 4 | 赵姨娘 | 79 | 90 | 93 |
| 5 | 唐三藏 | 72 | 60 | 56 |
| 6 | 沙悟净 | 77 | 87 | 72 |
| 7 | 白龙马 | 90 | 46 | 50 |
+----+-----------+---------+------+---------+
6 rows in set (0.00 sec)这个语法就是如果没有重复那么就是插入,如果有重复就讲重复替换。
下面看一下重复后替换:
mysql> replace into exam_result (id, name, chinese, math, english) values(7, '小白龙', 99, 20, 19);
Query OK, 2 rows affected (0.00 sec)
mysql> select * from exam_result;
+----+-----------+---------+------+---------+
| id | name | chinese | math | english |
+----+-----------+---------+------+---------+
| 1 | 林黛玉 | 98 | 90 | 99 |
| 3 | 薛宝钗 | 88 | 90 | 88 |
| 4 | 赵姨娘 | 79 | 90 | 93 |
| 5 | 唐三藏 | 72 | 60 | 56 |
| 6 | 沙悟净 | 77 | 87 | 72 |
| 7 | 小白龙 | 99 | 20 | 19 |
+----+-----------+---------+------+---------+
6 rows in set (0.00 sec)下面就是重复后替换。
Retrive
select
select 是mysql 里面最常用的一个,下面看一下查询。
查询全部数据:
select [表达式][列名] from table_name;简单查询的语法下面看一下:
mysql> select * from exam_result;
+----+-----------+---------+------+---------+
| id | name | chinese | math | english |
+----+-----------+---------+------+---------+
| 1 | 林黛玉 | 98 | 90 | 99 |
| 3 | 薛宝钗 | 88 | 90 | 88 |
| 4 | 赵姨娘 | 79 | 90 | 93 |
| 5 | 唐三藏 | 72 | 60 | 56 |
| 6 | 沙悟净 | 77 | 87 | 72 |
| 7 | 小白龙 | 99 | 20 | 19 |
+----+-----------+---------+------+---------+
6 rows in set (0.00 sec)想要查询所有的数据就是 select * ,但是如果数据库里面数据量太大的话, select * 传输的数据太大,所以不适合 select * 查询,但是如果在自己的数据库里面,那么就是无所谓的。
select 不光能查询表里面的数据,还可以在后面输入表达式:
mysql> select 1 + 1;
+-------+
| 1 + 1 |
+-------+
| 2 |
+-------+
1 row in set (0.00 sec)
mysql> select NULL;
+------+
| NULL |
+------+
| NULL |
+------+
1 row in set (0.00 sec)
mysql> select database();
+------------+
| database() |
+------------+
| CURD |
+------------+
1 row in set (0.00 sec)select 后面还可以跟函数。
下面看一下select 查询表里面的数据:
mysql> select id, name, chinese, math, english from exam_result;
+----+-----------+---------+------+---------+
| id | name | chinese | math | english |
+----+-----------+---------+------+---------+
| 1 | 林黛玉 | 98 | 90 | 99 |
| 3 | 薛宝钗 | 88 | 90 | 88 |
| 4 | 赵姨娘 | 79 | 90 | 93 |
| 5 | 唐三藏 | 72 | 60 | 56 |
| 6 | 沙悟净 | 77 | 87 | 72 |
| 7 | 小白龙 | 99 | 20 | 19 |
+----+-----------+---------+------+---------+
6 rows in set (0.00 sec)也可以这样查询表里面的数据,也可以改变查询的内容:
mysql> select name, id from exam_result;
+-----------+----+
| name | id |
+-----------+----+
| 林黛玉 | 1 |
| 薛宝钗 | 3 |
| 赵姨娘 | 4 |
| 唐三藏 | 5 |
| 沙悟净 | 6 |
| 小白龙 | 7 |
+-----------+----+
6 rows in set (0.01 sec)既然 select 后面可以计算,那么也可以计算,下面可以算一下他们的总分:
mysql> select name, chinese, math, english, chinese+math+english from exam_result;
+-----------+---------+------+---------+----------------------+
| name | chinese | math | english | chinese+math+english |
+-----------+---------+------+---------+----------------------+
| 林黛玉 | 98 | 90 | 99 | 287 |
| 薛宝钗 | 88 | 90 | 88 | 266 |
| 赵姨娘 | 79 | 90 | 93 | 262 |
| 唐三藏 | 72 | 60 | 56 | 188 |
| 沙悟净 | 77 | 87 | 72 | 236 |
| 小白龙 | 99 | 20 | 19 | 138 |
+-----------+---------+------+---------+----------------------+
6 rows in set (0.00 sec)但是这里看到输出出来的数据不好看,其实 myslq 也可以重命名的:
... as new_namemysql> select name, chinese, math, english, chinese+math+english as 总分 from exam_result;
+-----------+---------+------+---------+--------+
| name | chinese | math | english | 总分 |
+-----------+---------+------+---------+--------+
| 林黛玉 | 98 | 90 | 99 | 287 |
| 薛宝钗 | 88 | 90 | 88 | 266 |
| 赵姨娘 | 79 | 90 | 93 | 262 |
| 唐三藏 | 72 | 60 | 56 | 188 |
| 沙悟净 | 77 | 87 | 72 | 236 |
| 小白龙 | 99 | 20 | 19 | 138 |
+-----------+---------+------+---------+--------+
6 rows in set (0.00 sec)除了上面的 as 重命名,其实也可以不带 as 直接空格也可以:
mysql> select name, chinese, math, english, chinese+math+english 总分 from exam_result;
+-----------+---------+------+---------+--------+
| name | chinese | math | english | 总分 |
+-----------+---------+------+---------+--------+
| 林黛玉 | 98 | 90 | 99 | 287 |
| 薛宝钗 | 88 | 90 | 88 | 266 |
| 赵姨娘 | 79 | 90 | 93 | 262 |
| 唐三藏 | 72 | 60 | 56 | 188 |
| 沙悟净 | 77 | 87 | 72 | 236 |
| 小白龙 | 99 | 20 | 19 | 138 |
+-----------+---------+------+---------+--------+
6 rows in set (0.00 sec)where 子句查询
select 查询除了可以查询表里面的数据,还可以筛选,而 where 就可以筛选。
where 既然可以筛选,那么也可以有判断,下面看一下 where 后面跟些判断的内容。
| 运算符 | 说明 |
|---|---|
| >, >=, <, <= | 大于,大于等于,小于,小于等于 |
| = | 等于,NULL 不安全,例如 NULL = NULL 的结果是 NULL |
| <=> | 等于,NULL 安全,例如 NULL <=> NULL 的结果是 TRUE(1) |
| !=, <> | 不等于 |
| BETWEEN a and b | 范围匹配,[a0,a1],如果 a0 <= value <= a1,返回 TRUE(1) |
| IN (option) | 如果是 option 中的任意一个,返回 TRUE(1) |
| IS NULL | 是 NULL |
| IS NOT NULL | 不是 NULL |
| LIKE | 模糊匹配。% 表示任意多个 (包括 0 个) 任意字符,_表示任意一个字符 |
| 运算符 | 说明 |
|---|---|
| AND | 多个条件必须都为 TRUE()1结果才是 TRUE(1) |
| OR | 任意一个条件为 TRUE1), 结果为 TRUE(1) |
| NOT | 条件为 TRUE(1),结果为 FALSE(0) |
上面就是 where 后面可以跟的运算符。
根据下面的表来看一下运算符:
+----+-----------+---------+------+---------+
| id | name | chinese | math | english |
+----+-----------+---------+------+---------+
| 1 | 林黛玉 | 98 | 90 | 99 |
| 3 | 薛宝钗 | 88 | 90 | 88 |
| 4 | 赵姨娘 | 79 | 90 | 93 |
| 5 | 唐三藏 | 72 | 60 | 56 |
| 6 | 沙悟净 | 77 | 87 | 72 |
| 7 | 小白龙 | 99 | 20 | 19 |
+----+-----------+---------+------+---------+1.查找数学成绩小于 80 的同学。
mysql> select name, math from exam_result where math<90;
+-----------+------+
| name | math |
+-----------+------+
| 唐三藏 | 60 |
| 沙悟净 | 87 |
| 小白龙 | 20 |
+-----------+------+
3 rows in set (0.00 sec)上面就查询到了数学小于90分的同学。
2.查询数学成绩等于90分的同学。
mysql> select name, math from exam_result where math=90;
+-----------+------+
| name | math |
+-----------+------+
| 林黛玉 | 90 |
| 薛宝钗 | 90 |
| 赵姨娘 | 90 |
+-----------+------+
3 rows in set (0.00 sec)上面看到 = 显示 NULL 不安全,= 不能查询 NULL,下面看一下:
3.查询总分大于240 的学生
mysql> select name, chinese+english+math from exam_result where chinese+english+math > 240;
+-----------+----------------------+
| name | chinese+english+math |
+-----------+----------------------+
| 林黛玉 | 287 |
| 薛宝钗 | 266 |
| 赵姨娘 | 262 |
+-----------+----------------------+
3 rows in set (0.00 sec)虽然查询出来了,但是上面的写法太难看了,我们可以使用重命名:
mysql> select name, chinese+english+math 总分 from exam_result where chinese+english+math > 240;
+-----------+--------+
| name | 总分 |
+-----------+--------+
| 林黛玉 | 287 |
| 薛宝钗 | 266 |
| 赵姨娘 | 262 |
+-----------+--------+
3 rows in set (0.00 sec)这样写就好多了,但是后面 where 这样写也有点长骂我们可不可以用 重命名:
mysql> select name, chinese+english+math 总分 from exam_result where 总分 > 240;
ERROR 1054 (42S22): Unknown column '总分' in 'where clause'这里显示不认识 “总分”为什么?
这里其实是因为mysql 的执行是有顺序的,如果我们想要查询得到的数据,书不是先要有数据,也就是有表,有了表之后我们还要对数据进行筛选也就是 where 等筛选之后才可以讲数据得到然后在显示出来,所以说 where 一定在显示重命名之前,所以数据还没有重命名然后就被拿来当筛选,那么当然是不认识的,那么我们能不能在 where 处之间重命名然后在前面使用?
mysql> select name, 总分 from exam_result where chinese+english+math 总分 > 240;
ERROR 1064 (42000): You have an error in your SQL syntax; check the manual that corresponds to your MySQL server version for the right syntax to use near '总分 > 240' at line 1这样也是不可以的,因为与发出规定 where 后面不能重命名。
所以我们在写 sql 语句的时候一定要注意其执行顺序,否则就是一条错误的 sql 语句。
4.查询空值或者非空值
下面重新创建一个表插入一些空值:
mysql> create table test_null(
-> id int,
-> name varchar(12));
Query OK, 0 rows affected (0.01 sec)
mysql> desc test_null;
+-------+-------------+------+-----+---------+-------+
| Field | Type | Null | Key | Default | Extra |
+-------+-------------+------+-----+---------+-------+
| id | int(11) | YES | | NULL | |
| name | varchar(12) | YES | | NULL | |
+-------+-------------+------+-----+---------+-------+
2 rows in set (0.01 sec)下面插入数据,插入部分空值:
mysql> insert into test_null(id, name) values(1, '张三');
Query OK, 1 row affected (0.00 sec)
mysql> insert into test_null(id, name) values(null, '李四');
Query OK, 1 row affected (0.00 sec)
mysql> insert into test_null(id, name) values(3, null);
Query OK, 1 row affected (0.00 sec)
mysql> select * from test_null;
+------+--------+
| id | name |
+------+--------+
| 1 | 张三 |
| NULL | 李四 |
| 3 | NULL |
+------+--------+
3 rows in set (0.00 sec)下面测试 = NULL:
mysql> select * from test_null where name=NULL;
Empty set (0.00 sec)
mysql> select * from test_null where id=null;
Empty set (0.00 sec)上面两个查询都没有查询到结果,想要查询的NULL 的话可以使用 <=>
mysql> select * from test_null where id<=>null;
+------+--------+
| id | name |
+------+--------+
| NULL | 李四 |
+------+--------+
1 row in set (0.00 sec)
mysql> select * from test_null where name<=>null;
+------+------+
| id | name |
+------+------+
| 3 | NULL |
+------+------+
1 row in set (0.00 sec)这样就查询到了,下面要是查询不为空的呢?能不能用 !=(不等于):
mysql> select * from test_null where name != null;
Empty set (0.00 sec)
mysql> select * from test_null where id != null;
Empty set (0.00 sec)上面都没有查询到,其实查询不为空的话可以使用 <>:
但是其实查询 null 或者不为 null 还是喜欢用 is null 或者是 is not null:
mysql> select * from test_null where name is null;
+------+------+
| id | name |
+------+------+
| 3 | NULL |
+------+------+
1 row in set (0.00 sec)
mysql> select * from test_null where name is not null;
+------+--------+
| id | name |
+------+--------+
| 1 | 张三 |
| NULL | 李四 |
+------+--------+
2 rows in set (0.00 sec)5.查询语文成绩在70~80之间的同学
mysql> select name, chinese from exam_result where chinese between 70 and 80;
+-----------+---------+
| name | chinese |
+-----------+---------+
| 赵姨娘 | 79 |
| 唐三藏 | 72 |
| 沙悟净 | 77 |
+-----------+---------+
3 rows in set (0.00 sec)6.查询英语成绩是99 和 93 和 19 和 30
mysql> select name, english from exam_result where english=99 or english=93 or english=19 or english=30;
+-----------+---------+
| name | english |
+-----------+---------+
| 林黛玉 | 99 |
| 赵姨娘 | 93 |
| 小白龙 | 19 |
+-----------+---------+
3 rows in set (0.00 sec)除了上面的方法还有一种方法:
mysql> select name, english from exam_result where english in (99, 93, 19, 30);
+-----------+---------+
| name | english |
+-----------+---------+
| 林黛玉 | 99 |
| 赵姨娘 | 93 |
| 小白龙 | 19 |
+-----------+---------+
3 rows in set (0.00 sec)下面的这个看起更好一点。
7.模糊匹配
%可以表示任意一个或者多个字符,_表示任意一个字符。
查询名字叫黛玉的:
mysql> select id, name from exam_result where name like '_黛玉';
+----+-----------+
| id | name |
+----+-----------+
| 1 | 林黛玉 |
+----+-----------+
1 row in set (0.00 sec)上面就是匹配任意一个字符,下面看一下匹配任意字符。
查询名字里面有“三” 的:
mysql> select id, name from exam_result where name like '%三%';
+----+-----------+
| id | name |
+----+-----------+
| 5 | 唐三藏 |
+----+-----------+
1 row in set (0.00 sec)排序
有时候我们需要对查询出来的数据进行排序,我们现在查询一下总分的排序:
mysql> select *, chinese+math+english from exam_result order by chinese+english+math;
+----+-----------+---------+------+---------+----------------------+
| id | name | chinese | math | english | chinese+math+english |
+----+-----------+---------+------+---------+----------------------+
| 7 | 小白龙 | 99 | 20 | 19 | 138 |
| 5 | 唐三藏 | 72 | 60 | 56 | 188 |
| 6 | 沙悟净 | 77 | 87 | 72 | 236 |
| 4 | 赵姨娘 | 79 | 90 | 93 | 262 |
| 3 | 薛宝钗 | 88 | 90 | 88 | 266 |
| 1 | 林黛玉 | 98 | 90 | 99 | 287 |
+----+-----------+---------+------+---------+----------------------+
6 rows in set (0.00 sec)我们上面这样写太繁琐了,我们可不可以使用重命名?
mysql> select *, chinese+math+english 总分 from exam_result order by 总分;
+----+-----------+---------+------+---------+--------+
| id | name | chinese | math | english | 总分 |
+----+-----------+---------+------+---------+--------+
| 7 | 小白龙 | 99 | 20 | 19 | 138 |
| 5 | 唐三藏 | 72 | 60 | 56 | 188 |
| 6 | 沙悟净 | 77 | 87 | 72 | 236 |
| 4 | 赵姨娘 | 79 | 90 | 93 | 262 |
| 3 | 薛宝钗 | 88 | 90 | 88 | 266 |
| 1 | 林黛玉 | 98 | 90 | 99 | 287 |
+----+-----------+---------+------+---------+--------+
6 rows in set (0.00 sec)这里又可以使用总分了,但是前面 where 不可以使用总分,为什么?
还是执行顺序的问题,首先我们要排序是不是要前面的数据都准备好了才进行排序,也就是说排序在重命名的后面,所以既然已经又重命名了所以排序就可以使用重命名。
我们看到上面的排序都是降序那么怎样可以让其升序呢?
order by 列名 ASC 降序 默认
desc 升序下面可以试一下:
mysql> select *, chinese+math+english 总分 from exam_result order by 总分 ASC;
+----+-----------+---------+------+---------+--------+
| id | name | chinese | math | english | 总分 |
+----+-----------+---------+------+---------+--------+
| 7 | 小白龙 | 99 | 20 | 19 | 138 |
| 5 | 唐三藏 | 72 | 60 | 56 | 188 |
| 6 | 沙悟净 | 77 | 87 | 72 | 236 |
| 4 | 赵姨娘 | 79 | 90 | 93 | 262 |
| 3 | 薛宝钗 | 88 | 90 | 88 | 266 |
| 1 | 林黛玉 | 98 | 90 | 99 | 287 |
+----+-----------+---------+------+---------+--------+
6 rows in set (0.00 sec)
mysql> select *, chinese+math+english 总分 from exam_result order by 总分 DESC;
+----+-----------+---------+------+---------+--------+
| id | name | chinese | math | english | 总分 |
+----+-----------+---------+------+---------+--------+
| 1 | 林黛玉 | 98 | 90 | 99 | 287 |
| 3 | 薛宝钗 | 88 | 90 | 88 | 266 |
| 4 | 赵姨娘 | 79 | 90 | 93 | 262 |
| 6 | 沙悟净 | 77 | 87 | 72 | 236 |
| 5 | 唐三藏 | 72 | 60 | 56 | 188 |
| 7 | 小白龙 | 99 | 20 | 19 | 138 |
+----+-----------+---------+------+---------+--------+
6 rows in set (0.00 sec)LIMIT
在 mysql 查询的时候其实防止一次性查出来的数据太多还有一个 limit 可以让数据可以分多次打印。
下面看一下 limit 的使用:
mysql> select * from exam_result limit 1;
+----+-----------+---------+------+---------+
| id | name | chinese | math | english |
+----+-----------+---------+------+---------+
| 1 | 林黛玉 | 98 | 90 | 99 |
+----+-----------+---------+------+---------+
1 row in set (0.00 sec)
mysql> select * from exam_result limit 3;
+----+-----------+---------+------+---------+
| id | name | chinese | math | english |
+----+-----------+---------+------+---------+
| 1 | 林黛玉 | 98 | 90 | 99 |
| 3 | 薛宝钗 | 88 | 90 | 88 |
| 4 | 赵姨娘 | 79 | 90 | 93 |
+----+-----------+---------+------+---------+
3 rows in set (0.00 sec)其实 limit 还可以打印中间的内容:
mysql> select * from exam_result limit 0,3;
+----+-----------+---------+------+---------+
| id | name | chinese | math | english |
+----+-----------+---------+------+---------+
| 1 | 林黛玉 | 98 | 90 | 99 |
| 3 | 薛宝钗 | 88 | 90 | 88 |
| 4 | 赵姨娘 | 79 | 90 | 93 |
+----+-----------+---------+------+---------+
3 rows in set (0.00 sec)
mysql> select * from exam_result limit 3,3;
+----+-----------+---------+------+---------+
| id | name | chinese | math | english |
+----+-----------+---------+------+---------+
| 5 | 唐三藏 | 72 | 60 | 56 |
| 6 | 沙悟净 | 77 | 87 | 72 |
| 7 | 小白龙 | 99 | 20 | 19 |
+----+-----------+---------+------+---------+
3 rows in set (0.00 sec)还可以给两个数字,前面的表示从第一个数字的下一行开始打印,第二个数字表示打印几行。
limit 还可以结合 offset 使用:文章来源:https://www.toymoban.com/news/detail-689060.html
mysql> select * from exam_result limit 3 offset 0;
+----+-----------+---------+------+---------+
| id | name | chinese | math | english |
+----+-----------+---------+------+---------+
| 1 | 林黛玉 | 98 | 90 | 99 |
| 3 | 薛宝钗 | 88 | 90 | 88 |
| 4 | 赵姨娘 | 79 | 90 | 93 |
+----+-----------+---------+------+---------+
3 rows in set (0.00 sec)
mysql> select * from exam_result limit 3 offset 1;
+----+-----------+---------+------+---------+
| id | name | chinese | math | english |
+----+-----------+---------+------+---------+
| 3 | 薛宝钗 | 88 | 90 | 88 |
| 4 | 赵姨娘 | 79 | 90 | 93 |
| 5 | 唐三藏 | 72 | 60 | 56 |
+----+-----------+---------+------+---------+
3 rows in set (0.00 sec)也可以让 limit 后面跟一个数字,然后加 offset 后面跟一个数字,其中 limit 后面的数字代表打印几行, offset 后面的数字代表从第几行开始打印。文章来源地址https://www.toymoban.com/news/detail-689060.html
到了这里,关于MySQL 基本操作1的文章就介绍完了。如果您还想了解更多内容,请在右上角搜索TOY模板网以前的文章或继续浏览下面的相关文章,希望大家以后多多支持TOY模板网!





![[MySQL]基本数据类型及表的基本操作](https://imgs.yssmx.com/Uploads/2024/02/781101-1.gif)