Valgrind是一款用于内存调试、内存泄漏检测以及性能分析的神器,能够帮助我们快速定位到程序的内存问题,比如内存泄漏导致的 段错误 (核心已转储)
包含以下工具:
-
Memcheck:检查程序中的内存问题,如泄漏、越界、非法指针等 -
Callgrind:主要用来检查程序中函数调用过程中出现的问题。 -
Cachegrind:分析CPU的cache命中率、丢失率,用于进行代码优化。 -
Helgrind:主要用来检查多线程程序中出现的竞争问题。 -
Massif:主要用来检查程序中堆栈使用中出现的问题。 -
Extension:可利用core提供的功能,自己编写特定的内存调试工具
使用语法如下:
valgrind [options] ./prog_file
usage: valgrind [options] prog-and-args
tool-selection option, with default in [ ]:
--tool=<name> use the Valgrind tool named <name> [memcheck]
basic user options for all Valgrind tools, with defaults in [ ]:
-h --help show this message
--help-debug show this message, plus debugging options
--version show version
-q --quiet run silently; only print error msgs
-v --verbose be more verbose -- show misc extra info
--trace-children=no|yes Valgrind-ise child processes (follow execve)? [no]
--trace-children-skip=patt1,patt2,... specifies a list of executables
that --trace-children=yes should not trace into
--trace-children-skip-by-arg=patt1,patt2,... same as --trace-children-skip=
but check the argv[] entries for children, rather
than the exe name, to make a follow/no-follow decision
--child-silent-after-fork=no|yes omit child output between fork & exec? [no]
--vgdb=no|yes|full activate gdbserver? [yes]
full is slower but provides precise watchpoint/step
--vgdb-error=<number> invoke gdbserver after <number> errors [999999999]
to get started quickly, use --vgdb-error=0
and follow the on-screen directions
--vgdb-stop-at=event1,event2,... invoke gdbserver for given events [none]
where event is one of:
startup exit valgrindabexit all none
--track-fds=no|yes track open file descriptors? [no]
--time-stamp=no|yes add timestamps to log messages? [no]
--log-fd=<number> log messages to file descriptor [2=stderr]
--log-file=<file> log messages to <file>
--log-socket=ipaddr:port log messages to socket ipaddr:port
user options for Valgrind tools that report errors:
--xml=yes emit error output in XML (some tools only)
--xml-fd=<number> XML output to file descriptor
--xml-file=<file> XML output to <file>
--xml-socket=ipaddr:port XML output to socket ipaddr:port
--xml-user-comment=STR copy STR verbatim into XML output
--demangle=no|yes automatically demangle C++ names? [yes]
--num-callers=<number> show <number> callers in stack traces [12]
--error-limit=no|yes stop showing new errors if too many? [yes]
--error-exitcode=<number> exit code to return if errors found [0=disable]
--error-markers=<begin>,<end> add lines with begin/end markers before/after
each error output in plain text mode [none]
--show-below-main=no|yes continue stack traces below main() [no]
--default-suppressions=yes|no
load default suppressions [yes]
--suppressions=<filename> suppress errors described in <filename>
--gen-suppressions=no|yes|all print suppressions for errors? [no]
--input-fd=<number> file descriptor for input [0=stdin]
--dsymutil=no|yes run dsymutil on Mac OS X when helpful? [yes]
--max-stackframe=<number> assume stack switch for SP changes larger
than <number> bytes [2000000]
--main-stacksize=<number> set size of main thread's stack (in bytes)
[min(max(current 'ulimit' value,1MB),16MB)]
user options for Valgrind tools that replace malloc:
--alignment=<number> set minimum alignment of heap allocations [16]
--redzone-size=<number> set minimum size of redzones added before/after
heap blocks (in bytes). [16]
--xtree-memory=none|allocs|full profile heap memory in an xtree [none]
and produces a report at the end of the execution
none: no profiling, allocs: current allocated
size/blocks, full: profile current and cumulative
allocated size/blocks and freed size/blocks.
--xtree-memory-file=<file> xtree memory report file [xtmemory.kcg.%p]
uncommon user options for all Valgrind tools:
--fullpath-after= (with nothing after the '=')
show full source paths in call stacks
--fullpath-after=string like --fullpath-after=, but only show the
part of the path after 'string'. Allows removal
of path prefixes. Use this flag multiple times
to specify a set of prefixes to remove.
--extra-debuginfo-path=path absolute path to search for additional
debug symbols, in addition to existing default
well known search paths.
--debuginfo-server=ipaddr:port also query this server
(valgrind-di-server) for debug symbols
--allow-mismatched-debuginfo=no|yes [no]
for the above two flags only, accept debuginfo
objects that don't "match" the main object
--smc-check=none|stack|all|all-non-file [all-non-file]
checks for self-modifying code: none, only for
code found in stacks, for all code, or for all
code except that from file-backed mappings
--read-inline-info=yes|no read debug info about inlined function calls
and use it to do better stack traces. [yes]
on Linux/Android/Solaris for Memcheck/Helgrind/DRD
only. [no] for all other tools and platforms.
--read-var-info=yes|no read debug info on stack and global variables
and use it to print better error messages in
tools that make use of it (Memcheck, Helgrind,
DRD) [no]
--vgdb-poll=<number> gdbserver poll max every <number> basic blocks [5000]
--vgdb-shadow-registers=no|yes let gdb see the shadow registers [no]
--vgdb-prefix=<prefix> prefix for vgdb FIFOs [/tmp/vgdb-pipe]
--run-libc-freeres=no|yes free up glibc memory at exit on Linux? [yes]
--run-cxx-freeres=no|yes free up libstdc++ memory at exit on Linux
and Solaris? [yes]
--sim-hints=hint1,hint2,... activate unusual sim behaviours [none]
where hint is one of:
lax-ioctls lax-doors fuse-compatible enable-outer
no-inner-prefix no-nptl-pthread-stackcache fallback-llsc none
--fair-sched=no|yes|try schedule threads fairly on multicore systems [no]
--kernel-variant=variant1,variant2,...
handle non-standard kernel variants [none]
where variant is one of:
bproc android-no-hw-tls
android-gpu-sgx5xx android-gpu-adreno3xx none
--merge-recursive-frames=<number> merge frames between identical
program counters in max <number> frames) [0]
--num-transtab-sectors=<number> size of translated code cache [32]
more sectors may increase performance, but use more memory.
--avg-transtab-entry-size=<number> avg size in bytes of a translated
basic block [0, meaning use tool provided default]
--aspace-minaddr=0xPP avoid mapping memory below 0xPP [guessed]
--valgrind-stacksize=<number> size of valgrind (host) thread's stack
(in bytes) [1048576]
--show-emwarns=no|yes show warnings about emulation limits? [no]
--require-text-symbol=:sonamepattern:symbolpattern abort run if the
stated shared object doesn't have the stated
text symbol. Patterns can contain ? and *.
--soname-synonyms=syn1=pattern1,syn2=pattern2,... synonym soname
specify patterns for function wrapping or replacement.
To use a non-libc malloc library that is
in the main exe: --soname-synonyms=somalloc=NONE
in libxyzzy.so: --soname-synonyms=somalloc=libxyzzy.so
--sigill-diagnostics=yes|no warn about illegal instructions? [yes]
--unw-stack-scan-thresh=<number> Enable stack-scan unwind if fewer
than <number> good frames found [0, meaning "disabled"]
NOTE: stack scanning is only available on arm-linux.
--unw-stack-scan-frames=<number> Max number of frames that can be
recovered by stack scanning [5]
--resync-filter=no|yes|verbose [yes on MacOS, no on other OSes]
attempt to avoid expensive address-space-resync operations
--max-threads=<number> maximum number of threads that valgrind can
handle [500]
user options for Memcheck:
--leak-check=no|summary|full search for memory leaks at exit? [summary]
--leak-resolution=low|med|high differentiation of leak stack traces [high]
--show-leak-kinds=kind1,kind2,.. which leak kinds to show?
[definite,possible]
--errors-for-leak-kinds=kind1,kind2,.. which leak kinds are errors?
[definite,possible]
where kind is one of:
definite indirect possible reachable all none
--leak-check-heuristics=heur1,heur2,... which heuristics to use for
improving leak search false positive [all]
where heur is one of:
stdstring length64 newarray multipleinheritance all none
--show-reachable=yes same as --show-leak-kinds=all
--show-reachable=no --show-possibly-lost=yes
same as --show-leak-kinds=definite,possible
--show-reachable=no --show-possibly-lost=no
same as --show-leak-kinds=definite
--xtree-leak=no|yes output leak result in xtree format? [no]
--xtree-leak-file=<file> xtree leak report file [xtleak.kcg.%p]
--undef-value-errors=no|yes check for undefined value errors [yes]
--track-origins=no|yes show origins of undefined values? [no]
--partial-loads-ok=no|yes too hard to explain here; see manual [yes]
--expensive-definedness-checks=no|yes
Use extra-precise definedness tracking [no]
--freelist-vol=<number> volume of freed blocks queue [20000000]
--freelist-big-blocks=<number> releases first blocks with size>= [1000000]
--workaround-gcc296-bugs=no|yes self explanatory [no]. Deprecated.
Use --ignore-range-below-sp instead.
--ignore-ranges=0xPP-0xQQ[,0xRR-0xSS] assume given addresses are OK
--ignore-range-below-sp=<number>-<number> do not report errors for
accesses at the given offsets below SP
--malloc-fill=<hexnumber> fill malloc'd areas with given value
--free-fill=<hexnumber> fill free'd areas with given value
--keep-stacktraces=alloc|free|alloc-and-free|alloc-then-free|none
stack trace(s) to keep for malloc'd/free'd areas [alloc-and-free]
--show-mismatched-frees=no|yes show frees that don't match the allocator? [yes]
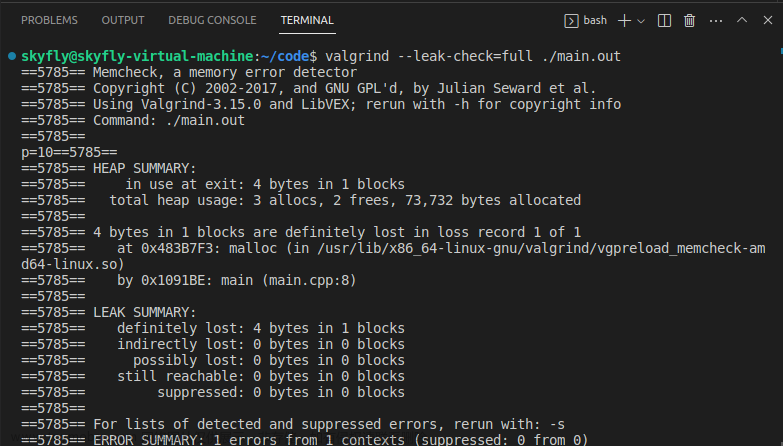
博主最常用的是内存诊断工具,使用方法如下:文章来源:https://www.toymoban.com/news/detail-690178.html
valgrind --tool=memcheck ./test_file
注意: 编译时添加-g选项,使用memcheck检查时的错误信息可精确到行。文章来源地址https://www.toymoban.com/news/detail-690178.html
到了这里,关于Valgrind内存诊断工具的使用笔记的文章就介绍完了。如果您还想了解更多内容,请在右上角搜索TOY模板网以前的文章或继续浏览下面的相关文章,希望大家以后多多支持TOY模板网!