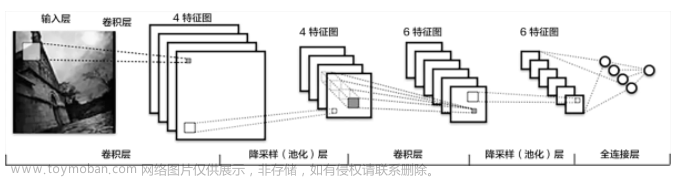
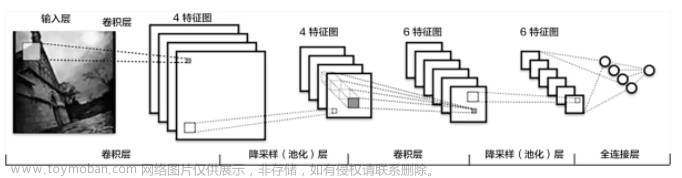
神经网络的基本骨架

1. nn.Module的使用
- 所有的模型都要继承 Module 类
- 需要重写初始化函数和运算步骤函数
eg:
import torch.nn as nn
import torch.nn.functional as F
class Model(nn.Module): # 继承父类Module
def __init__(self): # 重写初始化函数
super().__init__() # 调用父类初始化
self.conv1 = nn.Conv2d(1, 20, 5)
self.conv2 = nn.Conv2d(20, 20, 5)
def forward(self, x): # 神经网络的运算步骤--前向传播
x = F.relu(self.conv1(x)) # x->卷积->非线性
return F.relu(self.conv2(x)) # x->卷积->非线性
代码示例:
import torch
from torch import nn
class Kun(nn.Module):
def __init__(self):
super().__init__()
def forward(self, input):
output = input+1 # 实现输出加1
return output
kun = Kun()
x = torch.tensor(1.0)
output = kun(x)
print(output) # tensor(2.)
2. 卷积
conv2可选参数

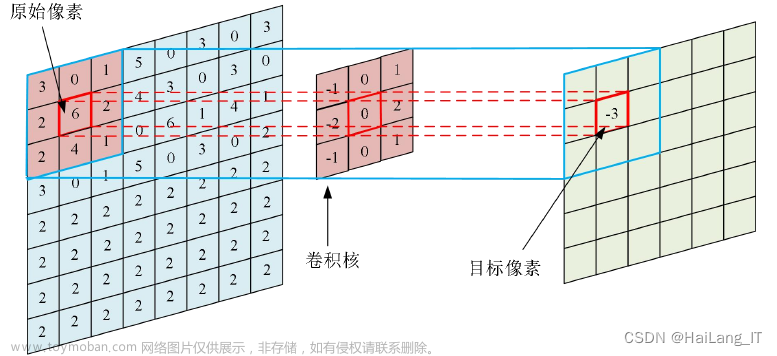
卷积计算过程示意:

import torch
# 输入图像(5*5)
input = torch.tensor([[1, 2, 0, 3, 1],
[0, 1, 2, 3, 1],
[1, 2, 1, 0, 0],
[5, 2, 3, 1, 1],
[2, 1, 0, 1, 1]]) # 输入tensor数据类型的二维矩阵
# 卷积核
kernel = torch.tensor([[1, 2, 1],
[0, 1, 0],
[2, 1, 0]])
print(input.shape)
print(kernel.shape)
torch.Size([5, 5])
torch.Size([3, 3])
如果不调整尺寸会报错:Expected 3D(unbatched) or 4D(batched) input to conv2d, but got input of size: [5, 5]
所以需要调整
input = torch.reshape(input, (1, 1, 5, 5))
kernel = torch.reshape(kernel, (1, 1, 3, 3))
output = F.conv2d(input, kernel, stride=1)
print(output)
--------------------------------------------------------------------------
tensor([[[[10, 12, 12],
[18, 16, 16],
[13, 9, 3]]]])
stride可以选择移动的步长
output2 = F.conv2d(input, kernel, stride=2)
print(output2)
----------------------------------------------------------------------------
tensor([[[[10, 12],
[13, 3]]]])
padding进行填充(默认填充0)
output3 = F.conv2d(input, kernel, stride=1, padding=1)
print(output3)
-----------------------------------------------------------------------------
tensor([[[[ 1, 3, 4, 10, 8],
[ 5, 10, 12, 12, 6],
[ 7, 18, 16, 16, 8],
[11, 13, 9, 3, 4],
[14, 13, 9, 7, 4]]]])
示例代码:
import torch
import torch.nn.functional as F
# 输入图像(5*5)
input = torch.tensor([[1, 2, 0, 3, 1],
[0, 1, 2, 3, 1],
[1, 2, 1, 0, 0],
[5, 2, 3, 1, 1],
[2, 1, 0, 1, 1]]) # 输入tensor数据类型的二维矩阵
# 卷积核
kernel = torch.tensor([[1, 2, 1],
[0, 1, 0],
[2, 1, 0]])
# 调整输入的尺寸
# 如果不调整尺寸会报错
# Expected 3D(unbatched) or 4D(batched) input to conv2d, but got input of size: [5, 5]
input = torch.reshape(input, (1, 1, 5, 5))
kernel = torch.reshape(kernel, (1, 1, 3, 3))
# print(input.shape) # torch.Size([1, 1, 5, 5])
# print(kernel.shape) # torch.Size([1, 1, 3, 3])
output = F.conv2d(input, kernel, stride=1)
print(output)
output2 = F.conv2d(input, kernel, stride=2)
print(output2)
output3 = F.conv2d(input, kernel, stride=1, padding=1)
print(output3)
import torch
import torchvision
from torch import nn
from torch.nn import Conv2d
from torch.utils.data import DataLoader
from torch.utils.tensorboard import SummaryWriter
dataset = torchvision.datasets.CIFAR10("../dataset", train=False, transform=torchvision.transforms.ToTensor(),
download=True)
dataloader = DataLoader(dataset, batch_size=64)
class Kun2(nn.Module):
def __init__(self): # 初始化
super(Kun2, self).__init__()
self.conv1 = Conv2d(in_channels=3, out_channels=6, kernel_size=3, stride=1, padding=0) # 卷积层
def forward(self, x):
x = self.conv1(x)
return x
# 初始化网络
kun = Kun2()
# print(kun)
writer = SummaryWriter("../logs")
step = 0
for data in dataloader:
imgs, target = data
output = kun(imgs)
print(imgs.shape)
print(output.shape)
# torch.Size([64, 3, 32, 32])
writer.add_images("input", imgs, step)
# torch.Size([64, 6, 30, 30])
# 报错:输出6个channel,系统不知道怎么显示.最粗暴的方法reshape输出
# torch.Size([64, 6, 30, 30]) ->[**, 3, 30, 30]
output = torch.reshape(output, (-1, 3, 30, 30))
writer.add_images("output", output, step)
step = step + 1
3. 最大池化的使用
池化的作用:减少数据量-> 训练更快
Maxpool最大池化/下采样
MaxUnpool 下采样

步长默认是kernel_size大小
ceil_model
- true 不足会保留
- false不足不会保留(默认)
import torch
from torch import nn
from torch.nn import MaxPool2d
# RuntimeError: "max_pool2d" not implemented for 'Long'处理:
# 添加数据类型dtype=torch.float32 转整型为浮点型
input = torch.tensor([[1, 2, 0, 3, 1],
[0, 1, 2, 3, 1],
[1, 2, 1, 0, 0],
[5, 2, 3, 1, 1],
[2, 1, 0, 1, 1]], dtype=torch.float32
)
input = torch.reshape(input, (-1, 1, 5, 5))
print(input.shape) # torch.Size([1, 1, 5, 5])
class Kun(nn.Module):
def __init__(self): # 初始化
super(Kun, self).__init__() # 父类进行继承
self.maxpool1 = MaxPool2d(kernel_size=3, ceil_mode=True)
def forward(self, input):
output = self.maxpool1(input)
return output
# 创建神经网络
kun = Kun()
output = kun(input)
print(output) # tensor([[[[2., 3.], [5., 1.]]]])
使用数据集
import torch
import torchvision
from torch import nn
from torch.nn import MaxPool2d
from torch.utils.data import DataLoader
from torch.utils.tensorboard import SummaryWriter
dataset = torchvision.datasets.CIFAR10("../dataset", train=False, download=True,
transform=torchvision.transforms.ToTensor())
dataloader = DataLoader(dataset, batch_size=64)
class Kun(nn.Module):
def __init__(self): # 初始化
super(Kun, self).__init__() # 父类进行继承
self.maxpool1 = MaxPool2d(kernel_size=3, ceil_mode=True)
def forward(self, input):
output = self.maxpool1(input)
return output
# 创建神经网络
kun = Kun()
writer = SummaryWriter("../logs_maxpool")
step = 0
for data in dataloader:
imgs, targets = data
writer.add_images("input", imgs, step)
output = kun(imgs)
writer.add_images("output", output, step)
step = step + 1
writer.close()
结果:

4. 非线性激活
- RELU示例
CLASStorch.nn.ReLU(inplace=False)[SOURCE]
Applies the rectified linear unit function element-wise:
-
Parameters:
inplace (bool) – can optionally do the operation in-place. Default:
False- 是否对原变量进行替换
- True进行变换
- False保留原始数据input,返回变换值output
代码示例:
import torch
from torch import nn
from torch.nn import ReLU
input = torch.tensor([[1, -0.5],
[-1, 3]])
input = torch.reshape(input, (-1, 1, 2, 2))
print(input.shape)
class Kun(nn.Module):
def __init__(self):
super(Kun, self).__init__()
self.relu1 = ReLU()
def forward(self, input):
output = self.relu1(input)
return output
# 创建神经网络
kun = Kun()
output = kun(input)
print(output)
-------------------------------------
tensor([[[[1., 0.],
[0., 3.]]]])
import torch
import torchvision
from torch import nn
from torch.nn import ReLU, Sigmoid
from torch.utils.data import DataLoader
from torch.utils.tensorboard import SummaryWriter
input = torch.tensor([[1, -0.5],
[-1, 3]])
input = torch.reshape(input, (-1, 1, 2, 2))
print(input.shape)
dataset = torchvision.datasets.CIFAR10("../dataset", train=False, download=True,
transform=torchvision.transforms.ToTensor())
dataloader = DataLoader(dataset, batch_size=64)
class Kun(nn.Module):
def __init__(self):
super(Kun, self).__init__()
self.sigmoid1 = Sigmoid()
def forward(self, input):
output = self.sigmoid1(input)
return output
# 创建神经网络
kun = Kun()
step = 0
writer = SummaryWriter("../logs_relu")
for data in dataloader:
imgs, target = data
writer.add_images("input", imgs, global_step=step)
output = kun(imgs)
writer.add_images("output", output, global_step=step)
step = step+1
writer.close()
结果
5. 线性层和其他层介绍
import torch
import torchvision
from torch import nn
from torch.nn import Linear
from torch.utils.data import DataLoader
dataset = torchvision.datasets.CIFAR10("../dataset", train=False, transform=torchvision.transforms.ToTensor(),
download=True)
dataloader = DataLoader(dataset, batch_size=64)
class Kun(nn.Module):
def __init__(self):
super(Kun, self).__init__()
self.linear1 = Linear(196608, 10)
def forward(self, input):
output = self.linear1(input)
return output
kun = Kun()
for data in dataloader:
imgs, target = data
print(imgs.shape)
# output = torch.reshape(imgs, (1, 1, 1, -1))
output = torch.flatten(imgs) # 同上句reshape,主要用于将数据摊平 变成一行
print(output.shape)
output = kun(output)
print(output.shape)
6. 神经网络搭建实例
完成如下图所示神经网络的搭建

计算相应参数:

示例:(可使用Sequential来简化代码量)
import torch
from torch import nn
from torch.nn import Conv2d, MaxPool2d, Flatten, Linear, Sequential
from torch.utils.tensorboard import SummaryWriter
class Kun(nn.Module):
def __init__(self):
super(Kun, self).__init__()
# self.conv1 = Conv2d(in_channels=3, out_channels=32, kernel_size=5, stride=1, padding=2) # 新建卷积层1
# self.maxpool1 = MaxPool2d(kernel_size=2) # 池化
# self.conv2 = Conv2d(in_channels=32, out_channels=32, kernel_size=5,padding=2) # 新建卷积层2
# self.maxpool2 = MaxPool2d(kernel_size=2)
# self.conv3 = Conv2d(in_channels=32, out_channels=64, kernel_size=5, padding=2)
# self.maxpool3 = MaxPool2d(kernel_size=2)
# self.flatten = Flatten() # 将数据进行展平 64*4*4 =1024
# self.linear1 = Linear(in_features=1024, out_features=64)
# self.linear2 = Linear(64, 10)
self.model1 = Sequential(
Conv2d(in_channels=3, out_channels=32, kernel_size=5, stride=1, padding=2),
MaxPool2d(kernel_size=2),
Conv2d(in_channels=32, out_channels=32, kernel_size=5, padding=2),
MaxPool2d(kernel_size=2),
Conv2d(in_channels=32, out_channels=64, kernel_size=5, padding=2),
MaxPool2d(kernel_size=2),
Flatten(), # 将数据进行展平 64*4*4 =1024
Linear(in_features=1024, out_features=64),
Linear(64, 10)
)
def forward(self, x):
# x = self.conv1(x)
# x = self.maxpool1(x)
# x = self.conv2(x)
# x = self.maxpool2(x)
# x = self.conv3(x)
# x = self.maxpool3(x)
# x = self.flatten(x)
# x = self.linear1(x)
# x = self.linear2(x)
x = self.model1(x)
return x
# 实例化神经网络
kun = Kun()
# 对网络结构进行测试
input = torch.ones((64, 3, 32, 32))
output = kun(input)
print(output.shape) # torch.Size([64, 10])
writer = SummaryWriter("../logs_seq")
writer.add_graph(kun, input)
writer.close()
结果示例:

7. 现有网络模型的使用及修改
import torchvision
from torch import nn
vgg16_false = torchvision.models.vgg16(pretrained=False) # 不下载对应网络模型
vgg16_true = torchvision.models.vgg16(pretrained=True)
# print(vgg16_true)
# 是10分类数据集,但是vgg16是1000分类,所以要修改vgg16的参数out_features
train_true = torchvision.datasets.CIFAR10('../dataset', train=True, transform=torchvision.transforms.ToTensor(),
download=True)
# 方法一:在最后classifier添加一层
vgg16_true.classifier.add_module('add_linear', nn.Linear(1000, 10))
print(vgg16_true)
# 方法二:直接修改
vgg16_false.classifier[6] = nn.Linear(4096, 10, True)
print(vgg16_false)
vgg16网络:
VGG(
(features): Sequential(
(0): Conv2d(3, 64, kernel_size=(3, 3), stride=(1, 1), padding=(1, 1))
(1): ReLU(inplace=True)
(2): Conv2d(64, 64, kernel_size=(3, 3), stride=(1, 1), padding=(1, 1))
(3): ReLU(inplace=True)
(4): MaxPool2d(kernel_size=2, stride=2, padding=0, dilation=1, ceil_mode=False)
(5): Conv2d(64, 128, kernel_size=(3, 3), stride=(1, 1), padding=(1, 1))
(6): ReLU(inplace=True)
(7): Conv2d(128, 128, kernel_size=(3, 3), stride=(1, 1), padding=(1, 1))
(8): ReLU(inplace=True)
(9): MaxPool2d(kernel_size=2, stride=2, padding=0, dilation=1, ceil_mode=False)
(10): Conv2d(128, 256, kernel_size=(3, 3), stride=(1, 1), padding=(1, 1))
(11): ReLU(inplace=True)
(12): Conv2d(256, 256, kernel_size=(3, 3), stride=(1, 1), padding=(1, 1))
(13): ReLU(inplace=True)
(14): Conv2d(256, 256, kernel_size=(3, 3), stride=(1, 1), padding=(1, 1))
(15): ReLU(inplace=True)
(16): MaxPool2d(kernel_size=2, stride=2, padding=0, dilation=1, ceil_mode=False)
(17): Conv2d(256, 512, kernel_size=(3, 3), stride=(1, 1), padding=(1, 1))
(18): ReLU(inplace=True)
(19): Conv2d(512, 512, kernel_size=(3, 3), stride=(1, 1), padding=(1, 1))
(20): ReLU(inplace=True)
(21): Conv2d(512, 512, kernel_size=(3, 3), stride=(1, 1), padding=(1, 1))
(22): ReLU(inplace=True)
(23): MaxPool2d(kernel_size=2, stride=2, padding=0, dilation=1, ceil_mode=False)
(24): Conv2d(512, 512, kernel_size=(3, 3), stride=(1, 1), padding=(1, 1))
(25): ReLU(inplace=True)
(26): Conv2d(512, 512, kernel_size=(3, 3), stride=(1, 1), padding=(1, 1))
(27): ReLU(inplace=True)
(28): Conv2d(512, 512, kernel_size=(3, 3), stride=(1, 1), padding=(1, 1))
(29): ReLU(inplace=True)
(30): MaxPool2d(kernel_size=2, stride=2, padding=0, dilation=1, ceil_mode=False)
)
(avgpool): AdaptiveAvgPool2d(output_size=(7, 7))
(classifier): Sequential(
(0): Linear(in_features=25088, out_features=4096, bias=True)
(1): ReLU(inplace=True)
(2): Dropout(p=0.5, inplace=False)
(3): Linear(in_features=4096, out_features=4096, bias=True)
(4): ReLU(inplace=True)
(5): Dropout(p=0.5, inplace=False)
(6): Linear(in_features=4096, out_features=1000, bias=True) # 分类为1000
)
)
8. 网络模型的保存与读取
保存:
import torch
import torchvision
from torch import nn
vgg16 = torchvision.models.vgg16(weights=None)
# 保存方式1 即保存模型,也保存了结构
torch.save(vgg16, "vgg16_method1.pth")
# 保存方式2 模型参数 (官方推荐,因为占用空间小)
torch.save(vgg16.state_dict(), "vgg16_method2.pth")
# 陷阱
class Kun(nn.Module):
def __init__(self):
super(Kun, self).__init__()
self.conv1 = nn.Conv2d(3, 64, kernel_size=3)
def forward(self, x):
x = self.conv1(x)
return x
kun = Kun()
torch.save(kun, "kun_method1.pth")
读取:
import torchvision
import torch
# # 方式1-》保存方式1来加载模型
# model = torch.load("vgg16_method1.pth")
# print(model)
# 方式2-》保存方式2 加载模型 直接输出的是字典结构
# 恢复网络模型结构
from torch import nn
vgg16 = torchvision.models.vgg16(weights=None)
vgg16.load_state_dict(torch.load("vgg16_method2.pth"))
model2 = torch.load("vgg16_method2.pth")
print(vgg16)
注意:陷阱1 直接用会报错Can’t get attribute ‘Kun’ on <module ‘main’ from ‘E:/pythonProject/src/model_load.py’>
所以要引入class 或者from model_save import *
陷阱1 直接用回报错Can't get attribute 'Kun' on <module '__main__' from 'E:/pythonProject/src/model_load.py'>
所以要引入class 或者from model_save import *
class Kun(nn.Module):
def __init__(self):
super(Kun, self).__init__()
self.conv1 = nn.Conv2d(3, 64, kernel_size=3)
def forward(self, x):
x = self.conv1(x)
return x
model = torch.load("kun_method1.pth")
print(model)
9. 完整的模型训练套路
以CRF10数据集的分类为例
model.py
# 搭建神经网络
import torch
from torch import nn
class Kun(nn.Module):
def __init__(self):
super(Kun, self).__init__()
self.model = nn.Sequential(
nn.Conv2d(3, 32, 5, 1, 2),
nn.MaxPool2d(2),
nn.Conv2d(32, 32, 5, 1, 2),
nn.MaxPool2d(2),
nn.Conv2d(32, 64, 5, 1, 2),
nn.MaxPool2d(2),
nn.Flatten(),
nn.Linear(1024, 64),
nn.Linear(64, 10)
)
def forward(self, x):
x = self.model(x)
return x
# 测试
if __name__ == '__main__':
kun = Kun()
input = torch.ones((64, 3, 32, 32))
output = kun(input)
print(output.shape)
train.py
import torch
import torchvision
# 准备训练数据集
from torch import nn
from torch.utils.data import DataLoader
from torch.utils.tensorboard import SummaryWriter
from model import *
# 准备训练数据集
train_data = torchvision.datasets.CIFAR10("../dataset", train=True, transform=torchvision.transforms.ToTensor(),
download=True)
# 准备测试数据集
test_data = torchvision.datasets.CIFAR10("../dataset", train=False, transform=torchvision.transforms.ToTensor(),
download=True)
# 查看训练和测试数据集的长度
train_data_size = len(train_data)
test_data_size = len(test_data)
print("训练数据集的长度为:{}".format(train_data_size))
print("测试数据集的长度为:{}".format(test_data_size))
# 利用dataloader来加载数据集
train_dataloader = DataLoader(train_data, batch_size=64)
test_dataloader = DataLoader(test_data, batch_size=64)
# 创建网络模型
kun = Kun()
# 定义损失函数
loss_fn = nn.CrossEntropyLoss()
# 定义优化器
# learning_rate = 0.01 # 方便修改学习速率
learning_rate = 1e-2
optim = torch.optim.SGD(kun.parameters(), lr=learning_rate)
# 设置训练网络的一些参数
total_train_step = 0 # 记录训练的次数
total_test_step = 0 # 记录测试的次数
epoch = 10 # 循环的轮数
# 添加tensorboard
writer = SummaryWriter("../logs_train")
for i in range(epoch):
print("-------------------第{}轮训练开始--------------------".format(i+1))
# 训练步骤开始
kun.train()
for data in train_dataloader:
imgs, targets = data
outputs = kun(imgs) # 将数据送入网络
loss = loss_fn(outputs, targets) # 记录损失值,参数分别是实际输出和真实值
# 优化器优化模型
optim.zero_grad()
loss.backward()
optim.step()
total_train_step += 1 # 记录训练次数
if total_train_step % 100 == 0:
# print("训练次数:{},损失值为:{}".format(total_train_step, loss.item()))
writer.add_scalar("train_loss", loss.item(), global_step=total_train_step)
# 测试步骤开始
kun.eval()
total_test_loss = 0
total_accuracy = 0 # 记录整体正确的个数
with torch.no_grad(): # 只是测试,可以去除梯度
for data in test_dataloader:
imgs, targets = data
outputs = kun(imgs)
loss = loss_fn(outputs, targets)
total_test_loss += loss.item()
accuracy = (outputs.argmax(1) == targets).sum() # 横向找出最大
total_accuracy += accuracy
print("整体测试集上的loss为:{}".format(total_test_loss))
print("整体测试集上的正确率为:{}".format(total_accuracy/test_data_size))
writer.add_scalar("test_loss", total_test_loss, total_test_step)
writer.add_scalar("test_accuracy", total_accuracy/test_data_size, total_test_step)
total_test_step += 1
# 保存每一轮的训练结果
torch.save(kun, "kun_{}.pth".format(i+1))
print("模型已保存")
writer.close()
结果:

10. 完整的模型验证套路
利用已经训练好的模型,然后给他提供输入进行测试
以上一节保存好的第十轮训练模型为例
代码示例:
import torchvision
from PIL import Image
import torch
from torch import nn
img_path = "../images/dog.png" # 传入狗的图
image = Image.open(img_path)
# print(image) # <PIL.PngImagePlugin.PngImageFile image mode=RGBA size=340x296 at 0x23DBF0CBD00>
image = image.convert('RGB') # 因为png格式是4通道,除了RGB三通道外还有一个透明度通道,所以要使用.convert保留其颜色通道
transform = torchvision.transforms.Compose([torchvision.transforms.Resize((32, 32)),
torchvision.transforms.ToTensor()])
image = transform(image)
# print(image.shape) # torch.Size([4, 32, 32])
# 网络模型
class Kun(nn.Module):
def __init__(self):
super(Kun, self).__init__()
self.model = nn.Sequential(
nn.Conv2d(3, 32, 5, 1, 2),
nn.MaxPool2d(2),
nn.Conv2d(32, 32, 5, 1, 2),
nn.MaxPool2d(2),
nn.Conv2d(32, 64, 5, 1, 2),
nn.MaxPool2d(2),
nn.Flatten(),
nn.Linear(1024, 64),
nn.Linear(64, 10)
)
def forward(self, x):
x = self.model(x)
return x
# 使用之前训练保存好的模型
model = torch.load("kun_10.pth")
# print(model)
image = torch.reshape(image, (1, 3, 32, 32))
# 测试
model.eval()
with torch.no_grad():
output = model(image)
print(output)
print(output.argmax(1)) # tensor([5]) 预测成功
 文章来源:https://www.toymoban.com/news/detail-690360.html
文章来源:https://www.toymoban.com/news/detail-690360.html
利用GPU进行训练只需要对网络模型、数据(输入,标注)、损失函数加.cuda()方法
例如:文章来源地址https://www.toymoban.com/news/detail-690360.html
loss_fn = nn.CrossEntropyLoss()
loss_fu = loss_fun.cuda()
imgs = imgs.cuda()
targets = targets.cuda()
到了这里,关于神经网络入门的文章就介绍完了。如果您还想了解更多内容,请在右上角搜索TOY模板网以前的文章或继续浏览下面的相关文章,希望大家以后多多支持TOY模板网!