1. 背景说明
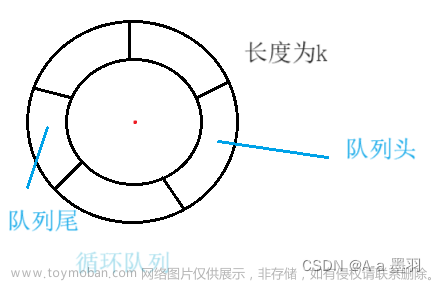
和顺序栈相类似,在队列的顺序存储结构中,除了用一组地址连续的存储单元依次存放从队列头到队列尾的元素之外,
尚需附设两个指针 front 和 rear 分别指示队列头元素及队列尾元素的位置。约定:初始化建空队列时,令 fronts = rear = 0,
每当插入新的队列尾元素时,“尾指针增 1”;每当删除队列头元素时,“头指针增 1”。因此,在非空队列中,头指针始终指向
队列头元素,而尾指针始终指向队列尾元素的下一个位置。



2. 示例代码
1) status.h
/* DataStructure 预定义常量和类型头文件 */
#ifndef STATUS_H
#define STATUS_H
/* 函数结果状态码 */
#define TRUE 1 /* 返回值为真 */
#define FALSE 0 /* 返回值为假 */
#define RET_OK 0 /* 返回值正确 */
#define INFEASIABLE 2 /* 返回值未知 */
#define ERR_MEMORY 3 /* 访问内存错 */
#define ERR_NULL_PTR 4 /* 空指针错误 */
#define ERR_MEMORY_ALLOCATE 5 /* 内存分配错 */
#define ERR_NULL_STACK 6 /* 栈元素为空 */
#define ERR_PARA 7 /* 函数参数错 */
#define ERR_OPEN_FILE 8 /* 打开文件错 */
#define ERR_NULL_QUEUE 9 /* 队列为空错 */
#define ERR_FULL_QUEUE 10 /* 队列为满错 */
typedef int Status; /* Status 是函数的类型,其值是函数结果状态代码,如 RET_OK 等 */
typedef int Bollean; /* Boolean 是布尔类型,其值是 TRUE 或 FALSE */
#endif // !STATUS_H2) cycleQueue.h
/* 循环队列实现头文件 */
#ifndef CYCLEQUEUE_H
#define CYCLEQUEUE_H
#include "status.h"
#define MAX_QUEUE_SIZE 5
typedef int QElemType;
typedef struct {
QElemType *base;
int front;
int rear;
} SqQueue;
/* 构造一个空队列 Q */
Status InitQueue(SqQueue *Q);
/* 销毁队列 Q */
Status DestroyQueue(SqQueue *Q);
/* 将 Q 清为空队列 */
void ClearQueue(SqQueue *Q);
/* 若队列 Q 为空队列,则返回 TRUE,否则返回 FALSE */
Bollean QueueEmpty(const SqQueue *Q);
/* 返回 Q 的元素个数,即队列的长度 */
int QueueLength(const SqQueue *Q);
/* 若队列不空,则用 e 返回 Q 的队头元素,并返回 OK */
Status GetQueueHead(const SqQueue *Q, QElemType *e);
/* 插入元素 e 为 Q 的新的队尾元素 */
Status EnQueue(QElemType e, SqQueue *Q);
/* 若队列不空,则删除 Q 的队头元素,用 e 返回其值,并返回 OK */
Status DeQueue(SqQueue *Q, QElemType *e);
/* 从队头到队尾依次对队列 Q 中每个元素调用函数 vi() */
Status QueueTraverse(const SqQueue *Q, void(*vi)(QElemType));
#endif // !CYCLEQUEUE_H
3) cycleQueue.c
/* 循环队列实现源文件 */
#include "cycleQueue.h"
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
static Bollean QueueFull(const SqQueue *Q)
{
return (((Q->rear + 1) % MAX_QUEUE_SIZE) == Q->front) ? TRUE : FALSE;
}
/* 构造一个空队列 Q */
Status InitQueue(SqQueue *Q)
{
Q->base = (QElemType *)malloc(sizeof(QElemType) * MAX_QUEUE_SIZE);
if (!Q->base) {
printf("FuncName: %-15s Line: %-5d ErrorCode: %-3d\n", __func__, __LINE__, ERR_MEMORY_ALLOCATE);
return ERR_MEMORY_ALLOCATE;
}
Q->front = Q->rear = 0;
return RET_OK;
}
/* 销毁队列 Q */
Status DestroyQueue(SqQueue *Q)
{
if (Q->base) {
free(Q->base);
}
Q->base = NULL;
Q->front = Q->rear = 0;
return RET_OK;
}
/* 将 Q 清为空队列 */
void ClearQueue(SqQueue *Q)
{
Q->front = Q->rear = 0;
}
/* 若队列 Q 为空队列,则返回 TRUE,否则返回 FALSE */
Bollean QueueEmpty(const SqQueue *Q)
{
return (Q->front == Q->rear) ? TRUE : FALSE;
}
/* 返回 Q 的元素个数,即队列的长度, 模运算可以起到类似于绝对值的作用 */
int QueueLength(const SqQueue *Q)
{
return ((Q->rear - Q->front + MAX_QUEUE_SIZE) % MAX_QUEUE_SIZE);
}
/* 若队列不空,则用 e 返回 Q 的队头元素,并返回 OK */
Status GetQueueHead(const SqQueue *Q, QElemType *e)
{
if (Q->front == Q->rear) {
printf("FuncName: %-15s Line: %-5d ErrorCode: %-3d\n", __func__, __LINE__, ERR_NULL_QUEUE);
return ERR_NULL_QUEUE;
}
*e = *(Q->base + Q->front);
return RET_OK;
}
/* 插入元素 e 为 Q 的新的队尾元素 */
Status EnQueue(QElemType e, SqQueue *Q)
{
if (QueueFull(Q)) {
printf("FuncName: %-15s Line: %-5d ErrorCode: %-3d\n", __func__, __LINE__, ERR_FULL_QUEUE);
return ERR_FULL_QUEUE;
}
Q->base[Q->rear] = e;
Q->rear = (Q->rear + 1) % MAX_QUEUE_SIZE;
return RET_OK;
}
/* 若队列不空,则删除 Q 的队头元素,用 e 返回其值,并返回 OK */
Status DeQueue(SqQueue *Q, QElemType *e)
{
if (QueueEmpty(Q)) {
printf("FuncName: %-15s Line: %-5d ErrorCode: %-3d\n", __func__, __LINE__, ERR_NULL_QUEUE);
return ERR_NULL_QUEUE;
}
*e = Q->base[Q->front];
Q->front = (Q->front + 1) % MAX_QUEUE_SIZE;
return RET_OK;
}
/* 从队头到队尾依次对队列 Q 中每个元素调用函数 vi() */
Status QueueTraverse(const SqQueue *Q, void(*vi)(QElemType))
{
int pos = Q->front;
while (pos != Q->rear) {
vi(Q->base[pos]);
pos = (pos + 1) % MAX_QUEUE_SIZE;
}
return RET_OK;
}4) auxiliary.h
/* 辅助函数头文件 */
#ifndef AUXILIARY_H
#define AUXILIARY_H
#include "cycleQueue.h"
/* 打印栈元素 */
void Print(QElemType e);
#endif // !AUXILIARY_H5) auxiliary.c
/* 辅助函数实现源文件 */
#include "auxiliary.h"
#include <stdio.h>
/* 打印栈元素 */
void Print(QElemType e)
{
printf("%d ", e);
}6) main.c
/* 入口程序源文件 */
#include "status.h"
#include "auxiliary.h"
#include "cycleQueue.h"
#include <stdio.h>
int main(void)
{
SqQueue Q;
int ret = InitQueue(&Q);
if (ret != RET_OK) {
printf("FuncName: %-15s Line: %-5d ErrorCode: %-3d\n", __func__, __LINE__, ret);
return ret;
}
printf("After initialize the queue, the queue is %s\n",
(QueueEmpty(&Q) == TRUE) ? "empty" : "not empty");
printf("Please input the element of the queue, no more than %d elements(-1 to break): ",
MAX_QUEUE_SIZE - 1);
QElemType e;
int length = 0;
do {
scanf_s("%d", &e);
if (e == -1) {
break;
}
ret = EnQueue(e, &Q);
if (ret != RET_OK) {
break;
}
++length;
} while (length < MAX_QUEUE_SIZE - 1);
printf("The length of the queue is %d\n", QueueLength(&Q));
printf("The queue is %s\n", (QueueEmpty(&Q) == TRUE) ? "empty" : "not empty");
printf("Delete from the head of the queue and insert into the rear of the queue for"
" %d times:\n", MAX_QUEUE_SIZE);
for (int i = 0; i < MAX_QUEUE_SIZE; ++i) {
DeQueue(&Q, &e);
printf("The elment deleted is %d, please input the element to be insert: ", e);
scanf_s("%d", &e);
EnQueue(e, &Q);
}
printf("The element of the queue is: ");
QueueTraverse(&Q, Print);
printf("\n");
length = QueueLength(&Q);
if (length - 2 > 0) {
printf("Now delete %d elements of the queue in the head of the queue\n", length - 2);
}
while (QueueLength(&Q) > 2) {
DeQueue(&Q, &e);
printf("The element of the queue deleted is %d\n", e);
}
ret = GetQueueHead(&Q, &e);
if (ret == RET_OK) {
printf("Now the element of the head of the queue is %d\n", e);
}
ClearQueue(&Q);
printf("After clear the queue, the queue is %s\n", (QueueEmpty(&Q) == TRUE) ? "empty" : "not empty");
DestroyQueue(&Q);
return 0;
}3. 输出示例文章来源:https://www.toymoban.com/news/detail-694472.html
 文章来源地址https://www.toymoban.com/news/detail-694472.html
文章来源地址https://www.toymoban.com/news/detail-694472.html
到了这里,关于第 3 章 栈和队列 (循环队列)的文章就介绍完了。如果您还想了解更多内容,请在右上角搜索TOY模板网以前的文章或继续浏览下面的相关文章,希望大家以后多多支持TOY模板网!