个人学习记录,代码难免不尽人意。
The left-view of a binary tree is a list of nodes obtained by looking at the tree from left hand side and from top down. For example, given a tree shown by the figure, its left-view is { 1, 2, 3, 4, 5 }
Given the inorder and preorder traversal sequences of a binary tree, you are supposed to output its left-view.
Input Specification:
Each input file contains one test case. For each case, the first line contains a positive integer N (≤20), which is the total number of nodes in the tree. Then given in the following 2 lines are the inorder and preorder traversal sequences of the tree, respectively. All the keys in the tree are distinct positive integers in the range of int.
Output Specification:
For each case, print in a line the left-view of the tree. All the numbers in a line are separated by exactly 1 space, and there must be no extra space at the beginning or the end of the line.
Sample Input:
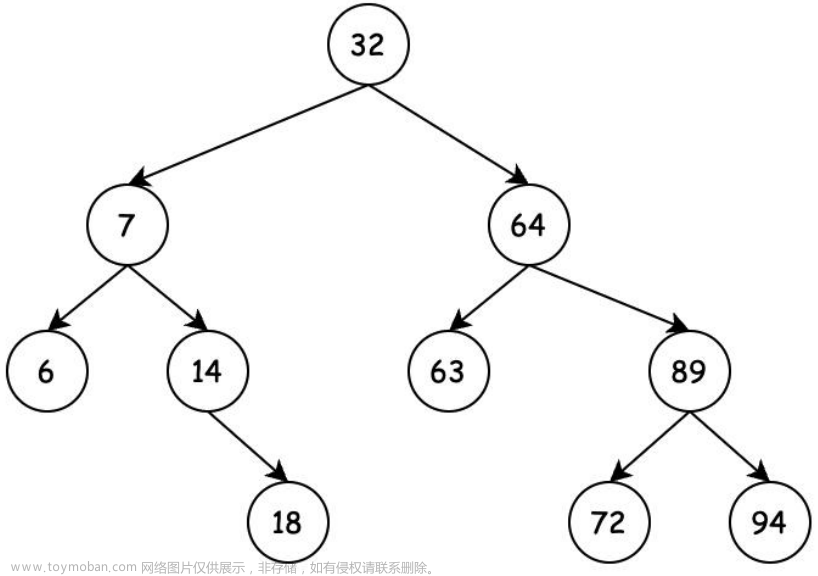
8
2 3 1 5 4 7 8 6
1 2 3 6 7 4 5 8
Sample Output:
1 2 3 4 5文章来源:https://www.toymoban.com/news/detail-696808.html
#include<cstdio>
#include<iostream>
#include<algorithm>
#include<cmath>
#include<set>
#include<queue>
#include<string>
#include<vector>
using namespace std;
struct node{
int data;
node* lchild;
node* rchild;
int height;
};
node* newnode(int data){
node* root=new node;
root->data=data;
root->lchild=NULL;
root->rchild=NULL;
root->height=1;
return root;
}
int pre[25];
int in[25];
node* create(int prel,int prer,int inl,int inr){
if(prel>prer) return NULL;
int mid=pre[prel];
int index;
for(int i=inl;i<=inr;i++){
if(in[i]==mid){
index=i;
break;
}
}
int leftnum=index-inl;
node* root=newnode(mid);
root->lchild=create(prel+1,prel+leftnum,inl,index-1);
root->rchild=create(prel+leftnum+1,prer,index+1,inr);
return root;
}
vector<int> v;
void bfs(node* root){
queue<node*> q;
q.push(root);
while(!q.empty()){
node* now=q.front();
q.pop();
if(now->lchild!=NULL){
now->lchild->height=now->height+1;
q.push(now->lchild);
}
if(now->rchild!=NULL){
now->rchild->height=now->height+1;
q.push(now->rchild);
}
}
q.push(root);
int num=1;
bool flag=true;
while(!q.empty()){
node* now=q.front();
q.pop();
if(now->height==num&&flag){
v.push_back(now->data);
flag=false;
}
if(now->lchild!=NULL){
num=now->lchild->height;
flag=true;
q.push(now->lchild);
}
if(now->rchild!=NULL){
num=now->rchild->height;
flag=true;
q.push(now->rchild);
}
}
}
int main(){
int n;
scanf("%d",&n);
for(int i=0;i<n;i++){
scanf("%d",&in[i]);
}
for(int i=0;i<n;i++){
scanf("%d",&pre[i]);
}
node* root=create(0,n-1,0,n-1);
bfs(root);
for(int i=0;i<v.size();i++){
printf("%d",v[i]);
if(i!=v.size()-1) printf(" ");
else printf("\n");
}
}
强烈谴责这道题的出题人!要么出题人觉得这道题题干描述的很“清楚”了,居高临下没有站在考生的角度思考问题,要么就是故意玩文字游戏加大难度!
我们来看这道题的描述:The left-view of a binary tree is a list of nodes obtained by looking at the tree from left hand side and from top down. For example, given a tree shown by the figure, its left-view is { 1, 2, 3, 4, 5 },翻译成汉语就是二叉树的左视图是通过从左侧和从上到下查看树获得的节点列表。例如,给定如图所示的树,其左视图为{1,2,3,4,5}
问题是,例题给的树太随意了,根本让人理解不了什么是“left hand side”,我一开始以为是这样子:先遍历左子树,左子树遍历完了再从右子树低于左子树最后一个节点的左子树开始遍历!是不是很绕!后来基本只能通过几个测试点我就知道不是这样做。后来看了别人的做法才知道是输出每一行的最左侧的节点!真的是无语了,就不能在题目中直说啊,或者你多举几个普通点的树让大伙猜一猜啊,真的是。下面附上知道做法时候的代码:文章来源地址https://www.toymoban.com/news/detail-696808.html
#include<cstdio>
#include<iostream>
#include<algorithm>
#include<cmath>
#include<set>
#include<queue>
#include<string>
#include<vector>
using namespace std;
struct node{
int data;
node* lchild;
node* rchild;
int height;
};
node* newnode(int data){
node* root=new node;
root->data=data;
root->lchild=NULL;
root->rchild=NULL;
root->height=1;
return root;
}
int pre[25];
int in[25];
node* create(int prel,int prer,int inl,int inr){
if(prel>prer) return NULL;
int mid=pre[prel];
int index;
for(int i=inl;i<=inr;i++){
if(in[i]==mid){
index=i;
break;
}
}
int leftnum=index-inl;
node* root=newnode(mid);
root->lchild=create(prel+1,prel+leftnum,inl,index-1);
root->rchild=create(prel+leftnum+1,prer,index+1,inr);
return root;
}
vector<int> v;
void bfs(node* root){
queue<node*> q;
q.push(root);
while(!q.empty()){
node* now=q.front();
q.pop();
if(now->lchild!=NULL){
now->lchild->height=now->height+1;
q.push(now->lchild);
}
if(now->rchild!=NULL){
now->rchild->height=now->height+1;
q.push(now->rchild);
}
}
q.push(root);
int num=1;
bool flag=true;
while(!q.empty()){
node* now=q.front();
q.pop();
if(now->height==num&&flag){
v.push_back(now->data);
flag=false;
}
if(now->lchild!=NULL){
num=now->lchild->height;
flag=true;
q.push(now->lchild);
}
if(now->rchild!=NULL){
num=now->rchild->height;
flag=true;
q.push(now->rchild);
}
}
}
int main(){
int n;
scanf("%d",&n);
for(int i=0;i<n;i++){
scanf("%d",&in[i]);
}
for(int i=0;i<n;i++){
scanf("%d",&pre[i]);
}
node* root=create(0,n-1,0,n-1);
bfs(root);
for(int i=0;i<v.size();i++){
printf("%d",v[i]);
if(i!=v.size()-1) printf(" ");
else printf("\n");
}
}
到了这里,关于PAT 1174 Left-View of Binary Tree 题干不知所云的文章就介绍完了。如果您还想了解更多内容,请在右上角搜索TOY模板网以前的文章或继续浏览下面的相关文章,希望大家以后多多支持TOY模板网!