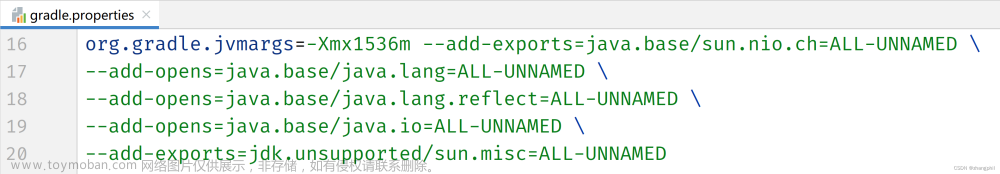
Path、File、Files是什么?
Path:用于操作路径
File:用于操作文件
Files:文件工具类
Path
创建Path
可使用静态Paths.get()创建相对/绝对路径,路径并不需要真实存在,若路径不合法则抛InvalidPathException
Path path = Paths.get("/storage/emulated/0/Android/data/com.demo.demo0/files/Download","data.txt");
System.out.println(path);
会默认使用当前文件系统路径分隔符连接路径(Linux是/,windows是\)
File
Files
读文件
读取文件所有内容,参数为Path
Path path = Paths.get("/storage/emulated/0/Android/data/com.demo.demo0/files/Download","data.txt");
try {
byte[] bytes = Files.readAllBytes(path);
System.out.println(new String(bytes));
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
按行读取文件内容
Path path = Paths.get("/storage/emulated/0/Android/data/com.demo.demo0/files/Download","data.txt");
try {
List<String> list = Files.readAllLines(path);
System.out.println(list);
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
写文件
写文件,参数为Path和byte[]
Path path = Paths.get("/storage/emulated/0/Android/data/com.demo.demo0/files/Download","data.txt");
try {
Files.write(new File(path ,"0".getBytes());
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
如要对文件追加内容,则加入参数StandardOpenOption.APPEND
Path path = Paths.get("/storage/emulated/0/Android/data/com.demo.demo0/files/Download","data.txt");
try {
Files.write(path, "0".getBytes(), StandardOpenOption.APPEND);
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
从Files提取流
InputStream inputStream = Files.newInputStream(path);
OutputStream outputStream = Files.newOutputStream(path);
BufferedReader bufferedReader = Files.newBufferedReader(path);
BufferedWriter bufferedWriter = Files.newBufferedWriter(path);
创建目录
除最后一个路径外,前边路径必须是已存在的
Path path = Paths.get("/storage/emulated/0/Android/data/com.demo.demo0/files/Download/dir");
try {
Files.createDirectory(path);
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
创建文件
如果文件已经存在,则抛出异常,
Path path = Paths.get("/storage/emulated/0/Android/data/com.demo.demo0/files/Download/1.txt");
try {
Files.createFile(path);
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
复制、剪切文件
复制调用copy,若要覆盖,则可添加参数StandardCopyOption.REPLACE_EXISTING,StandardCopyOption.COPY_ATTRIBUTES
Path form = Paths.get("/storage/emulated/0/Android/data/com.demo.demo0/files/Download/1.txt");
Path to = Paths.get("/storage/emulated/0/Android/data/com.demo.demo0/files/Download/dir/1.txt");
try {
Files.copy(form, to);
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
剪切调用move,若要保证剪切的原子性,可添加参数StandardCopyOption.ATOMIC_MOVE
Path form = Paths.get("/storage/emulated/0/Android/data/com.demo.demo0/files/Download/1.txt");
Path to = Paths.get("/storage/emulated/0/Android/data/com.demo.demo0/files/Download/dir/1.txt");
try {
Files.move(form, to);
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
删除文件
删除调用delete,若文件不存在则抛出异常,用deleteIfExists可避免异常,还可用于删除空目录
Path path = Paths.get("/storage/emulated/0/Android/data/com.demo.demo0/files/Download/dir/1.txt");
try {
Files.delete(path);
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
获取文件信息
是否存在、是否隐藏、是否可读可写可执行、是否目录、是否普通文件、是否软连接文章来源:https://www.toymoban.com/news/detail-703432.html
boolean exists = Files.exists(path);
boolean hidden = Files.isHidden(path);
boolean readable = Files.isReadable(path);
boolean writable = Files.isWritable(path);
boolean executable = Files.isExecutable(path);
boolean directory = Files.isDirectory(path);
boolean regularFile = Files.isRegularFile(path);
boolean symbolicLink = Files.isSymbolicLink(path);
获取大小、拥有者、创建时间等文章来源地址https://www.toymoban.com/news/detail-703432.html
long size = Files.size(path);
UserPrincipal owner = Files.getOwner(path);
String name = owner.getName();
BasicFileAttributes basicFileAttributes = Files.readAttributes(path, BasicFileAttributes.class);
FileTime fileTime = basicFileAttributes.creationTime();
到了这里,关于Java基础——Path、File、Files的文章就介绍完了。如果您还想了解更多内容,请在右上角搜索TOY模板网以前的文章或继续浏览下面的相关文章,希望大家以后多多支持TOY模板网!