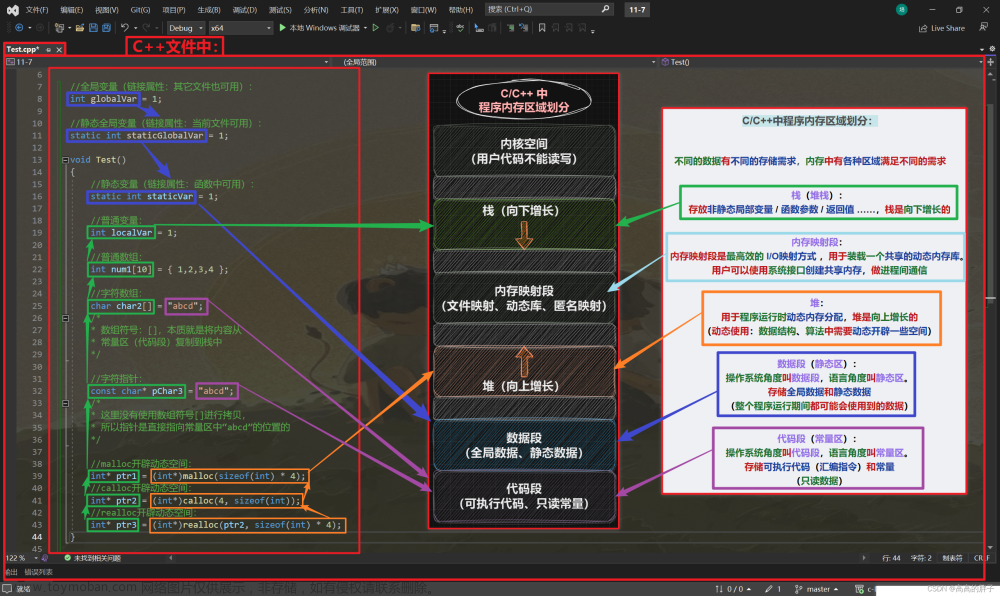
指针权限 用法
void Print(const char* SecretPointer)
{
cout << "绝密指令为:";
cout << SecretPointer << endl;
}
void Change(int& number, int* const FixedPointer)
{
cout << "更换站台数字为:";
cin >> number;
cout << *FixedPointer << endl;
}
int main()
{
char* SecretPointer_01 = (char*)malloc(sizeof(char) * 20);
cout << "请输入绝密指令:";
cin >> SecretPointer_01;
const char* SecretPointer = SecretPointer_01;
Print(SecretPointer);
int number = 100;
int* const FixedPointer = &number;
cout << "原站台数字为:" << *FixedPointer << endl;
Change(number, FixedPointer);
return 0;
}
new与delete 用法
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
int* CreateSpace1(int*& PointerOfSum1)
{
PointerOfSum1 = new int(0); // 1
return new int[5]{ 1,2,3,4,5 }; // 2
}
void AddArray1(int*& PointerOfSum1, int*& PointerOfArray1)
{
for (int i = 0; i < 5; i++)
{
(*PointerOfSum1) += (*(PointerOfArray1 + i));
}
}
//
class StupidPerson
{
public:
StupidPerson(int IQ = 10)
:_IQ(IQ)
{}
int GetIQ()
{
return _IQ;
}
private:
int _IQ;
};
StupidPerson* CreateSpace2(int*& PointerOfSum2)
{
PointerOfSum2 = new int(0);
return new StupidPerson[5]; // 3
}
void AddArray2(int*& PointerOfSum2, StupidPerson*& PointerOfArray2)
{
for (int i = 0; i < 5; i++)
{
(*PointerOfSum2) += ((*(PointerOfArray2 + i)).GetIQ());
}
}
//
class SmartPerson
{
public:
SmartPerson(int IQ = 100)
:_IQ(IQ)
{}
~SmartPerson()
{
_IQ = 0;
}
int GetIQ()
{
return _IQ;
}
private:
int _IQ;
};
SmartPerson* CreateSpace3(int*& PointerOfSum3)
{
PointerOfSum3 = new int(0);
return new SmartPerson[5]{ SmartPerson(),SmartPerson(101),SmartPerson(102) ,SmartPerson(99) ,SmartPerson(107) }; // 4
}
void AddArray3(int*& PointerOfSum3, SmartPerson*& PointerOfArray3)
{
for (int i = 0; i < 5; i++)
{
(*PointerOfSum3) += ((*(PointerOfArray3 + i)).GetIQ());
}
}
int main()
{
int* PointerOfSum1 = nullptr;
int* PointerOfArray1 = CreateSpace1(PointerOfSum1);
AddArray1(PointerOfSum1, PointerOfArray1);
cout << "总和为:" << (*PointerOfSum1) << endl;
delete PointerOfSum1; // 5
delete[] PointerOfArray1; // 6
//
int* PointerOfSum2 = nullptr;
StupidPerson* PointerOfArray2 = CreateSpace2(PointerOfSum2);
AddArray2(PointerOfSum2, PointerOfArray2);
cout << "IQ总和为:" << (*PointerOfSum2) << endl;
delete PointerOfSum2;
delete[] PointerOfArray2;
//
int* PointerOfSum3 = nullptr;
SmartPerson* PointerOfArray3 = CreateSpace3(PointerOfSum3);
AddArray3(PointerOfSum3, PointerOfArray3);
cout << "IQ总和为:" << (*PointerOfSum3) << endl;
delete PointerOfSum3;
delete[] PointerOfArray3;
//
SmartPerson* ps = (SmartPerson*)malloc(sizeof(SmartPerson) * 10);
cout << "内存池已经创建完成!" << endl;
new(ps)SmartPerson(110); // 7
new(ps + 1)SmartPerson(103);
cout << "第一个人智商为:" << ps->GetIQ() << endl;
cout << "第二个人智商为:" << (ps + 1)->GetIQ() << endl;
ps->~SmartPerson(); // 8
(ps + 1)->~SmartPerson();
return 0;
}
类与对象 用法
test.h
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
class Country
{
friend class Citizen;
friend istream& operator>>(istream& cin, Country& country);
friend ostream& operator<<(ostream& cout, const Country& country);
public:
//构造函数
Country();
//拷贝构造函数
Country(const Country& other);
//析构函数
~Country();
//赋值运算符重载
Country& operator=(const Country& other);
private:
char* _countryname;
char* _capital;
};
//流插入运算符重载
istream& operator>>(istream& cin, Country& country);
//流提取运算符重载
ostream& operator<<(ostream& cout, const Country& country);
//
class Citizen
{
friend int operator>(const Citizen& c1, const Citizen& c2);
friend istream& operator>>(istream& cin, Citizen& citizen);
friend ostream& operator<<(ostream& cout, const Citizen& citizen);
public:
//构造函数
explicit Citizen(bool iscriminal = false);
//拷贝构造函数
Citizen(const Citizen& other);
//析构函数
~Citizen();
//赋值运算符重载
Citizen& operator=(const Citizen& other);
//前置++运算符重载
Citizen& operator++();
//后置++运算符重载
Citizen operator++(int);
//普通运算符重载
Citizen& operator-(int num);
//静态成员函数
static int GetTotalCitizen();
//友元类的跨类访问
void GetCountry();
private:
//成员变量
char* _personalname;
int _age;
Country _nationality;
bool _iscriminal;
int _creditscore;
const int _maxcreditscore;
//类的静态区成员变量
static int _totalcitizen;
};
//普通运算符重载
int operator>(const Citizen& c1, const Citizen& c2);
//流插入运算符重载
istream& operator>>(istream& cin, Citizen& citizen);
//流提取运算符重载
ostream& operator<<(ostream& cout, const Citizen& citizen);
//func.cpp
#include "test.h"
//Country类相关
Country::Country()
{
_countryname = new char[20]{ '\0' };
_capital = new char[20]{ '\0' };
}
Country::Country(const Country& other)
{
_countryname = new char[20]{ '\0' };
_capital = new char[20]{ '\0' };
memcpy(_countryname, other._countryname, sizeof(char) * 20);
memcpy(_capital, other._capital, sizeof(char) * 20);
}
Country::~Country()
{
delete[] _countryname;
delete[] _capital;
}
Country& Country::operator=(const Country& other)
{
if (&other != this)
{
memcpy(_countryname, other._countryname, sizeof(char) * 20);
memcpy(_capital, other._capital, sizeof(char) * 20);
}
return *this;
}
istream& operator>>(istream& cin, Country& country)
{
cin >> country._countryname >> country._capital;
return cin;
}
ostream& operator<<(ostream& cout, const Country& country)
{
cout << country._countryname << " " << country._capital;
return cout;
}
//Citizen类相关
Citizen::Citizen(bool iscriminal)
:_age(0)
,_nationality()
,_iscriminal(iscriminal)
,_creditscore(0)
,_maxcreditscore(100)
{
_personalname = new char[20]{ '\0' };
_totalcitizen++;
}
Citizen::Citizen(const Citizen& other)
:_age(other._age)
, _nationality(other._nationality)
, _iscriminal(other._iscriminal)
, _creditscore(other._creditscore)
, _maxcreditscore(other._maxcreditscore)
{
_personalname = new char[20]{ '\0' };
memcpy(_personalname, other._personalname, sizeof(char) * 20);
_totalcitizen++;
}
Citizen::~Citizen()
{
delete[] _personalname;
_totalcitizen--;
}
Citizen& Citizen::operator=(const Citizen& other)
{
if (&other != this)
{
_age = other._age;
_nationality = other._nationality;
_iscriminal = other._iscriminal;
_creditscore = other._creditscore;
memcpy(_personalname, other._personalname, sizeof(char) * 20);
}
return *this;
}
Citizen& Citizen::operator++()
{
if (_creditscore < _maxcreditscore)
{
_creditscore++;
}
return *this;
}
Citizen Citizen::operator++(int)
{
Citizen tmp(*this);
if (_creditscore < _maxcreditscore)
{
_creditscore++;
}
return tmp;
}
Citizen& Citizen::operator-(int num)
{
if (_creditscore > 0)
{
_creditscore -= num;
if (_creditscore < 0)
{
_creditscore = 0;
}
}
return *this;
}
int operator>(const Citizen& c1, const Citizen& c2)
{
if (c1._creditscore > c2._creditscore)
{
return 1;
}
else if (c1._creditscore < c2._creditscore)
{
return 2;
}
else
{
return 0;
}
}
istream& operator>>(istream& cin, Citizen& citizen)
{
cin >> citizen._personalname >> citizen._age >> citizen._nationality
>> citizen._iscriminal >> citizen._creditscore;
return cin;
}
ostream& operator<<(ostream& cout, const Citizen& citizen)
{
cout << citizen._personalname << " " << citizen._age << " " << citizen._nationality
<< " " << citizen._iscriminal << " " << citizen._creditscore;
return cout;
}
int Citizen::GetTotalCitizen()
{
return _totalcitizen;
}
void Citizen::GetCountry()
{
cout << _nationality._countryname << " " << _nationality._capital << endl;
}
//类的静态区成员变量定义
int Citizen::_totalcitizen = 0;
//test.cpp
#include "test.h"
int main()
{
Citizen Shen(0);
cin >> Shen;
cout << Shen << endl;
Citizen Jun(Shen);
cout << Jun << endl;
Citizen Elon(0);
cin >> Elon;
cout << Elon << endl;
cout << "此时人数:" << Citizen::GetTotalCitizen() << endl;
return 0;
}
函数模板 用法
// test.h
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
template <typename T>
void Swap(T& a, T& b)
{
T tmp = a;
a = b;
b = tmp;
}
template <typename T1, typename T2, typename T3>
void Print(const T1& a, const T2& b, const T3& c)
{
cout << a << " " << b << " " << c << endl;
}
// test.cpp
#include "test.h"
int main()
{
int x = 1;
int y = 2;
char m = 'x';
char n = 'y';
cout << "交换前:" << endl;
cout << x << " " << y << endl;
cout << m << " " << n << endl;
Swap(x, y);
Swap(m, n);
cout << "交换后:" << endl;
cout << x << " " << y << endl;
cout << m << " " << n << endl;
//
const char* pointer = "根据ASCII码表对应的(值/字符)为";
char obj1 = 'A';
int obj2 = 65;
Print(obj1, pointer, obj2);
Print<int, const char*, char>(obj1, pointer, obj2);
return 0;
}
类模板 用法
// test.h
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
template <typename T>
class Person
{
friend istream& operator>>(istream& cin, Person<T>& person)
{
cin >> person._name >> *(person._luckysymbol);
return cin;
}
friend ostream& operator<<(ostream& cout, Person<T>& person)
{
cout << person._name << " " << *(person._luckysymbol);
return cout;
}
public:
Person();
Person(const Person& other);
~Person();
Person& operator=(const Person& other);
private:
char* _name;
T* _luckysymbol;
};
template <typename T>
Person<T>::Person()
{
_name = new char[20]{ 0 };
_luckysymbol = new T(0);
}
template <typename T>
Person<T>::Person(const Person& other)
:_name(new char[20]{ 0 })
, _luckysymbol(new T(0))
{
memcpy(_name, other._name, sizeof(char) * 20);
*_luckysymbol = *(other._luckysymbol);
}
template <typename T>
Person<T>::~Person()
{
delete _luckysymbol;
delete[] _name;
}
template <typename T>
Person<T>& Person<T>::operator=(const Person& other)
{
if (&other != this)
{
memcpy(_name, other._name, sizeof(char) * 20);
*_luckysymbol = *(other._luckysymbol);
}
return *this;
}
// test.cpp
#include "test.h"
int main()
{
Person<int> Shen;
Person<char> Hu;
Person<double> Ye;
cin >> Shen >> Hu >> Ye;
Person<int> Junyang(Shen);
Person<char> Yao;
Yao = Hu;
cout << Shen << endl;
cout << Hu << endl;
cout << Ye << endl;
cout << Junyang << endl;
cout << Yao << endl;
return 0;
}
文章来源地址https://www.toymoban.com/news/detail-709245.html
文章来源:https://www.toymoban.com/news/detail-709245.html
到了这里,关于指针权限,new与delete,类与对象,函数模板,类模板的用法的文章就介绍完了。如果您还想了解更多内容,请在右上角搜索TOY模板网以前的文章或继续浏览下面的相关文章,希望大家以后多多支持TOY模板网!