知识总览

2.3.1 单链表的定义
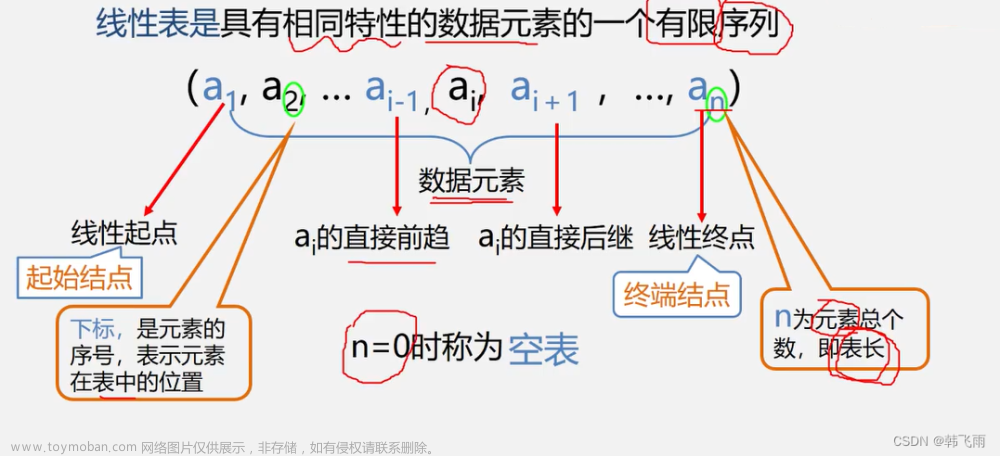
知识总览

单链表定义
#include<stdio.h>
#include<string.h>
#include<stdlib.h>
struct LNode{
int data;
struct LNode *next;
};
int main(){
struct LNode *p=(struct LNode*)malloc(sizeof(struct LNode));
return 0;
}typedef重命名
typedef struct LNode{
int data;
struct LNode *next;
}LNode,*LinkList;
等同于
struct LNode{
int data;
struct LNode *next;
};
typedef struct LNode LNode;
typedef struct LNode *LinkList;
头插法建立单链表
头插法
#include<stdio.h>
#include<string.h>
#include<stdlib.h>
typedef struct LNode{
int data;
struct LNode *next;
}LNode,*LinkList;
LinkList List_HeadInsert(LinkList &L){
LNode *s;
int x;
L=(LinkList)malloc(sizeof(LNode)); //创建头节点
L->next=NULL; //初始为空链表
scanf("%d",&x); //输入节点的值
while(x!=9999){ //输出9999表示结束
s=(LNode*)malloc(sizeof(LNode)); //创建新节点
s->data=x;
s->next=L->next;
L->next=s; //将新节点插入表中,L为头指针
scanf("%d",&x);
}
return L;
}
int main(){
LinkList L;
List_HeadInsert(L);
}强调这是一个单链表 ————使用LinkList
强调这是一个节点 ————使用LNode*
不带头节点的单链表
#include<stdio.h>
#include<string.h>
#include<stdlib.h>
typedef struct LNode{
int data;
struct LNode *next;
}LNode,*LinkList;
//初始化一个空的单链表
bool InitList(LinkList &L){
L=NULL; //空表,//防止脏数据
return true;
}
//判断单链表是否为空
bool Empty(LinkList L){
return (L==NULL);
}
int main(){
LinkList L; //声明一个指向单链表的指针 //此处并没有创建一个节点
InitList(L);
Empty(L);
}带头结点的单链表
#include<stdio.h>
#include<string.h>
#include<stdlib.h>
typedef struct LNode{
int data;
struct LNode *next;
}LNode,*LinkList;
//初始化一个单链表 (带头结点)
bool InitList(LinkList &L){
L=(LNode*)malloc(sizeof(LNode));
if(L==NULL)
return false;
L->next=NULL;
return true;
}
//判断单链表是否为空 (带头结点)
bool Empty(LinkList L){
if(L->next==NULL)
return true;
else
return false;
}
int main(){
LinkList L; //声明一个指向单链表的指针
InitList(L);
Empty(L);
}

按位序插入(带头结点)
#include<stdio.h>
#include<string.h>
#include<stdlib.h>
typedef struct LNode{
int data;
struct LNode *next;
}LNode,*LinkList;
//初始化一个单链表 (带头结点)
bool InitList(LinkList &L){
L=(LNode*)malloc(sizeof(LNode));
if(L==NULL)
return false;
L->next=NULL;
return true;
}
//判断单链表是否为空 (带头结点)
bool Empty(LinkList L){
if(L->next==NULL)
return true;
else
return false;
}
//在第i个位置插入元素e(带头结点)
bool ListInsert(LinkList &L,int i,int e){
if(i<1)
return false;
LNode *p; //指针p指向当前扫描到的结点
int j=0; //当前p指向的是第几个结点
p=L; //L指向头结点,头结点是第0个结点(不存数据)
while(p!=NULL&&j<i-1){ //循环找到第i-1 个结点 //找位置
p=p->next;
j++;
}
if(p==NULL) //i值不合法
return false;
LNode *s=(LNode*)malloc(sizeof(LNode));
s->data=e;
s->next=p->next;
p->next=s; //将结点s连到p之后
return true; //插入成功
}
int main(){
LinkList L; //声明一个指向单链表的指针
InitList(L);
Empty(L);
ListInsert(L,1,9);
}按位序插入(不带头结点)
#include<stdio.h>
#include<string.h>
#include<stdlib.h>
typedef struct LNode{
int data;
struct LNode *next;
}LNode,*LinkList;
//初始化一个空的单链表
bool InitList(LinkList &L){
L=NULL; //空表,//防止脏数据
return true;
}
//判断单链表是否为空
bool Empty(LinkList L){
return (L==NULL);
}
bool ListInsert(LinkList &L,int i,int e){
if(i<1)
return false;
if(i==1){ //插入第1个结点的操作与其他操作不同
LNode *s=(LNode*)malloc(sizeof(LNode));
s->data=e;
s->next=L;
L=s; //头指针指向新结点
return true;
}
LNode *p; //指针p指向当前扫描到的结点
int j=1; //当前p指向的是第几个结点
p=L; //p指向第1个结点(注意:不是头节点)
while(p!=NULL&&j<i-1){ //循环找到第i-1 个结点 //找位置
p=p->next;
j++;
}
if(p==NULL) //i值不合法
return false;
LNode *s=(LNode*)malloc(sizeof(LNode));
s->data=e;
s->next=p->next;
p->next=s;
return true; //插入成功
}
int main(){
LinkList L; //声明一个指向单链表的指针
InitList(L);
Empty(L);
ListInsert(L,1,9);
}指定结点的后插操作
#include<stdio.h>
#include<string.h>
#include<stdlib.h>
typedef struct LNode{
int data;
struct LNode *next;
}LNode,*LinkList;
//初始化一个单链表 (带头结点)
bool InitList(LinkList &L){
L=(LNode*)malloc(sizeof(LNode));
if(L==NULL)
return false;
L->next=NULL;
return true;
}
//判断单链表是否为空 (带头结点)
bool Empty(LinkList L){
if(L->next==NULL)
return true;
else
return false;
}
//后插操作:在p结点之后插入元素e
bool InsertNextNode(LNode *p,int e){
if(p==NULL) //i值不合法
return false;
LNode *s=(LNode*)malloc(sizeof(LNode));
if(s==NULL) //内存分配失败 //在某些情况下可能分配失败(如内存不足)
return false;
s->data=e; //用结点s保存数据元素e
s->next=p->next;
p->next=s; //将节点s连到p之后
return true;
}
//在第i个位置插入元素e(带头结点)
bool ListInsert(LinkList &L,int i,int e){
if(i<1)
return false;
LNode *p; //指针p指向当前扫描到的结点
int j=0; //当前p指向的是第几个结点
p=L; //L指向头结点,头结点是第0个结点(不存数据)
while(p!=NULL&&j<i-1){ //循环找到第i-1 个结点 //找位置
p=p->next;
j++;
}
return InsertNextNode(p,e); //插入成功
}
int main(){
LinkList L; //声明一个指向单链表的指针
InitList(L);
Empty(L);
ListInsert(L,1,9);
}指定结点的前插操作
1.使用带头结点的单链表,遍历指定结点的位置
(待完成)
#include<stdio.h>
#include<string.h>
#include<stdlib.h>
typedef struct LNode{
int data;
struct LNode *next;
}LNode,*LinkList;
//初始化一个单链表 (带头结点)
bool InitList(LinkList &L){
L=(LNode*)malloc(sizeof(LNode));
if(L==NULL)
return false;
L->next=NULL;
return true;
}
//判断单链表是否为空 (带头结点)
bool Empty(LinkList L){
if(L->next==NULL)
return true;
else
return false;
}
//在第i个位置插入元素e(带头结点)
LNode* ListInsert(LinkList &L,int i,int e){
LNode *p; //指针p指向当前扫描到的结点
int j=0; //当前p指向的是第几个结点
p=L; //L指向头结点,头结点是第0个结点(不存数据)
while(p!=NULL&&j<i-1){ //循环找到第i-1 个结点 //找位置
p=p->next;
j++;
}
if(p==NULL||i<1) //i值不合法
{
printf("i值:%d,小于1,i不合法",i);
return p;
}
LNode *s=(LNode*)malloc(sizeof(LNode));
s->data=e;
s->next=p->next;
p->next=s; //将结点s连到p之后
return s; //插入成功
}
bool InsertPriorNode(LinkList L,LNode *p,int e){
LNode *q; //指针p指向当前扫描到的结点
int j=0; //当前p指向的是第几个结点
q=L->next; //L指向头结点,头结点是第0个结点(不存数据)
while(q->data!=p->data){ //比较元素,找到位置
q=q->next;
j++;
}
j--;
q=L->next;
while(q!=NULL&&j<j-1){ //循环找到第i-1 个结点 //找位置
q=q->next;
j++;
}
if(p==NULL)
return false;
q->next=s;
LNode *s=(LNode*)malloc(sizeof(LNode));
s->data=e;
s->next=p;
if(L->next!=NULL){
printf("%d",L->data);
// do{
// printf("%d",p->data);
// p=p->next;
// }while(p!=NULL);
}
// while(q!=NULL){
// q=q->next;
// printf("%d",q->data);
// }
return true; //插入成功
}
int main(){
LinkList L; //声明一个指向单链表的指针
InitList(L);
Empty(L);
InsertPriorNode(L,ListInsert(L,1,9),22);
}
2.偷天换日(使用中间变量,数据互换)
(未完成)
#include<stdio.h>
#include<string.h>
#include<stdlib.h>
typedef struct LNode{
int data;
struct LNode *next;
}LNode,*LinkList;
//初始化一个单链表 (带头结点)
bool InitList(LinkList &L){
L=(LNode*)malloc(sizeof(LNode));
if(L==NULL)
return false;
L->next=NULL;
return true;
}
//判断单链表是否为空 (带头结点)
bool Empty(LinkList L){
if(L->next==NULL)
return true;
else
return false;
}
//在第i个位置插入元素e(带头结点)
LNode* ListInsert(LinkList &L,int i,int e){
LNode *p; //指针p指向当前扫描到的结点
int j=0; //当前p指向的是第几个结点
p=L; //L指向头结点,头结点是第0个结点(不存数据)
while(p!=NULL&&j<i-1){ //循环找到第i-1 个结点 //找位置
p=p->next;
j++;
}
if(p==NULL||i<1) //i值不合法
{
printf("i值:%d,小于1,i不合法",i);
return p;
}
LNode *s=(LNode*)malloc(sizeof(LNode));
s->data=e;
s->next=p->next;
p->next=s; //将结点s连到p之后
return s; //插入成功
}
//前插操作:在p结点之前插入元素e
bool InsertPriorNode(LNode *p,int e){
if(p==NULL)
return false;
LNode *s=(LNode*)malloc(sizeof(LNode));
if(s==NULL){
return false;
}
s->next=p->next;
p->next=s; //新结点s连到p之后
s->data=p->data; //将p元素复制到s中
p->data=e; //p中元素覆盖为e
return true;
}
int main(){
LinkList L; //声明一个指向单链表的指针
InitList(L);
Empty(L);
InsertPriorNode(ListInsert(L,1,77),2);
}文章来源:https://www.toymoban.com/news/detail-710921.html
LNode * GetElem(LinkList L ,int i){
int j=1;
LNode *p=L->next;
if(i==0)
return L;
if(i<1)
return NULL;
while(p!=NULL&&j<i){
p=p->next;
j++;
}文章来源地址https://www.toymoban.com/news/detail-710921.html
到了这里,关于2.3 线性表的链式表示的文章就介绍完了。如果您还想了解更多内容,请在右上角搜索TOY模板网以前的文章或继续浏览下面的相关文章,希望大家以后多多支持TOY模板网!