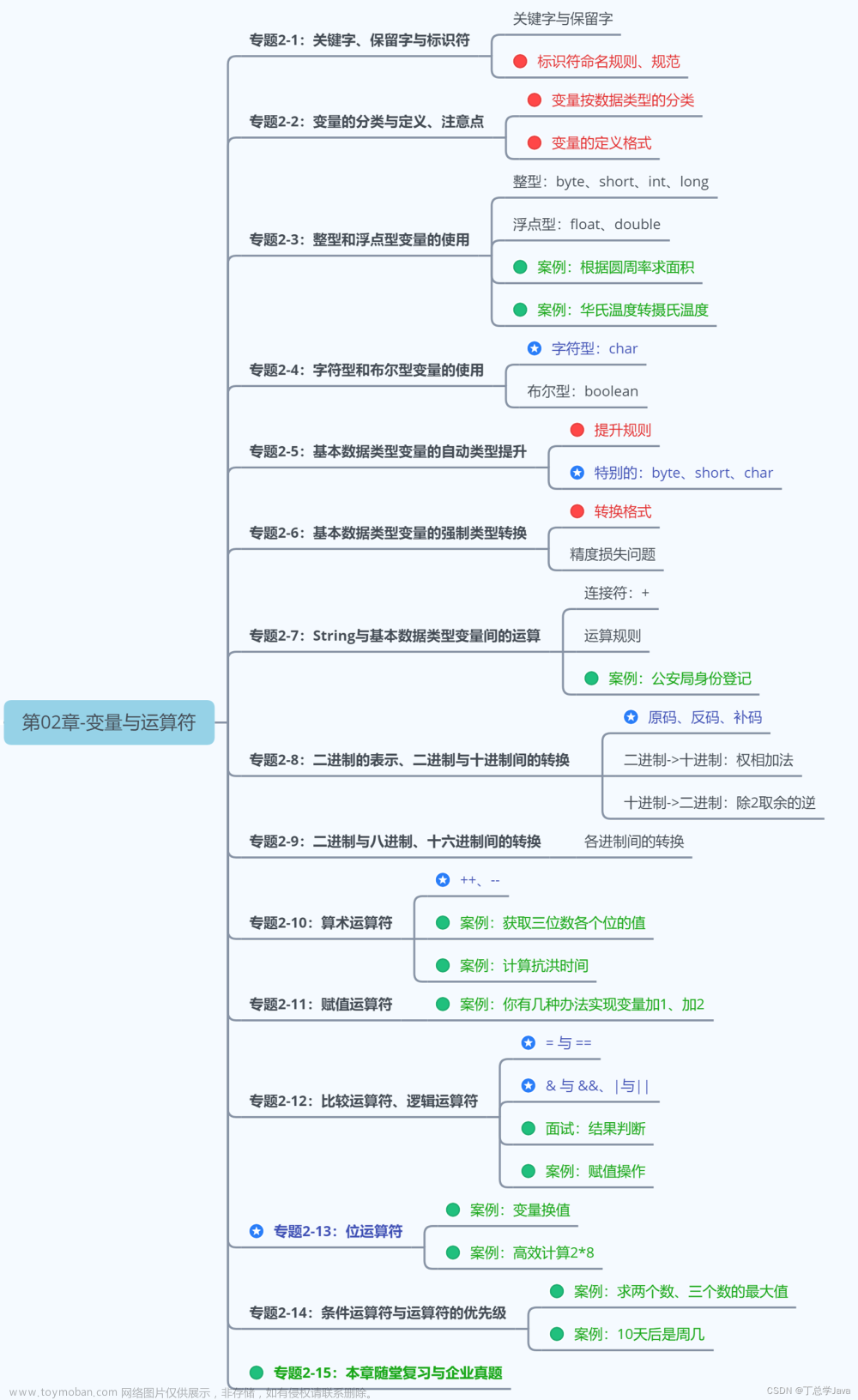
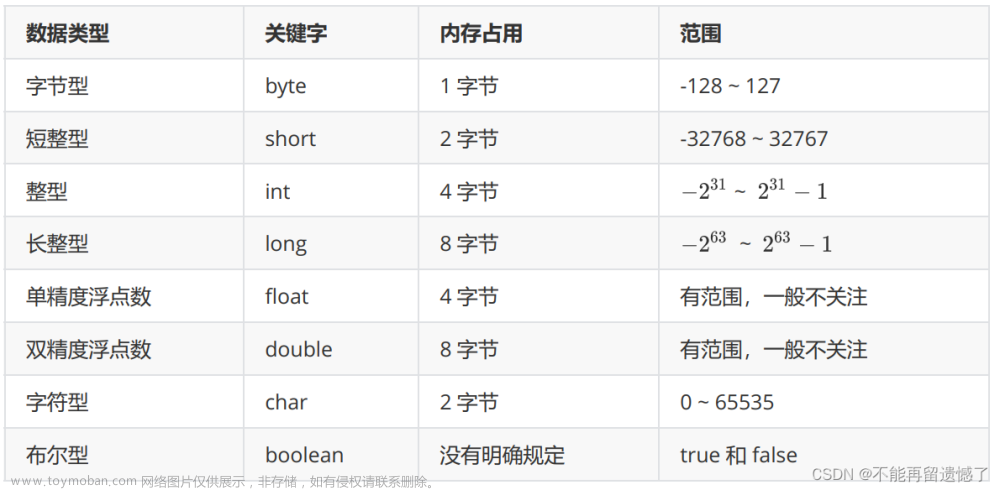
异常捕获
使用异常捕获可以捕获出现异常的代码块,防止因为异常抛出造成的程序卡死的情况发生。
try{}catch{}finally{}结构
//异常捕获
try
{
string str=Console.ReadLine();
int i=int.Parse(str);
Console.WriteLine("输入的字符串数值转为int的数值"+i);
}catch
{
Console.WriteLine("请输入合法数字");
}finally
{
//无论正常执行还是是否进行异常捕获 都会执行
Console.WriteLine("执行完毕");
}
运算符
算术运算符
算术运算符是英语数值类型变量运算的运算符,运算结果仍旧为数值。
赋值运算符:=
注意:赋值运算符理解将右边数值赋值给左边变量。
算术运算符:
//算术数运算符
//加+
int i1=5;
int sum=1+2+3+i1*2;
//减 -
int j1=6;
int sub=15-j1-2;
//乘 *
int c=5;
int c1=5*c;
//除 /
int d=28;
int d1=d/4;
//取模 (取余) %
int e=12;
e=e%5;
Console.WriteLine(e);
算术运算符的优先级
乘除取余 > 加减
int a = 1 + 2 * 3 / 2 + 1 + 2 * 3; //=11
Console.WriteLine(a);
a = 1 + 4 % 2 * 3 / 2 + 1; //2
Console.WriteLine(a);
//括号可以改变优先级 优先计算括号内内容
a = 1 + 4 % (2 * 3 / 2) + 1; //3
Console.WriteLine(a);
//多组括号 先算最里层括号 依次往外算
a = 1 + (4 % (2 * (3 / 2))) + 1; //2
Console.WriteLine(a);
复合运算符
+= -= *= /= %= 相当于对自身进行某项算术操作之后的结果重新赋给自己
//符合运算符
int i3 = 1;
i3 = i3 + 2;
Console.WriteLine(i3);
i3 = 1;
i3 += 2;//i3 = i3 + 2;
Console.WriteLine(i3);
i3 = 2;
i3 += 2;//4
i3 -= 2;//2
i3 /= 2;//1
i3 *= 2;//2
i3 %= 2;//0
Console.WriteLine(i3);
int i4 = 10;
// i4 += 4
i4 += 20 * 2 / 10;
Console.WriteLine(i4);
//注意:复合运算符 只能进行一种运算 不能混合运算
//i4 */-= 2;
自增/减运算符
注意理解前置还是后置的运算符,区别先用后自增/减还是先自增/减再使用。
可以理解为电击小子打怪物,小光先变身成电击小子打怪兽还是打完怪兽再变身。
//自增运算符
//自增运算符 让自己+1
a2 = 1;
a2++;//先用再加
Console.WriteLine(a2);
++a2;//先加再用
Console.WriteLine(a2);
a2 = 1;
Console.WriteLine(a2++);//1
//2
Console.WriteLine(++a2);//3
//自减运算符 让自己-1
a2 = 1;
a2--;//先用再减
--a2;//先减再用
a2 = 1;
Console.WriteLine(a2--);//1
//0
Console.WriteLine(--a2);//-1
//思考?这个
int a = 10, b = 20;
// 11 + 20
int number1 = ++a + b;
Console.WriteLine(number1);//31
a = 10;
b = 20;
//10 + 20
int number2 = a + b++;
Console.WriteLine(number2);//30
a = 10;
b = 20;
//10 + 21 + 11
int number3 = a++ + ++b + a++;
Console.WriteLine(number3);//42
Console.WriteLine(a);//12
字符串的拼接
-
使用+拼接
string str = "123"; //用+号进行字符串拼接 str = str + "456"; Console.WriteLine(str); str = str + 1; Console.WriteLine(str); //使用+= str = "123"; str += "1" + 4 + true; Console.WriteLine(str); //注意:只要遇到字符串,就是转为字符串 string str = "畅知"; str += 1 + 2 + 3 + 4; Console.WriteLine(str);//畅知10 str = ""; str += "" + 1 + 2 + 3 + 4;//开头就变为字符串 Console.WriteLine(str);//1234 str = ""; str += 1 + 2 + "" + (3 + 4);//先算括号,从首到尾计算 Console.WriteLine(str);//37 str = "123"; str = str + (1 + 2 + 3); Console.WriteLine(str);//1236 -
使用占位符替换方式拼接(占位符从0开始,用{}括起来)
string str2 = string.Format("我是{0}, 我今年{1}岁, 爱好:{2}", "畅知", 21, "我爱写博客!!"); Console.WriteLine(str2); str2 = string.Format("asdf{0},{1},sdfasdf{2}", 1, true, false); Console.WriteLine(str2);
条件运算符
条件运算符均为双目运算符,返回结果为bool类型的,使用其运算结果来做某些情况的判断。
条件运算符的优先级要低于算术运算符
//条件运算符
int a = 5;
int b = 10;
//大于
bool result = a > b;
Console.WriteLine(result);
//小于
result = a < b;
Console.WriteLine(result);
//大于等于
result = a >= b;
Console.WriteLine(result);
//小于等于
result = a <= b;
Console.WriteLine(result);
//等于
result = a == b;
Console.WriteLine(result);
//不等于
result = a != b;
Console.WriteLine(result);
//也可以直接和数值比较
result=10>5;
//优先级
// 先计算 再比较
result = a + 3 > a - 2 + 3;// true
result = 3 + 3 < 5 - 1;//false
//不同类型之间的比较
//不同数值类型之间 可以随意进行条件运算符比较
int i = 5;
float f = 1.2f;
double d = 12.4;
short s = 2;
byte by = 20;
uint ui = 666;
//只要是数值 就能够进行条件运算符比较 比较大于小于等于等等
int i = 5;
float f = 1.2f;
double d = 12.4;
short s = 2;
byte by = 20;
uint ui = 666;
bool result;
//只要是数值 就能够进行条件运算符比较 比较大于小于等于等等
result = i > f;//true
Console.WriteLine(result);
result = f < d;//true
Console.WriteLine(result);
result = i > by;//false
Console.WriteLine(result);
result = f > ui;//false
Console.WriteLine(result);
result = ui > d;//true
Console.WriteLine(result);
//特殊类型 char string bool 只能同类型进行 == 和 != 比较
string str = "123";
char c = 'A';
bool bo = true;
result = str == "234";//false
result = str == "123";//true
result = str != "123";//false
result = c == 'B';//false
//不仅可以和自己类型进行 == != 还可以和数值类型进行比较
//字符参与比较大小时候将自身作为ASCII码比较
//还可以和字符类型进行大小比较
result = c > 123;
result = c > 'B';
result = bo == true;//true;
逻辑运算符
逻辑与 & 逻辑或 || 逻辑非 !
逻辑运算符优先级 < 条件运算符 算术运算
条件运算符均为双目运算符,返回结果为bool类型的,使用其运算结果来做某些情况的判断。
条件运算符的优先级要低于算术运算符
//条件运算符
int a = 5;
int b = 10;
//大于
bool result = a > b;
Console.WriteLine(result);
//小于
result = a < b;
Console.WriteLine(result);
//大于等于
result = a >= b;
Console.WriteLine(result);
//小于等于
result = a <= b;
Console.WriteLine(result);
//等于
result = a == b;
Console.WriteLine(result);
//不等于
result = a != b;
Console.WriteLine(result);
//也可以直接和数值比较
result=10>5;
//优先级
// 先计算 再比较
result = a + 3 > a - 2 + 3;// true
result = 3 + 3 < 5 - 1;//false
//不同类型之间的比较
//不同数值类型之间 可以随意进行条件运算符比较
int i = 5;
float f = 1.2f;
double d = 12.4;
short s = 2;
byte by = 20;
uint ui = 666;
//只要是数值 就能够进行条件运算符比较 比较大于小于等于等等
int i = 5;
float f = 1.2f;
double d = 12.4;
short s = 2;
byte by = 20;
uint ui = 666;
bool result;
//只要是数值 就能够进行条件运算符比较 比较大于小于等于等等
result = i > f;//true
Console.WriteLine(result);
result = f < d;//true
Console.WriteLine(result);
result = i > by;//false
Console.WriteLine(result);
result = f > ui;//false
Console.WriteLine(result);
result = ui > d;//true
Console.WriteLine(result);
//特殊类型 char string bool 只能同类型进行 == 和 != 比较
string str = "123";
char c = 'A';
bool bo = true;
result = str == "234";//false
result = str == "123";//true
result = str != "123";//false
result = c == 'B';//false
//不仅可以和自己类型进行 == != 还可以和数值类型进行比较
//字符参与比较大小时候将自身作为ASCII码比较
//还可以和字符类型进行大小比较
result = c > 123;
result = c > 'B';
result = bo == true;//true;
逻辑运算符
逻辑与 & 逻辑或 || 逻辑非 !
逻辑运算符优先级 < 条件运算符 算术运算
逻辑运算符中: !(逻辑非)优先级最高 &&(逻辑与)优先级高于||(逻辑或)
//逻辑运算符
//逻辑与&& 并且
//规则: 对两个bool值进行逻辑运算 有假则假 同真为真
bool result = true && false;
Console.WriteLine(result);
result = true && true;
Console.WriteLine(result);
result = false && true;
Console.WriteLine(result);
//bool相关的类型 bool变量 条件运算符
//逻辑运算符优先级 低于 条件运算符 算术运算
// true && true
result = 3 > 1 && 1 < 2;
Console.WriteLine(result);
int i = 3;
// 1 < i < 5;
// true && true
result = i > 1 && i < 5;
Console.WriteLine(result);
//多个逻辑与 组合运用
int i2 = 5;
// true && false && true && true
//在没有括号的情况下 从左到右 依次看即可
//有括号 先看括号内
result = i2 > 1 && i2 < 5 && i > 1 && i < 5;
Console.WriteLine(result);
//符号 || 或者
//规则 对两个bool值进行逻辑运算 有真则真 同假为假
result = true || false;
Console.WriteLine(result);
result = true || true;
Console.WriteLine(result);
result = false || true;
Console.WriteLine(result);
result = false || false;
Console.WriteLine(result);
// false || true
result = 3 > 10 || 3 < 5;
Console.WriteLine(result);//true
int a = 5;
int b = 11;
// true || true || false
result = a > 1 || b < 20 || a > 5;
Console.WriteLine(result);
// ? && ?
// ? || ?
// ? 可以是写死的bool变量 或者 bool值
// 还可以是 条件运算符相关
//----------逻辑非!
//符号 !
//规则 对一个bool值进行取反 真变假 假变真
result = !true;
Console.WriteLine(result);
result = !false;
Console.WriteLine(result);
result = !!true;
Console.WriteLine(result);
//逻辑非的 优先级 较高
result = !(3 > 2);
Console.WriteLine(result);
a = 5;
result = !(a > 5);
Console.WriteLine(result);
//混合使用逻辑运算符的优先级问题
// 规则 !(逻辑非)优先级最高 &&(逻辑与)优先级高于||(逻辑或)
// 逻辑运算符优先级 低于 算数运算符 条件运算符(逻辑非除外)
bool gameOver = false;
int hp = 100;
bool isDead = false;
bool isMustOver = true;
//false || false && true || true;
//false || false || true;
result = gameOver || hp < 0 && !isDead || isMustOver;
Console.WriteLine(result);
逻辑运算符的短路原则(聪明的运算符)
//短路原则
//|| 判断原则为有真则真 所以第一个条件判断为真,则直接可以得出运算结果为真 便不会检查第二个
//个运算条件的真假
//同理,&& 若左边条件为假,则不会判断右边条件,直接可以得出运算结果为假
//逻辑或 有真则真 那左边只要为真了 右边就不重要
int i3=1;
bool result = i3 > 0 || ++i3 >= 1;
Console.WriteLine(i3);//1
Console.WriteLine(result);
// false && i3 ++ > 1;抛弃后面不去计算
//逻辑与 有假则假 那左边只要为假了 右边就不重要
result = i3 < 0 && i3++ > 1;
Console.WriteLine(i3);//1
Console.WriteLine(result);
//思考?
//求打印结果是什么?
//注意运算符的优先级
bool gameOver;
bool isWin;
int health = 100;
gameOver = true;
isWin = false;
// true || false && true
Console.Write(gameOver || isWin && health > 0);
位运算符
位运算是基于二进制编码的运算,首先将值转换为二进制数值,然后对于位进行操作运算。
运算符:位与& 位或| 异或^ 位或 | 位取反! 左移<< 右移>>
//位运算符
//位与& 有0则0 全1才1
// 对位运算 有0则0
int a = 1;// 001
int b = 5;// 101
// 001
//& 101
// 001 = 1
int c = a & b;
Console.WriteLine(c);
//多个数值进行位运算 没有括号时 从左到右 依次计算
a = 1;// 001
b = 5;// 101
c = 19;//10011
// 00001
//& 00101
// 00001
//& 10011
// 00001
int d = a & b & c;
Console.WriteLine(d);
//位或| 有1则1,全0则0
a = 1;//001
b = 3;//011
c = a | b;
// 001
//| 011
// 011
Console.WriteLine(c);
a = 5; // 101
b = 10;// 1010
c = 20;//10100
// 00101
//| 01010
// 01111
//| 10100
// 11111 => 1 + 2 + 4 + 8 + 16 =31
Console.WriteLine(a | b | c);
//异或^ =======
//不同为1 相同为0
// 对位运算 相同为0 不同为1
a = 1; //001
b = 5; //101
// 001
//^101
// 100
c = a ^ b;
Console.WriteLine(c);
a = 10; // 1010
b = 11; // 1011
c = 4; // 100
// 1010
//^ 1011
// 0001
//^ 0100
// 0101 = 5
Console.WriteLine(a ^ b ^ c);
//位取反 ~ 取反
// 对位运算 0变1 1变0
a = 5;
// 0000 0000 0000 0000 0000 0000 0000 0101
// 1111 1111 1111 1111 1111 1111 1111 1010
// 反码补码知识
// 计算机中的二进制是以补码形式存储的
//补码:正数的补码是本身 负数的补码是绝对值取反加一
c = ~a;
Console.WriteLine(c);
//左移 右移
// 规则 让一个数的2进制数进行左移和右移
// 左移几位 右侧加几个0
a = 5; // 101
c = a << 5;
// 1位 1010
// 2位 10100
// 3位 101000
// 4位 1010000
// 5位 10100000 = 32 + 128 = 160
Console.WriteLine(c);
// 右移几位 右侧去掉几个数
a = 5; // 101
c = a >> 2;
// 1位 10
// 2位 1
Console.WriteLine(c);
//练习----
//99 ^ 33 和 76 | 85 的结果为?
// 1100011 ^ 100001
// 1100011
//^0100001
// 1000010
Console.WriteLine(99 ^ 33);
// 1001100 | 1010101
// 1001100
//|1010101
// 1011101 => 64 + 29 = 93
Console.WriteLine(76 | 85);
三目运算符
条件?A :B 条件为真则走A逻辑否则走B文章来源:https://www.toymoban.com/news/detail-711688.html
//三目运算符
int a = 5;
str = a < 1 ? "a大于1" : "a不满条件";
Console.WriteLine(str);
int i = a > 1 ? 123 : 234;
//第一个空位 始终是结果为bool类型的表达式 bool变量 条件表达式 逻辑运算符表达式
//第二三个空位 什么表达式都可以 只要保证他们的结果类型是一致的
bool b = a > 1 ? a > 6 : !false;
======
我会每天更新C#学习笔记,感兴趣的可以给个订阅!
点个订阅,练习C#代码不迷路!文章来源地址https://www.toymoban.com/news/detail-711688.html
到了这里,关于C#学习笔记---异常捕获和变量运算符的文章就介绍完了。如果您还想了解更多内容,请在右上角搜索TOY模板网以前的文章或继续浏览下面的相关文章,希望大家以后多多支持TOY模板网!