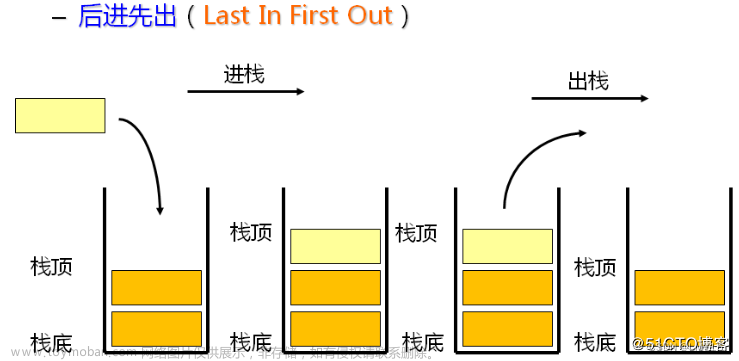
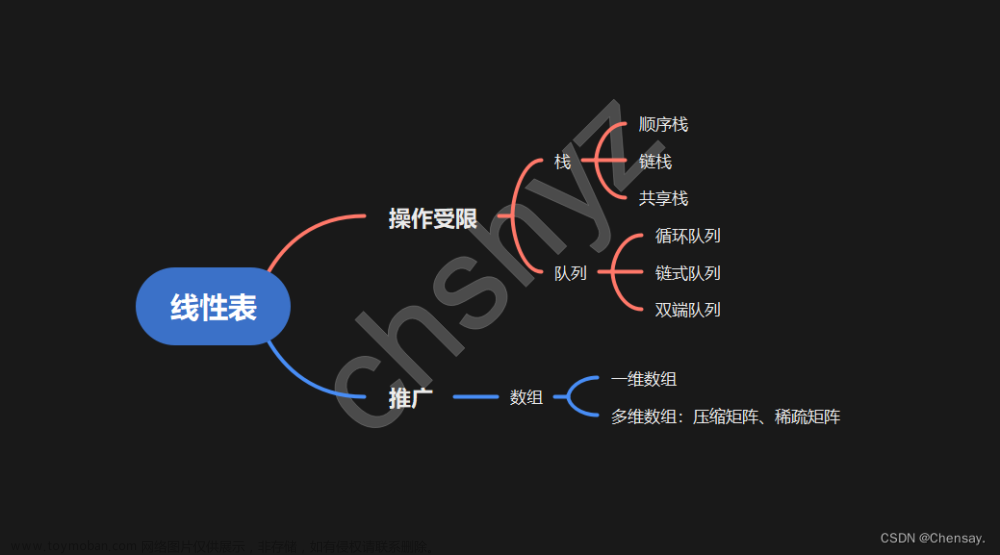
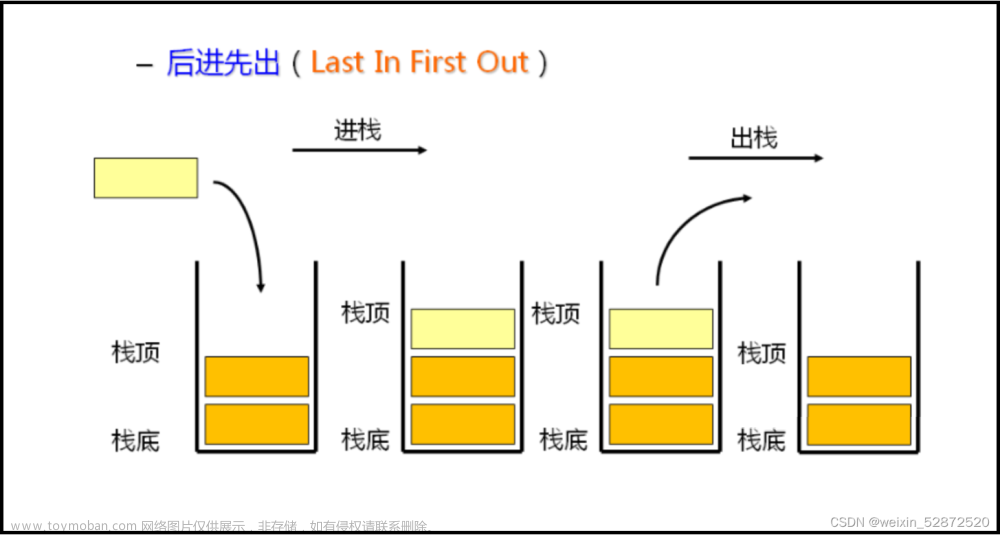
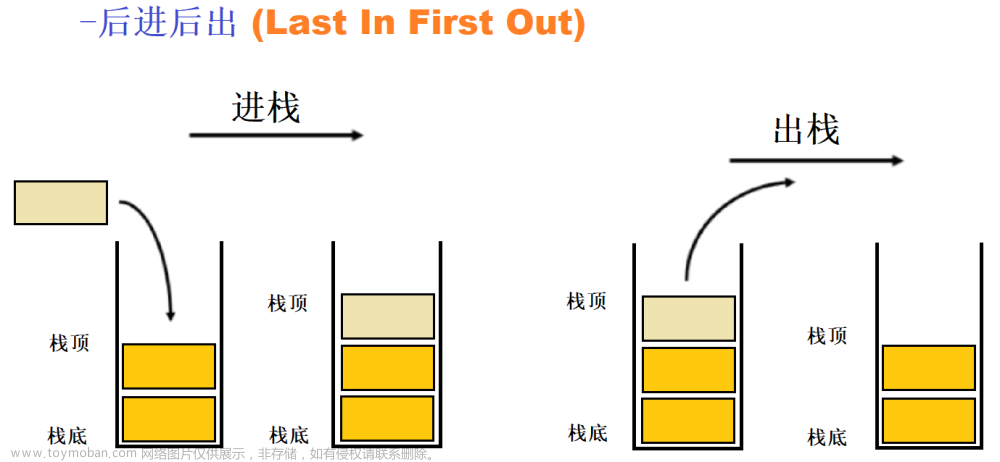
1.栈
1.1栈的抽象父类
#pragma once template<class T> class Stack { public: // 析构函数 virtual ~Stack() {} // 栈是否为空 virtual bool empty() const = 0; // 栈的大小 virtual int size() const = 0; // 栈顶元素 virtual T& top() = 0; // 出栈 virtual void pop() = 0; // 入栈 virtual void push(const T& theElement) = 0; };
1.2栈的数组实现
【数据结构】1.线性表的数组描述和链式描述 - imXuan - 博客园 (cnblogs.com)
#pragma once #include"stack.h" #include"arrayList.hpp" #include<iostream> using namespace std; template<class T> class DerivedArrayStack :private ArrayList<T>, public Stack<T> { public: DerivedArrayStack(int initialCapacity = 10) :ArrayList<T>(initialCapacity) {} // 栈是否为空 bool empty() const { return ArrayList<T>::empty(); } // 栈的大小 int size() const { return ArrayList<T>::size(); } // 栈顶元素 T& top() { if (ArrayList<T>::empty()) cout << "栈为空" << endl; else return ArrayList<T>::get(ArrayList<T>::size() - 1); } // 出栈 void pop() { if (ArrayList<T>::empty()) cout << "栈为空" << endl; else { cout << "出栈元素为:" << ArrayList<T>::get(ArrayList<T>::size() - 1) << endl; ArrayList<T>::erase(ArrayList<T>::size() - 1); } } // 入栈 void push(const T& theElement) { ArrayList<T>::insert(ArrayList<T>::size(), theElement); } };
1.3栈的链式实现
【数据结构】1.线性表的数组描述和链式描述 - imXuan - 博客园 (cnblogs.com)
#pragma once #include"chain.hpp" #include"stack.h" #include<iostream> using namespace std; template<class T> class DerivedLinkedStack :private Chain<T>, public Stack<T> { public: DerivedLinkedStack(int initialCapacity = 10) :Chain<T>(initialCapacity) {} // 栈是否为空 bool empty() const { return Chain<T>::empty(); } // 栈的大小 int size() const { return Chain<T>::size(); } // 栈顶元素 T& top() { if (Chain<T>::empty()) cout << "栈为空" << endl; else return Chain<T>::get(Chain<T>::listSize - 1); } // 出栈 void pop() { if (Chain<T>::empty()) cout << "栈为空" << endl; else { cout << "出栈元素为:" << Chain<T>::get(Chain<T>::listSize - 1) << endl; Chain<T>::erase(Chain<T>::listSize - 1); } } // 入栈 void push(const T& theElement) { Chain<T>::insert(Chain<T>::size(), theElement); } };
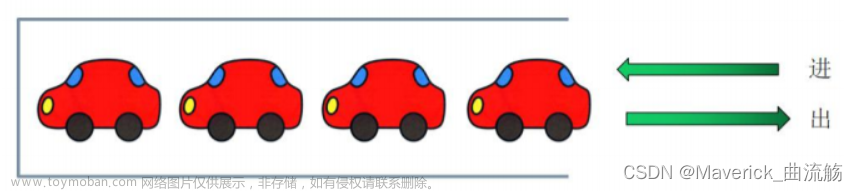
2.队列
2.1队列的抽象父类
#pragma once template<class T> class queue { public: virtual ~queue() {} virtual bool empty() const = 0; virtual int size() const = 0; virtual T& front() = 0; virtual T& back() = 0; virtual void pop() = 0; virtual void push(const T& theElement) = 0; };
2.2队列的数组实现
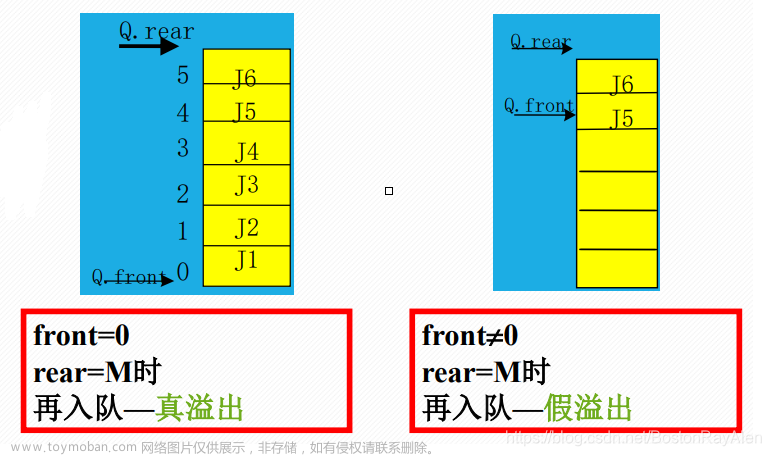
队列由一个数组来描述,队首指针是队首的前一个元素,队尾指针是队尾所在元素,当队首和队尾指针重叠时表示队列为空;当 (队尾指针+1)%数组长度 等于队首指针时队列为满

假设push数据时队列已满,需要为存储队列的数组进行扩充,我们将AB首先移动到起始位置,然后将C~G移动到AB之后,具体代码参见 push()

#pragma once #include"queue.h" #include"arrayList.hpp" #include<iostream> using namespace std; template<class T> class arrayQueue :public queue<T> { private: int theFront; // 第一个元素的前一个 int theBack; // 最后一个元素 int arrayLength; // 队列长度 T* queue; // 队列本体 public: arrayQueue(int initialCapacity = 10); ~arrayQueue() { delete[] queue; } bool empty() const { return theFront == theBack; } int size() const { return (theBack - theFront + arrayLength) % arrayLength; } T& front() { if (theFront == theBack) { cout << "队列为空" << endl; } return queue[(theFront + 1) % arrayLength]; } T& back() { if (theFront == theBack) { cout << "队列为空" << endl; } return queue[theBack]; } void pop() { if (theFront == theBack) { cout << "队列为空" << endl; return; } cout << queue[(theFront + 1) % arrayLength]; theFront = (theFront + 1) % arrayLength; queue[theFront].~T(); } void push(const T& theElement); }; template<class T> arrayQueue<T>::arrayQueue(int initialCapacity) { if (initialCapacity < 1) { cout << "initialCapacity 必须为正整数" << endl; return; } arrayLength = initialCapacity; queue = new T[arrayLength]; theFront = 0; theBack = 0; } template<class T> void arrayQueue<T>::push(const T& theElement) { if ((theBack + 1) % arrayLength == theFront) { T* newQueue = new T[2 * arrayLength]; int start = (theFront + 1) % arrayLength; if (start < 2) copy(queue + start, queue + start + arrayLength - 1, newQueue); else { copy(queue + start, queue + arrayLength, newQueue); copy(queue, queue + theBack + 1, newQueue + arrayLength - start); } theFront = 2 * arrayLength - 1; theBack = arrayLength - 2; arrayLength *= 2; queue = newQueue; } theBack = (theBack + 1) % arrayLength; queue[theBack] = theElement; }
2.3队列的链式实现
【数据结构】1.线性表的数组描述和链式描述 - imXuan - 博客园 (cnblogs.com)文章来源:https://www.toymoban.com/news/detail-711721.html
#pragma once #include "queue.h" #include "chainNode.hpp" #include <iostream> using namespace std; template<class T> class linkedQueue : public queue<T> { private: chainNode<T>* queueFront; // 头指针 chainNode<T>* queueBack; // 尾指针 int queueSize; // 队列大小 public: linkedQueue(int initialCapacity = 10) { queueFront = NULL; queueSize = 0; } ~linkedQueue(); bool empty() const {return queueSize == 0;} int size() const { return queueSize;} T& front() { if (queueSize == 0) cout << "队列为空" << endl; return queueFront->element; } T& back() { if (queueSize == 0) cout << "队列为空" << endl; return queueBack->element; } void pop(); void push(const T&); }; template<class T> linkedQueue<T>::~linkedQueue() { while (queueFront != NULL) { chainNode<T>* nextNode = queueFront->next; delete queueFront; queueFront = nextNode; } } template<class T> void linkedQueue<T>::pop() { if (queueFront == NULL) { cout << "队列为空" << endl; return; } chainNode<T>* nextNode = queueFront->next; delete queueFront; queueFront = nextNode; queueSize--; } template<class T> void linkedQueue<T>::push(const T& theElement) { chainNode<T>* newNode = new chainNode<T>(theElement, NULL); if (queueSize == 0) queueFront = newNode; else queueBack->next = newNode; queueBack = newNode; queueSize++; }
文章来源地址https://www.toymoban.com/news/detail-711721.html
到了这里,关于【数据结构】2.栈和队列的文章就介绍完了。如果您还想了解更多内容,请在右上角搜索TOY模板网以前的文章或继续浏览下面的相关文章,希望大家以后多多支持TOY模板网!