1. 线性表抽象类
#pragma once template <class T> class LinearList { public: // 线性表是否为空 virtual bool empty() const = 0; // 线性表大小 virtual int size() const = 0; // 根据ID获取线性表元素 virtual T& get(int theIndex) const = 0; // 根据元素获取元素对应ID virtual int indexOf(const T& theElement) const = 0; // 删除ID处的元素 virtual void erase(int theIndex) = 0; // 在ID处插入元素 virtual void insert(int theIndex, const T& theElement) = 0; // 输出线性表 virtual void output() = 0; };
2. 线性表的数组描述
#include"linearList.h" #include<iostream> using namespace std; template<class T> class ArrayList :public LinearList<T> { protected: T* element; // 线性表元素指针 int arrayLength; // 容量 int listSize; // 元素个数 bool checkIndex(int theIndex) const; // 检查索引是否有效 void changeLength(); // 扩充数组长度 public: // 构造函数 ArrayList(int initialCapacity = 10); // 拷贝构造函数 ArrayList(const ArrayList<T>& theList); // 析构函数 ~ArrayList() { delete[] element; } // 线性表是否为空 bool empty() const { return listSize == 0; } // 线性表大小 int size() const { return listSize; } // 线性表容量 int capacity() const { return arrayLength; } // 根据ID获取线性表元素 T& get(int theIndex) const; // 根据元素获取元素对应ID int indexOf(const T& theElement) const; // 删除ID处的元素 void erase(int theIndex); // 在ID处插入元素 void insert(int theIndex, const T& theElement); // 输出线性表 void output(); }; // 构造函数 template<class T> ArrayList<T>::ArrayList(int initialCapacity) { if (initialCapacity < 1) { cout << "初始化容量必须大于0" << endl; return; } this->arrayLength = initialCapacity; this->element = new T[arrayLength]; listSize = 0; } // 复制构造函数 template<class T> ArrayList<T>::ArrayList(const ArrayList<T>& theList) { this->arrayLength = theList.arrayLength; this->listSize = theList.listSize; this->element = new T[arrayLength]; copy(theList.element, theList.element + listSize, element); } // 越界, false 表示越界, true 表示没有越界 template<class T> bool ArrayList<T>::checkIndex(int theIndex) const { bool ret = !(theIndex < 0 || theIndex > listSize); return ret; } // 获取元素 template<class T> T& ArrayList<T>::get(int theIndex) const { if (checkIndex(theIndex)) { return element[theIndex]; } } // 根据元素获取ID template<class T> int ArrayList<T>::indexOf(const T& theElement) const { int theIndex = (int)find(element, element + listSize, theElement); return theIndex == listSize ? -1 : (theIndex-(int)element)/sizeof(T); } // 删除ID处元素 template<class T> void ArrayList<T>::erase(int theIndex) { if (checkIndex(theIndex)) { copy(element + theIndex + 1, element + listSize, element + theIndex); element[--listSize].~T(); } } // 扩充数组长度 template<class T> void ArrayList<T>::changeLength() { T* temp = new T[arrayLength * 2]; copy(element, element + arrayLength, temp); delete[] element; element = temp; arrayLength = 2 * arrayLength; } // 在ID处插入元素 template<class T> void ArrayList<T>::insert(int theIndex, const T& theElement) { if (!checkIndex(theIndex)) { cout << "无效索引" << endl; return; } if (listSize == arrayLength) { changeLength(); } copy_backward(element + theIndex, element + listSize, element + listSize + 1); element[theIndex] = theElement; listSize++; } // 输出线性表 template<class T> void ArrayList<T>::output() { for (int i = 0; i < listSize; i++) { cout << element[i] << " "; } cout << endl; }
3. 线性表的链式描述
3.1 结点结构体
#pragma once #include<iostream> using namespace std; template <class T> struct ChainNode { // 数据成员 T element; ChainNode<T>* next; // 方法 ChainNode() {} ChainNode(const T& element) { this->element = element; } ChainNode(const T& element, ChainNode<T>* next) { this->element = element; this->next = next; } };
3.2 线性表实现
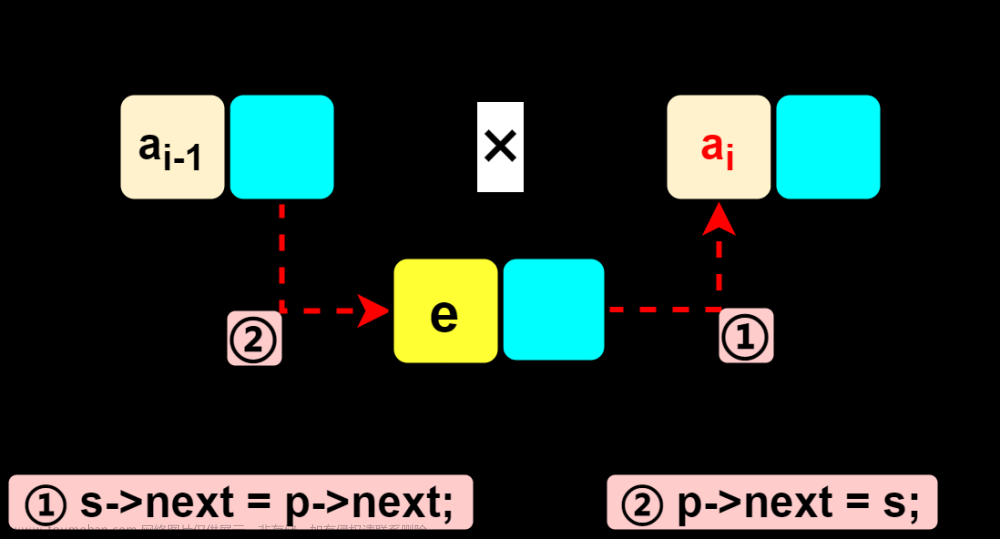
#include"linearList.h" #include"chianNode.h" #include<iostream> using namespace std; template<class T> class Chain :public LinearList<T> { protected: ChainNode<T>* firstNode; int listSize; bool checkIndex(int theIndex) const; public: Chain(int initialCapacity = 10); Chain(const Chain<T>&); ~Chain(); bool empty() const { return listSize == 0; }; // 线性表大小 int size() const { return listSize; } // 根据ID获取线性表元素 T& get(int theIndex) const; // 根据元素获取元素对应ID int indexOf(const T& theElement) const; // 删除ID处的元素 void erase(int theIndex); // 在ID处插入元素 void insert(int theIndex, const T& theElement); // 输出线性表 void output(); }; // 普通的构造函数 template<class T> Chain<T>::Chain(int initialCapacity) { if (initialCapacity < 1) { cout << "初始容量设置必须大于0" << endl; } firstNode = NULL; listSize = 0; } // 拷贝构造函数 template<class T> Chain<T>::Chain(const Chain<T>& theList) { listSize = theList.listSize; if (listSize == 0) { firstNode = NULL; return; } ChainNode<T>* sourceNode = theList.firstNode; firstNode = new ChainNode<T>(sourceNode->element); sourceNode = sourceNode->next; ChainNode<T>* targetNode = firstNode; while (sourceNode != NULL) { targetNode->next = new ChainNode<T>(sourceNode->element); targetNode = targetNode->next; sourceNode = sourceNode->next; } targetNode->next = NULL; } // 析构函数 template<class T> Chain<T>::~Chain() { while (firstNode != NULL) { ChainNode<T>* nextNode = firstNode->next; delete firstNode; firstNode = nextNode; } } template<class T> T& Chain<T>::get(int theIndex) const { if (checkIndex(theIndex)) { ChainNode<T>* currentNode = firstNode; for (int i = 0; i < theIndex; i++) { currentNode = currentNode->next; } return currentNode->element; } } template<class T> int Chain<T>::indexOf(const T& theElement) const { ChainNode<T>* currentNode = firstNode; int index = 0; while (currentNode->element != theElement && currentNode != NULL) { currentNode = currentNode->next; index++; } return currentNode == NULL ? -1 : index; } template<class T> void Chain<T>::erase(int theIndex) { if (checkIndex(theIndex)) { ChainNode<T>* deleteNode; if (theIndex == 0) { deleteNode = firstNode; firstNode = firstNode->next; } else if (theIndex < listSize - 1) { ChainNode<T>* p = firstNode; for (int i = 0; i < theIndex - 1; i++) { p = p->next; } deleteNode = p->next; p->next = p->next->next; } else { ChainNode<T>* p = firstNode; for (int i = 0; i < theIndex; i++) { p = p->next; } deleteNode = p; p->next = NULL; } listSize--; delete deleteNode; } } template<class T> void Chain<T>::insert(int theIndex, const T& theElement) { if (checkIndex(theIndex)) { if (theIndex == 0) { firstNode = new ChainNode<T>(theElement, firstNode); } else { ChainNode<T>* p = firstNode; for (int i = 0; i < theIndex - 1; i++) { p = p->next; } p->next = new ChainNode<T>(theElement, p->next); } listSize++; } } template<class T> void Chain<T>::output() { ChainNode<T>* currentNode = firstNode; while (currentNode != NULL) { cout << currentNode->element << " "; currentNode = currentNode->next; } cout << endl; } template<class T> bool Chain<T>::checkIndex(int theIndex) const { bool ret = !(theIndex < 0 || theIndex > listSize); return ret; }
文章来源地址https://www.toymoban.com/news/detail-711778.html
文章来源:https://www.toymoban.com/news/detail-711778.html
到了这里,关于【数据结构】1.线性表的数组描述和链式描述的文章就介绍完了。如果您还想了解更多内容,请在右上角搜索TOY模板网以前的文章或继续浏览下面的相关文章,希望大家以后多多支持TOY模板网!