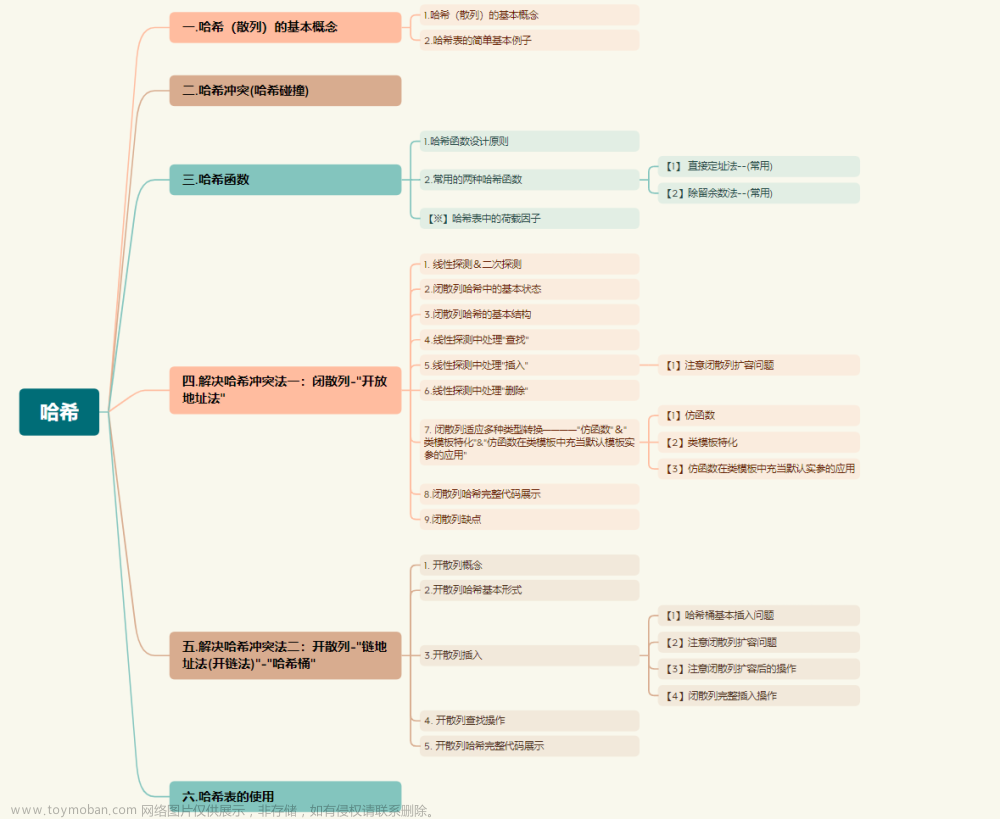
这里的闭散列和开散列解决哈希冲突的方法都是除留余数法。
一些哈希函数:字符串哈希算法
一.闭散列
概念
闭散列:也叫开放定址法,当发生哈希冲突时,如果哈希表未被装满,说明在哈希表中必然还有
空位置,那么可以把key存放到冲突位置中的“下一个” 空位置中去。
如何找到下一个位置?
线性探测
线性探测:从发生冲突的位置开始,依次向后探测,直到寻找到下一个空位置为止。
- 线性探测优点:实现非常简单。
- 线性探测缺点:一旦发生哈希冲突,所有的冲突连在一起,容易产生数据“堆积”,即:不同关键码占据了可利用的空位置,使得寻找某关键码的位置需要许多次比较,导致搜索效率降低。
模拟实现
闭散列是用一个数组实现的,每一个位置都有三种状态:
- EMPTY :表示此位置为空
- EXIST:表示此位置存在数据
- DELETE:表示此位置处于删除状态
当我们去查找数据时,直到找到空才停止,如果哈希冲突非常多,那么很可能数组里的空位置非常少,此时查找效率大幅下降,还有可能把数组填满了,没有空位置,就陷入了死循环,所以需要扩容。
那么何时扩容?扩容的时机不合适可能导致空间浪费或是效率降低。
我们可以加一个负载因子,负载因子表示有效数据的个数,当 负载因子/数组容量 大于等于 0.7 时,此时是扩容的最佳时机
插入
- 利用哈希函数,获取需要插入的位置
- 如果该位置状态为 EXIST, 那么继续向后探测,直到找到状态为空的位置

已经知道扩容时机了,那么具体该如何扩容?
采用旧表映射到新表的方式,最后再把旧表和新表交换一下即可。
- 首先创建一个新表
- 遍历旧表,调用新表的 Insert 把旧表的有效数据插入到新表中
- 交换旧表与新表
删除
闭散列的删除不能直接删,而是采用伪删除的方式,即把给位置的1状态置为DELETE
源码
//哈希表闭散列线性探测实现
namespace Close_Hash
{
//哈希函数
template<class K>
class HashFunc
{
public:
size_t operator()(const K& val)
{
return val;
}
};
template<>
class HashFunc<string>
{
public:
size_t operator()(const string& s)
{
const char* str = s.c_str();
unsigned int seed = 131; // 31 131 1313 13131 131313
unsigned int hash = 0;
while (*str)
{
hash = hash * seed + (*str++);
}
return hash;
}
};
//枚举变量,表示状态信息
enum State
{
EMPTY,
EXIST,
DELETE
};
template<class K,class V>
struct HashNode
{
pair<K, V> _kv;
State _state=EMPTY; //初始状态下,每个位置都是空
};
template<class K,class V,class HF=HashFunc<K>>
class HashTable
{
typedef HashNode<K, V> Node;
public:
HashTable()
{
_table.resize(5); //初始化数组
}
//查找
bool Find(const K& key)
{
HF hf;
size_t hashi = hf(key) % _table.size();
while (_table[hashi]._state != EMPTY)
{
if (_table[hashi]._kv.first == key)
return true;
hashi++;
}
return false;
}
//插入
bool Insert(const pair<K, V>& kv)
{
HF hf;
if (Find(kv.first) == true)
return false;
if (_n * 10 / _table.size() >= 7) //判断是否需要增容
{
size_t newsize = 2 * _table.size();
// 遍历旧表,重新映射到新表
HashTable<K, V, HF> newTable; //创建新表
newTable._table.resize(newsize); //初始化新表
for (size_t i = 0; i < _table.size(); i++)
{
if (_table[i]._state == EXIST)
{
newTable.Insert(_table[i]._kv);
}
}
_table.swap(newTable._table); //交换新旧表
}
size_t hashi = hf(kv.first) % _table.size();
while (_table[hashi]._state ==EXIST)
{
hashi++;
hashi = hashi % _table.size();
}
_table[hashi]._kv = kv;
_table[hashi]._state = EXIST;
_n++;
return true;
}
// 删除
bool Erase(const K& key)
{
if (Find(key) == false)
return false;
HF hf;
size_t hashi = hf(key) % _table.size();
while (_table[hashi]._state != EMPTY&&hashi<_table.size())
{
if (_table[hashi]._kv.first == key)
{
_table[hashi]._state = DELETE; //删除只需要把该位置的状态置为DELETE
return true;
}
hashi++;
}
return false;
}
size_t Size()const
{
return _n;
}
bool Empty() const
{
return _n == 0;
}
void Swap(HashTable<K, V>& ht)
{
swap(_n, ht._n);
ht._table.swap(_table);
}
private:
vector<Node> _table;
size_t _n; //负载因子
};
}二.开散列
概念
开散列就是我们平时说的哈希桶。
开散列:又叫链地址法(开链法)
首先对关键码集合用散列函数计算散列地址,具有相同地址的关键码归于同一子集合,每一个子集合称为一个桶,各个桶中的元素通过一个单链表链接起来,各链表的头结点存储在哈希表中。
即开散列的每一个位置挂着一个单链表,这个单链表称为桶,每个桶里放的都是冲突的数据。

模拟实现
插入
- 利用哈希函数,找到插入位置
- 接下来就是单链表的插入,推荐使用头插,单链表的头插效率是 O(1)
同样需要扩容。
当哈希桶里的数据满了时,开始扩容,仍然使用旧表遍历到新表的方式。
源码
namespace OpenHash
{
//哈希函数
template<class T>
class HashFunc
{
public:
size_t operator()(const T& val)
{
return val;
}
};
template<>
class HashFunc<string>
{
public:
size_t operator()(const string& s)
{
const char* str = s.c_str();
unsigned int seed = 131; // 31 131 1313 13131 131313
unsigned int hash = 0;
while (*str)
{
hash = hash * seed + (*str++);
}
return hash;
}
};
template<class K> //节点
struct HashBucketNode
{
HashBucketNode<K>* _pNext;
K _data;
HashBucketNode(const K& data)
: _pNext(nullptr)
, _data(data)
{}
};
// 本文所实现的哈希桶中key是唯一的
template<class K,class HF = HashFunc<K>>
class HashBucket
{
typedef HashBucketNode<K> Node;
typedef HashBucket<K,HF> Self;
public:
HashBucket()
{
_table.resize(10, nullptr);
_size = 0;
}
~HashBucket()
{
Clear();
}
// 哈希桶中的元素不能重复
bool Insert(const K& data)
{
if(Find(data)!=nullptr)
return false;
HF hf;
if (_size == _table.size()) //扩容
{
size_t newsize = 2 * _table.size();
vector<Node*> newtable(newsize, nullptr);
for (size_t i = 0; i < _table.size(); i++)
{
Node* cur = _table[i];
while (cur)
{
Node* next = cur->_pNext;
size_t hashi = hf(data) % newsize;
Node* newnode = new Node(cur->_data);
if (newtable[hashi] == nullptr)
newtable[hashi] = newnode;
else
{
newnode->_pNext = newtable[hashi]->_pNext;
newtable[hashi]->_pNext = newnode;
}
cur = next;
}
_table[i] = nullptr;
}
_table.swap(newtable);
}
Node* newnode = new Node(data);
size_t hashi = hf(data) % _table.size();
if (_table[hashi] == nullptr)
_table[hashi] = newnode;
else
{
newnode->_pNext = _table[hashi]->_pNext;
_table[hashi]->_pNext = newnode;
}
_size++;
return true;
}
//删除哈希桶中为data的元素(data不会重复)
bool Erase(const K& data)
{
HF hf;
size_t hashi = hf(data) % _table.size();
Node* cur = _table[hashi];
Node* prev = nullptr;
if (cur->_data == data)
{
delete _table[hashi];
_table[hashi] = cur->_pNext;
return true;
}
while (cur)
{
if (cur->_data == data)
{
prev->_pNext = cur->_pNext;
delete cur;
cur = nullptr;
return true;
}
prev = cur;
cur = cur->_pNext;
}
return false;
}
bool Find(const K& data)
{
HF hf;
size_t hashi = hf(data) % _table.size();
Node* cur = _table[hashi];
while (cur)
{
if (cur->_data == data)
return true;
else
cur = cur->_pNext;
}
return false;
}
size_t Count(const K& data) const
{
HF hf;
size_t hashi = hf(data) % _table.size();
Node* cur = _table[hashi];
size_t ret = 0;
while (cur)
{
if (cur->_data == data)
ret++;
cur = cur->_pNext;
}
return ret;
}
size_t size()const
{
return _size;
}
bool empty()const
{
return 0 == _size;
}
void Clear()
{
for (size_t i = 0; i < _table.size(); i++)
{
Node* cur = _table[i];
while (cur)
{
Node* next = cur->_pNext;
delete cur;
cur = next;
}
_table[i] = nullptr;
}
_table.resize(0);
}
size_t BucketCount()const
{
return _table.capacity();
}
size_t BucketSize() const
{
return _table.size();
}
void Swap(Self& ht)
{
_table.swap(ht._table);
swap(_size, ht._size);
}
private:
size_t HashFunc(const T& data)
{
return HF()(data) % _table.capacity();
}
private:
vector<Node*> _table;
size_t _size; // 哈希表中有效元素的个数
};
}三.开散列与闭散列比较
应用链地址法处理溢出,需要增设链接指针,似乎增加了存储开销。
事实上:
由于开地址法必须保持大量的空闲空间以确保搜索效率,如二次探查法要求装载因子a <=0.7,而表项所占空间又比指针大的多,所以使用链地址法反而比开地址法节省存储空间。
🐬🤖本篇文章到此就结束了, 若有错误或是建议的话,欢迎小伙伴们指出;🕊️👻
😄😆希望小伙伴们能支持支持博主啊,你们的支持对我很重要哦;🥰🤩文章来源:https://www.toymoban.com/news/detail-715561.html
😍😁谢谢你的阅读。😸😼文章来源地址https://www.toymoban.com/news/detail-715561.html
到了这里,关于【C++进阶】哈希表开散列和闭散列的模拟实现(附源码)的文章就介绍完了。如果您还想了解更多内容,请在右上角搜索TOY模板网以前的文章或继续浏览下面的相关文章,希望大家以后多多支持TOY模板网!



![【C++入门到精通】 哈希结构 | 哈希冲突 | 哈希函数 | 闭散列 | 开散列 [ C++入门 ]](https://imgs.yssmx.com/Uploads/2024/02/713477-1.jpeg)