💗 💗 博客:小怡同学
💗 💗 个人简介:编程小萌新
💗 💗 如果博客对大家有用的话,请点赞关注再收藏 🌞
list的节点类
template
struct list_Node
{
public:
list_Node* _prev;
list_Node* _next;
T _val;
list_Node(const T& val = T())
{
_prev = _next = nullptr;
_val = val;
}
};`文章来源:https://www.toymoban.com/news/detail-715712.html
list的迭代器类
//这里写入多个参数的目的是区分const迭代器
//传入不同的模板就会有不同的类
template<class T,class Ref ,class Ptr>
struct list_iterator
{
public:
typedef list_Node<T> Node;
typedef list_iterator<T,Ref,Ptr> self;
list_iterator(Node* node = nullptr)
{
_node = node;
}
list_iterator(const self& i)
{
_node(i._node);
}
//const对象不改变原数据
T& operator*()
{
return _node->_val;
}
T* operator->()
{
return &_node->val;
}
self& operator++()
{
_node = _node->_next;
return *this;
}
self operator++(int)
{
self tmp(_node);
_node = _node->_next;
return tmp;
}
self& operator--()
{
_node = _node->_prev;
return *this;
}
self& operator--(int)
{
self tmp(_node);
_node = _node->_prev;
return tmp;
}
bool operator!=(const self& l)
{
return _node != l._node;
}
bool operator==(const self& l)
{
return _node == l._node;
}
Node* _node;
};
构造函数
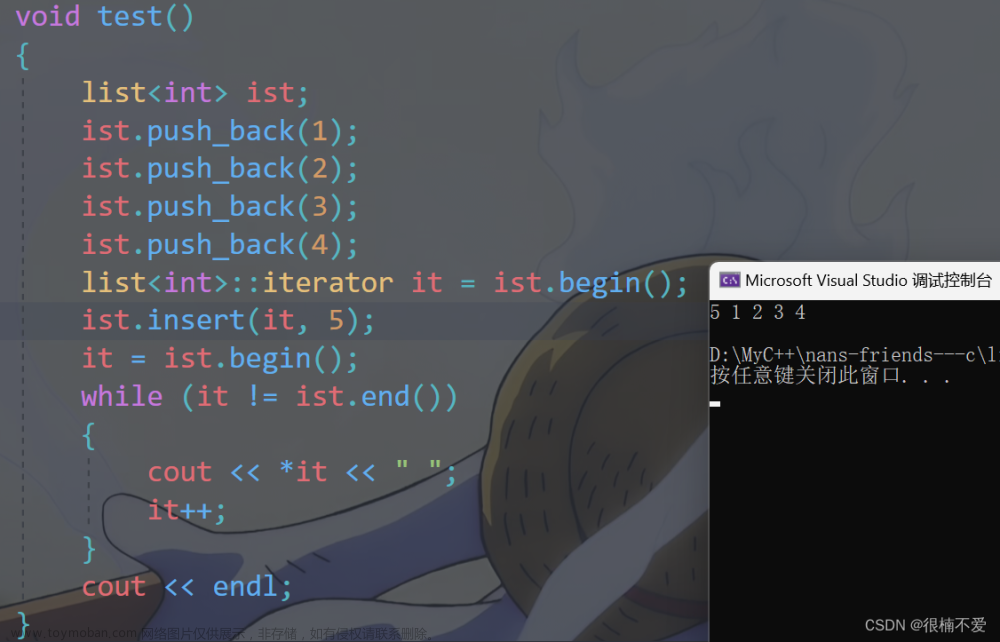
list(int n, const T& value = T())
{
_head = new Node();
_head->_prev = _head;
_head->_next = _head;
while (n--)
{
push_back(value);
}
}
template <class Intiterator>
list(Intiterator first, Intiterator last)
{
//这三行代码的作用是制造一个头结点
_head = new Node();
_head->_prev = _head;
_head->_next = _head;
while (first != last)
{
push_back(*first);
first++;
}
}
list(const list<T>& l)
{
_head = new Node();
_head->_prev = _head;
_head->_next = _head;
//这里制造一个list对象,构建与l对象一样的元素,在与*this进行调换。
list<T> tmp (l.begin(),l.end());
swap(tmp);
}
析构函数
~list()
{
clear();//复用clear()函数,如果元素是自定义类型,则一一析构,
delete _head;
_head = nullptr;
}
赋值运算符=
list<T>& operator=(const list<T> l)
{
swap(l);
return *this;
}
迭代器的使用
iterator begin()
{
return iterator(_head->_next);
}
iterator end()
{
return itertor(_head);
}
//const对象迭代器的使用返回的是const指针(实际上迭代器是一个模板,只是类型不同)
const_iterator begin()const
{
return const_iterator(_head->_next);
}
const_iterator end()const
{
return itertor(_head);
}
list的元素大小和判空
size_t size()const//const与非const对象都可调用
{
return _size;
}
bool empty()const
{
return _size == 0;
}
访问list的头节点与尾节点
T& front()
{
return _head->_next->_val;
}
const T& front()const
{
return _head->_next->_val;
}
T& back()
{
return _head->_prev->_val;
}
const T& back()const
{
return _head->_prev->_val;
}
尾插,尾删,头插,尾删,插入,删除,交换,清空
//这里使用了函数的调用
void push_back(const T& val)
{
insert(end(), val);
}
void pop_back()
{
erase(--end());
}
void push_front(const T& val)
{
insert(begin(), val);
}
void pop_front()
{
erase(begin());
}
// 在pos位置前插入值为val的节点
//这里不会发生迭代器的失效,迭代器没有被改变,返回时返回pos之前的迭代器
iterator insert(iterator pos, const T& val)
{
Node* newnode = new Node(val);
Node* node_pos = pos.Node;
Node* prev = node_pos->_prev;
Node* next = node_pos->_next;
prev->_next = next;
next->_prev = prev;
return newnode;
}
// 删除pos位置的节点,返回该节点的下一个位置
//这里发生迭代器的失效。指向pos指针变成野指针,返回时需要更新到该节点的下一个位置
iterator erase(iterator pos)
{
Node* node_pos = pos.Node;
Node* node_next = pos.Node->_next;
node_pos->_prev->_next = node_pos->_next;
node_next->_prev = node_pos->_prev;
delete node_pos;
return iterator(node_next);
}
//清除链表,只保留头节点
void clear()
{
iterator it = begin();
while (it != end())
{
erase(it);
}
_head->_prev = _head;
_head->_next = _head;
}
//交换链表
void swap(const list<T>& L)
{
Node* tmp = L._head;
L._head = tmp;
tmp = _head;
}
#include <assert.h>
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
namespace zjy
{
template<class T>
struct list_Node
{
public:
list_Node* _prev;
list_Node* _next;
T _val;
list_Node(const T& val = T())
{
_prev = _next = nullptr;
_val = val;
}
};
template<class T,class Ref ,class Ptr>
struct list_iterator
{
public:
typedef list_Node<T> Node;
typedef list_iterator<T,Ref,Ptr> self;
list_iterator(Node* node = nullptr)
{
_node = node;
}
list_iterator(const self& i)
{
_node(i._node);
}
T& operator*()
{
return _node->_val;
}
T* operator->()
{
return &_node->val;
}
self& operator++()
{
_node = _node->_next;
return *this;
}
self operator++(int)
{
self tmp(_node);
_node = _node->_next;
return tmp;
}
self& operator--()
{
_node = _node->_prev;
return *this;
}
self& operator--(int)
{
self tmp(_node);
_node = _node->_prev;
return tmp;
}
bool operator!=(const self& l)
{
return _node != l._node;
}
bool operator==(const self& l)
{
return _node == l._node;
}
Node* _node;
};
template<class T>
class list
{
public:
typedef list_Node<T> Node;
typedef list_iterator<T,T&,T*> iterator;
typedef list_iterator<T, const T&, const T*> const_iterator;
list()
{
_head = new Node();
_head->_prev = _head;
_head->_next = _head;
}
/*list(int n, const T& value = T())
{
_head = new Node();
_head->_prev = _head;
_head->_next = _head;
while (n--)
{
Node* newnode = new Node(value);
Node* tail = _head->_prev;
tail -> _next = newnode;
newnode->_prev = _head;
newnode->_next = _head;
_head->_prev = newnode;
tail = newnode;
}
}*/
list(int n, const T& value = T())
{
_head = new Node();
_head->_prev = _head;
_head->_next = _head;
while (n--)
{
push_back(value);
}
}
/*template <class Intiterator>
list(Intiterator first, Intiterator last)
{
_head = new Node();
_head->_prev = _head;
_head->_next = _head;
Node* begin= first._node;
Node* end = last._node;
Node* tail = _head->_prev;
while (begin != last)
{
tail->_next = begin;
begin->_prev = tail;
begin->_next = _head;
_head->_prev = begin;
tail = begin;
begin++;
}
}*/
template <class Intiterator>
list(Intiterator first, Intiterator last)
{
_head = new Node();
_head->_prev = _head;
_head->_next = _head;
while (first != last)
{
push_back(*first);
first++;
}
}
void swap(const list<T>& L)
{
Node* tmp = L._head;
L._head = tmp;
tmp = _head;
}
list(const list<T>& l)
{
_head = new Node();
_head->_prev = _head;
_head->_next = _head;
list<T> tmp (l.begin(),l.end());
swap(tmp);
}
list<T>& operator=(const list<T> l)
{
swap(l);
return *this;
}
~list()
{
clear();
delete _head;
_head = nullptr;
}
iterator begin()
{
return iterator(_head->_next);
}
iterator end()
{
return itertor(_head);
}
const_iterator begin()const
{
return const_iterator(_head->_next);
}
const_iterator end()const
{
return const_itertor(_head);
}
size_t size()const
{
return _size;
}
bool empty()const
{
return _size == 0;
}
T& front()
{
return _head->_next->_val;
}
const T& front()const
{
return _head->_next->_val;
}
T& back()
{
return _head->_prev->_val;
}
const T& back()const
{
return _head->_prev->_val;
}
void push_back(const T& val) {
insert(end(), val);
}
void pop_back() { erase(--end()); }
void push_front(const T& val) { insert(begin(), val); }
void pop_front() { erase(begin()); }
// 在pos位置前插入值为val的节点
iterator insert(iterator pos, const T& val)
{
Node* newnode = new Node(val);
Node* node_pos = pos.Node;
Node* prev = node_pos->_prev;
Node* next = node_pos->_next;
prev->_next = next;
next->_prev = prev;
return newnode;
}
// 删除pos位置的节点,返回该节点的下一个位置
iterator erase(iterator pos)
{
Node* node_pos = pos.Node;
Node* node_next = pos.Node->_next;
node_pos->_prev->_next = node_pos->_next;
node_next->_prev = node_pos->_prev;
delete node_pos;
return iterator(node_next);
}
void clear()
{
iterator it = begin();
while (it != end())
{
erase(it);
}
_head->_prev = _head;
_head->_next = _head;
}
void test()
{
Node* tmp = _head->_next;
while (tmp != _head)
{
cout << tmp->_val << endl;
tmp = tmp->_next;
}
}
private:
Node* _head;
size_t _size;
};
}
 文章来源地址https://www.toymoban.com/news/detail-715712.html
文章来源地址https://www.toymoban.com/news/detail-715712.html
到了这里,关于C++系列之list的模拟实现的文章就介绍完了。如果您还想了解更多内容,请在右上角搜索TOY模板网以前的文章或继续浏览下面的相关文章,希望大家以后多多支持TOY模板网!

![[C++]:12:模拟实现list](https://imgs.yssmx.com/Uploads/2024/01/814378-1.png)