一、项目概述
这个项目是一个简单的计算器应用,它可以执行加、减、乘、除四种基本运算等计算器的基本功能。我们将使用Android Studio作为开发工具。
二、项目设计
1. 在Android Studio中创建新的Android项目。
2. 在布局文件(`activity_main.xml`)中,我们将添加一个按钮和一个用于显示结果的文本视图。
3. 在代码文件(`MainActivity.java`)中,我们将处理用户的输入并显示计算结果。
三、项目开发
1. 布局文件
在布局文件`activity_main.xml`中实现前端页面效果。使用一些组件例如`EditText`用于输入过程和结果,`Button`用于执行计算。
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?>
<GridLayout xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
xmlns:tools="http://schemas.android.com/tools"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="match_parent"
android:orientation="vertical"
tools:context=".MainActivity">
<GridLayout
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:layout_gravity="top"
android:columnCount="1"
android:orientation="vertical"
android:rowCount="2">
<EditText
android:id="@+id/mresult"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="100dp"
android:enabled="false"
android:hint="这里显示结果"
android:textColor="@color/black" />
<EditText
android:id="@+id/mjsgc"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="100dp"
android:hint="这里显示计算过程" />
</GridLayout>
<GridLayout
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:layout_gravity="center|top"
android:orientation="horizontal"
android:columnCount="4"
android:rowCount="5"
>
<Button
android:id="@+id/btnqc"
android:layout_width="180dp"
android:layout_height="60dp"
android:layout_columnSpan="2"
android:text="C" />
<Button
android:id="@+id/btndel"
android:layout_width="90dp"
android:layout_height="60dp"
android:layout_columnSpan="1"
android:text="del" />
<Button
android:id="@+id/btnc"
android:layout_width="90dp"
android:layout_height="60dp"
android:text="/" />
<Button
android:id="@+id/btn7"
android:layout_width="90dp"
android:layout_height="60dp"
android:text="7" />
<Button
android:id="@+id/btn8"
android:layout_width="90dp"
android:layout_height="60dp"
android:text="8" />
<Button
android:id="@+id/btn9"
android:layout_width="90dp"
android:layout_height="60dp"
android:text="9" />
<Button
android:id="@+id/btnx"
android:layout_width="90dp"
android:layout_height="60dp"
android:text="*" />
<Button
android:id="@+id/btn4"
android:layout_width="90dp"
android:layout_height="60dp"
android:text="4" />
<Button
android:id="@+id/btn5"
android:layout_width="90dp"
android:layout_height="60dp"
android:text="5" />
<Button
android:id="@+id/btn6"
android:layout_width="90dp"
android:layout_height="60dp"
android:text="6" />
<Button
android:id="@+id/btnj"
android:layout_width="90dp"
android:layout_height="63dp"
android:text="-" />
<Button
android:id="@+id/btn1"
android:layout_width="90dp"
android:layout_height="60dp"
android:text="1" />
<Button
android:id="@+id/btn2"
android:layout_width="90dp"
android:layout_height="60dp"
android:text="2" />
<Button
android:id="@+id/btn3"
android:layout_width="90dp"
android:layout_height="60dp"
android:text="3" />
<Button
android:id="@+id/btn1j"
android:layout_width="90dp"
android:layout_height="60dp"
android:layout_rowSpan="1"
android:text="+" />
<Button
android:id="@+id/zhengfu"
android:layout_width="90dp"
android:layout_height="60dp"
android:text="预留" />
<Button
android:id="@+id/btn0"
android:layout_width="90dp"
android:layout_height="60dp"
android:layout_columnSpan="1"
android:text="0" />
<Button
android:id="@+id/btnd"
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="60dp"
android:text="." />
<Button
android:id="@+id/btn1d"
android:layout_width="90dp"
android:layout_height="60dp"
android:text="=" />
<Space />
</GridLayout>
</GridLayout>GridLayout布局:如果要实现行合并的布局效果,采用GridLayout布局是最简单轻松的实现方式。
常用属性:android:orientation设置水平或垂直显示 android:columnCount设置列数android:rowCount 设置行数
子控件属性:android:layout_rowSpan纵向跨合并几列 android:layout_columSpan横向合并几行 android:layout_gravity父组件的位置

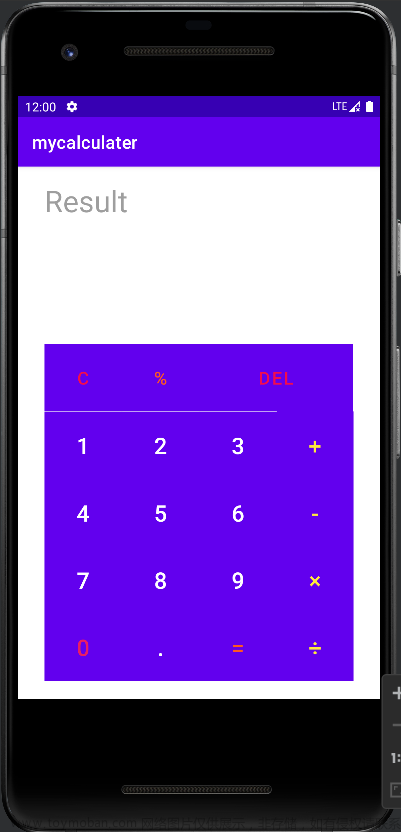
上图是前端页面效果
2. 代码文件
在代码文件`MainActivity.java`中我们将添加按钮的点击事件监听器,处理用户输入,并显示计算结果。
package com.example.a4_11;
import androidx.appcompat.app.AppCompatActivity;
import android.os.Bundle;
import android.util.Log;
import android.view.View;
import android.widget.Button;
import android.widget.EditText;
import android.widget.Toast;
public class MainActivity extends AppCompatActivity implements View.OnClickListener {
//显式结果和计算过程
private EditText mresult, mjsgc;
//数字0-9
private Button btn1, btn2, btn3, btn4, btn5, btn6, btn7, btn8, btn9, btn0;
private Button btnd; //小数点
//运算符
private Button btn1j, btnj, btnx, btnc, btn1d; //加减乘除等于
//功能键
private Button btndel, btnqc;//回退键和清除所有键
boolean equals_flag = false;//等号标识
boolean del_flag = false;
@Override
protected void onCreate(Bundle savedInstanceState) {
super.onCreate(savedInstanceState);
setContentView(R.layout.activity_main);
//数字0-9
btn1 = findViewById(R.id.btn1);
btn2 = findViewById(R.id.btn2);
btn3 = findViewById(R.id.btn3);
btn4 = findViewById(R.id.btn4);
btn5 = findViewById(R.id.btn5);
btn6 = findViewById(R.id.btn6);
btn7 = findViewById(R.id.btn7);
btn8 = findViewById(R.id.btn8);
btn9 = findViewById(R.id.btn9);
btn0 = findViewById(R.id.btn0);
//运算符
btn1j = findViewById(R.id.btn1j);// +
btnj = findViewById(R.id.btnj);// -
btnx = findViewById(R.id.btnx);// *
btnc = findViewById(R.id.btnc); // /
btnd = findViewById(R.id.btnd);//小数点
btn1d = findViewById(R.id.btn1d);// =
btndel = findViewById(R.id.btndel);//退回
btnqc = findViewById(R.id.btnqc);//清除
mresult = findViewById(R.id.mresult);//结果框
mjsgc = findViewById(R.id.mjsgc);//输入过程框
//点击事件0-9
btn0.setOnClickListener(this);
btn1.setOnClickListener(this);
btn2.setOnClickListener(this);
btn3.setOnClickListener(this);
btn4.setOnClickListener(this);
btn5.setOnClickListener(this);
btn6.setOnClickListener(this);
btn7.setOnClickListener(this);
btn8.setOnClickListener(this);
btn9.setOnClickListener(this);
btnd.setOnClickListener(this);
//点击事件运算符
btn1j.setOnClickListener(this);
btnj.setOnClickListener(this);
btnx.setOnClickListener(this);
btnc.setOnClickListener(this);
btn1d.setOnClickListener(this);
btndel.setOnClickListener(this);
btnqc.setOnClickListener(this);
}
//读取每个按钮的点击的内容
@Override
public void onClick(View v) {
//获取输入框和结果框的内容
String input = mjsgc.getText().toString();
String output = mresult.getText().toString();
switch (v.getId()) {
case R.id.btn0:
case R.id.btn1:
case R.id.btn2:
case R.id.btn3:
case R.id.btn4:
case R.id.btn5:
case R.id.btn6:
case R.id.btn7:
case R.id.btn8:
case R.id.btn9:
case R.id.btnd:
if (equals_flag) {
//按过等号之后,重新点数字们
equals_flag = false;
mjsgc.setText(((Button) v).getText());
mresult.setText(((Button) v).getText());
} else {
mjsgc.setText(input + ((Button) v).getText());
mresult.setText(((Button) v).getText());
}
break;
case R.id.btn1j:
case R.id.btnj:
case R.id.btnx:
case R.id.btnc:
if (equals_flag) {
//按过等号之后,重新点数字
equals_flag = false;
mjsgc.setText(output + " " + ((Button) v).getText() + " ");
} else {
mjsgc.setText(input + " " + ((Button) v).getText() + " ");
}
break;
case R.id.btndel:
equals_flag = false;
if (input.length() > 0) {//如果获取到的内容不为空
mjsgc.setText(input.substring(0, input.length() - 1));
} else {
mresult.setText(null);
mjsgc.setText(null);
}
break;
case R.id.btnqc:
mresult.setText(null);
mjsgc.setText(null);
break;
case R.id.btn1d://运算结果 =
getResult();//调用处理结果集的方法
break;
}
}
//运算结果的方法
public void getResult() {
try {
String JSGC = mjsgc.getText().toString();//获取计算过程文本框的内容
double dResult = 0;
int iResult = 0;
//如果直接点等号
if (JSGC.equals("") || JSGC == null) {
return;
}
if (equals_flag) {
equals_flag = false;
return;
}
equals_flag = true;//点击过等号之后,标识亮起
String s1, s2, op;
//运算符前的数字
s1 = JSGC.substring(0, JSGC.indexOf(" "));
//运算符
op = JSGC.substring(JSGC.indexOf(" ") + 1, JSGC.indexOf(" ") + 2);
//运算符后的数字
s2 = JSGC.substring(JSGC.indexOf(" ") + 3);
double d1, d2;
//s1转化成double型
if (!s1.equals("")) {
if (s1.charAt(0) == '.') {
s1 = "0" + s1;//如果简写小数(如0.03简写.03,需要帮它完整输出数字)
}
d1 = Double.parseDouble(s1);//正常转化
} else {
d1 = 0;//如果首次只输入了“运算符 数字”,如: + 4,则返回:0 + 4
mjsgc.setText("0" + JSGC);
}
//s2转化成double型
if (!s2.equals("")) {
if (s2.charAt(0) == '.') {
s2 = "0" + s2;
}
d2 = Double.parseDouble(s2);
} else {
d2 = d1;
if (s1.equals("")) {
mjsgc.setText("0" + JSGC + "0");//如果只输入了运算符,如 + ,输出0 + 0,得结果0
} else {
mjsgc.setText(JSGC + s1);//如果不输入s2,如,9 * ,输出9 * 9 ,得结果81
}
}
if (op.equals("+")) {//如果是 +
dResult = d1 + d2;
} else if (op.equals("-")) {
dResult = d1 - d2;
} else if (op.equals("*")) {
dResult = d1 * d2;
} else if (op.equals("/")) {
if (d2 == 0) { //如果被除数是0
Toast.makeText(this, "除数不能为0", Toast.LENGTH_SHORT).show();
return;
} else {//否则执行正常是除法运算
dResult = d1 / d2;
}
}
if (s1.contains(".") || s2.contains(".") || op.equals("/")) {
mresult.setText(dResult + "");//如果是小数、或者除法运算
} else {
iResult = (int) dResult; //否则都是整型
mresult.setText(iResult + "");
}
} catch (Exception e) {
Toast.makeText(this, e.toString(), Toast.LENGTH_SHORT).show();
Log.i("JSQ", e.toString());
}
}
}3. 运行项目
点击运行按钮,即可运行成功。

运行效果图
三、心得体会
1.理解布局设计
理解如何设计和实现一个计算器的用户界面是一个重要的步骤。我需要考虑如何将各种控件(如文本框,按钮等)放置在屏幕上以获得最佳的用户体验。
2.理解Android事件处理
当用户在计算器上进行操作时(如点击按钮或输入数字),需要有相应的事件处理逻辑来响应这些操作。这涉及到理解Android的事件处理机制,如点击事件,输入事件等。
3.学习与创新
开发Android计算器让我了解到,学习新的技术和知识是必要的,但更重要的是能够将这些知识应用到实际的问题中,并进行创新。这个过程让我对学习有了新的理解。
4.理解Android数据存储
在这个项目中,我需要在应用中存储一些数据,如用户输入的数字和操作。我需要了解如何使用Android的数据存储技术来实现这一点。
5.调试和测试
在开发过程中,我需要花大量的时间进行调试和测试,以确保计算器的功能正常,用户界面友好。这让我了解到测试的重要性,以及如何编写有效的测试用例来发现和修复错误。文章来源:https://www.toymoban.com/news/detail-722916.html
四、总结
这次项目中学习到如何在Android应用中实现计算器功能。如何在Activity中创建和管理视图。解如何使用XML布局文件来设计和布局界面。需要熟悉各种布局元素,如`GridLayout`。学习到如何使用各种UI组件来实现用户交互。这包括如何使用`EditText`、`Button`、`TextView`等组件来输入和显示文本。在实现计算器功能时,你需要了解各种运算的规则和算法。这包括加法、减法、乘法和除法的基本原理,以及如何处理浮点数和括号等复杂表达式。可以掌握Android应用开发的基本概念,包括布局、事件处理和计算功能。这将在Android开发领域的进一步学习打下坚实的基础。文章来源地址https://www.toymoban.com/news/detail-722916.html
到了这里,关于Android计算器实现的文章就介绍完了。如果您还想了解更多内容,请在右上角搜索TOY模板网以前的文章或继续浏览下面的相关文章,希望大家以后多多支持TOY模板网!