目录
前言
长轮询
1.实现步骤
1.1客户端轮询发送请求
1.2服务端处理数据
1.3客户端接收数据
2.实现实例
RocketMQ长轮询
1.PullMessage服务
2.PullMessageProcessor服务
3.PullCallback回调
总结
前言
消息队列一般在消费端都会提供push和pull两种模式,RocketMQ同样实现了这两种模式,分别提供了两个实现类:DefaultMQPushConsumer和DefaultMQPullConsumer;两种方式各有优势:
push模式:推送模式,即服务端有数据之后立马推送消息给客户端,需要客户端和服务器建立长连接,实时性很高,对客户端来说也简单,接收处理消息即可;缺点就是服务端不知道客户端处理消息的能力,可能会导致数据积压,同时也增加了服务端的工作量,影响服务端的性能;
pull模式:拉取模式,即客户端主动去服务端拉取数据,主动权在客户端,拉取数据,然后处理数据,再拉取数据,一直循环下去,具体拉取数据的时间间隔不好设定,太短可能会导致大量的连接拉取不到数据,太长导致数据接收不及时; RocketMQ使用了长轮询的方式,兼顾了push和pull两种模式的优点,下面首先对长轮询做简单介绍,进而分析RocketMQ内置的长轮询模式。
长轮询
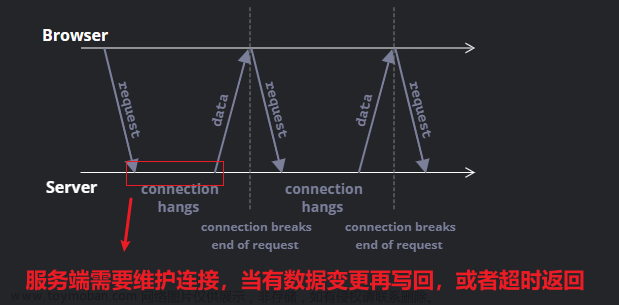
长轮询通过客户端和服务端的配合,达到主动权在客户端,同时也能保证数据的实时性;长轮询本质上也是轮询,只不过对普通的轮询做了优化处理,服务端在没有数据的时候并不是马上返回数据,会hold住请求,等待服务端有数据,或者一直没有数据超时处理,然后一直循环下去;下面看一下如何简单实现一个长轮询;
1.实现步骤
1.1客户端轮询发送请求
客户端应该存在一个一直循环的程序,不停的向服务端发送获取消息请求;
1.2服务端处理数据
服务器接收到客户端请求之后,首先查看是否有数据,如果有数据则直接返回,如果没有则保持连接,等待获取数据,服务端获取数据之后,会通知之前的请求连接来获取数据,然后返回给客户端;
1.3客户端接收数据
正常情况下,客户端会马上接收到服务端的数据,或者等待一段时间获取到数据;如果一直获取不到数据,会有超时处理;在获取数据或者超时处理之后会关闭连接,然后再次发起长轮询请求;
2.实现实例
以下使用netty模拟一个http服务器,使用HttpURLConnection模拟客户端发送请求,使用BlockingQueue存放数据;
服务端代码
public class Server {
public static void start(final int port) throws Exception {
EventLoopGroup boss = new NioEventLoopGroup();
EventLoopGroup woker = new NioEventLoopGroup();
ServerBootstrap serverBootstrap = new ServerBootstrap();
try {
serverBootstrap.channel(NioServerSocketChannel.class).group(boss, woker)
.childOption(ChannelOption.SO_KEEPALIVE, true).option(ChannelOption.SO_BACKLOG, 1024)
.childHandler(new ChannelInitializer<SocketChannel>() {
@Override
protected void initChannel(SocketChannel ch) throws Exception {
ch.pipeline().addLast("http-decoder", new HttpServerCodec());
ch.pipeline().addLast(new HttpServerHandler());
}
});
ChannelFuture future = serverBootstrap.bind(port).sync();
System.out.println("server start ok port is " + port);
DataCenter.start();
future.channel().closeFuture().sync();
} finally {
boss.shutdownGracefully();
woker.shutdownGracefully();
}
}
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
start(8080);
}
}
netty默认支持http协议,直接使用即可,启动端口为8080;同时启动数据中心服务,相关代码如下:
public class DataCenter {
private static Random random = new Random();
private static BlockingQueue<String> queue = new LinkedBlockingQueue<>();
private static AtomicInteger num = new AtomicInteger();
public static void start() {
while (true) {
try {
Thread.sleep(random.nextInt(5) * 1000);
String data = "hello world" + num.incrementAndGet();
queue.put(data);
System.out.println("store data:" + data);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
public static String getData() throws InterruptedException {
return queue.take();
}
}
为了模拟服务端没有数据,需要等待的情况,这里使用BlockingQueue来模拟,不定期的往队列里面插入数据,同时对外提供获取数据的方法,使用的是take方法,没有数据会阻塞知道有数据为止;getData在类HttpServerHandler中使用,此类也很简单,如下:
public class HttpServerHandler extends ChannelInboundHandlerAdapter {
public void channelRead(ChannelHandlerContext ctx, Object msg) throws Exception {
if (msg instanceof HttpRequest) {
FullHttpResponse httpResponse = new DefaultFullHttpResponse(HttpVersion.HTTP_1_1, HttpResponseStatus.OK);
httpResponse.content().writeBytes(DataCenter.getData().getBytes());
httpResponse.headers().set(HttpHeaders.Names.CONTENT_TYPE, "text/plain; charset=UTF-8");
httpResponse.headers().set(HttpHeaders.Names.CONTENT_LENGTH, httpResponse.content().readableBytes());
ctx.writeAndFlush(httpResponse);
}
}
}
获取到客户端的请求之后,从数据中心获取一条消息,如果没有数据,会进行等待,直到有数据为止;然后使用FullHttpResponse返回给客户端;客户端使用HttpURLConnection来和服务端建立连接,不停的拉取数据,代码如下:
public class Client {
public static void main(String[] args) {
while (true) {
HttpURLConnection connection = null;
try {
URL url = new URL("http://localhost:8080");
connection = (HttpURLConnection) url.openConnection();
connection.setReadTimeout(10000);
connection.setConnectTimeout(3000);
connection.setRequestMethod("GET");
connection.connect();
if (200 == connection.getResponseCode()) {
BufferedReader reader = null;
try {
reader = new BufferedReader(new InputStreamReader(connection.getInputStream(), "UTF-8"));
StringBuffer result = new StringBuffer();
String line = null;
while ((line = reader.readLine()) != null) {
result.append(line);
}
System.out.println("时间:" + new Date().toString() + "result = " + result);
} finally {
if (reader != null) {
reader.close();
}
}
}
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} finally {
if (connection != null) {
connection.disconnect();
}
}
}
}
}
以上只是简单的模拟了长轮询的方式,下面重点来看看RocketMQ是如何实现长轮询的;
RocketMQ长轮询
RocketMQ的消费端提供了两种消费模式分别是:DefaultMQPushConsumer和DefaultMQPullConsumer,其中DefaultMQPushConsumer就是使用的长轮询,所以下面重点分析此类;
1.PullMessage服务
从名字可以看出来就是客户端从服务端拉取数据的服务,看里面的一个核心方法:
@Override
public void run() {
log.info(this.getServiceName() + " service started");
while (!this.isStopped()) {
try {
PullRequest pullRequest = this.pullRequestQueue.take();
this.pullMessage(pullRequest);
} catch (InterruptedException ignored) {
} catch (Exception e) {
log.error("Pull Message Service Run Method exception", e);
}
}
log.info(this.getServiceName() + " service end");
}
服务启动之后,会一直不停的循环调用拉取数据,PullRequest可以看作是拉取数据需要的参数,部分代码如下:
public class PullRequest {
private String consumerGroup;
private MessageQueue messageQueue;
private ProcessQueue processQueue;
private long nextOffset;
private boolean lockedFirst = false;
...省略...
}
每个MessageQueue 对应了封装成了一个PullRequest,因为拉取数据是以每个Broker下面的Queue为单位,同时里面还一个ProcessQueue,每个MessageQueue也同样对应一个ProcessQueue,保存了这个MessageQueue消息处理状态的快照;还有nextOffset用来标识读取的位置;继续看一段pullMessage中的内容,给服务端发送请求的头内容:
PullMessageRequestHeader requestHeader = new PullMessageRequestHeader();
requestHeader.setConsumerGroup(this.consumerGroup);
requestHeader.setTopic(mq.getTopic());
requestHeader.setQueueId(mq.getQueueId());
requestHeader.setQueueOffset(offset);
requestHeader.setMaxMsgNums(maxNums);
requestHeader.setSysFlag(sysFlagInner);
requestHeader.setCommitOffset(commitOffset);
requestHeader.setSuspendTimeoutMillis(brokerSuspendMaxTimeMillis);
requestHeader.setSubscription(subExpression);
requestHeader.setSubVersion(subVersion);
requestHeader.setExpressionType(expressionType);
String brokerAddr = findBrokerResult.getBrokerAddr();
if (PullSysFlag.hasClassFilterFlag(sysFlagInner)) {
brokerAddr = computPullFromWhichFilterServer(mq.getTopic(), brokerAddr);
}
PullResult pullResult = this.mQClientFactory.getMQClientAPIImpl().pullMessage(
brokerAddr,
requestHeader,
timeoutMillis,
communicationMode,
pullCallback);
return pullResult;其中有一个参数是SuspendTimeoutMillis,作用是设置Broker的最长阻塞时间,默认为15秒,前提是没有消息的情况下,有消息会立刻返回;
2.PullMessageProcessor服务
从名字可以看出,服务端用来处理pullMessage的服务,下面重点看一下processRequest方法,其中包括对获取不同结果做的处理:
switch (response.getCode()) {
case ResponseCode.SUCCESS:
...省略...
break;
case ResponseCode.PULL_NOT_FOUND:
if (brokerAllowSuspend && hasSuspendFlag) {
long pollingTimeMills = suspendTimeoutMillisLong;
if (!this.brokerController.getBrokerConfig().isLongPollingEnable()) {
pollingTimeMills = this.brokerController.getBrokerConfig().getShortPollingTimeMills();
}
String topic = requestHeader.getTopic();
long offset = requestHeader.getQueueOffset();
int queueId = requestHeader.getQueueId();
PullRequest pullRequest = new PullRequest(request, channel, pollingTimeMills,
this.brokerController.getMessageStore().now(), offset, subscriptionData);
this.brokerController.getPullRequestHoldService().suspendPullRequest(topic, queueId, pullRequest);
response = null;
break;
}
case ResponseCode.PULL_RETRY_IMMEDIATELY:
break;
case ResponseCode.PULL_OFFSET_MOVED:
...省略...
break;
default:
assert false;
一共处理了四个类型,我们关心的是在没有获取到数据的情况下是如何处理的,可以重点看一下ResponseCode.PULL_NOT_FOUND,表示没有拉取到数据,此时会调用PullRequestHoldService服务,从名字可以看出此服务用来hold住请求,不会立马返回,response被至为了null,不给客户端响应;下面重点看一下PullRequestHoldService:
@Override
public void run() {
log.info("{} service started", this.getServiceName());
while (!this.isStopped()) {
try {
if (this.brokerController.getBrokerConfig().isLongPollingEnable()) {
this.waitForRunning(5 * 1000);
} else {
this.waitForRunning(this.brokerController.getBrokerConfig().getShortPollingTimeMills());
}
long beginLockTimestamp = this.systemClock.now();
this.checkHoldRequest();
long costTime = this.systemClock.now() - beginLockTimestamp;
if (costTime > 5 * 1000) {
log.info("[NOTIFYME] check hold request cost {} ms.", costTime);
}
} catch (Throwable e) {
log.warn(this.getServiceName() + " service has exception. ", e);
}
}
log.info("{} service end", this.getServiceName());
}
此方法主要就是通过不停的检查被hold住的请求,检查是否已经有数据了,具体检查哪些就是在ResponseCode.PULL_NOT_FOUND中调用的suspendPullRequest方法:
private ConcurrentHashMap<String/* topic@queueId */, ManyPullRequest> pullRequestTable =
new ConcurrentHashMap<String, ManyPullRequest>(1024);
public void suspendPullRequest(final String topic, final int queueId, final PullRequest pullRequest) {
String key = this.buildKey(topic, queueId);
ManyPullRequest mpr = this.pullRequestTable.get(key);
if (null == mpr) {
mpr = new ManyPullRequest();
ManyPullRequest prev = this.pullRequestTable.putIfAbsent(key, mpr);
if (prev != null) {
mpr = prev;
}
}
mpr.addPullRequest(pullRequest);
}
将需要hold处理的PullRequest放入到一个ConcurrentHashMap中,等待被检查;具体的检查代码在checkHoldRequest中:
private void checkHoldRequest() {
for (String key : this.pullRequestTable.keySet()) {
String[] kArray = key.split(TOPIC_QUEUEID_SEPARATOR);
if (2 == kArray.length) {
String topic = kArray[0];
int queueId = Integer.parseInt(kArray[1]);
final long offset = this.brokerController.getMessageStore().getMaxOffsetInQuque(topic, queueId);
try {
this.notifyMessageArriving(topic, queueId, offset);
} catch (Throwable e) {
log.error("check hold request failed. topic={}, queueId={}", topic, queueId, e);
}
}
}
}
此方法用来获取指定messageQueue下最大的offset,然后用来和当前的offset来比较,来确定是否有新的消息到来;往下看notifyMessageArriving方法:
public void notifyMessageArriving(final String topic, final int queueId, final long maxOffset, final Long tagsCode) {
String key = this.buildKey(topic, queueId);
ManyPullRequest mpr = this.pullRequestTable.get(key);
if (mpr != null) {
List<PullRequest> requestList = mpr.cloneListAndClear();
if (requestList != null) {
List<PullRequest> replayList = new ArrayList<PullRequest>();
for (PullRequest request : requestList) {
long newestOffset = maxOffset;
if (newestOffset <= request.getPullFromThisOffset()) {
newestOffset = this.brokerController.getMessageStore().getMaxOffsetInQuque(topic, queueId);
}
if (newestOffset > request.getPullFromThisOffset()) {
if (this.messageFilter.isMessageMatched(request.getSubscriptionData(), tagsCode)) {
try {
this.brokerController.getPullMessageProcessor().executeRequestWhenWakeup(request.getClientChannel(),
request.getRequestCommand());
} catch (Throwable e) {
log.error("execute request when wakeup failed.", e);
}
continue;
}
}
if (System.currentTimeMillis() >= (request.getSuspendTimestamp() + request.getTimeoutMillis())) {
try {
this.brokerController.getPullMessageProcessor().executeRequestWhenWakeup(request.getClientChannel(),
request.getRequestCommand());
} catch (Throwable e) {
log.error("execute request when wakeup failed.", e);
}
continue;
}
replayList.add(request);
}
if (!replayList.isEmpty()) {
mpr.addPullRequest(replayList);
}
}
}
}
方法中两个重要的判定就是:比较当前的offset和maxoffset,看是否有新的消息到来,有新的消息返回客户端;另外一个就是比较当前的时间和阻塞的时间,看是否超过了最大的阻塞时间,超过也同样返回; 此方法不光在PullRequestHoldService服务类中循环调用检查,同时在DefaultMessageStore中消息被存储的时候调用;其实就是主动检查和被动通知两种方式。
3.PullCallback回调
服务端处理完之后,给客户端响应,回调其中的PullCallback,其中在处理完消息之后,重要的一步就是再次把pullRequest放到PullMessageService服务中,等待下一次的轮询;文章来源:https://www.toymoban.com/news/detail-724725.html
总结
本文首先介绍了两种消费消息的模式,介绍了其中的优缺点,然后引出了长轮询,并且在本地简单模拟了长轮询,最后重点介绍了RocketMQ中是如何实现的长轮询文章来源地址https://www.toymoban.com/news/detail-724725.html
到了这里,关于RocketMQ的长轮询(Long Polling)实现分析的文章就介绍完了。如果您还想了解更多内容,请在右上角搜索TOY模板网以前的文章或继续浏览下面的相关文章,希望大家以后多多支持TOY模板网!