前言
Spring注解结合XML配置是指在Spring应用中,使用注解和XML配置的方式来进行Bean的定义、依赖注入和其他配置。这种方式可以充分利用Spring框架的注解和XML配置两种不同的配置方式的特点。
在Spring框架中,我们可以使用注解来定义Bean,如@Component、@Service、@Repository等注解,也可以使用XML配置文件来定义Bean,例如<bean>标签。通常情况下,我们可以使用其中一种方式来定义Bean,但在某些复杂的场景下,我们需要同时使用这两种方式来定义Bean。具体来说:
使用注解来定义Bean,这样可以减少XML配置文件中的内容,使代码更加简洁,易于阅读和维护。例如:
@Component("userService")
public class UserServiceImpl implements UserService {
// ...
}
使用XML配置来定义Bean,这样可以提供更多的灵活性,使得对Bean的配置更加详细和准确。例如:
<bean id="userService" class="com.example.UserServiceImpl">
<!-- 注入依赖 -->
<property name="userDao" ref="userDao"/>
</bean>
使用注解和XML配置结合的方式来定义Bean,可以根据具体要求灵活地选择采用XML配置或注解来定义Bean。例如:
<context:component-scan base-package="com.example"/>
<bean id="userDao" class="com.example.UserDaoImpl"/>
<bean id="userService" class="com.example.UserServiceImpl">
<!-- 注入依赖,在XML配置中引用注解定义的Bean -->
<property name="userDao" ref="userDao"/>
</bean>
在这种方式下,我们可以使用注解来扫描指定包下的所有组件,使用XML配置来定义和配置Bean,实现依赖注入、AOP等功能。
综上所述,Spring注解结合XML配置是指通过同时使用注解和XML配置的方式,以适应不同的需求和场景,提供更加灵活和精细的配置。
一、开始学习注解
1、本次我们要学习的有四个注解 @Component @Repository @Service @Controller,那么他们分别是什么意思呢?
在Spring框架中,@Component、@Repository、@Service和@Controller是用于标记类的注解,用于定义Bean的角色和作用。
@Component:它是一个通用的注解,用于表示一个普通的组件类,可用于任意层次。当我们使用@Component将一个类标记为组件时,Spring容器会自动扫描并创建这个类的实例作为Bean。@Repository:它用于标记数据访问层(DAO)的组件类。主要用于对数据库的操作,包括数据的增删改查等。通过@Repository注解,Spring会将这个类识别为持久化层的Bean,常与@Autowired配合使用,进行依赖注入。@Service:它用于标记服务层(Service)的组件类。主要负责业务逻辑的处理,比如事务管理、数据校验、调用DAO层等。通过@Service注解,Spring会将这个类识别为服务层的Bean,常与@Autowired配合使用,进行依赖注入。@Controller:它用于标记控制器层(Controller)的组件类。主要用于接收用户请求,处理请求参数,调用Service层处理业务逻辑,并返回相应的视图或数据。通过@Controller注解,Spring会将这个类识别为控制器层的Bean,常与@RequestMapping等注解一起使用。
以上四个注解都是用于标记组件类,并将其注册为Spring容器中的Bean。它们的作用是告诉Spring容器哪些类需要被实例化为Bean,并提供相应的功能,如依赖注入、AOP切面等。
使用这些注解可以使代码更加清晰和模块化,也有利于后续的扩展和维护。同时,结合不同的注解,我们可以将一个大型应用程序分成不同层次的组件,使开发更加高效和可管理。
了解完这四个注解后,我们就来完成一个案例,通过案例去更直观的了解它们吧。
2、新建项目,结果如下

3、导入 spring 依赖
<!-- spring 的核心依赖 -->
<dependencies>
<!-- https://mvnrepository.com/artifact/org.springframework/spring-context -->
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-context</artifactId>
<version>5.3.23</version>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>ch.qos.logback</groupId>
<artifactId>logback-classic</artifactId>
<version>1.4.5</version>
</dependency>
</dependencies>4、在 dao 包下新建一个 UserDao 接口,在 impl 包下新建 UserDaoImpl 实现类
userDao 接口
public interface UserDao {
void save();
}UserDaoImpl 实现类
@Component("userDao")
@Slf4j
public class UserDaoImpl implements UserDao {
@Override
public void save() {
log.info("insert into user_info...... ");
}
}@Component:用于标识当前类为一个 Bena ,这样就会被 spring 容器扫描到,可以通过 value 来指定, Bean 的 id,如果不指定 value,默认的 id 就是当前类名并,将首字母改为小写(例如:userDaoImpl)
5、在 service 包下新建一个 UserService 接口,在 impl 包下新建一个 UserServiceImpl 实现类
UserService 接口
public interface UserService {
void add();
}
UserServiceImpl 实现类
@Component("userService")
public class UserServiceImpl implements UserService {
private UserDao userDao;
/**
* 通过构造方法注入 dao
*
* @param userDao
*
* @Autowired注解进行注入
*/
@Autowired
public UserServiceImpl(UserDao userDao) {
this.userDao = userDao;
}
@Override
public void add() {
userDao.save();
}
}
6、在 controller 包下,新建 UserController 类
@Component("userController")
public class UserController {
private UserService userService;
/**
* 通过构造方法注入
*
* @param userService
*/
@Autowired
public UserController(UserService userService) {
this.userService = userService;
}
public void add() {
userService.add();
}
}7、 在 resources 下新建一个 spring 的 xml 文件 application.xml,在配置文件中完成 Bean 的装配
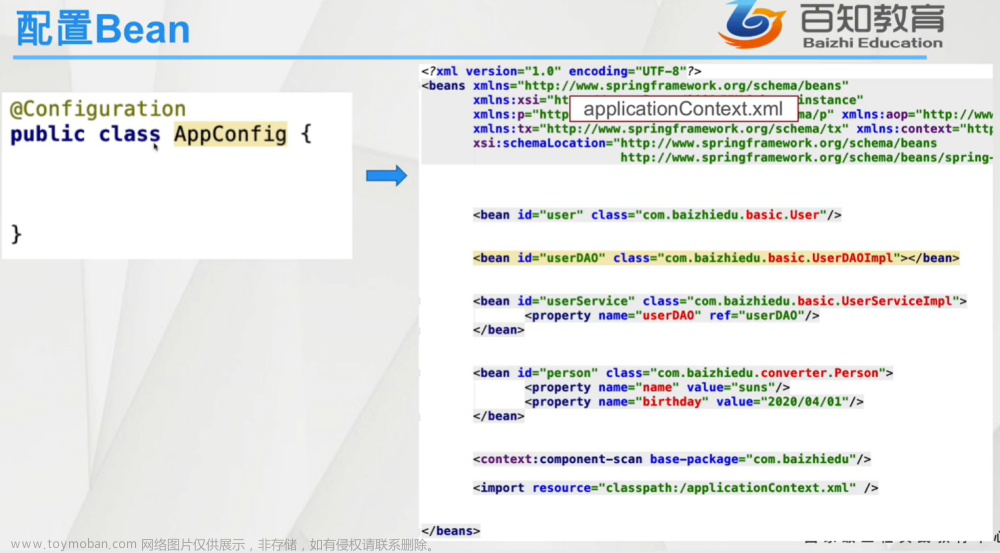
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd
">
<bean id="userDao" class="edu.nf.ch07.dao.impl.UserDaoImpl"/>
<bean id="userService" class="edu.nf.ch07.service.impl.UserServiceImpl">
<constructor-arg name="userDao" ref="userDao"/>
</bean>
<bean id="userController" class="edu.nf.ch07.controller.UserController">
<constructor-arg name="userService" ref="userService"/>
</bean>
</beans>这个案例是通过使用 @Component 注解去装配一个 bean。
8、测试
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) {
ApplicationContext context = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("application.xml");
UserController bean = context.getBean(UserController.class);
bean.add();
}
}
测试结果

9、分析
在实现类和 UserControlelr 类都是用了 @Component 注解去装配一个 bean ,而且还是带参数的,那么这个参数有什么用呢?看下图:

使用Spring框架进行依赖注入的配置文件,它采用了XML格式来描述组件及其之间的依赖关系。
在这个配置文件中,定义了三个Bean:
userDao:它的类为edu.nf.ch07.dao.impl.UserDaoImpl。这个Bean用于访问数据库,并提供了数据访问操作。
userService:它的类为edu.nf.ch07.service.impl.UserServiceImpl。这个Bean用于封装一些具体的业务逻辑操作,并调用userDao进行数据访问。
userController:它的类为edu.nf.ch07.controller.UserController。这个Bean用于接收用户请求,通过调用userService处理业务逻辑,最终返回相应的视图或数据。在XML配置文件中,
name用于指定要注入的属性或构造函数参数的名称。它通常和value、ref等属性一起使用,在显式配置Bean时指定相应的属性或构造函数参数。name属性的取值为一个字符串,表示目标属性或构造函数参数的名称。在XML配置文件中,
ref用于指定依赖注入的目标Bean。它的取值为一个Bean的ID。在给某个属性或构造函数参数注入值时,通过ref指定目标Bean的ID,Spring容器会自动解析这个依赖关系,并将相应的Bean实例注入到目标位置。
在这些Bean之间,存在一定的依赖关系。userDao被userService依赖,因此在userService的构造函数中使用constructor-arg标签注入userDao。同样,userService被userController依赖,因此在userController的构造函数中使用constructor-arg标签注入userService。
这种基于XML的配置方式被称为“显式配置”,它会告诉Spring容器哪些Bean需要被实例化,并建立它们之间的依赖关系。通过使用这种方式,我们可以将组件之间的关系直观地描述出来,同时可以灵活地进行配置和修改。
二、使用特定注解定义各个类
1、 Dao 层 @Repository
@Repository("userDao")
public class UserDaoImpl implements UserDao {
@Override
public void save() {
log.info("insert into user_info...... ");
}
}
2、service 层 @Service
@Service("userService")
public class UserServiceImpl implements UserService {
private UserDao userDao;
/**
* 通过构造方法注入 dao
*
* @param userDao
*
* @Autowired注解进行注入
*/
public UserServiceImpl(UserDao userDao) {
this.userDao = userDao;
}
@Override
public void add() {
userDao.save();
}
}
3、controller 层 @Controller
@Controller("userController")
public class UserController {
private UserService userService;
/**
* 通过构造方法注入
*
* @param userService
*/
public UserController(UserService userService) {
this.userService = userService;
}
public void add() {
userService.add();
}
}
4、改配置文件
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xmlns:context="http://www.springframework.org/schema/context"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd
http://www.springframework.org/schema/context
http://www.springframework.org/schema/context/spring-context-4.2.xsd
">
<!-- 启用注解扫描 , 指定扫描的包 -->
<context:component-scan base-package="edu.nf.ch07"/>
</beans>在Spring配置文件中,
<context:component-scan>用于启用注解扫描,并指定要扫描的包路径。通过这个配置,Spring容器会自动扫描指定包及其子包下的类,并将它们注册为Bean。上述示例中,使用<context:component-scan>配置启用了注解扫描功能,并通过base-package属性指定了要扫描的包路径为edu.nf.ch07。这意味着Spring容器将会扫描该包及其子包下的类,查找带有特定注解(如@Component、@Service、@Repository等)的类,并将其注册为Bean。
5、测试
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) {
ApplicationContext context = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("application.xml");
UserController bean = context.getBean(UserController.class);
bean.add();
}
}
测试结果

6、使用@Component 和使用 @Controller @Repository @Service 的区别
@Component、@Controller、@Repository、@Service都是Spring中的注解,它们都是@Component注解的扩展。使用它们可以标记一个类作为组件,并将其注册到Spring容器中。它们之间的区别如下:
@Component:通用注解,可用于任何类。@Controller:用于标记控制器层的组件,常用于SpringMVC应用程序。@Repository:用于标记数据访问层的组件,表示该组件负责数据访问,常用于与数据库交互的场景。@Service:用于标记业务逻辑层的组件,表示该组件负责业务处理,常用于编写业务逻辑。
使用<context:component-scan>配置时,它会扫描指定包及其子包下的标记了@Component、@Controller、@Repository、@Service注解的类,并将其注册为Bean。因此,在使用<context:component-scan>时,使用哪种注解来标记类并没有影响。
但是,建议在不同层次的组件上使用相应的注解,以便更好地组织代码,并使代码更易于理解和维护。这也是所谓的“约定优于配置”原则的一种体现,即通过预定义的注解来简化配置,提高代码清晰度和可读性。文章来源:https://www.toymoban.com/news/detail-724939.html
三、使用注解结合 xml 开发有什么好处?
注解和XML配置结合的方式可以提供更灵活和可扩展的依赖注入配置方案。下面是使用注解和XML配置结合的几个好处:
增加可读性和易维护性:通过使用注解,可以将依赖注入相关的配置信息直接写在类的代码中,使得代码更加直观和可读。同时,将一些通用的配置信息(比如数据库连接等)放在XML配置文件中,可以提高配置信息的可维护性和重用性。
灵活性和扩展性:注解可以灵活地应用于各种情况,例如使用 @Autowired 注解进行自动注入、使用 @Qualifier 注解指定具体的Bean、使用 @Primary 注解指定默认的Bean等。这些注解可以与XML配置文件结合使用,提供更细粒度的依赖注入控制和配置灵活性。
降低耦合性:通过使用注解和XML配置结合的方式,可以将实现类与接口之间解耦。使用 @Qualifier 注解可以根据需要选择具体的实现类,在不改变代码的情况下更换依赖的实现类。同时,@Primary 注解可以指定默认的实现类,减少了代码中对具体实现类的直接引用,进一步降低了耦合性。
总的来说,注解和XML配置结合的方式可以提供更灵活、可读性更好、可维护性更高、扩展性更强、耦合性更低的依赖注入配置方案。通过合理选择和使用注解和XML配置,可以更好地管理和控制对象之间的依赖关系。
四、gitee 案例
案例完整地址:https://gitee.com/qiu-feng1/spring-framework.git文章来源地址https://www.toymoban.com/news/detail-724939.html
到了这里,关于Sprint framework Day07:注解结合 xml 配置的文章就介绍完了。如果您还想了解更多内容,请在右上角搜索TOY模板网以前的文章或继续浏览下面的相关文章,希望大家以后多多支持TOY模板网!