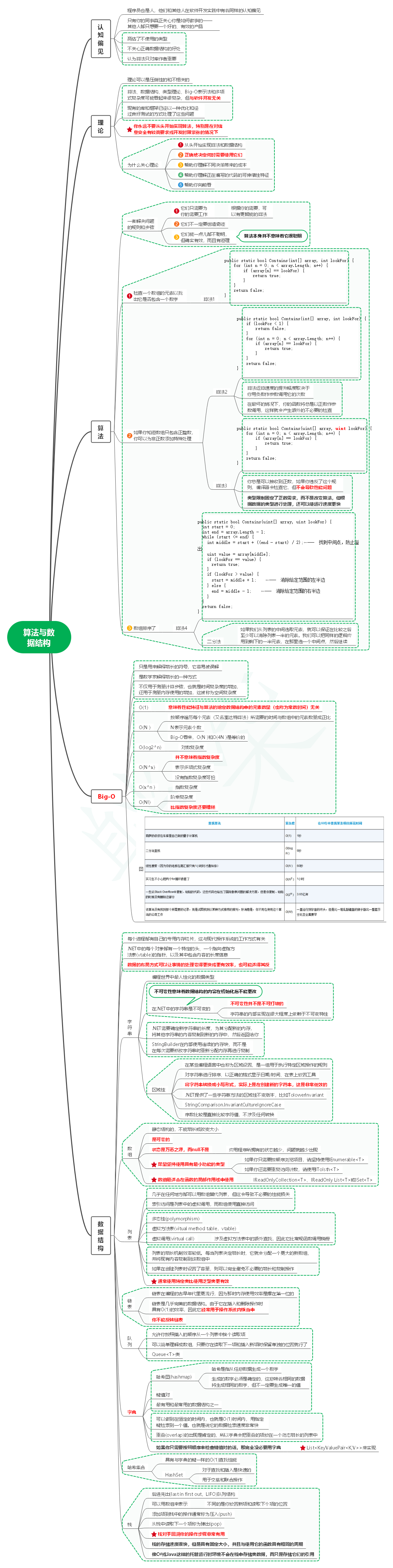
目录
线性结构
队列结构的队列
链表结构的队列
链表的面试题
单向链表应用场景
约瑟夫环问题
栈结构
中缀表达式
前缀表达式
后缀表达式
非线性结构
图
递归解决迷宫问题
递归解决八皇后问题
线性结构
顺序存储方式,顺序表
常见的顺序存储结构有:数组、队列、链表、栈
链式存储方式,链表
数组结构
队列结构的队列
队列可以使用数组结构或者链表结构来存储,先入先出,后进后出。
数组结构的队列:
public class Demo {
public static void main(String[] args) {
CircleArrayQueue arrayQueue = new CircleArrayQueue(3);
char key;
Scanner scanner = new Scanner(System.in);
boolean loop = true;
while (loop) {
System.out.println("s(show):显示队列");
System.out.println("e(exit):退出程序");
System.out.println("a(add):添加数据到队列");
System.out.println("g(get):从队列取出数据");
System.out.println("h(head):查看队列头的数据");
key = scanner.next().charAt(0);
switch (key) {
case 's':
arrayQueue.showQueue();
break;
case 'a':
System.out.println("请输入一个数字");
int value = scanner.nextInt();
arrayQueue.addQueue(value);
break;
case 'g':
try {
int res = arrayQueue.getQueue();
System.out.println("取出的数据为=" + res);
} catch (Exception e) {
System.out.println(e.getMessage());
}
break;
case 'e':
loop = false;
scanner.close();
System.out.println("程序退出...");
break;
case 'h':
try {
int res = arrayQueue.headQueue();
System.out.println("查看的数据为=" + res);
} catch (Exception e) {
System.out.println(e.getMessage());
}
break;
default:
break;
}
}
}
}
class CircleArrayQueue {
private int maxSize;
// 指向队列头的位置
private int front;
// 指向队列尾的数据的下一个的位置,它指向的队尾的数据代表有值的
private int rear;
private int[] arr;
public CircleArrayQueue(int arrMaxSize) {
// 实际上队列有maxSize个元素,因为空出了一个位置
maxSize = arrMaxSize + 1;
arr = new int[maxSize];
front = rear = 0;
}
public boolean isFull() {
return (rear + 1) % maxSize == front;
}
public boolean isEmpty() {
return front == rear;
}
public void addQueue(int n) {
if (isFull()) {
System.out.println("队列为满,不能加入数据");
return;
}
arr[rear] = n;
rear++;
if (rear % maxSize == 0) {
rear = 0;
}
}
public int getQueue() {
if (isEmpty()) {
throw new RuntimeException("队列为空,不能取值");
}
int res = arr[front];
front++;
if (front % maxSize == 0) {
front = 0;
}
return res;
}
public void showQueue() {
if (isEmpty()) {
System.out.println("队列为空,没有数据");
return;
}
// for (int i = front; i != rear; i = (i + 1) % maxSize) {
for (int i = front; i < front + size(); i++) {
System.out.printf("arr[%d]=%d\n", i % maxSize, arr[i % maxSize]);
}
}
public int headQueue() {
if (isEmpty()) {
throw new RuntimeException("队列为空,没有头数据");
}
return arr[front];
}
private int size() {
return (rear + maxSize - front) % maxSize;
}
}栈结构
public class ArrayStackDemo {
public static void main(String[] args) {
ArrayStack stack = new ArrayStack(4);
String key;
boolean loop = true;
Scanner scanner = new Scanner(System.in);
while (loop) {
System.out.println("show:表示显示栈");
System.out.println("exit:表示退出栈");
System.out.println("push:表示压栈");
System.out.println("pop:表示出栈");
System.out.println("请输入你的选择:");
key = scanner.next();
switch (key) {
case "s":
stack.list();
break;
case "e":
loop = false;
break;
case "pu":
try {
System.out.println("请输入要压栈的数据");
int value = scanner.nextInt();
stack.push(value);
} catch (Exception e) {
System.out.println(e.getMessage());
}
break;
case "po":
try {
System.out.println(stack.pop());
} catch (Exception e) {
System.out.println(e.getMessage());
}
break;
default:
System.out.println("输入有误");
break;
}
}
System.out.println("程序退出了...");
}
}
class ArrayStack {
private int maxSize;
private int[] stack;
private int top = -1;
public ArrayStack(int maxSize) {
this.maxSize = maxSize;
stack = new int[maxSize];
}
public boolean isFull() {
return top == maxSize - 1;
}
public boolean isEmpty() {
return top == -1;
}
public void push(int value) {
if (isFull()) {
System.out.println("栈满");
return;
}
top++;
stack[top] = value;
}
public int pop() {
if (isEmpty()) {
throw new RuntimeException("栈空,没有数据");
}
int res = stack[top];
top--;
return res;
}
public void list() {
if (isEmpty()) {
System.out.println("栈空,没有数据");
return;
}
for (int i = top; i >= 0; i--) {
System.out.printf("a[%d]=%d\n", i, stack[i]);
}
}
}
中缀表达式
人阅读的表达式。用来实现一个简单的计算器:

public class Calculator {
public static void main(String[] args) {
String expression = "7*2*2-5+1-5+3-4";
ArrayStack2 numStack = new ArrayStack2(10);
ArrayStack2 operStack = new ArrayStack2(10);
int index = 0;
int num1 = 0;
int num2 = 0;
int oper = 0;
int res = 0;
char ch = ' ';
while (true) {
ch = expression.substring(index, index + 1).charAt(0);
if (operStack.isOper(ch)) {
if (!operStack.isEmpty()) {
if (operStack.priority(ch) <= operStack.priority(operStack.peek())) {
num1 = numStack.pop();
num2 = numStack.pop();
oper = operStack.pop();
res = numStack.cal(num1, num2, (char) oper);
numStack.push(res);
operStack.push(ch);
} else {
operStack.push(ch);
}
} else {
operStack.push(ch);
}
} else {
// numStack.push(ch - '0');
int keepNum = ch - '0';
while (index < expression.length() - 1) {
index++;
ch = expression.substring(index, index + 1).charAt(0);
if (!operStack.isOper(ch)) {
keepNum = keepNum * 10 + (ch - '0');
} else {
index--;
break;
}
}
numStack.push(keepNum);
}
index++;
if (index == expression.length()) {
break;
}
}
while (true) {
if (operStack.isEmpty()) {
break;
}
num1 = numStack.pop();
num2 = numStack.pop();
oper = operStack.pop();
res = numStack.cal(num1, num2, (char) oper);
numStack.push(res);
}
System.out.printf("表达式 %s = %d\n", expression, numStack.pop());
}
}
class ArrayStack2 {
private int maxSize;
private int[] stack;
private int top = -1;
public ArrayStack2(int maxSize) {
this.maxSize = maxSize;
stack = new int[maxSize];
}
public boolean isFull() {
return top == maxSize - 1;
}
public boolean isEmpty() {
return top == -1;
}
public void push(int value) {
if (isFull()) {
System.out.println("栈满");
return;
}
top++;
stack[top] = value;
}
public int pop() {
if (isEmpty()) {
throw new RuntimeException("栈空,没有数据");
}
int res = stack[top];
top--;
return res;
}
public void list() {
if (isEmpty()) {
System.out.println("栈空,没有数据");
return;
}
for (int i = top; i >= 0; i--) {
System.out.printf("a[%d]=%d\n", i, stack[i]);
}
}
public int priority(int oper) {
if (oper == '*' || oper == '/') {
return 1;
} else if (oper == '+' || oper == '-') {
return 0;
}
return -1;
}
public boolean isOper(char val) {
return val == '+' || val == '-' || val == '*' || val == '/';
}
public int cal(int num1, int num2, char oper) {
int res = 0;
switch (oper) {
case '+':
res = num1 + num2;
break;
case '-':
res = num2 - num1;
break;
case '*':
res = num1 * num2;
break;
case '/':
res = num2 / num1;
break;
default:
break;
}
return res;
}
public int peek() {
return stack[top];
}
}前缀表达式
也叫波兰表达式,(3+4)x5-6对应的前缀表达式为 - x + 3 4 5 6,从右向左扫描,遇到数字的时,将数字压入,遇到运算符时,弹出栈顶的两个数字进行计算,将结果压入栈,
后缀表达式
也叫逆波兰表达式,(3+4)x5-6 对应的逆波兰表达式为 3 4 + 5 x 6 - ,从左到右扫描,遇到数字把数字压栈,遇到运算符弹出栈顶的两个数字,进行运算,最后将结果压栈。可以用来写计算器:
代码:
public class PolandNotation {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// 逆波兰表达式
// (3+4)*5-6
// String suffixExpression = "3 4 + 5 * 6 -";
// 4*5-8+60+8/2
String suffixExpression = "4 5 * 8 - 60 + 8 2 / +";
List<String> list = getListString(suffixExpression);
int res = calculate(list);
}
public static List<String> getListString(String suffixExpression) {
String[] s = suffixExpression.split(" ");
List<String> list = new ArrayList<>();
for (String ele : s) {
list.add(ele);
}
return list;
}
public static int calculate(List<String> list) {
Stack<String> stack = new Stack<>();
for (String item : list) {
if (item.matches("\\d+")) {
stack.push(item);
} else {
int n2 = Integer.parseInt(stack.pop());
int n1 = Integer.parseInt(stack.pop());
int res = 0;
if (item.equals("+")) {
res = n1 + n2;
} else if (item.equals("-")) {
res = n1 - n2;
} else if (item.equals("*")) {
res = n1 * n2;
} else if (item.equals("/")) {
res = n1 / n2;
} else {
throw new RuntimeException("运算符有误");
}
stack.push(res + "");
}
}
return Integer.parseInt(stack.pop());
}
}
如何中缀转后缀表达式:
1)初始化两个栈,运算符栈s1和存储中间结果的栈s2;
2)从左到右扫描中缀表达式;
3)遇到数时,压入栈s2;
4)遇到运算符时,比较其与栈s1栈顶的优先级:
1.如果栈s1为空,或栈顶运算符为左括号,则直接将此运算符压栈s1;
2.否则,若优先级比栈顶的高,也将运算符压入栈s1;
3.否则,将栈s1栈顶的运算符弹出并压入栈s2,再次(4 - 1)与 s1 中新的栈顶运算符比较;
5)遇到括号时:
1.如果是左括号,则直接压入栈s1;
2.如果是右括号,则依次弹出s1栈顶的运算符,并压入栈s2,直到遇到左括号为止,此时将一对括号丢弃;
6)重复步骤2至5,直到表达式最右边;
7)将s1中剩余的运算符依次弹出并压入栈s2;
8)依次弹出栈s2中的元素并输出,结果逆序即为中缀表达式对应的后缀表达式。
代码:
public class PolandNotation {
public static void main(String[] args) {
String expression = "1+((2+3)*4)-5"; // 后缀表达式:1 2 3 + 4 * + 5 -
List<String> list = infixExpressionList(expression);
List<String> result = parseSuffixExpreesionList(list);
}
public static List<String> parseSuffixExpreesionList(List<String> list) {
Stack<String> s1 = new Stack<>(); // 运算符栈
List<String> s2 = new ArrayList<>(); // 存储中间结果的栈
for (String item : list) {
if (item.matches("\\d+")) {
s2.add(item);
} else if (item.equals("(")) {
s1.push(item);
} else if (item.equals(")")) {
while (!s1.peek().equals("(")) {
s2.add(s1.pop());
}
s1.pop(); // 弹栈 (
} else {
while (!s1.isEmpty() && Operation.getValue(s1.peek()) >= Operation.getValue(item)) {
s2.add(s1.pop());
}
s1.add(item);
}
}
while (!s1.isEmpty()) {
s2.add(s1.pop());
}
return s2;
}
private static List<String> infixExpressionList(String s) {
ArrayList<String> list = new ArrayList<>();
int i = 0;
String str;
char c;
do {
c = s.charAt(i);
if (c < '0' || c > '9') {
list.add("" + c);
i++;
} else {
str = "";
while (i < s.length() && (c = s.charAt(i)) >= '0' && c <= '9') {
str += c;
i++;
}
list.add(str);
}
} while (i < s.length());
return list;
}
}
class Operation {
private static int ADD = 1;
private static int SUB = 1;
private static int MUL = 1;
private static int DIV = 1;
public static int getValue(String operation) {
int result = 0;
switch (operation) {
case "+":
result = ADD;
break;
case "-":
result = SUB;
break;
case "*":
result = MUL;
break;
case "/":
result = DIV;
break;
default:
System.out.println("不存在该运算符");
break;
}
return result;
}
}链表结构的队列
public class SingleLinkListDemo {
public static void main(String[] args) {
HeroNode hero1 = new HeroNode(1, "宋江", "及时雨");
HeroNode hero2 = new HeroNode(2, "卢俊义", "玉麒麟");
HeroNode hero3 = new HeroNode(3, "吴用", "智多星");
SingleLinkList singleLinkList = new SingleLinkList();
singleLinkList.add(hero3);
singleLinkList.add(hero2);
singleLinkList.add(hero1);
// singleLinkList.add(hero3);
// HeroNode newHero = new HeroNode(3, "张三", "法外狂徒");
// singleLinkList.update(newHero);
HeroNode delHero1 = new HeroNode(1, "", "");
singleLinkList.del(delHero1);
singleLinkList.reverse();
singleLinkList.list();
}
}
class SingleLinkList {
private HeroNode headNode = new HeroNode(0, "", "");
// 非递归反转
public void reverse3() {
if (headNode.getNext() == null || headNode.getNext().getNext() == null) {
return;
}
HeroNode nextNode1, nextNode2, nextNode3;
nextNode1 = headNode.getNext();
nextNode2 = nextNode1.getNext();
nextNode3 = nextNode2.getNext();
nextNode2.setNext(nextNode1);
nextNode1.setNext(null);
while (nextNode3 != null) {
nextNode1 = nextNode2;
nextNode2 = nextNode3;
nextNode3 = nextNode3.getNext();
nextNode2.setNext(nextNode1);
}
headNode.setNext(nextNode2);
}
// 递归反转
public void reverse() {
HeroNode nextNode = headNode.getNext();
headNode.setNext(reverse2(headNode.getNext()));
nextNode.setNext(null);
}
private HeroNode reverse2(HeroNode heroNode) {
if (heroNode.getNext() != null) {
HeroNode lastNode = reverse2(heroNode.getNext());
heroNode.getNext().setNext(heroNode);
return lastNode;
}
return heroNode;
}
public void del(HeroNode delHeroNode) {
if (headNode.getNext() == null) {
System.out.println("链表为空");
return;
}
HeroNode preNode, nextNode;
preNode = headNode;
nextNode = headNode.getNext();
while (nextNode != null) {
if (nextNode.getNo() == delHeroNode.getNo()) {
preNode.setNext(nextNode.getNext());
// nextNode.setNext(null);
return;
}
preNode = nextNode;
nextNode = nextNode.getNext();
}
System.out.println("删除编号= " + delHeroNode.getNo() + " 的元素没有找到");
}
public void update(HeroNode newHeroNode) {
if (headNode.getNext() == null) {
System.out.println("链表为空");
return;
}
HeroNode preNode, nextNode;
preNode = headNode;
nextNode = headNode.getNext();
while (nextNode != null) {
if (nextNode.getNo() == newHeroNode.getNo()) {
newHeroNode.setNext(nextNode.getNext());
preNode.setNext(newHeroNode);
return;
}
preNode = nextNode;
nextNode = nextNode.getNext();
}
System.out.println("编号= " + newHeroNode.getNo() + " 的元素没有找到");
}
public void add(HeroNode heroNode) {
HeroNode nextNode, preNode;
preNode = headNode;
nextNode = headNode.getNext();
// 头插法
if (nextNode == null) {
headNode.setNext(heroNode);
heroNode.setNext(null);
return;
}
// 中插法
while (nextNode != null) {
if (heroNode.getNo() < nextNode.getNo()) {
preNode.setNext(heroNode);
heroNode.setNext(nextNode);
return;
}
// 相同的数据不能进行插入
if (heroNode.getNo() == nextNode.getNo()) {
System.out.println("编号=" + heroNode.getNo() + " 已存在,不能添加");
return;
}
preNode = nextNode;
nextNode = nextNode.getNext();
}
// 尾插法
preNode.setNext(heroNode);
heroNode.setNext(null);
}
public void list() {
HeroNode tmpNode = headNode.getNext();
if (tmpNode == null) {
System.out.println("链表为空");
return;
}
while (tmpNode != null) {
System.out.println("node= " + tmpNode + " -->");
tmpNode = tmpNode.getNext();
}
}
}
@Data
class HeroNode {
private int no;
private String name;
private String nickName;
private HeroNode next;
public HeroNode(int hNo, String hName, String hNickName) {
this.no = hNo;
this.name = hName;
this.nickName = hNickName;
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return "HeroNode{" +
"no=" + no +
", name='" + name + '\'' +
", nickName='" + nickName + '\'' +
'}';
}
}
约瑟夫环问题
public class Josephu {
public static void main(String[] args) {
CircleSingleLinkedList list = new CircleSingleLinkedList();
list.addBoy(5);
list.countBoy(1, 2, 5);
// list.showBoy();
}
}
class CircleSingleLinkedList {
private Boy first = null;
public void addBoy(int nums) {
if (nums < 2) {
System.out.println("nums的值不正确");
return;
}
Boy curBoy = null;
for (int i = 0; i < nums; i++) {
Boy boy = new Boy(i + 1);
if (i == 0) {
first = boy;
first.setNext(first);
curBoy = first;
} else {
curBoy.setNext(boy);
boy.setNext(first);
curBoy = boy;
}
}
}
public void showBoy() {
if (first == null) {
System.out.println("链表为空");
return;
}
Boy curBoy = first;
do {
System.out.println("编号= " + curBoy.getNo() + " -->");
curBoy = curBoy.getNext();
} while (curBoy != first);
}
/**
* @param startNo 从第几个开始
* @param countNum 数几下
* @param nums 最初有多少个小孩
*/
public void countBoy(int startNo, int countNum, int nums) {
if (first == null || startNo < 1 || startNo > nums) {
System.out.println("参数输入有误,请重新输入");
return;
}
Boy helper = first;
while (helper.getNext() != first) {
helper = helper.getNext();
}
for (int i = 0; i < startNo - 1; i++) {
first = first.getNext();
helper = helper.getNext();
}
while (helper != first) {
for (int i = 0; i < countNum - 1; i++) {
first = first.getNext();
helper = helper.getNext();
}
System.out.println("小孩 " + first.getNo() + " 出圈");
first = first.getNext();
helper.setNext(first);
// nums--;
}
System.out.println("最后留在圈中的小孩编号 " + first.getNo());
}
}
class Boy {
private int no;
private Boy next;
public Boy(int no) {
this.no = no;
}
//#region get|set
public int getNo() {
return no;
}
public void setNo(int no) {
this.no = no;
}
public Boy getNext() {
return next;
}
public void setNext(Boy next) {
this.next = next;
}
//#endregion
}
非线性结构
常见的非线性结构有:二维数组、多维数组、广义表、树结构、图结构。
图结构
递归解决迷宫问题
public class MiGong {
public static void main(String[] args) {
int[][] map = new int[8][7]; // 1 墙 0 未走 2 已走
for (int i = 0; i < 7; i++) {
map[0][i] = 1;
map[7][i] = 1;
map[i][0] = 1;
map[i][6] = 1;
}
map[3][1] = 1;
map[3][2] = 1;
setWay(map, 1, 1);
}
public static boolean setWay(int[][] map, int i, int j) {
if (map[6][5] == 2) {
return true;
} else {
if (map[i][j] == 0) {
map[i][j] = 2;
if (setWay(map, i + 1, j)) { // 上
return true;
} else if (setWay(map, i, j + 1)) { // 又
return true;
} else if (setWay(map, i - 1, j)) { // 下
return true;
} else if (setWay(map, i, j - 1)) { // 左
return true;
} else {
map[i][j] = 3; // 已走未通过
return false;
}
} else {
return false; // 值可能是 1、2、3
}
}
}
}
递归解决八皇后问题
public class Queue8 {
int max = 8;
int[] array = new int[max];
/**
* 有几种解法
**/
int count = 0;
// int judgeCount=0;
public static void main(String[] args) {
Queue8 queue8 = new Queue8();
queue8.check(0);
// System.out.println("解法count=" + queue8.count + "种");
}
/**
* 放置第n个皇后
*
* @param n
*/
private void check(int n) {
if (n == max) {
print();
return;
}
for (int i = 0; i < max; i++) {
array[n] = i;
if (judge(n)) { // 不冲突
check(n + 1);
}
}
}
/**
* 是否与之前的皇后冲突
*
* @param n 第n个皇后,从0开始
* @return
*/
private boolean judge(int n) {
// judgeCount++;
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
if (array[i] == array[n] || Math.abs(n - i) == Math.abs(array[i] - array[n])) { // 同列 同斜线
return false;
}
}
return true;
}
private void print() {
for (int i = 0; i < array.length; i++) {
System.out.print(array[i] + " ");
}
System.out.println();
count++;
}
}
树结构
数据结构和算法——树结构-CSDN博客
增强的顺序结构
哈希表
是数组加链表的数据结构,用到了拉链法。
实例问题:
有一个公司,当有新员工来报道时,要求将该员工的信息加入(id,性别,年龄,住址...),当输入该员工的id时,要求查找到该员工的所有信息。
public class HashTableDemo {
public static void main(String[] args) {
HashTable hashTable = new HashTable(7);
String key = "";
Scanner scanner = new Scanner(System.in);
boolean loop = true;
while (loop) {
System.out.println("add:添加雇员");
System.out.println("list:显示雇员");
System.out.println("find:查找雇员");
System.out.println("del:删除雇员");
System.out.println("exit:退出系统");
key = scanner.nextLine();
switch (key) {
case "a":
System.out.println("输入id:");
int id = scanner.nextInt();
System.out.println("输入名字:");
String name = scanner.next();
Emp emp = new Emp(id, name);
hashTable.add(emp);
continue;
case "l":
hashTable.list();
break;
case "d":
System.out.println("输入id:");
id = scanner.nextInt();
hashTable.delEmpById(id);
break;
case "f":
System.out.println("输入id:");
id = scanner.nextInt();
emp = hashTable.findEmpById(id);
if (emp == null) {
System.out.println("该雇员不存在");
} else {
System.out.println(emp);
}
break;
case "e":
loop = false;
break;
default:
loop = true;
break;
}
}
}
}
class Emp {
public int id;
public String name;
public Emp next;
public Emp(int id, String name) {
this.id = id;
this.name = name;
this.next = next;
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return "Emp{" +
"id=" + id +
", name='" + name + '\'' +
'}';
}
}
class EmpLinkedList {
private Emp head;
public EmpLinkedList(Emp head) {
this.head = head;
}
public void add(Emp emp) {
if (head == null) {
head = emp;
} else {
Emp curEmp = head;
while (curEmp.next != null) {
curEmp = curEmp.next;
}
curEmp.next = emp;
}
}
public void list() {
if (head == null) {
System.out.println("当前链表为空");
return;
}
System.out.println("当前链表的信息为:");
Emp curEmp = head;
while (curEmp != null) {
System.out.println("emp= " + curEmp);
curEmp = curEmp.next;
}
}
public Emp findEmpById(int id) {
Emp curEmp = head;
while (curEmp != null) {
if (curEmp.id == id) {
return curEmp;
}
curEmp = curEmp.next;
}
return null;
}
public void delEmpById(int id) {
if (head == null) {
System.out.println("该雇员不存在");
return;
}
if (head.id == id) {
head = null;
return;
}
Emp curEmp = head;
while (curEmp.next != null) {
if (curEmp.next.id == id) {
curEmp.next = curEmp.next.next;
System.out.println("删除雇员成功");
return;
}
curEmp = curEmp.next;
}
System.out.println("该雇员不存在");
}
}
class HashTable {
private EmpLinkedList[] empListedListArray;
private int size;
public HashTable(int size) {
this.size = size;
this.empListedListArray = new EmpLinkedList[this.size];
}
public void add(Emp emp) {
// 根据id得到下标
int index = hashFun(emp.id);
if (empListedListArray[index] == null) {
EmpLinkedList empLinkedList = new EmpLinkedList(emp);
empListedListArray[index] = empLinkedList;
} else {
empListedListArray[index].add(emp);
}
}
public int hashFun(int id) {
return id % this.size;
}
public void list() {
for (int i = 0; i < this.size; i++) {
EmpLinkedList empLinkedList = empListedListArray[i];
if (empLinkedList != null) {
empLinkedList.list();
System.out.println("----------------");
}
}
}
public Emp findEmpById(int id) {
int index = hashFun(id);
if (empListedListArray[index] == null) {
return null;
}
Emp emp = empListedListArray[index].findEmpById(id);
return emp;
}
public void delEmpById(int id) {
int index = hashFun(id);
if (empListedListArray[index] == null) {
System.out.println("该雇员不存在");
return;
}
empListedListArray[index].delEmpById(id);
}
}数组加二叉树的结构。文章来源:https://www.toymoban.com/news/detail-728660.html
参考教程视频:【尚硅谷】数据结构与算法(Java数据结构与算法)_哔哩哔哩_bilibili文章来源地址https://www.toymoban.com/news/detail-728660.html
到了这里,关于数据结构和算法——数据结构的文章就介绍完了。如果您还想了解更多内容,请在右上角搜索TOY模板网以前的文章或继续浏览下面的相关文章,希望大家以后多多支持TOY模板网!