王道数据结构强化课——【“栈、队列”的应用】代码,持续更新
文章来源地址https://www.toymoban.com/news/detail-728857.html
链式存储栈(单链表实现),并基于上述定义,栈顶在链头,实现“出栈、入栈、判空、判满”四个基本操作
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
// 定义链表节点
struct Node {
int data;
struct Node* next;
};
// 定义栈结构
struct Stack {
struct Node* top; // 栈顶指针
};
// 初始化栈
void initStack(struct Stack* stack) {
stack->top = NULL;
}
// 入栈操作
void push(struct Stack* stack, int value) {
struct Node* newNode = (struct Node*)malloc(sizeof(struct Node));
if (newNode == NULL) {
printf("内存分配失败,无法执行入栈操作\n");
return;
}
newNode->data = value;
newNode->next = stack->top;
stack->top = newNode;
}
// 出栈操作
int pop(struct Stack* stack) {
if (stack->top == NULL) {
printf("栈为空,无法执行出栈操作\n");
return -1; // 返回一个错误值
}
struct Node* temp = stack->top;
int poppedValue = temp->data;
stack->top = temp->next;
free(temp);
return poppedValue;
}
// 判空操作
int isEmpty(struct Stack* stack) {
return (stack->top == NULL);
}
// 判满操作(对于链式存储的栈,通常不会满,所以返回0表示不满)
int isFull(struct Stack* stack) {
return 0;
}
// 释放栈内存
void freeStack(struct Stack* stack) {
while (stack->top != NULL) {
struct Node* temp = stack->top;
stack->top = temp->next;
free(temp);
}
}
int main() {
struct Stack stack;
initStack(&stack);
// 入栈操作
push(&stack, 1);
push(&stack, 2);
push(&stack, 3);
// 出栈操作
printf("出栈操作: %d\n", pop(&stack));
// 判空操作
printf("栈是否为空: %s\n", isEmpty(&stack) ? "是" : "否");
// 判满操作
printf("栈是否满: %s\n", isFull(&stack) ? "是" : "否");
// 释放栈内存
freeStack(&stack);
return 0;
}
链式存储栈(双向链表实现)
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
// 定义链表节点
struct Node {
int data;
struct Node* next;
struct Node* prev;
};
// 定义栈结构
struct Stack {
struct Node* top; // 栈顶指针,链尾
};
// 初始化栈
void initStack(struct Stack* stack) {
stack->top = NULL;
}
// 入栈操作
void push(struct Stack* stack, int value) {
struct Node* newNode = (struct Node*)malloc(sizeof(struct Node));
if (newNode == NULL) {
printf("内存分配失败,无法执行入栈操作\n");
return;
}
newNode->data = value;
newNode->next = NULL;
if (stack->top == NULL) {
newNode->prev = NULL;
stack->top = newNode;
} else {
newNode->prev = stack->top;
stack->top->next = newNode;
stack->top = newNode;
}
}
// 出栈操作
int pop(struct Stack* stack) {
if (stack->top == NULL) {
printf("栈为空,无法执行出栈操作\n");
return -1; // 返回一个错误值
}
struct Node* temp = stack->top;
int poppedValue = temp->data;
if (stack->top->prev != NULL) {
stack->top = stack->top->prev;
stack->top->next = NULL;
} else {
stack->top = NULL;
}
free(temp);
return poppedValue;
}
// 判空操作
int isEmpty(struct Stack* stack) {
return (stack->top == NULL);
}
// 判满操作(对于链式存储的栈,通常不会满,所以返回0表示不满)
int isFull(struct Stack* stack) {
return 0;
}
// 释放栈内存
void freeStack(struct Stack* stack) {
while (stack->top != NULL) {
struct Node* temp = stack->top;
stack->top = temp->prev;
free(temp);
}
}
int main() {
struct Stack stack;
initStack(&stack);
// 入栈操作
push(&stack, 1);
push(&stack, 2);
push(&stack, 3);
// 出栈操作
printf("出栈操作: %d\n", pop(&stack));
// 判空操作
printf("栈是否为空: %s\n", isEmpty(&stack) ? "是" : "否");
// 判满操作
printf("栈是否满: %s\n", isFull(&stack) ? "是" : "否");
// 释放栈内存
freeStack(&stack);
return 0;
}
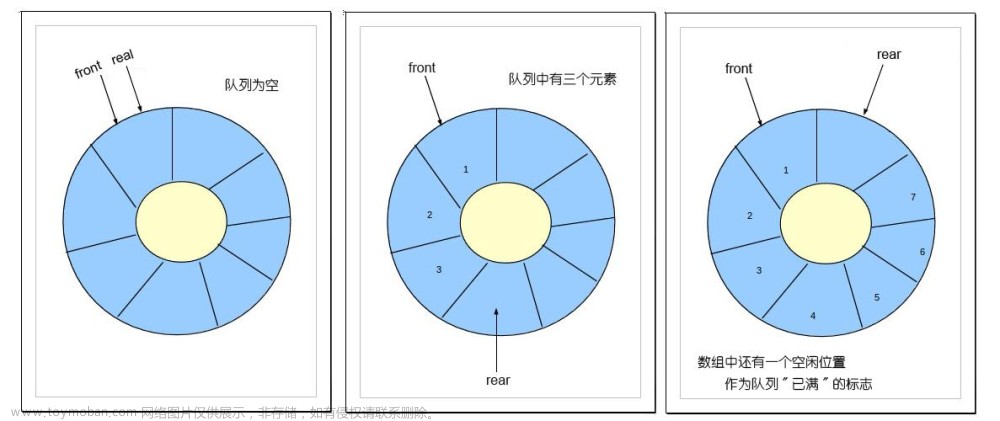
顺序存储的队列(数组实现)
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#define MAX_QUEUE_SIZE 10 // 队列的最大容量
// 定义队列结构
struct Queue {
int front, rear; // 前后指针
int data[MAX_QUEUE_SIZE];
};
// 初始化队列
void initQueue(struct Queue* queue) {
queue->front = -1;
queue->rear = -1;
}
// 判空操作
int isEmpty(struct Queue* queue) {
return (queue->front == -1);
}
// 判满操作
int isFull(struct Queue* queue) {
return ((queue->rear + 1) % MAX_QUEUE_SIZE == queue->front);
}
// 入队操作
void enqueue(struct Queue* queue, int value) {
if (isFull(queue)) {
printf("队列已满,无法执行入队操作\n");
return;
}
if (isEmpty(queue)) {
queue->front = 0;
}
queue->rear = (queue->rear + 1) % MAX_QUEUE_SIZE;
queue->data[queue->rear] = value;
}
// 出队操作
int dequeue(struct Queue* queue) {
if (isEmpty(queue)) {
printf("队列为空,无法执行出队操作\n");
return -1; // 返回一个错误值
}
int dequeuedValue = queue->data[queue->front];
if (queue->front == queue->rear) {
// 队列中只有一个元素,出队后队列为空
queue->front = -1;
queue->rear = -1;
} else {
queue->front = (queue->front + 1) % MAX_QUEUE_SIZE;
}
return dequeuedValue;
}
int main() {
struct Queue queue;
initQueue(&queue);
// 入队操作
enqueue(&queue, 1);
enqueue(&queue, 2);
enqueue(&queue, 3);
// 出队操作
printf("出队操作: %d\n", dequeue(&queue));
// 判空操作
printf("队列是否为空: %s\n", isEmpty(&queue) ? "是" : "否");
// 判满操作
printf("队列是否满: %s\n", isFull(&queue) ? "是" : "否");
return 0;
}
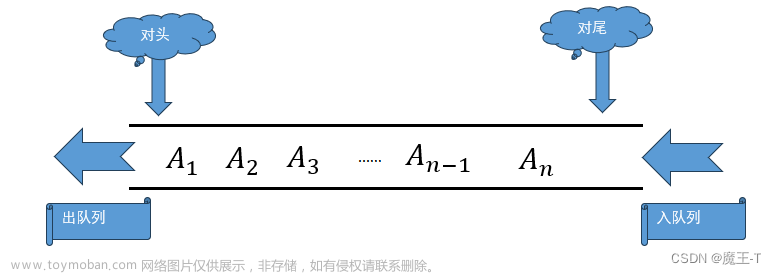
链式存储队列(单链表实现)
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
// 定义链表节点
struct Node {
int data;
struct Node* next;
};
// 定义队列结构
struct Queue {
struct Node* front; // 队列前端
struct Node* rear; // 队列后端
};
// 初始化队列
void initQueue(struct Queue* queue) {
queue->front = NULL;
queue->rear = NULL;
}
// 判空操作
int isEmpty(struct Queue* queue) {
return (queue->front == NULL);
}
// 判满操作(对于链式存储的队列,通常不会满,所以返回0表示不满)
int isFull(struct Queue* queue) {
return 0;
}
// 入队操作
void enqueue(struct Queue* queue, int value) {
struct Node* newNode = (struct Node*)malloc(sizeof(struct Node));
if (newNode == NULL) {
printf("内存分配失败,无法执行入队操作\n");
return;
}
newNode->data = value;
newNode->next = NULL;
if (isEmpty(queue)) {
queue->front = newNode;
} else {
queue->rear->next = newNode;
}
queue->rear = newNode;
}
// 出队操作
int dequeue(struct Queue* queue) {
if (isEmpty(queue)) {
printf("队列为空,无法执行出队操作\n");
return -1; // 返回一个错误值
}
struct Node* temp = queue->front;
int dequeuedValue = temp->data;
queue->front = temp->next;
free(temp);
if (queue->front == NULL) {
// 如果出队后队列为空,需要更新rear指针
queue->rear = NULL;
}
return dequeuedValue;
}
// 释放队列内存
void freeQueue(struct Queue* queue) {
while (queue->front != NULL) {
struct Node* temp = queue->front;
queue->front = temp->next;
free(temp);
}
}
int main() {
struct Queue queue;
initQueue(&queue);
// 入队操作
enqueue(&queue, 1);
enqueue(&queue, 2);
enqueue(&queue, 3);
// 出队操作
printf("出队操作: %d\n", dequeue(&queue));
// 判空操作
printf("队列是否为空: %s\n", isEmpty(&queue) ? "是" : "否");
// 判满操作
printf("队列是否满: %s\n", isFull(&queue) ? "是" : "否");
// 释放队列内存
freeQueue(&queue);
return 0;
}
文章来源:https://www.toymoban.com/news/detail-728857.html
到了这里,关于【“栈、队列”的应用】408数据结构代码的文章就介绍完了。如果您还想了解更多内容,请在右上角搜索TOY模板网以前的文章或继续浏览下面的相关文章,希望大家以后多多支持TOY模板网!