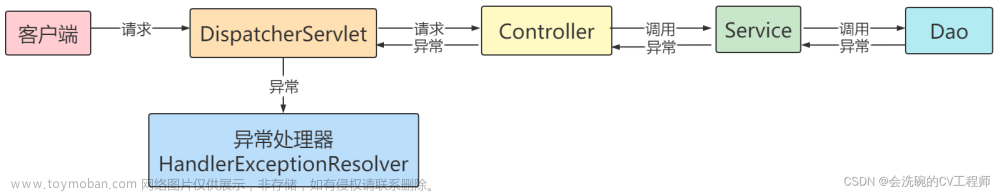
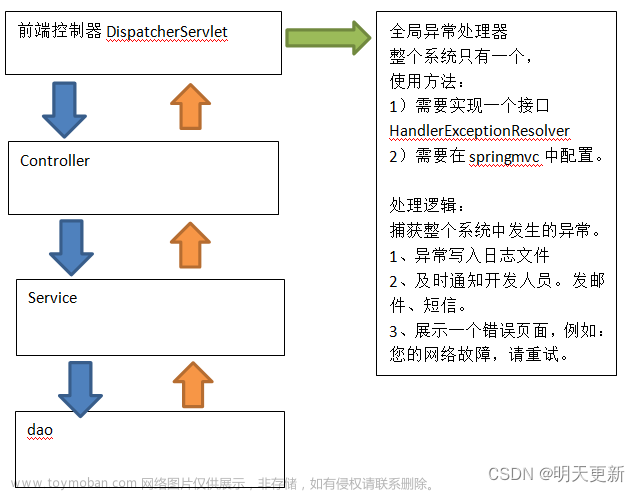
一、SpringMVC执行流程
今天这里叙述的全局异常处理是SpringBoot在Servlet场景下的处理机制,重点是
Servlet模式,当然WEBFLUX今天不做过多描述,SpringBoot2.2.x以后引入的一种响应式web开发,在SpringBoot启动类中可以看到:
SpringApplication.java
=> new SpringApplication(ResourceLoader resourceLoader, Class<?>... primarySources)
=> WebApplicationType.deduceFromClasspath();
deduceFromClasspath方法: 既然是SringBoot的webServlet场景,自然不可以放过的就是
既然是SringBoot的webServlet场景,自然不可以放过的就是DispatchServlet一整个执行流程,那就从面试书籍中cp一张 当然小编也有历史文档可以参考下:SpringMVC执行流程
当然小编也有历史文档可以参考下:SpringMVC执行流程 今天的异常处理,用草图画了下,就是红框框这里:
今天的异常处理,用草图画了下,就是红框框这里: 这里SpringBoot究竟如何设计了异常处理呢,走进源码,探索真相!
这里SpringBoot究竟如何设计了异常处理呢,走进源码,探索真相!
二、SpringBoot源码跟踪
说到DispatchServlet的请求处理,那就直接找到核心方法:doDispatch(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response) ;点进源码,不难发现寻找Handler和执行Handler这整整一大块,用了复合try–catch进行包裹:
try {
processedRequest = checkMultipart(request);
multipartRequestParsed = (processedRequest != request);
mappedHandler = getHandler(processedRequest);
if (mappedHandler == null) {
noHandlerFound(processedRequest, response);
return;
}
HandlerAdapter ha = getHandlerAdapter(mappedHandler.getHandler());
......
mv = ha.handle(processedRequest, response, mappedHandler.getHandler());
......
applyDefaultViewName(processedRequest, mv);
mappedHandler.applyPostHandle(processedRequest, response, mv);
}
catch (Exception ex) {
dispatchException = ex;
}
catch (Throwable err) {
dispatchException = new NestedServletException("Handler dispatch failed", err);
}
processDispatchResult(processedRequest, response, mappedHandler, mv, dispatchException);
在try的结束处,我们可以看到,小异常到大异常,源码中并没有打印堆栈,而是封装成dispatchException ,最后交给processDispatchResult方法去处理请求分发的结果
而processDispatchResult方法内部,则是对异常进行了解析,也叫resolveException:
if (exception != null) {
if (exception instanceof ModelAndViewDefiningException) {
logger.debug("ModelAndViewDefiningException encountered", exception);
mv = ((ModelAndViewDefiningException) exception).getModelAndView();
}
else {
Object handler = (mappedHandler != null ? mappedHandler.getHandler() : null);
mv = processHandlerException(request, response, handler, exception);
errorView = (mv != null);
}
}
再次进入非视图异常的处理方法processHandlerException中,我们看到了多个异常处理器去循环处理异常,直到循环结束,如果返回值不为NULL,说明该异常能够被解析并且处理完毕返回ModelAndView
if (this.handlerExceptionResolvers != null) {
for (HandlerExceptionResolver resolver : this.handlerExceptionResolvers) {
exMv = resolver.resolveException(request, response, handler, ex);
if (exMv != null) {
break;
}
}
}
DispatchServlet类初始化时从容器中获取handlerExceptionResolvers ,该类的接口表示Spring容器中处理异常的处理器类,根据debug可以看到,Spring容器中含有两个解析器类,一个是默认的兜底的异常解析器类,另一个是HandlerExceptionResolverComposite,内部维护着spring容器的异常解析器列表 那么
那么HandlerExceptionResolverComposite处理器类是从哪里来的,接着我们跳转到WebMvcConfigurationSupport类,观察其诞生之地
@Bean
public HandlerExceptionResolver handlerExceptionResolver(
@Qualifier("mvcContentNegotiationManager") ContentNegotiationManager contentNegotiationManager) {
List<HandlerExceptionResolver> exceptionResolvers = new ArrayList<>();
configureHandlerExceptionResolvers(exceptionResolvers);
if (exceptionResolvers.isEmpty()) {
addDefaultHandlerExceptionResolvers(exceptionResolvers, contentNegotiationManager);
}
extendHandlerExceptionResolvers(exceptionResolvers);
HandlerExceptionResolverComposite composite = new HandlerExceptionResolverComposite();
composite.setOrder(0);
composite.setExceptionResolvers(exceptionResolvers);
return composite;
}
这里有两个地方需要关注,首先是addDefaultHandlerExceptionResolvers,就是spring会默认添加三个异常解析器,一个是ExceptionHandlerExceptionResolver,这个处理的是程序中注解了@ExceptionHandler的,第二个DefaultHandlerExceptionResolver,这个是处理一些通常的异常,具体可查看官方文档。第三个是较少用的ResponseStatusExceptionResolver
另一个要关注的是extendHandlerExceptionResolvers方法,这个是留给子类重写,扩展使用的。
此时我们大概知道HandlerExceptionResolverComposite类的resolveException方法可以解析异常,那么我们打个断点,放行程序到此处,再观察: 那么一切就变的似乎很合理了,HandlerExceptionResolverComposite内部维护着异常解析器列表,循环去解析,解析成功就返回,并且还看到了列表清单的第一个解析器就是
那么一切就变的似乎很合理了,HandlerExceptionResolverComposite内部维护着异常解析器列表,循环去解析,解析成功就返回,并且还看到了列表清单的第一个解析器就是ExceptionHandlerExceptionResolver,于是到ExceptionHandlerExceptionResolver类中打上断点观察
protected ModelAndView doResolveHandlerMethodException(HttpServletRequest request,
HttpServletResponse response, @Nullable HandlerMethod handlerMethod, Exception exception) {
ServletInvocableHandlerMethod exceptionHandlerMethod = getExceptionHandlerMethod(handlerMethod, exception);
if (exceptionHandlerMethod == null) {
return null;
}
if (this.argumentResolvers != null) {
exceptionHandlerMethod.setHandlerMethodArgumentResolvers(this.argumentResolvers);
}
if (this.returnValueHandlers != null) {
exceptionHandlerMethod.setHandlerMethodReturnValueHandlers(this.returnValueHandlers);
}
ServletWebRequest webRequest = new ServletWebRequest(request, response);
ModelAndViewContainer mavContainer = new ModelAndViewContainer();
ArrayList<Throwable> exceptions = new ArrayList<>();
try {
if (logger.isDebugEnabled()) {
logger.debug("Using @ExceptionHandler " + exceptionHandlerMethod);
}
// Expose causes as provided arguments as well
Throwable exToExpose = exception;
while (exToExpose != null) {
exceptions.add(exToExpose);
Throwable cause = exToExpose.getCause();
exToExpose = (cause != exToExpose ? cause : null);
}
Object[] arguments = new Object[exceptions.size() + 1];
exceptions.toArray(arguments); // efficient arraycopy call in ArrayList
arguments[arguments.length - 1] = handlerMethod;
exceptionHandlerMethod.invokeAndHandle(webRequest, mavContainer, arguments);
}
catch (Throwable invocationEx) {
// Any other than the original exception (or a cause) is unintended here,
// probably an accident (e.g. failed assertion or the like).
if (!exceptions.contains(invocationEx) && logger.isWarnEnabled()) {
logger.warn("Failure in @ExceptionHandler " + exceptionHandlerMethod, invocationEx);
}
// Continue with default processing of the original exception...
return null;
}
if (mavContainer.isRequestHandled()) {
return new ModelAndView();
}
观察这一句
exceptionHandlerMethod.setHandlerMethodReturnValueHandlers(this.returnValueHandlers);
顾名思义,设置了返回值的处理器
那我们看看ExceptionHandlerExceptionResolver初始化经历了些啥,首先实现了InitializingBean,那么就直接先看afterProperties方法(Bean生命周期执行的钩子函数)
initExceptionHandlerAdviceCache方法: 言简意赅就是获取所有标有
言简意赅就是获取所有标有@ControllerAdvice注解的类,并封装成ControllerAdviceBean,随后又去根据这些类创建ExceptionHandlerMethodResolver类,点击进去ExceptionHandlerMethodResolver的构造函数 addMapping方法:
addMapping方法:
现在真相几乎大告于天下,这里先引入SpringBoot的异常处理机制@ControllerAdvice+@ExceptionHandler;用起来很简单,在处理类上添加ControllerAdvice注解、在类中方法上添加ExceptionHandler注解并标注捕获的类,那么SpringBoot整个webServlet执行过程中产生的异常都会被这个异常捕获并且返回对应方法的返回值;
所以,我们后续处理无非就是从mapCache中寻找异常对应的方法,因为addMapping方法已经将异常全部封装成exception-Method的map集合形式;再一层层返回给dispatchServlet。
三、自定义优雅的全局异常处理脚手架starter
上述的源码跟踪下来,@ControllerAdvice+@ExceptionHandler模式是不是有一些鸡肋?完全可以定义一个全局的ExceptionHandler类,内部封装自定义异常,再配合EnableAutoConfiguration,达到脚手架starter封装的效果;这里我大概叙述一下思路
自定义异常
定义一个类实现RuntimeException类,同时考虑到国际化的问题,这里加入了枚举类BaseError,并且框架常见异常和业务异常进行分类注册

国际化引入
枚举异常基类默认实现I18n接口,并返回resources文件中定义异常文件的文件名
[外链图片转存失败,源站可能有防盗在这里插入!链机制,建描述](https://img-blog议将存csdnimg下cn/d84acd6585a248f29c1d52d1084bbfdf.png

封装基础异常
既然作为脚手架使用,那么系统中常见的异常我们可以封装一下了,我们封装到国际化的Bundle中 然后定义枚举专门去getClass
然后定义枚举专门去getClass
封装基础异常扫描器,并注册到ExceptionHandler中
这里用了reflections.getSubTypesOf方法返回类路径基础异常SysBaseEnum类及其子类实现,封装成集合遍历并抽取其中的枚举类,最终枚举集合将注册到exceptionHandler方法中进行捕获
 ## 自定义全局异常处理注解以及异常解析器
## 自定义全局异常处理注解以及异常解析器
@Target({ElementType.TYPE})
@Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME)
@Documented
@Configuration
@ResponseBody
public @interface SangExceptionAdvice {
}
这里模仿ExceptionHandlerResolver去继承它:
public class SangExceptionHandlerExceptionResolver extends ExceptionHandlerExceptionResolver implements ApplicationContextAware, InitializingBean
核心代码:封装自定义注解@SangExceptionAdvice成为SangExceptionAdviceBean,并重写doResolveHandlerMethodException方法
项目分享以及改进点
SangExceptionAdviceBean类封装时可以根据设定加入Predicate断言器,配合ConfigurationProperties实现路径匹配捕获异常、全路径异常捕获等等功能 改进点:reflections.getSubTypesOf方法反射获取异常基类时有些许不合理,后期慢慢调整,也欢迎大家指教文章来源:https://www.toymoban.com/news/detail-730223.html
改进点:reflections.getSubTypesOf方法反射获取异常基类时有些许不合理,后期慢慢调整,也欢迎大家指教文章来源:https://www.toymoban.com/news/detail-730223.html
代码半成品框架开源地址:gitee地址,欢迎大家fork!多沟通,一起学习,一起进步!
如果喜欢本篇文章,点个赞吧!文章来源地址https://www.toymoban.com/news/detail-730223.html
到了这里,关于SpringBoot全局异常处理源码的文章就介绍完了。如果您还想了解更多内容,请在右上角搜索TOY模板网以前的文章或继续浏览下面的相关文章,希望大家以后多多支持TOY模板网!