💐 🌸 🌷 🍀 🌹 🌻 🌺 🍁 🍃 🍂 🌿 🍄🍝 🍛 🍤
📃个人主页 :阿然成长日记 👈点击可跳转
📆 个人专栏: 🔹数据结构与算法🔹C语言进阶
🚩 不能则学,不知则问,耻于问人,决无长进
🍭 🍯 🍎 🍏 🍊 🍋 🍒 🍇 🍉 🍓 🍑 🍈 🍌 🍐 🍍
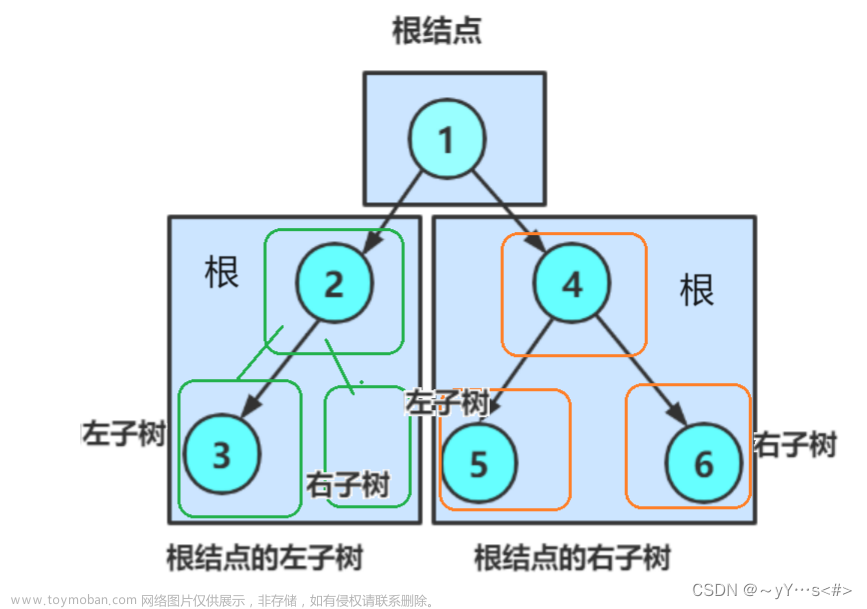
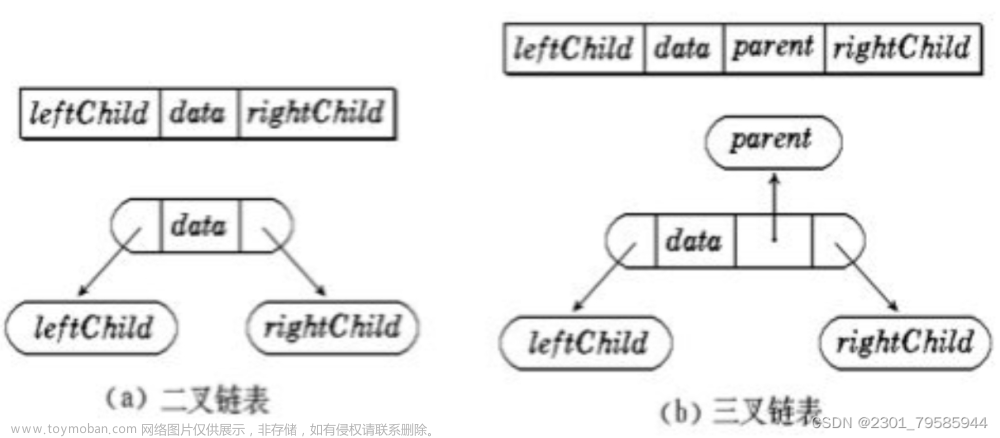
一、二叉数的结构体
每一个节点有
1.数据域_data;
2.指向左子树的指针:_left
3.指向右子树的执指针:_right
typedef char BTDataType;
typedef struct BinaryTreeNode
{
BTDataType _data;
struct BinaryTreeNode* _left;
struct BinaryTreeNode* _right;
}BTNode;
二、构建二叉树,供后续测试使用

三、二叉树销毁
// 二叉树销毁
void BinaryTreeDestory(BTNode* root)
{
if (root == NULL)
{
return;
}
BinaryTreeDestory(root->_left);
BinaryTreeDestory(root->_right);
free(root);
}
四、构建节点
//构建节点
BTNode* BuyNode(int x)
{
BTNode* node = (BTNode*)malloc(sizeof(BTNode));
if (node == NULL)
{
perror("malloc fail");
exit(-1);
}
node->_data = x;
node->_left = NULL;
node->_right = NULL;
return node;
}
五、二叉树的高度:
fmax函数的头文件:<math.h>
思路:每次选择左右子树中大的那一棵树,对其+1;
1.代码:
//树的高度
int TreeHeight(BTNode* root)
{
if (root == NULL)
return 0;
return fmax(TreeHeight(root->_left), TreeHeight(root->_right)) + 1;
}
2.测试结果:

二叉树节点个数
思路:如果当前节点为NULL;则返回0;如果不是NULL;则向左右子树递归并+1;
1.代码:
// 二叉树节点个数
int BinaryTreeSize(BTNode* root)
{
return root == NULL ? 0 : BinaryTreeSize(root->_left)
+ BinaryTreeSize(root->_right) + 1;
}
2.测试结果:

六、二叉树叶子节点个数
思路:
1.向下递归的条件是当前节点左或者右节点有一个为空,一个不为空。
2.当不满足下面的if语句时,就会return 左右两个节点,从而递归继续向下寻找叶子节点,
3.直到当前节点为空时,就停止返回0;或者找到叶子节点,返回1
1.代码:
// 二叉树叶子节点个数
int BinaryTreeLeafSize(BTNode* root)
{
//向下递归的条件是当前节点左或者右节点有一个为空,一个不为空。
//当不满足下面的if语句时,就会return 左右两个节点,从而递归继续向下寻找叶子节点,
//直到当前节点为空时,就停止返回0;或者找到叶子节点,返回1
if (root == NULL)
return 0;
if (root->_left == NULL && root->_right == NULL)
return 1;
return BinaryTreeLeafSize(root->_left)
+ BinaryTreeLeafSize(root->_right);
}
2.测试结果:

七、二叉树第k层节点个数
思路:
1.当找到第k==1,就返回1,意思是第k层个数+1;
2.当节点为空时,就结束向下递归,开始往回走。
3.如果不满足if条件,就继续向下递归。
1.代码:
// 二叉树第k层节点个数
int BinaryTreeLevelKSize(BTNode* root, int k)
{
//当找到第k==1,就返回1,意思是第k层个数+1;
//当节点为空时,就结束向下递归,开始往回走。
//如果不满足if条件,就继续向下递归。
if (root == NULL)
return 0;
if (k == 1)
return 1;
return BinaryTreeLevelKSize(root->_left, k - 1)
+ BinaryTreeLevelKSize(root->_right, k - 1);
}
2.测试结果:

八、二叉树查找值为x的节点
思路;
1.当root==NULL时,说明当前子树中没有没有找到,返回NULL
2.当root->_data==x时,就return 当前节点,停止向下递归,开始向上回。
3.如果不满足上面两个if条件,就向下递归左,再右节点,
4.如果root->_data == x成立,返回的就不是空值通过if判断,并返回tmp。
5.在一次递归中,如果没有找到等于x的节点,和root=NULL两个条件时,就返回NULL;
1.代码:
// 二叉树查找值为x的节点
BTNode* BinaryTreeFind(BTNode* root, BTDataType x)
{
//当root==NULL时,说明当前子树中没有没有找到,返回NULL
//当root->_data==x时,就return 当前节点,停止向下递归,开始向上回。
//如果不满足上面两个if条件,就向下递归左,再右节点,
//如果root->_data == x成立,返回的就不是空值通过if判断,并返回tmp。
//在一次递归中,如果没有找到等于x的节点,和root=NULL两个条件时,就返回NULL;
if (root == NULL)
return NULL;
if (root->_data == x)
return root;
BTNode* tmp = NULL;
tmp=BinaryTreeFind(root->_left, x);
if (tmp)
return tmp;
tmp = BinaryTreeFind(root->_right, x);
if (tmp)
return tmp;
return NULL;
}
2.测试结果:
查询二叉树中节点值=3的节点。 查询
查询
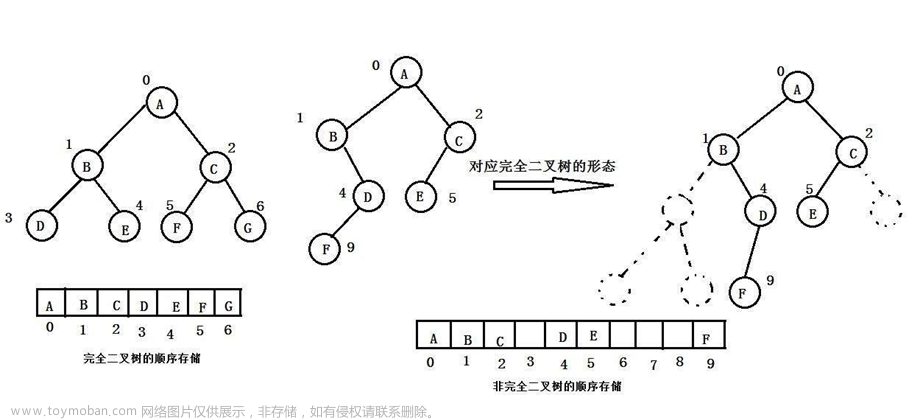
九、判断二叉树是否是完全二叉树
思路:
1.开始层序遍历,直到遇到NULL为止。
2.从遇到NULL的位置开始继续向下遍历,如果还能遇到非空节点,则说明不是完全二叉树。文章来源:https://www.toymoban.com/news/detail-732464.html
1.代码:
// 判断二叉树是否是完全二叉树
int BinaryTreeComplete(BTNode* root)
{
Que q;
QueueInit(&q);
//开始层序遍历,直到遇到NULL为止
if (root)
QueuePush(&q,root);
while (!QueueEmpty(&q))
{
BTNode* tmp = QueueFront(&q);
if (tmp == NULL)
return false;
QueuePush(&q,tmp->_left);
QueuePush(&q,tmp->_right);
QueuePop(&q);
}
//从遇到NULL的位置开始继续向下遍历,如果还能遇到非空节点,则说明不是完全二叉树。
while (!QueueEmpty(&q))
{
BTNode* tmp = QueueFront(&q);
QueuePop(&q);
if (tmp != NULL)
{
QueueDestroy(&q);
return false;
}
}
QueueDestroy(&q);
return true;
}
2.测试结果:
 文章来源地址https://www.toymoban.com/news/detail-732464.html
文章来源地址https://www.toymoban.com/news/detail-732464.html
十、补充:队列代码
Queue.h
#define _CRT_SECURE_NO_WARNINGS 1
#pragma once
#include<stdio.h>
#include<stdlib.h>
#include<assert.h>
#include<stdbool.h>
typedef struct BinaryTreeNode* QDataType;
typedef struct QueueNode
{
struct QueueNode* next;
QDataType data;
}QNode;
typedef struct Queue
{
QNode* head;
QNode* tail;
int size;
}Que;
void QueueInit(Que* pq);
void QueueDestroy(Que* pq);
void QueuePush(Que* pq, QDataType x);
void QueuePop(Que* pq);
QDataType QueueFront(Que* pq);
QDataType QueueBack(Que* pq);
bool QueueEmpty(Que* pq);
int QueueSize(Que* pq);
Queue.c
#include "Queue.h"
void QueueInit(Que* pq)
{
assert(pq);
pq->head = pq->tail = NULL;
pq->size = 0;
}
void QueueDestroy(Que* pq)
{
assert(pq);
QNode* cur = pq->head;
while (cur)
{
QNode* next = cur->next;
free(cur);
cur = next;
}
pq->head = pq->tail = NULL;
pq->size = 0;
}
void QueuePush(Que* pq, QDataType x)
{
assert(pq);
QNode* newnode = (QNode*)malloc(sizeof(QNode));
if (newnode == NULL)
{
perror("malloc fail");
exit(-1);
}
newnode->data = x;
newnode->next = NULL;
if (pq->tail == NULL)
{
pq->head = pq->tail = newnode;
}
else
{
pq->tail->next = newnode;
pq->tail = newnode;
}
pq->size++;
}
void QueuePop(Que* pq)
{
assert(pq);
assert(!QueueEmpty(pq));
if (pq->head->next == NULL)
{
free(pq->head);
pq->head = pq->tail = NULL;
}
else
{
QNode* next = pq->head->next;
free(pq->head);
pq->head = next;
}
pq->size--;
}
QDataType QueueFront(Que* pq)
{
assert(pq);
assert(!QueueEmpty(pq));
return pq->head->data;
}
QDataType QueueBack(Que* pq)
{
assert(pq);
assert(!QueueEmpty(pq));
return pq->tail->data;
}
bool QueueEmpty(Que* pq)
{
assert(pq);
return pq->head == NULL;
}
int QueueSize(Que* pq)
{
assert(pq);
return pq->size;
}
到了这里,关于【数据结构】二叉树的节点数,叶子数,第K层节点数,高度,查找x节点,判断是否为完全二叉树等方法的文章就介绍完了。如果您还想了解更多内容,请在右上角搜索TOY模板网以前的文章或继续浏览下面的相关文章,希望大家以后多多支持TOY模板网!