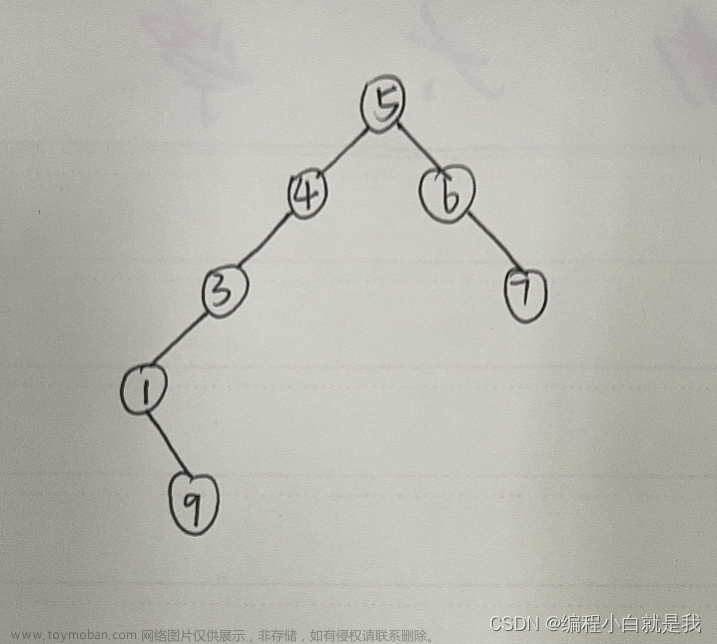
闲来无事,回顾一下以前的学过的数据结构知识,面试也可以用到!!!

1、创建一颗二叉树
typedef int ElemType;
typedef struct BiNode {
ElemType data;
BiNode* lchild;
BiNode* rchild;
}BiNode, * BiTree;
//构建二叉树
BiNode* Create(BiNode* bt) {
static int i = 0;
char ch;
//string str = "AB#D##C##";
//string str = "124##56##7##3##";
string str = "ABD#G##E##CF###";
ch = str[i++];
if (ch == '#')bt = NULL;//建立一棵空树
else {
bt = (BiTree)malloc(sizeof(BiNode)); bt->data = ch;//生成一个结点,数据域为ch
bt->lchild = Create(bt->lchild);//递归建立左子树
bt->rchild = Create(bt->rchild);//递归建立右子树
}
return bt;
}2、栈
#define MaxSize 100//定义栈中元素的最大个数
typedef struct {
BiTree data[MaxSize];//存放栈中元素
int top;//栈顶指针
}SqStack;
//(1)初始化
void InitStack(SqStack& S) {
S.top = -1;//初始化栈顶指针
//S.data[0] = NULL;
}
//(2)判栈空
bool IsEmpty(SqStack& S) {
if (S.top == -1) {//栈空
return true;
}
else {//不空
return false;
}
}
//(3)进栈
bool Push(SqStack& S, BiTree& p) {
if (S.top == MaxSize - 1) {//栈满,报错
return false;
}
S.data[++S.top] = p;//指针先加1,再加入栈
return true;
}
//(4)出栈
bool Pop(SqStack& S, BiTree& p) {
if (S.top == -1) {//栈空,报错
return false;
}
p = S.data[S.top--];//先出栈,指针再减1
return true;
}
//(5)读栈顶元素
bool GetTop(SqStack& S, BiTree& p) {
if (S.top == -1) {//栈空,报错
return false;
}
p = S.data[S.top];//先出栈,指针再减1
return true;
}3、非递归中序遍历
第一种:非递归中序遍历算法
void visit(int x) {
printf("%c ", x);
}
void InOrder(BiTree T) {
SqStack S;
InitStack(S);
BiNode* p, * r;
p = T;
r = NULL;
while (p || !IsEmpty(S)) {
if (p) {//一路向左
Push(S, p);
p = p->lchild;
}
else {
Pop(S, p);
visit(p->data);
p = p->rchild;//判断右孩子
}
}
}
第二种:非递归中序遍历算法
伪代码和算法详解:

void visit(int x) {
printf("%c ", x);
}
void InOrder(BiTree T) {
SqStack S;
InitStack(S);
BiNode* p, * r;
p = T;
r = NULL;
while (p || !IsEmpty(S)) {
while (p) {//一路向左
Push(S, p);
p = p->lchild;
}
if(!IsEmpty(S)) {
Pop(S, p);
visit(p->data);
p = p->rchild;//判断右孩子
}
}//while
}4.非递归中序遍历完整代码
#include<stdio.h>
#include<stdlib.h>
#include<iostream>
using namespace std;
typedef int ElemType;
typedef struct BiNode {
ElemType data;
BiNode* lchild;
BiNode* rchild;
}BiNode, * BiTree;
//构建二叉树
BiNode* Create(BiNode* bt) {
static int i = 0;
char ch;
//string str = "AB#D##C##";
//string str = "124##56##7##3##";
string str = "ABD#G##E##CF###";
ch = str[i++];
if (ch == '#')bt = NULL;//建立一棵空树
else {
bt = (BiTree)malloc(sizeof(BiNode)); bt->data = ch;//生成一个结点,数据域为ch
bt->lchild = Create(bt->lchild);//递归建立左子树
bt->rchild = Create(bt->rchild);//递归建立右子树
}
return bt;
}
#define MaxSize 100//定义栈中元素的最大个数
typedef struct {
BiTree data[MaxSize];//存放栈中元素
int top;//栈顶指针
}SqStack;
//(1)初始化
void InitStack(SqStack& S) {
S.top = -1;//初始化栈顶指针
//S.data[0] = NULL;
}
//(2)判栈空
bool IsEmpty(SqStack& S) {
if (S.top == -1) {//栈空
return true;
}
else {//不空
return false;
}
}
//(3)进栈
bool Push(SqStack& S, BiTree& p) {
if (S.top == MaxSize - 1) {//栈满,报错
return false;
}
S.data[++S.top] = p;//指针先加1,再加入栈
return true;
}
//(4)出栈
bool Pop(SqStack& S, BiTree& p) {
if (S.top == -1) {//栈空,报错
return false;
}
p = S.data[S.top--];//先出栈,指针再减1
return true;
}
//(5)读栈顶元素
bool GetTop(SqStack& S, BiTree& p) {
if (S.top == -1) {//栈空,报错
return false;
}
p = S.data[S.top];//先出栈,指针再减1
return true;
}
void visit(int x) {
printf("%c ", x);
}
void InOrder(BiTree T) {
SqStack S;
InitStack(S);
BiNode* p, * r;
p = T;
r = NULL;
while (p || !IsEmpty(S)) {
if (p) {//一路向左
Push(S, p);
p = p->lchild;
}
else {
Pop(S, p);
visit(p->data);
p = p->rchild;//判断右孩子
}
}//while
}
void DInOrder(BiTree T) {
if (T != NULL) {
DInOrder(T->lchild);//后序遍历左子树
visit(T->data);//访问根节点的数据域
DInOrder(T->rchild);//后序遍历右子树
}
}
int main() {
//创建一棵二叉树
BiTree T = (BiTree)malloc(sizeof(BiNode));//创建一颗二叉树
T = Create(T);
//递归先序遍历
printf("递归中序遍历 \n");
DInOrder(T);
printf("\n非递归中序遍历 \n");
//非递归后序遍历
InOrder(T);
}演示效果:




5.非递归先序遍历
第一种:非递归先序遍历
void visit(int x) {
printf("%c ", x);
}
void PreOrder(BiTree T) {
SqStack S;
InitStack(S);
BiNode* p, * r;
p = T;
r = NULL;
while (p || !IsEmpty(S)) {
if (p) {//一路向左
visit(p->data);//访问该结点
Push(S, p);
p = p->lchild;
}
else {
//GetTop(S, p);
Pop(S, p);//栈顶元素出栈
p = p->rchild;//向右寻找
}//else
}//while
}
第二种:非递归先序遍历

void visit(int x) {
printf("%c ", x);
}
void PreOrder(BiTree T) {
SqStack S;
InitStack(S);
BiNode* p, * r;
p = T;
r = NULL;
while (p || !IsEmpty(S)) {
while (p) {//一路向左
visit(p->data);//访问该结点
Push(S, p);
p = p->lchild;
}
if(!IsEmpty(S)) {
Pop(S, p);//栈顶元素出栈
p = p->rchild;//向右寻找
}
}
}演示效果:




6.非递归先序遍历完整代码
#include<stdio.h>
#include<stdlib.h>
#include<iostream>
using namespace std;
typedef int ElemType;
typedef struct BiNode {
ElemType data;
BiNode* lchild;
BiNode* rchild;
}BiNode, * BiTree;
//构建二叉树
BiNode* Create(BiNode* bt) {
static int i = 0;
char ch;
//string str = "AB#D##C##";
//string str = "124##56##7##3##";
string str = "ABD#G##E##CF###";
ch = str[i++];
if (ch == '#')bt = NULL;//建立一棵空树
else {
bt = (BiTree)malloc(sizeof(BiNode)); bt->data = ch;//生成一个结点,数据域为ch
bt->lchild = Create(bt->lchild);//递归建立左子树
bt->rchild = Create(bt->rchild);//递归建立右子树
}
return bt;
}
#define MaxSize 100//定义栈中元素的最大个数
typedef struct {
BiTree data[MaxSize];//存放栈中元素
int top;//栈顶指针
}SqStack;
//(1)初始化
void InitStack(SqStack& S) {
S.top = -1;//初始化栈顶指针
//S.data[0] = NULL;
}
//(2)判栈空
bool IsEmpty(SqStack& S) {
if (S.top == -1) {//栈空
return true;
}
else {//不空
return false;
}
}
//(3)进栈
bool Push(SqStack& S, BiTree& p) {
if (S.top == MaxSize - 1) {//栈满,报错
return false;
}
S.data[++S.top] = p;//指针先加1,再加入栈
return true;
}
//(4)出栈
bool Pop(SqStack& S, BiTree& p) {
if (S.top == -1) {//栈空,报错
return false;
}
p = S.data[S.top--];//先出栈,指针再减1
return true;
}
//(5)读栈顶元素
bool GetTop(SqStack& S, BiTree& p) {
if (S.top == -1) {//栈空,报错
return false;
}
p = S.data[S.top];//先出栈,指针再减1
return true;
}
void visit(int x) {
printf("%c ", x);
}
void PreOrder(BiTree T) {
SqStack S;
InitStack(S);
BiNode* p, * r;
p = T;
r = NULL;
while (p || !IsEmpty(S)) {
if (p) {//一路向左
visit(p->data);//访问该结点
Push(S, p);
p = p->lchild;
}
else {
//GetTop(S, p);
Pop(S, p);//栈顶元素出栈
p = p->rchild;//向右寻找
}//else
}//while
}
void DPreOrder(BiTree T) {
if (T != NULL) {
visit(T->data);//访问根节点的数据域
DPreOrder(T->lchild);//后序遍历左子树
DPreOrder(T->rchild);//后序遍历右子树
}
}
int main() {
//创建一棵二叉树
BiTree T = (BiTree)malloc(sizeof(BiNode));//创建一颗二叉树
T = Create(T);
//递归先序遍历
printf("递归先序遍历 \n");
DPreOrder(T);
printf("\n非递归先序遍历 \n");
//非递归后序遍历
PreOrder(T);
}7.非递归后序遍历
void visit(int x) {
printf("%c ", x);
}
void PostOrder(BiTree T) {
SqStack S;
InitStack(S);
BiNode* p,*r;
p = T;
r = NULL;
while (p || !IsEmpty(S)) {
if (p) {//走到最左边
Push(S, p);
p = p->lchild;
}
else {//向右
GetTop(S, p);//向右
if (p->rchild && p->rchild != r) {//如果右子树存在,且未被访问过
p = p->rchild;//转向右
Push(S, p);//压入栈
p = p->lchild;//再走到最左
}
else {
Pop(S, p);//将结点弹出
visit(p->data);//访问该结点
r = p;//记录最近访问过的结点
p = NULL;//结点访问完后,重置p指针
}
}//else
}//while
}
演示效果:




8.非递归后序遍历完整代码
#include<stdio.h>
#include<stdlib.h>
#include<iostream>
using namespace std;
typedef int ElemType;
typedef struct BiNode {
ElemType data;
BiNode* lchild;
BiNode* rchild;
}BiNode, *BiTree;
//构建二叉树
BiNode* Create(BiNode* bt) {
static int i = 0;
char ch;
//string str = "AB#D##C##";
//string str = "124##56##7##3##";
string str = "ABD#G##E##CF###";
ch = str[i++];
if (ch == '#')bt = NULL;//建立一棵空树
else {
bt = (BiTree)malloc(sizeof(BiNode)); bt->data = ch;//生成一个结点,数据域为ch
bt->lchild = Create(bt->lchild);//递归建立左子树
bt->rchild = Create(bt->rchild);//递归建立右子树
}
return bt;
}
#define MaxSize 100//定义栈中元素的最大个数
typedef struct {
BiTree data[MaxSize];//存放栈中元素
int top;//栈顶指针
}SqStack;
//(1)初始化
void InitStack(SqStack &S) {
S.top = -1;//初始化栈顶指针
//S.data[0] = NULL;
}
//(2)判栈空
bool IsEmpty(SqStack& S) {
if (S.top == -1) {//栈空
return true;
}
else {//不空
return false;
}
}
//(3)进栈
bool Push(SqStack& S, BiTree &p) {
if (S.top == MaxSize-1) {//栈满,报错
return false;
}
S.data[++S.top] = p;//指针先加1,再加入栈
return true;
}
//(4)出栈
bool Pop(SqStack& S, BiTree& p) {
if (S.top == - 1) {//栈空,报错
return false;
}
p = S.data[S.top--];//先出栈,指针再减1
return true;
}
//(5)读栈顶元素
bool GetTop(SqStack& S, BiTree& p) {
if (S.top == -1) {//栈空,报错
return false;
}
p = S.data[S.top];//先出栈,指针再减1
return true;
}
void visit(int x) {
printf("%c ", x);
}
void PostOrder(BiTree T) {
SqStack S;
InitStack(S);
BiNode* p,*r;
p = T;
r = NULL;
while (p || !IsEmpty(S)) {
if (p) {//走到最左边
Push(S, p);
p = p->lchild;
}
else {//向右
GetTop(S, p);//向右
if (p->rchild && p->rchild != r) {//如果右子树存在,且未被访问过
p = p->rchild;//转向右
Push(S, p);//压入栈
p = p->lchild;//再走到最左
}
else {
Pop(S, p);//将结点弹出
visit(p->data);//访问该结点
r = p;//记录最近访问过的结点
p = NULL;//结点访问完后,重置p指针
}
}//else
}//while
}
void DPostOrder(BiTree T) {
if (T != NULL) {
DPostOrder(T->lchild);//后序遍历左子树
DPostOrder(T->rchild);//后序遍历右子树
//visit(T->data);//访问根节点的数据域
//cout << "heheda" << endl;
visit(T->data);//访问根节点的数据域
}
}
int main() {
//创建一棵二叉树
BiTree T = (BiTree)malloc(sizeof(BiNode));//创建一颗二叉树
T = Create(T);
//递归后序遍历
printf("递归后序遍历 \n");
DPostOrder(T);
printf("\n非递归后序遍历 \n");
//非递归后序遍历
PostOrder(T);
}过程推演是小编的想法,如有不对的地方,欢迎指正,我将继续制作出更加有质量的博客内容,希望个位小伙伴能够点个赞,这是对我的付出的肯定,谢谢您们!!!
我的近期文章,C++版本:
C++ 图解二叉树非递归中序 + 实战力扣题-CSDN博客https://blog.csdn.net/weixin_41987016/article/details/134287291?csdn_share_tail=%7B%22type%22%3A%22blog%22%2C%22rType%22%3A%22article%22%2C%22rId%22%3A%22134287291%22%2C%22source%22%3A%22weixin_41987016%22%7D
C++ 图解二叉树非递归后序 + 实战力扣题-CSDN博客https://blog.csdn.net/weixin_41987016/article/details/134287728?csdn_share_tail=%7B%22type%22%3A%22blog%22%2C%22rType%22%3A%22article%22%2C%22rId%22%3A%22134287728%22%2C%22source%22%3A%22weixin_41987016%22%7D文章来源:https://www.toymoban.com/news/detail-732748.html
文章来源地址https://www.toymoban.com/news/detail-732748.html
到了这里,关于C语言实现非递归先序、中序、后序遍历的文章就介绍完了。如果您还想了解更多内容,请在右上角搜索TOY模板网以前的文章或继续浏览下面的相关文章,希望大家以后多多支持TOY模板网!