大家好,本文结合具体的问题实例,详细讲解一下TCP/IP协议栈的心跳机制、丢包重传机制等内容,给大家提供一个借鉴和参考。
1、问题概述
虽然软件底层模块在网络恢复后能自动重连上服务器,但会议因为网络问题已经退出,需要重新加入会议。
因为客户特殊的网络运行环境,会频繁出现网络抖动不稳定的情况,客户要求必须要实现60秒内网络恢复后能依然保持在会议中,保证会议流程不被中断。
客户坚持要实现这个特殊的功能点,项目已经接近尾声,目前处于客户试用阶段,不实现该功能,项目无法通过验收,客户不给钱。
前方同事将当前问题及项目进展情况向研发部门领导反馈,研发部紧急召开讨论会议,商讨60秒不掉会的实现方案。
这里面涉及到两大类的网络连接,一类是传输控制信令的TCP连接,另一类是传输音视频码流的UDP连接。UDP连接的问题不大,主要是TCP连接的断链与重连问题,下面主要讨论TCP连接相关问题。
在出现网络不稳定掉会时,可能是系统TCPIP协议栈已经检测到网络异常,系统协议层已经将网络断开了;也可能软件应用层的心跳机制检测到网络故障,断开了与服务器的链接。
对于系统TCPIP协议栈自身检测出来的网络异常,则可能存在两种情况,一是TCPIP协议栈自身的心跳机制检测出来的;二是TCP连接的丢包重传机制检测出异常。
对于应用层的心跳检测机制,我们可以放大超时检测时间。本文我们主要讨论一下TCPIP协议栈的TCP连接的心跳、丢包重传、连接超时等机制。
在检测到网络异常后,我们底层可以自动发起重连或者信令发送触发自动重连,业务模块将会议相关资源保存不释放,在网络恢复后可以继续保持在会议中,可以继续接收到会议中的音视频码流,可以继续进行会议中的一些操作!
2、TCPIP协议栈的心跳机制
2.1、TCP中的ACK机制
TCP建链时的三次握手流程如下所示:
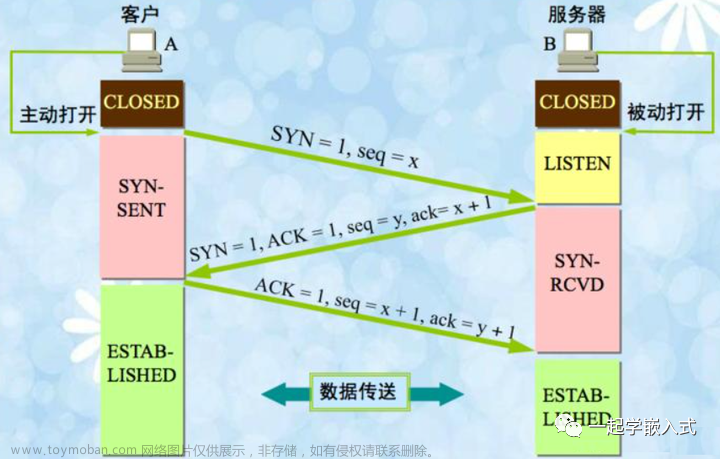
之所以说TCP连接是可靠的,首先是发送数据前要建立连接,再就是收到数据后都会给对方恢复一个ACK包,表明我收到你的数据包了。对于数据发送端,如果数据发出去后没有收到ACK包,则会触发丢包重传机制。
不管是建链时,还是建链后的数据收发时,都有ACK包,TCP/IP协议栈的心跳包也不例外。
2.2、TCPIP协议栈的心跳机制说明
TCP/IP协议栈有个默认的TCP心跳机制,这个心跳机制是和socket套接字(TCP套接字)绑定的,可以对指定的套接字开启协议栈的心跳检测机制。默认情况下,协议栈的心跳机制对socket套接字是关闭的,如果要使用需要人为开启的。
在Windows中,默认是每隔2个小时发一次心跳包,客户端程序将心跳包发给服务器后,接下来会有两种情况:
1)网络正常时:服务器收到心跳包,会立即回复ACK包,客户端收到ACK包后,再等2个小时发送下一个心跳包。其中,心跳包发送时间间隔时间keepalivetime,Windows系统中默认是2小时,可配置。如果在2个小时的时间间隔内,客户端和服务器有数据交互,客户端会收到服务器的ACK包,也算作心跳机制的心跳包,2个小时的时间间隔会重新计时。
2)网络异常时:服务器收不到客户端发过去的心跳包,没法回复ACK,Windows系统中默认的是1秒超时,1秒后会重发心跳包。如果还收不到心跳包的ACK,则1秒后重发心跳包,如果始终收不到心跳包,则在发出10个心跳包就达到了系统的上限,就认为网络出故障了,协议栈就会直接将连接断开了。其中,发出心跳包收不到ACK的超时时间称为 keepaliveinterval,Windows系统中默认是1秒,可配置;收不到心跳包对应的ACK包的重发次数probe,Windows系统是固定的,是固定的10次,不可配置的。
所以TCP/IP协议栈的心跳机制也能检测出网络异常,不过在默认配置下可能需要很久才能检测出来,除非网络异常出现在正在发送心跳包后等待对端的回应时,这种情况下如果多次重发心跳包都收不到ACK回应,协议栈就会判断网络出故障,主动将连接关闭掉。
2.3、修改TCP/IP协议栈的默认心跳参数
TCP/IP协议栈的默认心跳机制的开启,不是给系统整个协议栈开启心跳监测,而是对某个socket套接字开启。
开启心跳机制后,还可以修改心跳的时间参数。从代码上看,先调用setsockopt给目标套接字开启心跳监测机制,再调用WSAIoctl去修改心跳检测的默认时间参数,相关代码如下所示:
SOCKET socket;
// ......(中间代码省略)
int optval = 1;
int nRet = setsockopt(fd, SOL_SOCKET, SO_KEEPALIVE, (const char *)&optval,
sizeof(optval));
if (nRet != 0)
return;
tcp_keepalive alive;
alive.onoff = TRUE;
alive.keepalivetime = 10*1000;
alive.keepaliveinterval = 2*1000;
DWORD dwBytesRet = 0;
nRet = WSAIoctl(socket, SIO_KEEPALIVE_VALS, &alive, sizeof(alive), NULL, 0,
&dwBytesRet, NULL, NULL);
if (nRet != 0)
return;
上面的代码可以看到,先调用setsockopt函数,传入SO_KEEPALIVE参数,打开TCP连接的心跳开关,此时心跳参数使用系统默认的心跳参数值。
紧接着,调用WSAIoCtrl函数,传入SIO_KEEPALIVE_VALS参数,同时将设置好时间值的心跳参数结构体传进去。
下面对心跳参数结构体tcp_keepalive做个详细的说明:(以Windows系统为例)
1)keepalivetime:默认2小时发送一次心跳保活包,比如发送第1个保活包之后,间隔2个小时后再发起下一个保活包。如果这期间有数据交互,也算是有效的保活包,这个时间段就不再发送保活包,发送下个保活包的时间间隔会从收发的最后一条数据的时刻开始重新从0计时。
2)keepaliveinterval:发送保活包后,没有收到对端的ack的超时时间默认为1秒。假设和对端的网络出问题了,给对端发送第1个保活包,1秒内没有收到对端的ack,则发第2个保活包,1秒内没有收到对端的保活包,再发送下一个保活包,.....,直到发送第10个保活包后,1秒钟还没收到ack回应,则达到发送10次保活包的探测次数上限,则认为网络出问题了。
3)probe探测次数:Windows系统上的探测次数被固定为10次,不可修改。
MSDN上对心跳机制检测出的网络异常的说明如下:
If a connection is dropped as the result of keep-alives the error code WSAENETRESET is returned to any calls in progress on the socket, and any subsequent calls will fail with WSAENOTCONN.
因为保活次数达到上限导致连接被丢弃掉,所有正在调用中的套接字接口会返回WSAENETRESET错误码,后续的套接字api函数的调用都会返回WSAENOTCONN。
3、libwebsockets开源库中的心跳机制使用的就是TCPIP协议栈的心跳机制
我们的产品之前在使用websocket时,就遇到没有设置心跳机制导致TCP长连接被网络设备无故释放的问题。
我们客户端程序在登录时,会去连接某业务的注册服务器,建立的是websocket长连接。这个长连接一直保持着,只有使用该业务模块的业务时才会使用到该连接,在该连接上进行数据交互。软件登录后,如果一直没有操作该业务模块的业务,这个长连接会一直处于闲置状态,即这个连接上没有数据交互。
结果在某次测试过程中出现了问题,排查下来发现,这个长连接因为长时间没有数据交互,被中间的网络设备关闭了。后来为了解决这个问题,我们在初始化websocket库时设置心跳参数,这样上述websocket长连接在空闲的时候能跑一跑心跳包,这样就能确保该长连接不会因为长时间没有跑数据被无故关闭的问题了。
我们在调用lws_create_context接口创建websockets会话上下文时,该接口的结构体参数lws_context_creation_info中,有设置心跳参数的字段:
/**
* struct lws_context_creation_info - parameters to create context with
*
* This is also used to create vhosts.... if LWS_SERVER_OPTION_EXPLICIT_VHOSTS
* is not given, then for backwards compatibility one vhost is created at
* context-creation time using the info from this struct.
*
* If LWS_SERVER_OPTION_EXPLICIT_VHOSTS is given, then no vhosts are created
* at the same time as the context, they are expected to be created afterwards.
*
* @port: VHOST: Port to listen on... you can use CONTEXT_PORT_NO_LISTEN to
* suppress listening on any port, that's what you want if you are
* not running a websocket server at all but just using it as a
* client
* @iface: VHOST: NULL to bind the listen socket to all interfaces, or the
* interface name, eg, "eth2"
* If options specifies LWS_SERVER_OPTION_UNIX_SOCK, this member is
* the pathname of a UNIX domain socket. you can use the UNIX domain
* sockets in abstract namespace, by prepending an @ symbole to the
* socket name.
* @protocols: VHOST: Array of structures listing supported protocols and a protocol-
* specific callback for each one. The list is ended with an
* entry that has a NULL callback pointer.
* It's not const because we write the owning_server member
* @extensions: VHOST: NULL or array of lws_extension structs listing the
* extensions this context supports. If you configured with
* --without-extensions, you should give NULL here.
* @token_limits: CONTEXT: NULL or struct lws_token_limits pointer which is initialized
* with a token length limit for each possible WSI_TOKEN_***
* @ssl_cert_filepath: VHOST: If libwebsockets was compiled to use ssl, and you want
* to listen using SSL, set to the filepath to fetch the
* server cert from, otherwise NULL for unencrypted
* @ssl_private_key_filepath: VHOST: filepath to private key if wanting SSL mode;
* if this is set to NULL but sll_cert_filepath is set, the
* OPENSSL_CONTEXT_REQUIRES_PRIVATE_KEY callback is called
* to allow setting of the private key directly via openSSL
* library calls
* @ssl_ca_filepath: VHOST: CA certificate filepath or NULL
* @ssl_cipher_list: VHOST: List of valid ciphers to use (eg,
* "RC4-MD5:RC4-SHA:AES128-SHA:AES256-SHA:HIGH:!DSS:!aNULL"
* or you can leave it as NULL to get "DEFAULT"
* @http_proxy_address: VHOST: If non-NULL, attempts to proxy via the given address.
* If proxy auth is required, use format
* "username:password@server:port"
* @http_proxy_port: VHOST: If http_proxy_address was non-NULL, uses this port at
* the address
* @gid: CONTEXT: group id to change to after setting listen socket, or -1.
* @uid: CONTEXT: user id to change to after setting listen socket, or -1.
* @options: VHOST + CONTEXT: 0, or LWS_SERVER_OPTION_... bitfields
* @user: CONTEXT: optional user pointer that can be recovered via the context
* pointer using lws_context_user
* @ka_time: CONTEXT: 0 for no keepalive, otherwise apply this keepalive timeout to
* all libwebsocket sockets, client or server
* @ka_probes: CONTEXT: if ka_time was nonzero, after the timeout expires how many
* times to try to get a response from the peer before giving up
* and killing the connection
* @ka_interval: CONTEXT: if ka_time was nonzero, how long to wait before each ka_probes
* attempt
* @provided_client_ssl_ctx: CONTEXT: If non-null, swap out libwebsockets ssl
* implementation for the one provided by provided_ssl_ctx.
* Libwebsockets no longer is responsible for freeing the context
* if this option is selected.
* @max_http_header_data: CONTEXT: The max amount of header payload that can be handled
* in an http request (unrecognized header payload is dropped)
* @max_http_header_pool: CONTEXT: The max number of connections with http headers that
* can be processed simultaneously (the corresponding memory is
* allocated for the lifetime of the context). If the pool is
* busy new incoming connections must wait for accept until one
* becomes free.
* @count_threads: CONTEXT: how many contexts to create in an array, 0 = 1
* @fd_limit_per_thread: CONTEXT: nonzero means restrict each service thread to this
* many fds, 0 means the default which is divide the process fd
* limit by the number of threads.
* @timeout_secs: VHOST: various processes involving network roundtrips in the
* library are protected from hanging forever by timeouts. If
* nonzero, this member lets you set the timeout used in seconds.
* Otherwise a default timeout is used.
* @ecdh_curve: VHOST: if NULL, defaults to initializing server with "prime256v1"
* @vhost_name: VHOST: name of vhost, must match external DNS name used to
* access the site, like "warmcat.com" as it's used to match
* Host: header and / or SNI name for SSL.
* @plugin_dirs: CONTEXT: NULL, or NULL-terminated array of directories to
* scan for lws protocol plugins at context creation time
* @pvo: VHOST: pointer to optional linked list of per-vhost
* options made accessible to protocols
* @keepalive_timeout: VHOST: (default = 0 = 60s) seconds to allow remote
* client to hold on to an idle HTTP/1.1 connection
* @log_filepath: VHOST: filepath to append logs to... this is opened before
* any dropping of initial privileges
* @mounts: VHOST: optional linked list of mounts for this vhost
* @server_string: CONTEXT: string used in HTTP headers to identify server
* software, if NULL, "libwebsockets".
*/
struct lws_context_creation_info {
int port; /* VH */
const char *iface; /* VH */
const struct lws_protocols *protocols; /* VH */
const struct lws_extension *extensions; /* VH */
const struct lws_token_limits *token_limits; /* context */
const char *ssl_private_key_password; /* VH */
const char *ssl_cert_filepath; /* VH */
const char *ssl_private_key_filepath; /* VH */
const char *ssl_ca_filepath; /* VH */
const char *ssl_cipher_list; /* VH */
const char *http_proxy_address; /* VH */
unsigned int http_proxy_port; /* VH */
int gid; /* context */
int uid; /* context */
unsigned int options; /* VH + context */
void *user; /* context */
int ka_time; /* context */
int ka_probes; /* context */
int ka_interval; /* context */
#ifdef LWS_OPENSSL_SUPPORT
SSL_CTX *provided_client_ssl_ctx; /* context */
#else /* maintain structure layout either way */
void *provided_client_ssl_ctx;
#endif
short max_http_header_data; /* context */
short max_http_header_pool; /* context */
unsigned int count_threads; /* context */
unsigned int fd_limit_per_thread; /* context */
unsigned int timeout_secs; /* VH */
const char *ecdh_curve; /* VH */
const char *vhost_name; /* VH */
const char * const *plugin_dirs; /* context */
const struct lws_protocol_vhost_options *pvo; /* VH */
int keepalive_timeout; /* VH */
const char *log_filepath; /* VH */
const struct lws_http_mount *mounts; /* VH */
const char *server_string; /* context */
/* Add new things just above here ---^
* This is part of the ABI, don't needlessly break compatibility
*
* The below is to ensure later library versions with new
* members added above will see 0 (default) even if the app
* was not built against the newer headers.
*/
void *_unused[8];
};
其中的ka_time、ka_probes和ka_interval三个字段就是心跳相关的设置参数。我们初始化websockets上下文的代码如下:
static lws_context* CreateContext()
{
lws_set_log_level( 0xFF, NULL );
lws_context* plcContext = NULL;
lws_context_creation_info tCreateinfo;
memset(&tCreateinfo, 0, sizeof tCreateinfo);
tCreateinfo.port = CONTEXT_PORT_NO_LISTEN;
tCreateinfo.protocols = protocols;
tCreateinfo.ka_time = LWS_TCP_KEEPALIVE_TIME;
tCreateinfo.ka_interval = LWS_TCP_KEEPALIVE_INTERVAL;
tCreateinfo.ka_probes = LWS_TCP_KEEPALIVE_PROBES;
tCreateinfo.options = LWS_SERVER_OPTION_DISABLE_IPV6;
plcContext = lws_create_context(&tCreateinfo);
return plcContext;
}
通过查阅libwebsockets开源库代码得知,此处设置的心跳使用的就是TCPIP协议栈的心跳机制,如下所示:
LWS_VISIBLE int
lws_plat_set_socket_options(struct lws_vhost *vhost, lws_sockfd_type fd)
{
int optval = 1;
int optlen = sizeof(optval);
u_long optl = 1;
DWORD dwBytesRet;
struct tcp_keepalive alive;
int protonbr;
#ifndef _WIN32_WCE
struct protoent *tcp_proto;
#endif
if (vhost->ka_time) {
/* enable keepalive on this socket */
// 先调用setsockopt打开发送心跳包(设置)选项
optval = 1;
if (setsockopt(fd, SOL_SOCKET, SO_KEEPALIVE,
(const char *)&optval, optlen) < 0)
return 1;
alive.onoff = TRUE;
alive.keepalivetime = vhost->ka_time*1000;
alive.keepaliveinterval = vhost->ka_interval*1000;
if (WSAIoctl(fd, SIO_KEEPALIVE_VALS, &alive, sizeof(alive),
NULL, 0, &dwBytesRet, NULL, NULL))
return 1;
}
/* Disable Nagle */
optval = 1;
#ifndef _WIN32_WCE
tcp_proto = getprotobyname("TCP");
if (!tcp_proto) {
lwsl_err("getprotobyname() failed with error %d\n", LWS_ERRNO);
return 1;
}
protonbr = tcp_proto->p_proto;
#else
protonbr = 6;
#endif
setsockopt(fd, protonbr, TCP_NODELAY, (const char *)&optval, optlen);
/* We are nonblocking... */
ioctlsocket(fd, FIONBIO, &optl);
return 0;
}
4、TCPIP丢包重传机制
如果网络出故障时,客户端与服务器之间正在进行TCP数据交互,客户端给服务器发送数据包后因为网络故障收不到服务器的ACK包,就会触发客户端的TCP丢包重传,丢包重传机制也能判断出网络出现异常。
对于TCP连接,客户端给服务器发送数据后没有收到服务器的ACK包,会触发丢包重传。每次重传的时间间隔会加倍,当重传次数达到系统上限(Windows默认的上限是5次,Linux默认的上限是15次)后,协议栈就认为网络出故障了,会直接将对应的连接关闭了。
所以当网络出现故障时有数据交互,协议栈会在数十秒内检测到网路出现异常,就会直接将连接直接关闭掉。丢包重传机制的详细描述如下所示:


对于丢包重传机制,可以通过给PC插拔网线来查看,可以使用wireshark抓包看一下。快速插拔网线时(先拔掉网线,等待几秒钟再将网线插上),给服务器发送的操作指令会因为丢包重传会收到数据的。
5、使用非阻塞socket和select接口实现connect连接的超时控制
5.1、MSDN上对connect和select接口的说明
对于tcp套接字,我们需要调用套接字函数connect去建立TCP连接。我们先来看看微软MSDN上对套接字接口connect的描述:




On a blocking socket, the return value indicates success or failure of the connection attempt.
对于阻塞式的socket,通过connect的返回值就能确定有没有连接成功,返回0表示连接成功。
With a nonblocking socket, the connection attempt cannot be completed immediately. In this case, connect will return SOCKET_ERROR, and WSAGetLastError will return WSAEWOULDBLOCK. In this case, there are three possible scenarios: Use the select function to determine the completion of the connection request by checking to see if the socket is writeable.
对于非组赛式的socket,connect调用会立即返回,但连接操作还没有完成。connect返回SOCKET_ERROR,对于非阻塞式socket,返回SOCKET_ERROR并不表示失败,需要调用WSAGetLastError获取connect函数执行后的LastError值,一般此时WSAGetLastError会返回WSAEWOULDBLOCK:

表明连接正在进行中。可以使用select接口检测一下套接字是否可写(套接字是否在writefds集合中),如果可写,则表示连接成功。如果套接字在exceptfds集合中,则说明连接出现了异常,如下所示:

5.2、使用非阻塞socket和select实现连接超时的控制
对于阻塞式的socket,在Windows下,如果远端的IP和Port不可达,则会阻塞75s后返回SOCKET_ERROR,表明连接失败。所以当我们测试远端的IP和Port是否可以连接时,我们不使用阻塞式的socket,而是使用非阻塞式socket,然后调用select,通过select添加连接超时时间,实现连接超时的控制。
select函数因为超时返回,会返回0;如果发生错误,则返回SOCKET_ERROR,所以判断时要判断select返回值,如果小于等于0,则是连接失败,立即将套接字关闭掉。
如果select返回值大于0,则该返回值是已经准备就绪的socket个数,比如连接成功的socket。我们判断套接字是否在可写集合writefds中,如果在该集合中,则表示连接成功。文章来源:https://www.toymoban.com/news/detail-733103.html
根据MSDN上的相关描述,我们就能大概知道该如何实现connect的超时控制了,相关代码如下:文章来源地址https://www.toymoban.com/news/detail-733103.html
bool ConnectDevice( char* pszIP, int nPort )
{
// 创建TCP套接字
SOCKET connSock = socket(AF_INET, SOCK_STREAM, 0);
if (connSock == INVALID_SOCKET)
{
return false;
}
// 填充IP和端口
SOCKADDR_IN devAddr;
memset(&devAddr, 0, sizeof(SOCKADDR_IN));
devAddr.sin_family = AF_INET;
devAddr.sin_port = htons(nPort);
devAddr.sin_addr.s_addr = inet_addr(pszIP);
// 将套接字设置为非阻塞式的,为下面的select做准备
unsigned long ulnoblock = 1;
ioctlsocket(connSock, FIONBIO, &ulnoblock);
// 发起connnect,该接口立即返回
connect(connSock, (sockaddr*)&devAddr, sizeof(devAddr));
FD_SET writefds;
FD_ZERO(&writefds);
FD_SET(connSock, &writefds);
// 设置连接超时时间为1秒
timeval tv;
tv.tv_sec = 1; //超时1s
tv.tv_usec = 0;
// The select function returns the total number of socket handles that are ready and contained
// in the fd_set structures, zero if the time limit expired, or SOCKET_ERROR(-1) if an error occurred.
if (select(0, NULL, &writefds, NULL, &tv) <= 0)
{
closesocket(connSock);
return false; //超时未连接上就退出
}
ulnoblock = 0;
ioctlsocket(connSock, FIONBIO, &ulnoblock);
closesocket(connSock);
return true;
}
到了这里,关于TCP/IP协议栈的心跳、丢包重传、连接超时机制实例详解的文章就介绍完了。如果您还想了解更多内容,请在右上角搜索TOY模板网以前的文章或继续浏览下面的相关文章,希望大家以后多多支持TOY模板网!










