一、项目介绍
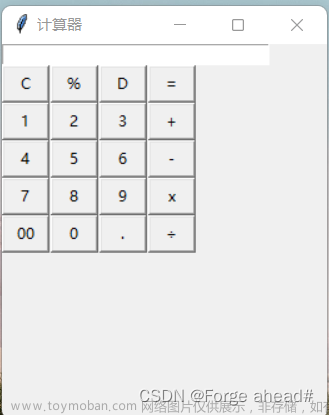
本项目实现了一个通过网页访问的简单计算器,它可以对带括号的加减乘除表达式进行计算并将计算结果返回给用户,并且可以对用户输入的表达式进行合法性判断,以下是项目的界面展示:
使用者可以通过点击网页上的按钮来输入一个算数表达式,之后点击等于号便可以将结果展示在界面上,具体效果如下:
二、技术使用
在这个计算器中主要使用了前端html,css,JavaScript,后端spring boot以及数据结构中栈的使用方式与相关的算法。
- 在前端中使用了html来对界面进行了整体的布局,然后使用了css来对界面效果做了美化,最后使用JavaScript来实现每个按钮的点击事件,并且通过Ajax将请求参数发给后台服务器,然后将后台处理的结果接收并处理,最后展示给用户。
- 在后端中主要使用了spring boot框架来搭建一个简单的服务器,并对前端发来的请求进行处理,最后将处理的结果返回给前端。
- 在处理表达式的时候主要使用了数据结构中有关栈的一些知识,通过对栈的使用来对表达式进行计算。
三、具体代码实现
1.前端部分
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<meta http-equiv="X-UA-Compatible" content="IE=edge">
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0">
<title>计算器</title>
<link rel="stylesheet" href="./css/style.css">
</head>
<body>
<div class="container">
<div class="calculator dark">
<div class="display-screen">
<div id="display"></div>
</div>
<div class="buttons">
<table>
<tr>
<td><button class="btn-operator" id="clear">C</button></td>
<td><button class="btn-operator" id="/">÷</button></td>
<td><button class="btn-operator" id="*">×</button></td>
<td><button class="btn-operator" id="backspace"><</button></td>
</tr>
<tr>
<td><button class="btn-number" id="7">7</button></td>
<td><button class="btn-number" id="8">8</button></td>
<td><button class="btn-number" id="9">9</button></td>
<td><button class="btn-operator" id="-">-</button></td>
</tr>
<tr>
<td><button class="btn-number" id="4">4</button></td>
<td><button class="btn-number" id="5">5</button></td>
<td><button class="btn-number" id="6">6</button></td>
<td><button class="btn-operator" id="+">+</button></td>
</tr>
<tr>
<td><button class="btn-number" id="1">1</button></td>
<td><button class="btn-number" id="2">2</button></td>
<td><button class="btn-number" id="3">3</button></td>
<td rowspan="2"><button class="btn-equal" id="equal" onclick="submit()">=</button></td>
</tr>
<tr>
<td><button class="btn-operator" id="(">(</button></td>
<td><button class="btn-number" id="0">0</button></td>
<td><button class="btn-operator" id=")">)</button></td>
</tr>
</table>
</div>
</div>
</div>
<script src="./js/script.js"></script>
</body>
</html>
以上为html部分的代码,主要是对使用者的界面进行了整体布局,确定了各个按钮的位置与功能。
*{
margin: 0;
padding: 0;
box-sizing: border-box;
outline: 0;
transition: all 0.5s ease;
}
body{
font-family: sans-serif;
}
a{
text-decoration: none;
color: #fff;
}
body{
background-image: linear-gradient(to bottom right, rgb(10, 88, 232), rgb(41, 231, 225));
}
.container{
height: 100vh;
width: 100vw;
display: grid;
place-items: center;
}
.calculator{
position: relative;
height: auto;
width: auto;
padding: 20px;
border-radius: 10px;
box-shadow: 0 0 30px #000;
}
#display{
margin: 0 10px;
height: 150px;
width: auto;
max-width: 270px;
display: flex;
align-items: flex-end;
justify-content: flex-end;
font-size: 30px;
overflow-x: scroll;
}
#display::-webkit-scrollbar{
display: block;
height: 3px;
}
button{
height: 60px;
width: 60px;
border: 0;
border-radius: 30px;
margin: 5px;
font-size: 20px;
cursor: pointer;
transition: all 200ms ease;
}
button:hover{
transform: scale(1.1);
}
button#equal{
height: 130px;
}
.calculator{
background-color: #fff;
}
.calculator #display{
color: #0a1e23;
}
.calculator button#clear{
background-color: #ffd5d8;
color: #fc4552;
}
.calculator button.btn-number{
background-color: #c3eaff;
color: #000;
}
.calculator button.btn-operator{
background-color: #7ed0b0;
color: #f39408;
}
.calculator button.btn-equal{
background-color: #adf9e7;
color: #000;
}
以上是css部分的代码,主要对界面的颜色样式进行了美化。
const display = document.querySelector('#display');
const buttons = document.querySelectorAll('button');
const submit = function () {
let subdata = null;
// 定义表单对象
const data = {}
// 获取input框内内容
const displayData = display.innerText
data.display = displayData
console.log(data);
const req = fetch('http://localhost:8081/cal/c', {
body: JSON.stringify(data),
method: "POST",
headers: {
'Content-Type': 'application/json'
}
})
req.then(res => res.text())
.then(res => {
subdata = JSON.parse(res);
if (!subdata.status)
display.innerText = '输入格式错误'
else {
console.log(subdata);
display.innerText = subdata.result
}
})
.catch(err => {
console.log(err)
})
}
buttons.forEach((item) => {
item.onclick = () => {
if (item.id == 'clear') {
display.innerText = '';
} else if (item.id == 'backspace') {
let string = display.innerText.toString();
display.innerText = string.substr(0, string.length - 1);
} else if (display.innerText != '' && item.id == 'equal') {
submit()
} else if (display.innerText == '' && item.id == 'equal') {
display.innerText = 'Empty!';
setTimeout(() => (display.innerText = ''), 2000);
} else {
display.innerText += item.id;
}
}
})
const calculator = document.querySelector('.calculator');
以上是JavaScript部分的代码,主要负责按钮的点击事件、给后端发送请求以及对后端返回结果的处理。
2.后端部分
@RestController
@RequestMapping("/cal")
public class Controller {
@Autowired
private ServiceImpl service;
@PostMapping("/c")
public Res calcula(@RequestBody data data) {
return service.calculate(data.getDisplay());
}
}
@Service
public class ServiceImpl {
public Res calculate(String text) {
return new Res(Calculator.isValidExpression(text) ?
Calculator.calculateExpression(text) : null,
Calculator.isValidExpression(text) ? 1 : 0);
}
}
以上是后端给出的请求接口以及业务逻辑层的方法。
@Data
@AllArgsConstructor
public class Res {
public Integer result;
public int status;
}
public class data {
private String display;
public data() {
}
public String getDisplay() {
return display;
}
public void setDisplay(String display) {
this.display = display;
}
public data(String display) {
this.display = display;
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return "data{" +
"display='" + display + '\'' +
'}';
}
}
以上是给前端返回结果的包装类以及接收前端数据的实体类。文章来源:https://www.toymoban.com/news/detail-734121.html
public class Calculator {
public static int priority(int oper) {
if (oper == '*' || oper == '/') {
return 1;
} else if (oper == '+' || oper == '-') {
return 0;
} else {
return -1;
}
}
public static boolean isOper(char val) {
return val == '+' || val == '-' || val == '*' || val == '/';
}
public static int cal(int num1, int num2, int oper) {
int res = 0;
switch (oper) {
case '+':
res = num1 + num2;
break;
case '-':
res = num2 - num1;
break;
case '*':
res = num1 * num2;
break;
case '/':
res = num2 / num1;
break;
}
return res;
}
public static int calculateExpression(String expression) {
Stack<Integer> numStack = new Stack<>();
Stack<Character> operStack = new Stack<>();
int index = 0;
int num1 = 0;
int num2 = 0;
int oper = 0;
int res = 0;
char ch = ' ';
String keepNum = "";
while (true) {
ch = expression.substring(index, index + 1).charAt(0);
if (isOper(ch)) {
if (!operStack.isEmpty()) {
if (priority(ch) <= priority(operStack.peek())) {
num1 = numStack.pop();
num2 = numStack.pop();
oper = operStack.pop();
res = cal(num1, num2, oper);
numStack.push(res);
operStack.push(ch);
} else {
operStack.push(ch);
}
} else {
operStack.push(ch);
}
} else if (ch == '(') {
int endIndex = getEndBracketIndex(expression, index);
String subExpression = expression.substring(index + 1, endIndex);
int subRes = calculateExpression(subExpression);
numStack.push(subRes);
index = endIndex;
} else {
keepNum += ch;
if (index == expression.length() - 1) {
numStack.push(Integer.parseInt(keepNum));
keepNum = "";
} else {
if (isOper(expression.substring(index + 1, index + 2).charAt(0))) {
numStack.push(Integer.parseInt(keepNum));
keepNum = "";
}
}
}
index++;
if (index >= expression.length()) {
break;
}
}
while (!operStack.isEmpty()) {
num1 = numStack.pop();
num2 = numStack.pop();
oper = operStack.pop();
res = cal(num1, num2, oper);
numStack.push(res);
}
return numStack.pop();
}
private static int getEndBracketIndex(String expression, int startIndex) {
Stack<Integer> stack = new Stack<>();
for (int i = startIndex; i < expression.length(); i++) {
char ch = expression.charAt(i);
if (ch == '(') {
stack.push(i);
} else if (ch == ')') {
stack.pop();
if (stack.isEmpty()) {
return i;
}
}
}
return 0;
}
public static boolean isValidExpression(String expr) {
// 去除空格
expr = expr.replaceAll("\\s", "");
// 使用栈保存左括号
Stack<Character> stack = new Stack<>();
for (int i = 0; i < expr.length(); i++) {
char c = expr.charAt(i);
if (isLeftParenthesis(c)) {
stack.push(c);
} else if (isRightParenthesis(c)) {
if (stack.isEmpty()) {
return false;
} else {
stack.pop();
}
} else if (isOperator(c)) {
if (i == 0 || i == expr.length() - 1 || isOperator(expr.charAt(i - 1)) || isOperator(expr.charAt(i + 1))) {
return false;
}
if (c == '/' && (i == expr.length() - 2 || expr.charAt(i + 2) == '0')) {
return false;
}
} else if (!Character.isDigit(c)) {
return false;
}
}
return stack.isEmpty();
}
public static boolean isLeftParenthesis(char c) {
return c == '(';
}
public static boolean isRightParenthesis(char c) {
return c == ')';
}
public static boolean isOperator(char c) {
return c == '+' || c == '-' || c == '*' || c == '/';
}
}
以上是对表达式进行处理并计算结果的一个简单的计算器类,该类提供了以下几个方法:文章来源地址https://www.toymoban.com/news/detail-734121.html
- priority(int oper):根据运算符的优先级,返回一个整数值,其中乘法和除法的优先级为1,加法和减法的优先级为0,其他情况返回-1。
- isOper(char val):判断给定字符是否为运算符(+、-、*、/)。
- cal(int num1, int num2, int oper):根据给定的两个数字和一个运算符,进行相应的计算并返回结果。运算符对应的计算包括加法、减法、乘法和除法。
- calculateExpression(String expression):通过指定的数学表达式进行计算,并返回计算结果。该方法使用两个栈来实现计算过程。一个栈用于存储数字,另一个栈用于存储运算符。遍历表达式的字符,根据字符的类型进行相应的操作。如果是运算符,则根据运算符的优先级决定是否进行计算;如果是左括号,则寻找对应的右括号,并将括号内的子表达式进行递归计算;如果是数字,则将数字压入数字栈中。最后,将剩余的运算符依次进行计算,直到栈为空,返回最终的计算结果。
- getEndBracketIndex(String expression, int startIndex):辅助方法,用于获取给定表达式中与指定左括号对应的右括号的位置。
- isValidExpression(String expr):判断给定的表达式是否为有效的数学表达式。方法首先去除字符串中的空格,然后使用栈来检查表达式中的括号是否匹配以及运算符的使用是否正确。具体规则如下:左括号入栈,遇到右括号出栈,如果栈为空则表示括号不匹配;如果遇到运算符,则判断其前后是否有运算符,以及除法运算符是否除以0,如果不符合规则则表达式无效;如果遇到非数字和非运算符的字符,则表达式无效。最后,如果栈为空,则表示括号匹配,返回true,否则返回false。
到了这里,关于数据结构Demo——简单计算器的文章就介绍完了。如果您还想了解更多内容,请在右上角搜索TOY模板网以前的文章或继续浏览下面的相关文章,希望大家以后多多支持TOY模板网!